Abstract
Adipose stem cells (ASCs) are a type of adult stem cells that share common characteristics with typical mesenchymal stem cells. In the last decade, ASCs have been shown to be a useful cell resource for tissue regeneration. The major role of regenerative medicine in this century is based on cell therapy in which ASCs hold a key position. Active research on this new type of adult stem cell has been ongoing and these cells now have several clinical applications, including fat grafting, overcoming wound healing difficulties, recovery from local tissue ischemia, and scar remodeling. The application of cultured cells will increase the efficiency of cell therapy. However, the use of cultured stem cells is strictly controlled by government regulation to ensure patient safety. Government regulation is a factor that can limit more versatile clinical application of ASCs. In this review, current clinical applications of ASCs in plastic surgery are introduced. Future stem cell applications in clinical field including culturing and banking of ASCs are also discussed in this review.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords: Adult Stem Cells, Adipose Stem Cells, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Stromal Cells, Wound Healing, Regeneration, Adipose Tissue, Ischemia, Tissue Engineering, Cell Therapy
INTRODUCTION
The regenerative potential of various types of adult stem cells are well known (1, 2). A new type of adult stem cells within fat tissue was identified at the end of the 20th century, when several plastic surgeons first discovered the existence of multilineage stromal cells within fat tissue (3, 4, 5, 6). Since their discovery, these cells have been referred to by several different names such as adipose-derived stem cells, adipose-derived stromal cells (ADSCs), and adipose stem cells (ASCs). The discovery of ASCs, imparts regenerative medicine with the potential to overcome critical impediments to actual clinical cell therapy applications. ASCs not only have characteristics similar to those of adult stem cells, but also possess two distinct advantages over bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs). Specifically, ASCs are easily harvested by liposuction under local anesthesia without leaving a conspicuous scar and repeated harvesting, if necessary, is not problematic. Additionally, a large number of cells can be acquired from any type of fat tissue from the body. Therefore, cell culturing may not be necessary to acquire a therapeutic amount of cells. Owing to these two advantages, stem cell therapy can be applied under several limited clinical situations. The International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS), which was established in 2003, has played a major role in the propagation of this new field of science throughout the world during last decade.
Plastic surgeons in Korea and Japan have played a leading role in pioneering the use of ASCs because government regulations in these countries are less strict than those in Western nations, enabling primary ASCs to be more liberally applied for clinical treatment (7, 8, 9, 10, 11). Early reports of the clinical application of ASCs have been presented at international meetings, including the IFATS. For example, Yoshimura group (9, 10, 11, 12) developed cell-assisted lipotransfer (CAL) and put forth theory of early cell death and fat regeneration describing the fate of graft.
In this review, current clinical applications of ASCs are introduced, including the use of these cells for fat grafts, management of difficult wounds, regeneration of local soft tissue defects, recovery from acute tissue ischemia of vascular origin, and scar management. These clinical applications are all based on primary ASCs rather than cultured cells. In most countries, the use of cultured stem cells for clinical purposes is currently strictly regulated. Although government regulations are necessary to ensure patient safety, they should still allow reasonable promotion of stem cell research and clinical studies.
A NEW METHOD OF FAT GRAFTING: CELL-ASSISTED LIPOTRANSFER
ASCs play an important role in fat graft survival. The increased survival of aspirated fat in response to the addition of ASCs in a process known as cell-assisted lipotransfer has been reported (9). An in vivo study by Eto et al. (12) showed that most adipocytes in the graft begin to die on day one and that only some of the adipocytes located within 300 µm of the tissue edge survive. Inside this region of survival, a small area of regeneration exists in which all adipocytes die and only ASCs survive. This is convincing evidence of the importance of ASCs in fat tissue survival after grafting. ASCs have also been shown to promote neoangiogenesis during the acute phase of fat transplantation and form microtubules within 24 hr of ischemia, while capillary networks are rapidly established within 3 days (7, 9).
Although there are still some questions regarding the effectiveness of CAL for clinical fat grafting, it is generally accepted by plastic surgeons that the risk of fat necrosis can be reduced and that fat graft survival is improved by using the CAL technique. This type of cell-enriched lipotransfer has become popular in East Asian countries such as Korea and Japan. Reports of effective clinical application of CAL for cosmetic facial soft tissue volume replacement and reconstruction of defects from facial lipoatrophy have been published (8, 11, 13). Additionally, large volume fat transfer for breast augmentation, in which improved graft survival is essential, has been reported (10).
