Abstract
The increasing use of endoscopy has led to more discernable abnormalities in the stomach, including polyps. Gastric polyps encompass a spectrum of pathologic conditions that can vary in histology, neoplastic potential, and management. Despite their high prevalence, there is a paucity of literature to support management and treatment decisions for endoscopists. The goal of this review is to summarize clinical, endoscopic, and histopathologic features of various polyps, review syndromes associated with such polyps, and provide management recommendations.
Keywords: Gastric polyps, stomach polyps, management
With the increasing use of endoscopy, visually discernible abnormalities, such as polyps in the gastrointestinal tract, are encountered more often. Gastric polyps most frequently originate in the mucosa but encompass a broad spectrum of pathologic conditions that may even be submucosal or extrinsic. Found in 6% of upper endoscopies, gastric polyps are a heterogeneous group of epithelial and subepithelial lesions that can vary in histology, neoplastic potential, and management (Table).1,2 Even though most are asymptomatic (>90%), larger polyps may present with bleeding, anemia, obstruction, or abdominal pain. Most have no risk of cancer, but there are certain subsets of polyps with malignant potential, necessitating further endoscopic treatment and/or periodic surveillance. These polyps are typically identified histologically because they have no reliable distinguishing endoscopic features. As many gastric polyps have similar endoscopic appearances, their classification depends on the histologic compartments from which they arise (ie, epithelial, hamartomatous, or mesenchymal).
Table.
Endoscopic and Histologic Features of Gastric Polyps
| Type of Polyp | Neoplastic Potential | Location | Initial Management | Follow-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fundic gland polyp (sporadic or FAP) | Low | Sporadic: body, fundus FAP: covers the entire stomach |
Biopsy unless >1 cm, then consider polypectomy | If no dysplasia, no follow-up If dysplastic, consider FAP diagnosis and perform colonoscopy |
| Hyperplastic polyp | Minimal but associated with synchronous cancers | Any location in the stomach | Biopsy or polypectomy Multiple biopsies of intervening mucosa Test and treat for Helicobacter pylori |
Repeat EGD in 1 year If polyp persists or dysplasia is present, remove via polypectomy and repeat EGD in 1 year If no residual polyp, no follow-up |
| Adenomatous polyp | High | Any location in the stomach | Complete polypectomy Sample surrounding mucosa Examine the entire stomach for abnormalities |
Incomplete resection or high-grade dysplasia: 6 months Completely resected polyp without high-grade dysplasia: 1 year |
| Inflammatory fibroid polyp | Very low | Antrum or prepylorus | Biopsy Remove for obstructive symptoms |
No follow-up |
| Gastric neuroendocrine tumor (formerly carcinoid) | Depends on the type | Anywhere in the stomach I: fundus and body, clusters II: fundus and body, clusters III: anywhere in the stomach, solitary IV: anywhere in the stomach, solitary, poor prognosis |
Biopsy or endoscopic removal of small lesions (<1 cm) and few numbers (3-5) for type I Random biopsies of flat mucosa |
Surveillance is controversial and should be individualized I: No further follow-up if completely resected; associated with AMAG II: Consider gastrin-secreting tumor or MEN 1 syndrome III: Assess for metastasis; consider surgical removal if no metastasis IV: Assess for metastasis; consider surgical removal if no metastasis |
| Ectopic pancreas | None | Small submucosal mass, central umbilication | Biopsy if uncertain | No follow-up |
| GIST | High | Submucosal mass, central ulceration | Biopsy or FNA with EUS | Controversial; if not removed, consider follow-up with EUS |
| Leiomyoma | Low | Rounded submucosal lesions, rubbery feel on endoscopy | Biopsy or FNA with EUS | None if asymptomatic |
| Granular cell tumor | Low | Proximal stomach, yellow subepithelial nodules in submucosa | Biopsy | None if benign |
The recommendations for initial management and follow-up should be followed at the discretion of the endoscopist.
AMAG, autoimmune metaplastic atrophic gastritis; EGD, esophagogastroduodenoscopy; EUS, endoscopic ultrasound; FAP, familial adenomatous polyposis; FNA, fine-needle aspiration; GIST, gastrointestinal stromal tumor; MEN, multiple endocrine neoplasia.
Epithelial Polyps
Epithelial polyps are the most commonly encountered gastric polyps. They include fundic gland polyps (FGPs), hyperplastic polyps, and adenomatous polyps, all of which are associated with distinctly different clinical contexts, as discussed below. Other less common epithelial lesions that may present as polyps include neuroendocrine tumors (formerly carcinoids), ectopic pancreatic tissue, and pyloric gland adenomas.