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP), which contains valuable cytokines, has become popular for use in various orthopedic surgical procedures to treat different conditions including osteoarthritis (14, 15). The positive effects of PRP on fat grafts have been reported along with synergistic effects of ASCs and PRP that improve fat graft survival (16, 17).
APPLICATION OF ASCS FOR TISSUE REPAIR AND REGENERATION
Diabetic ulcers and chronic radiation ulcers are notorious for their recurrence or failure to heal. These lesions do not improve over time and tend to become worse. Extensive reconstructive surgery may be necessary to treat even small defects because of the diffuse ischemia surrounding the lesion, and it may not be successful in these individuals due to patient debilitation or poor local regeneration capabilities.
Several types of conventional reconstructive surgery have been introduced for patients with chronic non-healing cutaneous lesions (18, 19, 20). Presently, cell therapy using ASCs may be a good alternative technique because it is less invasive than reconstructive surgery and the cells can be directly applied to target areas in cutaneous lesions (21). An adequate amount of ASCs can easily be harvested by liposuction and fat tissue digestion. Administration of cells to the defect may reinforce local regeneration capabilities that have been exhausted during the course of prolonged diseases.
A single session of cell therapy may be effective but the outcome depends on the size, depth, and type of defect. When the defect is very large or relatively deep, successful tissue regeneration may be accomplished by repeated cell therapy or by tissue engineering using adequate scaffold materials and cells. Allogeneic dermis or a collagen sponge may be used as a scaffold for regeneration of soft tissue underneath the skin. The scaffolds must be immersed in a cell suspension so that the cells can infiltrate the material. Adequate debridement of the wound is also essential before placing the scaffold material.
When the defect is flat and large, a type of artificial dermis (Terudermis®) containing a thin silicone membrane over collagen sponge may be an excellent choice since the silicone surface layer can be sutured to adjacent skin as a protective surface. The advantage of this type of tissue engineering is the ease of repeating the procedure during the course of regeneration. The thin silicone cover easily peels off after 10-14 days and another cell-treated artificial dermis can be applied over the previous one. At 2 weeks after the application, vascular ingrowth appears and a thin skin graft may be placed on the newly engineered vascular bed (Fig. 1). This type of cell-based therapy may be a good treatment option for small traumatic defects or skin cancers to avoid reconstructive surgeries using local flaps (22, 23, 24). When defects are deep with a small surface, the inner cavity may be filled with an ASC-impregnated dermis and covered with a piece of cell-treated Terudermis®. A small opening less than 10 mm in diameter usually re-epithelializes within 3 weeks when this technique is applied.
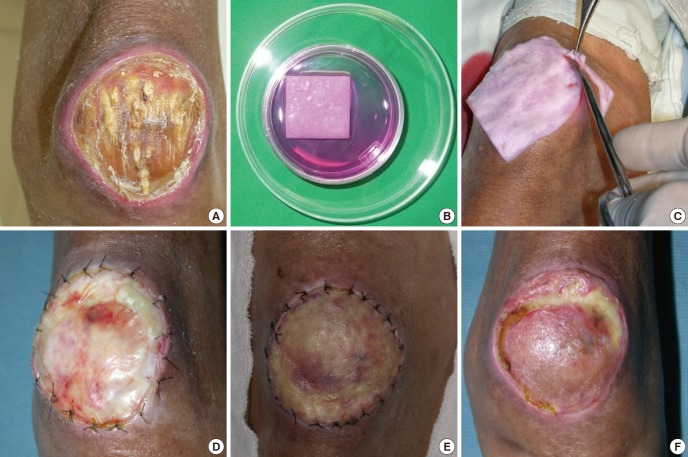
Fig. 1.
Management of a chronic diabetic ulcer on the knee area using adipose stem cell-based therapy and a collagen sponge. (A) Chronic open wound on the knee area with exposure of the patella bone (before treatment). (B) Adequate size of artificial dermis (Terudermis®) is submerged in cell suspension. (C) Debridement of wound and application of ASC-seeded artificial dermis is placed on the defect and sutured to the adjacent wound margin. (D) Vascular tissue ingrowth is noted after 2 weeks. (E) After removal of the silicone layer of the artificial dermis, a thin split thickness skin graft is placed on the engineered vascular bed. (F) Two weeks after skin graft placement.