Fundic Gland Polyps
FGPs are one of the most common polyps found in the stomach (47%),3 observed in 0.8% to 23% of all endoscopies.4-6 These polyps come in 3 distinct clinical contexts: sporadic polyps, polyps associated with proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use, and syndromic polyps (ie, familial adenomatous polyposis [FAP] syndrome).
Sporadic FGPs are sessile polyps located in the body and fundus.7 In general, their surface color is indistinguishable from that of normal gastric mucosa, and these lesions lack a stalk.8 On microscopy, they contain dilated glands lined by gastric body mucosa.4 Most endoscopists can diagnose these polyps on appearance alone with 89% accuracy4; the lesions appear as hyper-emic, translucent, broad-based polyps with a smooth surface. The lesions vary in size from 1 mm to 8 mm and are most commonly found in middle-aged women,9 although much larger polyps are also seen in adult men and women of all age groups.
These polyps are caused by an activating mutation of the beta-catenin gene, which is involved in cell growth signaling pathways.10-12 This subtype of FGP is not associated with atrophic gastritis, and the prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection is low.13-16 In fact, H pylori seems to have a protective effect on FGP, since H pylori eradication is associated with polyp regression.17 The risk of dysplasia in these polyps is diminutive, with a less-than-1% chance of malignancy.18-20
Since 1993, there have been multiple reports of the role of PPIs in the development of gastric polyps.6,7 One study found FGPs in 23% of patients on PPIs, compared with a 12% incidence in patients not taking PPIs.6 Other large studies of patients who have been on long-term PPI therapy (defined as ≥5 years) had a 4-times higher prevalence for development of FGP.6,21 Furthermore, withdrawal of PPI therapy subsequently led to a reduction in FGPs. In addition to inducing enterochromaffinlike (ECL) cell hyperplasia, PPIs cause characteristic dilation of oxyntic glands and parietal cell protrusions, resulting in a histologically serrated glandular appearance.7,22
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis and Fundic Gland Polyps
FAP is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by numerous epithelial-derived polyps located throughout the gastrointestinal tract, most commonly in the colon. This condition is caused by a germline mutation of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor suppressor gene. The overall incidence of the mutation is between 1 in 10,000 and 1 in 15,000 births. By age 35 years, 95% of persons with FAP have polyps (>100 adenomas). The mean age of colon cancer in untreated persons is 39 years (range, 34-43 years).
Gastric polyps are reported in 30% to 100% of patients with FAP7; the large majority—95%—are FGPs, while the remaining 5% are adenomatous polyps (discussed later). FGPs are exceptionally common in patients with FAP (20%-100%)23 and arise from a mutation in the APC gene.24 Unlike in the sporadic setting, FGPs associated with FAP usually carpet the body of the stomach. Dysplasia is seen in 25% to 41% of FAP-associated FGPs,8 whereas it is rare in sporadic FGPs. It follows that when dysplasia is identified in a sporadic FGP, one should have a high index of suspicion for FAP syndrome.5,10,23 Unfortunately, there are no reliable endoscopic or histologic characteristics to distinguish FAP-associated polyps from sporadic FGPs. Clinical history and number of polyps are critical in this assessment, although the precise number of polyps needed to prompt further investigation is not defined.7 When present, dysplasia is typically low grade, and risk factors for dysplasia include large polyp size, higher Spigelman classification of duodenal polyposis, and the presence of antral gastritis.23
Current guidelines7 do not require polypectomy for sporadic FGP due to its low malignancy potential. However, despite the characteristic endoscopic appearance of FGP, biopsy is recommended at the initial endoscopy to exclude dysplasia or adenocarcinoma as well as the need for further polypectomy if other types of polyps are present. FGPs greater than 1 cm should be resected due to sampling error from forceps biopsy alone.9 Colonic investigation should be performed to exclude FAP in patients with numerous polyps who are under the age of 40 years, especially in the absence of concurrent PPI use or when biopsies demonstrate dysplasia, although there is little evidentiary support for this recommendation.7 Surveillance endoscopy is not recommended for patients with nondysplastic sporadic FGPs.
Hyperplastic Polyps
The hyperplastic polyp is the second most common gastric polyp after the FGP. A common misnomer for this polyp is inflammatory polyp, a term that should be discouraged because it can be confused with inflammatory fibroid polyp (IFP), which is managed much differently.7 Hyperplastic polyps are usually sessile or pedunculated, are less than 2 cm in diameter,7 and typically occur in the antrum, although they can arise anywhere. Histologically, there is a proliferation of surface foveolar cells lining elongated, tortuous pits, imparting a corkscrew appearance that extends deep into the lamina propria. Gastric hyperplastic polyps may contain pyloric glands, chief cells, and parietal cells, and their histologic appearance can overlap with hamartomas and inflammatory conditions.7 The surface epithelium may also contain erosions or ulcerations leading to gastrointestinal bleeding.9
Unlike the incidental colonic hyperplastic polyp, gastric hyperplastic polyps do have clinical significance despite the similarities in nomenclature. Gastric hyper-plastic polyps are strongly associated with inflammatory disorders such as chronic gastritis, H pylori gastritis, pernicious anemia, and reactive or chemical gastritis.11,25 As such, it is worthwhile to biopsy the background fat mucosa to identify any etiologic factors. In fact, when H pylori is the culprit, 80% of hyperplastic polyps will regress with H pylori eradication, prior to endoscopic removal.26-28 Additionally, in areas adjacent to erosions/ ulcer or gastroenterostomy sites, there can be multiple hyperplastic polyps.4,22
Interestingly, these polyps themselves have little neoplastic potential but are associated with an increased risk of synchronous cancer elsewhere in the gastric mucosa, particularly if associated with chronic gastritis.29 Unfortunately, the prevalence of dysplasia arising in hyperplastic polyps varies greatly, ranging from 1.9% to 19%, and cases of adenocarcinoma range from 0.6% to 2.1%.29-36 This discrepancy is most likely due to the small series of patients in study populations; the location of the various studies, specifically in Asia, which tends to have a higher prevalence of gastric cancers in general; and the different sizes of hyperplastic polyps used as denominators in these studies.
Due to the low dysplastic potential of these polyps and the risk of synchronous cancers, it is not clear if hyperplastic polyps should be endoscopically resected or simply biopsied. The lack of consensus stems from the concern that forceps biopsy sampling may miss the dysplastic foci within a hyperplastic polyp.7 The size cutoff for resection is debatable as well, with some authors recommending a 2-cm minimum for polypectomy,37 while others recommend resection of all polyps greater than 0.5 cm.30 Furthermore, the risk of adenocarcinoma in the surrounding nonpolypoid tissue