SALVAGE OF IMPENDING SKIN NECROSIS: RECOVERY OF TISSUE ISCHEMIA
The use of hyaluronic acid (HA) and other types of filler has become popular worldwide for improvement of facial soft tissue contours, nose augmentation, and to reduce fine wrinkles on the face. Consequently, there are an increasing number of reports of complications associated with filler injection (25, 26, 27). Inadvertent arterial injection of HA filler results in arterial obstruction and local tissue ischemia. Involved areas are characterized by pale skin with central brownish spots and intense pain. If the ischemia is not relieved within 5 days, skin necrosis becomes obvious with the formation of eschar. The glabella and nasal ala are particularly vulnerable to tissue necrosis following filler injection (27).
A previous report showed that subcutaneous injection of hyaluronidase within 24 hr may reduce the area of skin necrosis in cases of impending skin necrosis after HA filler injection (28). Another case report demonstrated that treating this condition with ASCs harvested from autologous fat tissue produces satisfactory results with minimal scar formation (25). In Korea, HA filler-related complications are common and ASCs are widely used to manage this problem. Unlike hyaluronidase treatment, the use of ASCs is very effective at recovering ischemia until 4-5 days after the onset of complications and can reduce the area of necrosis even 7 days after the onset (Fig. 2). Subcutaneous injection of millions of ASCs harvested from 20-50 mL of fat tissue can rapidly relieve local ischemia and pain by promoting neoangiogenesis (Fig. 3). The cells may be suspended in 1-2 mL of saline or PRP before subcutaneous injection. Injection should be conducted as soon as possible after the cells are mixed with PRP because the ASC-PRP mixture may easily clot before delivery.
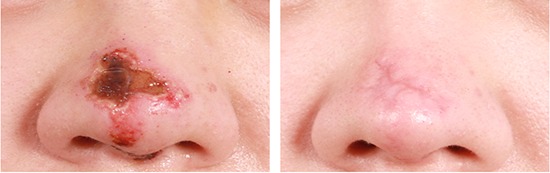
Fig. 2.
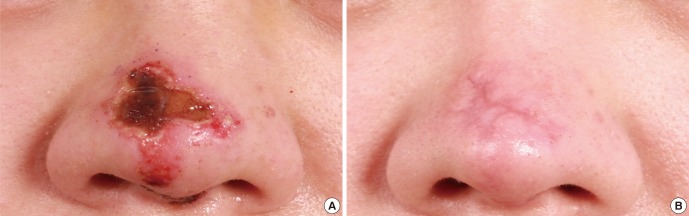
ASC-based cell therapy for a case of acute skin necrosis in the nose dorsum due to inadvertent arterial injection of hyaluronic acid (HA) filler. (A) Before stem cell therapy (seven days after HA filler injection). (B) Three weeks after stem cell therapy.
Fig. 3.
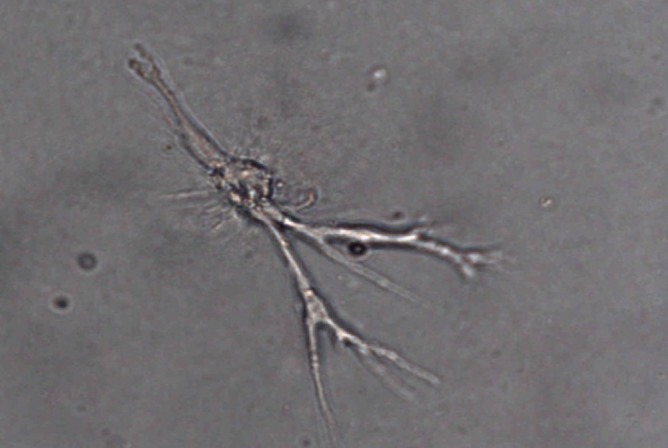
Adipose stem cells (ASCs) differentiate into microtubules to form capillaries under ischemic conditions.Under ischemic conditions, differentiation of ASCs into micro-vessels is noted at 24 hr. Typical microtubules are formed (×400 magnification).
MANAGEMENT OF SCARS WITH ASCS: SCAR REMODELING AND EARLY MATURATION
Scarring is a form of incomplete healing that leaves some degree of deformation and/or defect in animals and humans. Regeneration is another form of healing that does not leave any visible scar or defect in animals such as rodents or amphibians. A well-known example of tissue regeneration occurs in broken tails of lizards. Incomplete healing of defects in humans is related to a less effective system of adult stem cells. Important elements of coordinated cell mobilization, targeting, and functioning of adult stem cells during the healing process appear to be defective in humans (29, 30).