is greater than in the polyp itself. As such, current recommendations require multiple biopsies of the fat uninvolved mucosa surrounding the polyp.7 Ultimately, it is at the endoscopist’s discretion to determine whether a polypectomy is warranted, relying on the size of the lesions and the clinical context. Testing for H pylori and eradication when present should be performed.7 Surveillance is recommended with a single repeat endoscopy at 1 year, but further surveillance subsequently is not recommended due to lack of evidence and should be an area for future research.7
Adenomatous Polyps
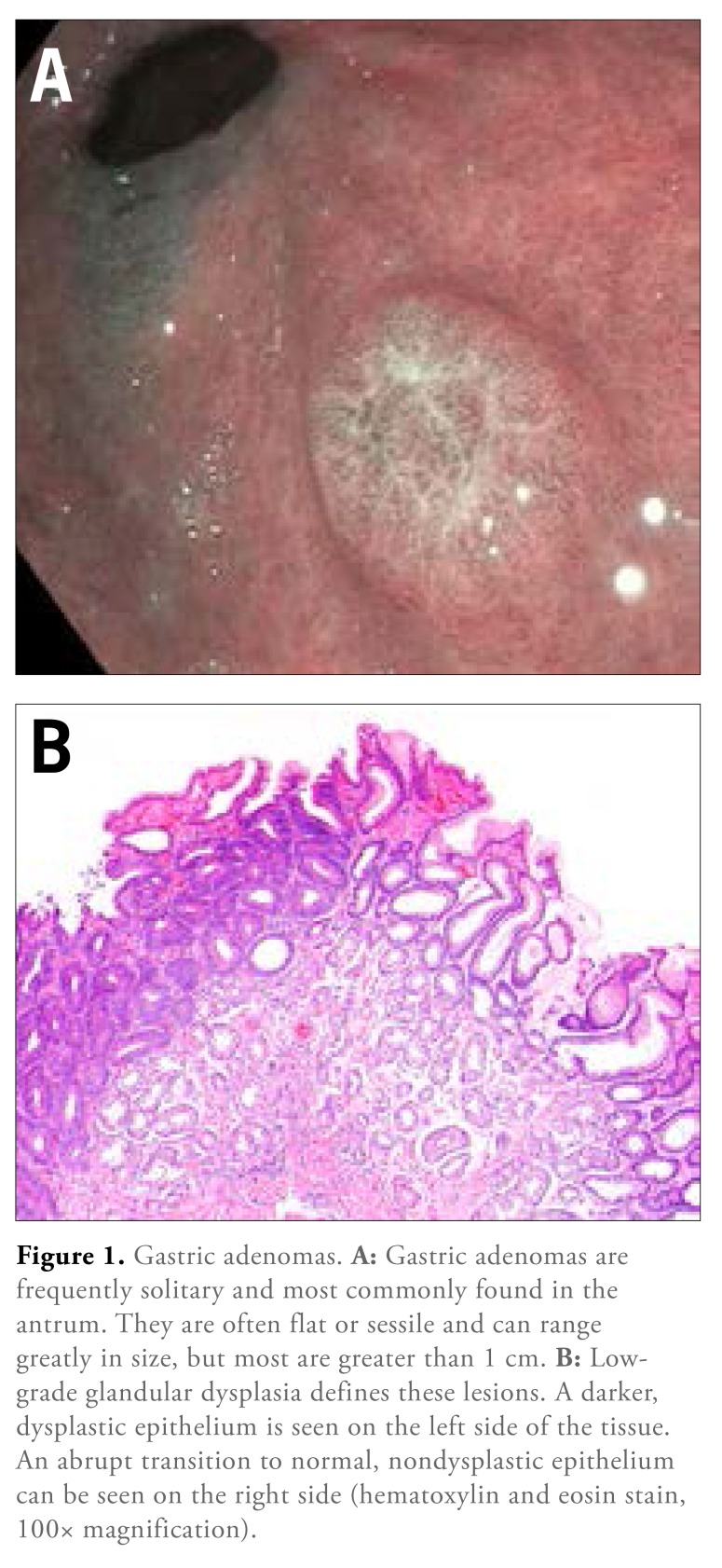
Gastric adenomas, or gastric polypoid dysplasia, are true neoplasms and precursors to gastric cancer. Although commonly seen in countries with high gastric cancer rates (eg, Korea, Japan, and China), they also account for 6% to 10% of all gastric polyps in Western populations.9 Histologically, they are classified similarly to colon adenomas with tubular, villous, and tubulovillous distinctions. Frequently solitary, they are most commonly found in the antrum but can be located anywhere in the stomach. Endoscopically, they are often fat or sessile rather than pedunculated and can range in size from a few millimeters to centimeters9 (Figure 1). Atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia are frequently associated with the development of these polyps, but there is no proven association with H pylori infection. Polyps that are greater than 2 cm and have villous histology have a higher risk of neoplasia (28%-40%).38-43 The presence of high-grade dysplasia is associated with an increased risk of invasive gastric cancer both within the polyp and in synchronous areas of the stomach.35,44
Figure 1.
Gastric adenomas. A: Gastric adenomas are frequently solitary and most commonly found in the antrum. They are often flat or sessile and can range greatly in size, but most are greater than 1 cm. B: Low-grade glandular dysplasia defines these lesions. A darker, dysplastic epithelium is seen on the left side of the tissue. An abrupt transition to normal, nondysplastic epithelium can be seen on the right side (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 100× magnification).
Due to the increased risk of malignancy associated with these polyps, recommendations include complete removal of the adenoma, with further examination of the entire gastric mucosa for abnormalities, all of which should be biopsied. Additionally, endoscopic follow-up is required after resection at 6 months (for incompletely resected polyps or high-grade dysplasia) or 1 year (for all other polyps). Operative resection should be considered for gastric adenomas that are not amenable to endoscopic resection. However, it should be noted that the most effective and optimal surveillance protocol for adenomatous polyps is yet to be established.