With the discovery of ASCs, it has become very easy to introduce large numbers of adult stem cells to the injured target area using a type of stem cell therapy. Since primary ASCs are so easily harvested from fat tissue, cell-based therapy can be repeated without cell culturing which is a great barrier against active clinical application. Although the exact number is not known, providing a massive amount of adult stem cells may change the course of the human healing process toward a more complete form that resembles scarless regeneration when the environment is ready. In Korea, this type of ASC-based therapy to modulate scar formation has become more popular (31, 32). For application, large amounts of primary ASCs are repeatedly injected into the firm scarred tissue bed to speed up the scar remodeling process. This treatment causes the scar become very soft within several months, at which time early secondary surgery may be possible. The appearance of abundant ASCs within the scar tissue bed may alter the scar remodeling process. Another type of ASC-based cell therapy is delivery of cells for the prevention of scarring from the beginning of wound healing in patients with severe facial trauma. Although no scientific data have been published, clinical result of ASC-based therapy for treatment of facial lacerations has been presented in scientific meetings of the Korean Society of Plastic Surgeons (31).
BANKING OF ASCS: PRESERVATION OF CELLS FOR FUTURE USE
There are several companies that provide cell banking services in Korea. This is in part because there have been many reports of adult stem cells from elderly patients being less effective than those from younger people (33, 34). For banking, customers' cells are safely collected, tested, and cryopreserved in a good manufacturing practice (GMP)-grade facility for the future use of adult stem cells at older age. These cells will likely play an important role in the treatment of diseases and regeneration of damaged tissue.
DISCUSSION
Since publication of the first paper on ASCs in 2000 (1), there has been a tremendous amount of investment and basic research devoted to this new type of adult stem cell. According to many scientific reports published during the last decade, ASCs can differentiate into osteoblasts, chondrocytes, vascular endothelial cells, cardiomyocytes, and neuronal cells (3, 4, 5, 6). More than 10 yr of animal experiments using comparative studies with BMSCs have produced evidence of the regeneration potential of ASCs. The major role of regenerative medicine in this century is based on cell therapy in which ASCs are going to play a primary role.
Efforts to integrate ASCs into clinical techniques and business investment ventures followed demonstration of their effectiveness in animal studies. Several types of machines designed to recover stromal vascular fraction (SVF) cells from suction fat tissue have also been developed and are now commercially available (35, 36). Cell recovery rates determined based on the SVF cells vary greatly among machines; however, they are generally much lower than those of manual recovery techniques.
Collagenase is a key element in effective recovery of cells from fat tissue by enzymatic digestion in a process known as adipo-dissociation. This enzyme is also a hurdle to more active clinical application of ASCs because it can be a potential harmful element in cell suspensions after adipo-dissociation. The FDA strictly prohibits the use of unapproved collagenase in clinical purposes. Indeed, Xiaflex (Pfizer Inc., New York, USA), which is a FDA-approved collagenase for the treatment of Dupuytren contracture (37), is the only collagenase that can be lawfully used to harvest SVF cells in clinical applications; however, its current price is so high that its use is not yet practical.
Plastic surgeons in Korea and Japan have played a leading role in clinical translation of ASCs because government regulations in these countries are less strict than those in Western nations. Clinical application of primary ASCs as a form of SVF cells has become increasingly popular in East Asian countries (7, 8, 9, 10, 11). SVF cells have been used in a limited number of clinical techniques such as fat grafting, wound care, control of local ischemia, and scar remodeling. The positive results of clinical application of ASCs in plastic surgery have led more doctors to engage in ASC-based therapy. However, further scientific clinical research is needed to define a therapeutic dose of cells for each indication and a safe and effective route of cell administration while avoiding potential complications of ASC-based therapy. In plastic surgery, many potential candidate conditions for ASC-based therapy are associated with the skin surface or the area immediately underneath the skin surface, which enables easy and effective application of cells to the target. This may be a reason for the more active clinical application of ASCs in plastic surgery relative to other fields of clinical medicine.