Gastric Neuroendocrine Tumors (Formerly Carcinoids)
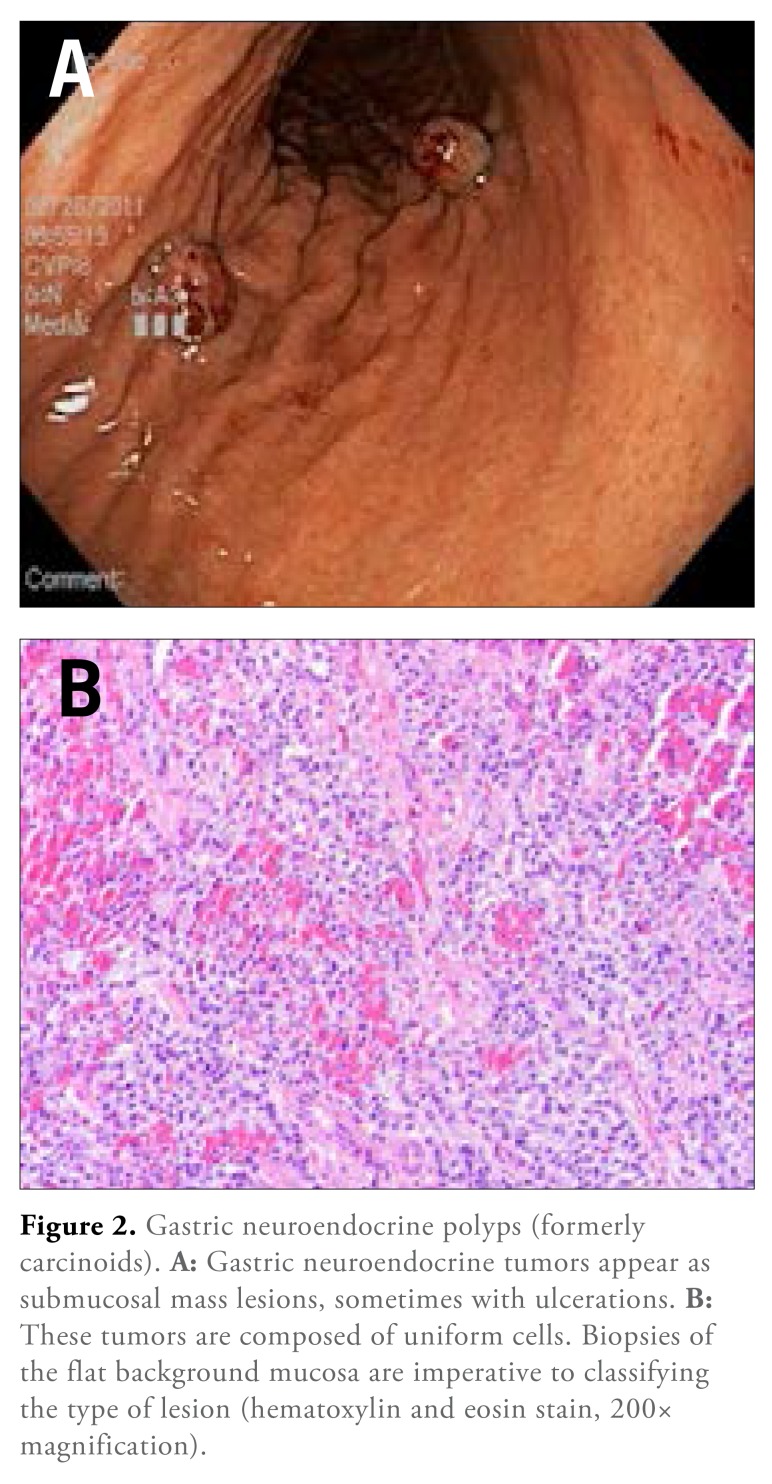
Most gastric neuroendocrine tumors are composed of ECL-like cells, typically in the corpus and fundus (90%),3 which stain with chromogranin A or synaptophysin by immunohistochemistry. There are 4 types of carcinoids in the stomach, each arising in different clinical contexts, and each with distinct prognoses and treatment protocols. This particular tumor underscores the importance of tandem biopsies of the background fat mucosa. Endoscopically, they appear as submucosal mass lesions, sometimes with ulcerations.45 In type I and II carcinoids, several polyps are seen in clusters arising nearly exclusively in the body-fundic–type mucosa. Type III lesions are usually solitary and may occur throughout the stomach. Type IV carcinoids may arise anywhere in the stomach and have a significantly worse prognosis. Histologically, these neuroendocrine tumors appear similar, and biopsies of the nonpolypoid mucosa are critical in distinguishing tumor type, prognosis, and treatment (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Gastric neuroendocrine polyps (formerly carcinoids). A: Gastric neuroendocrine tumors appear as submucosal mass lesions, sometimes with ulcerations. B: These tumors are composed of uniform cells. Biopsies of the flat background mucosa are imperative to classifying the type of lesion (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 200× magnification).
Type I neuroendocrine tumors are the most common. These occur in middle-aged women (70%-80%) and are the result of ECL cell hyperplasia arising in the setting of autoimmune metaplastic atrophic gastritis (also known as autoimmune gastritis). The pathogenesis of type I neuroendocrine tumors is as follows: the autoimmune destruction of parietal cells leads to reduced gastric acid production and loss of feedback inhibition of gastrin secretion in the antral G cells. The resulting high levels of gastrin stimulate ECL cells to proliferate, which appear as multiple small nodules in the body of the stomach. Technically, this represents a reversible hyperplasia but may progress to malignancy, especially as tumors enlarge.