The use of reconstruction ladder, which is representing the logical and reasonable approach for decision of methods of tissue reconstruction, is losing its foundation and should be revised. Currently, defects are reconstructed based on a new concept of plastic and regenerative surgery. For small defects, application of stem cells should be attempted before other surgical reconstruction techniques are performed. Tissue engineering method utilizing scaffolds should be considered for more challenging and larger defects. Relatively large defects may be treated with ASC-based cell therapy and tissue engineering to avoid further donor deformities. At present, few plastic surgeons are using ASCs for tissue repair and regeneration; however, more will likely participate in identification of new methods of clinical applications for ASCs and contribute to the development of regenerative medicine.
The distal portion of skin flaps are frequently compromised by inadequate blood flow. Many of the compromised flaps recover spontaneously, but flap failure is problematic in aesthetic surgery, especially in facial areas. Historically, plastic surgery has been intimately related with flap circulation and salvage of ischemic flaps has been a great topic for plastic surgeons (38, 39). Surgical delay before flap transfer is well-known to increase distal skin flap circulation and overall flap survival (40, 41). Several pharmacologic agents such as steroids and dextran have reported to improve flap circulation, but their effects in actual flap salvage may be limited (42, 43). It is now possible to utilize the angiogenic potency of ASCs as a potent support to improve blood flow of local skin flaps. Angiogenic differentiation of ASCs is reportedly initiated under ischemic conditions (7), and cells differentiate into micro-vessels within flap tissue, where oxygen tension is relatively low compared with normal tissue. In flap surgery, ASCs may be applied during flap elevation, and cells may be used alone as a cell suspension in a small amount of normal saline or cells may be mixed with a small amount of PRP.
Although we still do not understand the mechanism of mobilization and targeting of adult stem cells in humans, it is currently possible to apply a therapeutic number of cells directly into a target wound, which may result in improved healing. Accordingly, ASC-based cell therapy for scar improvement is becoming increasingly popular in the aesthetic surgery market within Korea. In the near future, ASC-based cell therapy will be a new therapeutic option for simple laceration wound management to enable complete healing without any scar formation.
Banking of ASCs or SVF cells is a new business in Korea; however, we still do not know how they will be utilized after decades of storage. Government regulation of cell preservatives used for cryopreservation of cells may also become an issue in the future. Di-methyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is the most commonly used cryopreservative; however, there has been a report of DMSO toxicity at concentrations below 10% (44). Recently in Korea, controlled clinical trials evaluating the use of cultured ASCs to treat major diseases were conducted under the surveillance of the Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Cell culturing, cell banking, and manipulation of cells will increase the effectiveness and feasibility of stem cell therapy. However, there is a risk of contamination or cell deterioration during these processes. Therefore, the Korean government strictly requires GMP-grade facilities for the clinical application of cultured cells.
In conclusion, the future of ASC-based cell therapy is wide open. The therapeutic potential of ASCs has been tested during the last decade and they have been effectively utilized in the field of plastic surgery. However, ASCs are not only useful for plastic surgery, but for all fields of regenerative medicine. Currently, the main obstacle inhibiting the progression of stem cell technology seems to be government regulation. Accordingly, government should try to find a way to promote new scientific endeavors while serving as regulatory entities to ensure the safety of their citizens.
Footnotes
This study was supported by a grant from the Yeungnam University Medical Center (2007).
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
- 1.Fuh E, Brinton TJ. Bone marrow stem cells for the treatment of ischemic heart disease: a clinical trial review. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2009;2:202–218. doi: 10.1007/s12265-009-9095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yang JD, Choi DS, Cho YK, Kim TK, Lee JW, Choi KY, Chung HY, Cho BC, Byun JS. Effect of amniotic fluid stem cells and amniotic fluid cells on the wound healing process in a white rat model. Arch Plast Surg. 2013;40:496–504. doi: 10.5999/aps.2013.40.5.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jeong JH. Chondrogenic differentiation of human adipo-derived precursor cells. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000;27:136–142. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, Huang J, Futrell JW, Katz AJ, Benhaim P, Lorenz HP, Hedrick MH. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7:211–228. doi: 10.1089/107632701300062859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tholpady SS, Llull R, Ogle RC, Rubin JP, Futrell JW, Katz AJ. Adipose tissue: stem cells and beyond. Clin Plast Surg. 2006;33:55–62. doi: 10.1016/j.cps.2005.