Compared with type II and type III neuroendocrine tumors, type I lesions have an excellent prognosis with exceedingly low rates of metastatic disease.46 Endoscopic mucosal resection of any visible lesions and close endoscopic follow-up are prudent, but no existing guidelines or recommendations exist at this time, and endoscopic mucosal resection is an area of future research. Antrectomy to remove the stimulatory G cells has also proven useful as long-term therapy, and treatment of any underlying pernicious anemia is recommended.47 Biopsies of the background fat mucosa are critical in separating this low-risk tumor from others in the group.
Type II neuroendocrine tumors are rare and arise in the setting of multiple endocrine neoplasia 1 syndrome, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, or a gastrin-secreting tumor elsewhere in the gastrointestinal tract. The uninhibited gastrin secretion stimulates ECL cells to proliferate, resulting in gastric neuroendocrine tumors (often multiple). These type II tumors have a worse prognosis than do type I tumors, with metastasis in approximately 30% of cases.46 However, type II tumors behave distinctly better than type III tumors, again underscoring the importance of differentiating neuroendocrine tumor type, which can be achieved by providing tandem biopsies of the uninvolved background mucosa to the pathologist. Local resection of the neuroendocrine tumor, evaluation of metastatic disease, and resection of the stimulatory gastrin-secreting tumor (usually found in the small bowel) are the mainstays of therapy.46
Type III neuroendocrine tumors, the second most common type, have no associated clinical syndrome or context; rather, these lesions are sporadic. Whereas type I and type II tumors arise predominantly in the gastric body and are multiple, type III tumors can arise anywhere in the stomach and are typically solitary. In contrast to the excellent prognosis of type I and type II tumors, lymph node metastasis is found in 71% of type III tumors measuring more than 2 cm.48 In nearly all cases of type III tumors, surgical resection is advised.
Type IV neuroendocrine tumors, also known as poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinomas, are rare solitary tumors. They can arise in any part of the stomach and occur mainly in elderly men (>60 years). When diagnosed, these tumors are often large (50-70 mm), ulcerated, and believed to be a result of a primary defect of acid secretion by parietal cells. Unfortunately, at the time of diagnosis, most of these tumors are already in an advanced stage, with extensive metastasis, and are associated with a poor prognosis.49-51
Ectopic Pancreas
Ectopic pancreas is pancreatic tissue lacking anatomic and vascular continuity with the main body of the pancreatic gland.52,53 Commonly located in the stomach, these lesions are small and found incidently. Endoscopically, they appear as submucosal masses and can be misinterpreted for other submucosal tumors (ie, gastrointestinal stromal tumors [GISTs] or leiomyomas).54 Central umbilication is frequently cited as the endoscopic clue to identify these lesions, although histologically proven ectopic pancreatic tissue can be seen without this endoscopic sign. These lesions have exceptionally low malignant potential.55,56
Pyloric Gland Adenomas
Pyloric gland adenomas are rare neoplasms that demonstrate gastric epithelial differentiation. They are composed of closely packed, pyloric gland–type tubules with a monolayer of cuboidal to low columnar epithelial cells. They often arise in the gastric body with background mucosa, showing features of autoimmune gastritis and intestinal metaplasia,57,58 and display a female predominance.59 These can often be mistaken for unusual gastric hyperplastic polyps; they are differentiated by displaying delicate ground glass cytoplasm without apical mucin.
Hamartomatous Polyps
Hamartomatous polyps are typically mucosal-based but can be derived from any of the 3 embryonic layers. These polyps result from disordered growth of tissues indigenous to the site. Examples include Peutz-Jeghers polyps and juvenile polyps, as well as hamartomatous polyps without specific names. These can be either sporadic in nature or are associated with various polyposis syndromes such as Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, juvenile polyposis syndrome, and Cowden syndrome (PTEN or multiple hamartoma syndrome), as discussed below.