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lee JH, Lee KH, Kim MH, Kim JP, Lee SJ, Yoon J. Possibility of undifferentiated human thigh adipose stem cells differentiating into functional. Arch Plast Surg. 2012;39:593–599. doi: 10.5999/aps.2012.39.6.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jeong JH. Adipose stem cells and skin repair. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2010;5:137–140. doi: 10.2174/157488810791268690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lee SK, Kim DW, Dhong ES, Park SH, Yoon ES, Lee SK, Kim DW, Dhong ES, Park SH, Yoon ES. Facial soft tissue augmentation using autologous fat mixed with stromal vascular fraction. Arch Plast Surg. 2012;39:534–539. doi: 10.5999/aps.2012.39.5.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Matsumoto D, Sato K, Gonda K, Takaki Y, Shigeura T, Sato T, Aiba-Kojima E, Iizuka F, Inoue K, Suga H, et al. Cell-assisted lipotransfer: supportive use of human adipose-derived cells for soft tissue augmentation with lipoinjection. Tissue Eng. 2006;12:3375–3382. doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.12.3375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yoshimura K, Sato K, Aoi N, Kurita M, Hirohi T, Harii K. Cell-assisted lipotransfer for cosmetic breast augmentation: supportive use of adipose-derived stem/stromal cells. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2008;32:48–55. doi: 10.1007/s00266-007-9019-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yoshimura K, Sato K, Aoi N, Kurita M, Inoue K, Suga H, Eto H, Kato H, Hirohi T, Harii K. Cell-assisted lipotransfer for facial lipoatrophy: efficacy of clinical use of adipose-derived stem cells. Dermatol Surg. 2008;34:1178–1185. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4725.2008.34256.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Eto H, Kato H, Suga H, Aoi N, Doi K, Kuno S, Yoshimura K. The fate of adipocytes after nonvascularized fat grafting: evidence of early death and replacement of adipocytes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;129:1081–1092. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e31824a2b19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Castro-Govea Y, De La Garza-Pineda O, Lara-Arias J, Chacón-Martínez H, Mecott-Rivera G, Salazar-Lozano A, Valdes-Flores E. Cell-assisted lipotransfer for the treatment of parry-romberg syndrome. Arch Plast Surg. 2012;39:659–662. doi: 10.5999/aps.2012.39.6.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lee JW, Kwon OH, Kim TK, Cho YK, Choi KY, Chung HY, Cho BC, Yang JD, Shin JH. Platelet-rich plasma: quantitative assessment of growth factor levels and comparative analysis of activated and inactivated groups. Arch Plast Surg. 2013;40:530–535. doi: 10.5999/aps.2013.40.5.530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Patel S, Dhillon MS, Aggarwal S, Marwaha N, Jain A. Treatment with platelet-rich plasma is more effective than placebo for knee osteoarthritis: a prospective, double-blind, randomized trial. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41:356–364. doi: 10.1177/0363546512471299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cervelli V, Palla L, Pascali M, De Angelis B, Curcio BC, Gentile P. Autologous platelet-rich plasma mixed with purified fat graft in aesthetic plastic surgery. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2009;33:716–721. doi: 10.1007/s00266-009-9386-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Choi J, Minn KW, Chang H. The efficacy and safety of platelet-rich plasma and adipose-derived stem cells: an update. Arch Plast Surg. 2012;39:585–592. doi: 10.5999/aps.2012.39.6.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Jeon H, Kim J, Yeo H, Jeong H, Son D, Han K. Treatment of diabetic foot ulcer using matriderm in comparison with a skin graft. Arch Plast Surg. 2013;40:403–408. doi: 10.5999/aps.2013.40.4.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zayakova Y, Stanev A, Mihailov H, Pashaliev N. Application of local axial flaps to scalp reconstruction. Arch Plast Surg. 2013;40:564–569. doi: 10.5999/aps.2013.40.5.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Park JS, Roh SG, Lee NH, Yang KM. Versatility of the distally-based sural artery fasciocutaneous flap on the lower leg and foot in patients with chronic disease. Arch Plast Surg. 2013;40:220–225. doi: 10.5999/aps.2013.40.3.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sorrell JM, Caplan AI. Topical delivery of mesenchymal stem cells and their function in wounds. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2010;1:30. doi: 10.1186/scrt30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lee NH, Pae WS, Roh SG, Oh KJ, Bae CS, Yang KM. Innervated cross-finger pulp flap for reconstruction of the fingertip. Arch Plast Surg. 2012;39:637–642. doi: 10.5999/aps.2012.39.6.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yun MJ, Park JU, Kwon ST. Surgical options for malignant skin tumors of the hand. Arch Plast Surg. 2013;40:238–243. doi: 10.5999/aps.2013.40.3.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kwon KH, Lee DG, Koo SH, Jo MS, Shin H, Seul JH. Usefulness of v-y advancement flap for defects after skin tumor excision. Arch Plast Surg. 2012;39:619–625. doi: 10.5999/aps.2012.39.6.