Peutz-Jeghers Polyps and Syndrome
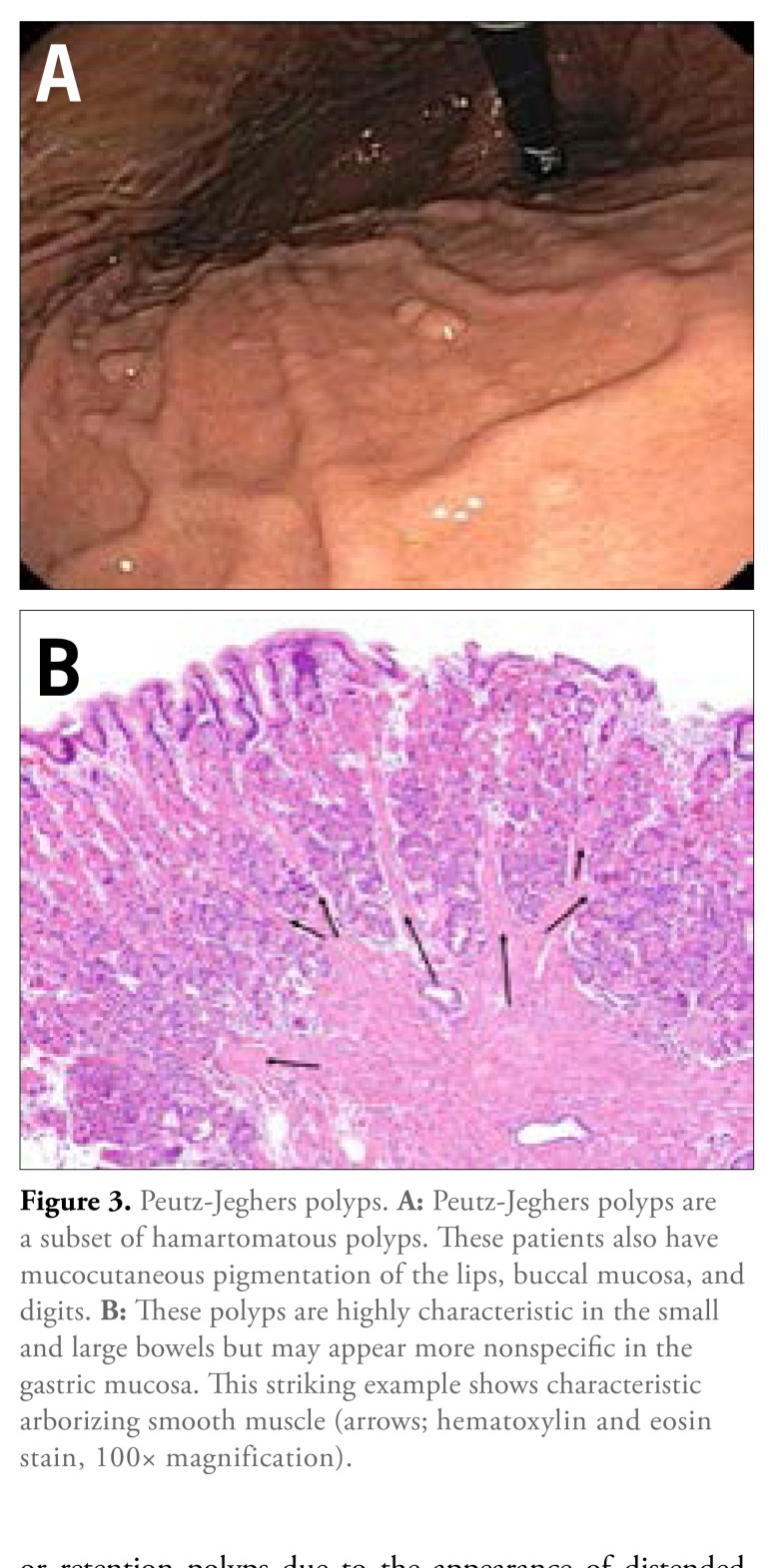
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is an autosomal dominant hereditary disorder with a unique constellation of findings, including hamartomatous polyps throughout the gastrointestinal tract and mucocutaneous hyperpigmentation, most notably of the lips.60 Although patients with this syndrome are more likely to have small bowel or colonic polyps, gastric polyps occur in approximately 15% to 30% of patients.61 Peutz-Jeghers polyps have a characteristic glandular epithelium with dilated cystic glands, which are supported by an arborizing framework of well-developed smooth muscle that is contiguous with the muscularis mucosa. In the small bowel and colon, these lesions can be differentiated from juvenile polyps, as Peutz-Jeghers polyps have intact lamina propria with a “fanning out” appearance of the smooth muscle fibers (Figure 3). However, gastric syndromic polyps are often indistinguishable from nonspecific gastric hyperplastic polyps.62 Consequently, it is imperative that the pathologist be provided with complete endoscopic and clinical information to ensure a proper diagnosis. Furthermore, it should be pointed out that when a hamartomatous syndrome is suspected, polyps from the small bowel and colon are more likely to be diagnostic.
Figure 3.
Peutz-Jeghers polyps. A: Peutz-Jeghers polyps are a subset of hamartomatous polyps. These patients also have mucocutaneous pigmentation of the lips, buccal mucosa, and digits. B: These polyps are highly characteristic in the small and large bowels but may appear more nonspecific in the gastric mucosa. This striking example shows characteristic arborizing smooth muscle (arrows; hematoxylin and eosin stain, 100× magnification).