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sung HM, Suh IS, Lee HB, Tak KS, Moon KM, Jung MS. Case reports of adipose-derived stem cell therapy for nasal skin necrosis after filler injection. Arch Plast Surg. 2012;39:51–54. doi: 10.5999/aps.2012.39.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Do ER, Shim JS. Long-term complications from breast augmentation by injected polyacrylamide hydrogel. Arch Plast Surg. 2012;39:267–269. doi: 10.5999/aps.2012.39.3.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Park TH, Seo SW, Kim JK, Chang CH. Clinical experience with hyaluronic acid-filler complications. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:892–896. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2011.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kim DW, Yoon ES, Ji YH, Park SH, Lee BI, Dhong ES. Vascular complications of hyaluronic acid fillers and the role of hyaluronidase in management. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:1590–1595. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2011.07.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dimarino AM, Caplan AI, Bonfield TL. Mesenchymal stem cells in tissue repair. Front Immunol. 2013;4:201. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Fong EL, Chan CK, Goodman SB. Stem cell homing in musculoskeletal injury. Biomaterials. 2011;32:395–409. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.08.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Oh YH. Use of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) treatment in rhinoplasty: abstract book of aesthetic plastic surgery. Seoul: EXCO; 2013. p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Jeong JH. Clinical stem cell therapy in plastic surgery: abstract book of aesthetic plastic surgery. Seoul: EXCO; 2013. p. 61. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kanawa M, Igarashi A, Ronald VS, Higashi Y, Kurihara H, Sugiyama M, Saskianti T, Pan H, Kato Y. Age-dependent decrease in the chondrogenic potential of human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells expanded with fibroblast growth factor-2. Cytotherapy. 2013;15:1062–1072. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2013.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Fan M, Chen W, Liu W, Du GQ, Jiang SL, Tian WC, Sun L, Li RK, Tian H. The effect of age on the efficacy of human mesenchymal stem cell transplantation after a myocardial infarction. Rejuvenation Res. 2010;13:429–438. doi: 10.1089/rej.2009.0986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Aronowitz JA, Ellenhorn JD. Adipose stromal vascular fraction isolation: a head-to-head comparison of four commercial cell separation systems. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;132:932e–939e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182a80652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wang L, Lu Y, Luo X, Fu MG, Hu X, Dong H, Fan ZH. Cell-assisted lipotransfer for breast augmentation: a report of 18 patients. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012;28:1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gilpin D, Coleman S, Hall S, Houston A, Karrasch J, Jones N. Injectable collagenase Clostridium histolyticum: a new nonsurgical treatment for Dupuytren's disease. J Hand Surg Am. 2010;35:2027–2038. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2010.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Baynosa RC, Zamboni WA. The effect of hyperbaric oxygen on compromised grafts and flaps. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2012;39:857–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Parry DJ, Byrne P, Kessel D, Robertson I, Patel J, Batchelor A, Scott DJ. Pharmacological salvage of a combined distal bypass and free flap with catheter-directed thrombolysis. Br J Plast Surg. 2002;55:140–144. doi: 10.1054/bjps.2002.3744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Atisha D, Alderman AK, Janiga T, Singal B, Wilkins EG. The efficacy of the surgical delay procedure in pedicle TRAM breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2009;63:383–388. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e31819516ba. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wang HT, Hartzell T, Olbrich KC, Erdmann D, Georgiade GS. Delay of transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap reconstruction improves flap reliability in the obese patient. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;116:613–618. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000172978.99778.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nakatsuka T, Pang CY, Neligan P, Lindsay WK, Zuker RM. Effect of glucocorticoid treatment on skin capillary blood flow and viability in cutaneous and myocutaneous flaps in the pig. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1985;76:374–385. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198509000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Rothkopf DM, Chu B, Bern S, May JW., Jr The effect of dextran on microvascular thrombosis in an experimental rabbit model. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1993;92:511–515. doi: 10.1097/00006534-199309000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Galvao J, Davis B, Tilley M, Normando E, Duchen MR, Cordeiro MF. Unexpected low-dose toxicity of the universal solvent DMSO. FASEB J. 2014 doi: 10.1096/fj.13-235440. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-235440fj.13-235440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]