Peutz-Jeghers polyps have malignant potential, and the average age of patients presenting with gastric carcinoma is estimated to be 30 years.61 Current recommendations suggest screening for gastric polyps as early as ages 8 to 21 years. Gastric Peutz-Jeghers polyps larger than 1 cm should be resected endoscopically, and patients should receive annual surveillance.7 For patients with smaller (<1 cm) polyps, surveillance endoscopy is recommended every 2 to 3 years,60 although it is recognized that small polyps can be removed in certain clinical settings.
Juvenile Polyps and Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome
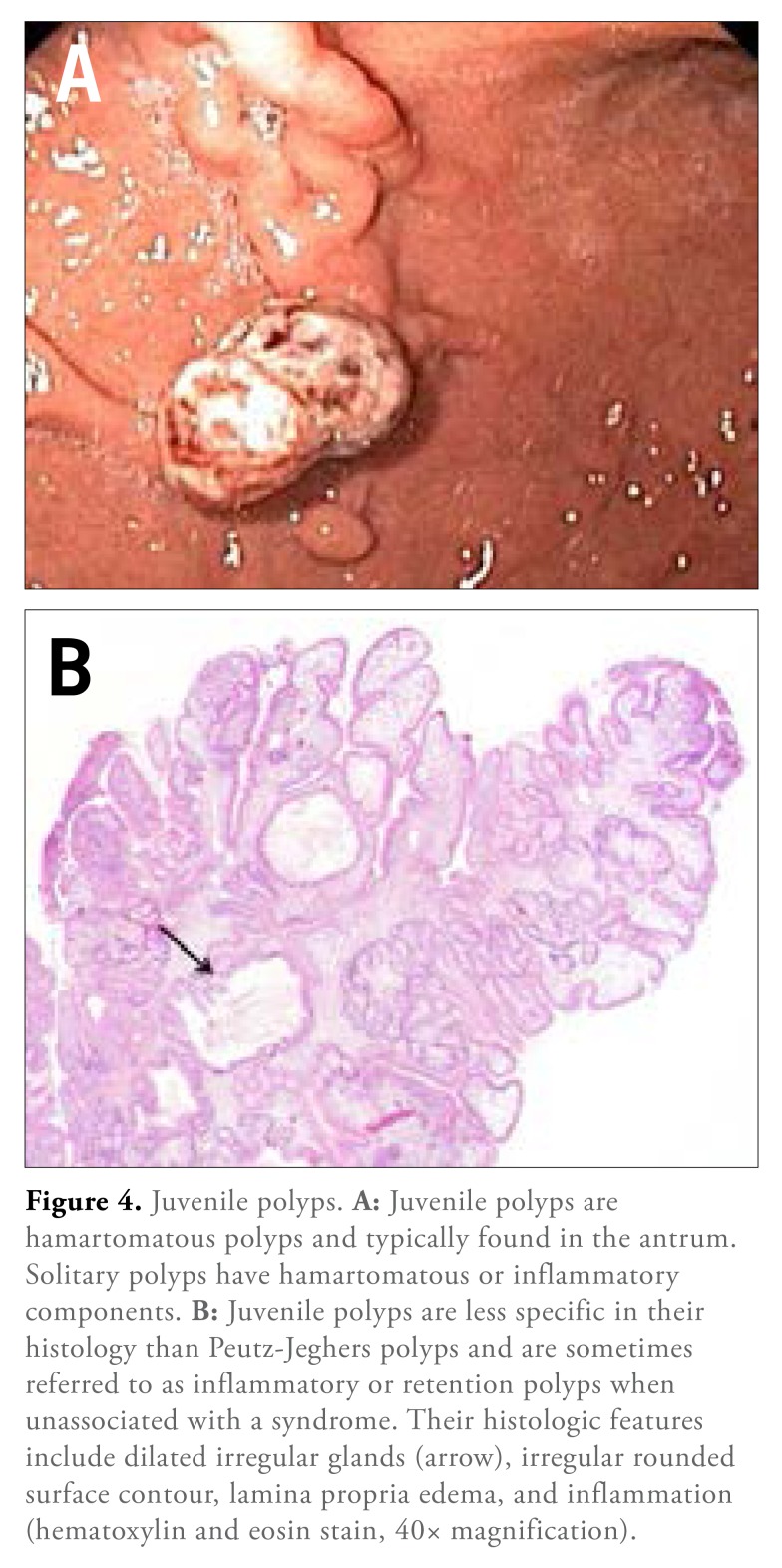
Juvenile polyps are mucosal tumors that consist primarily of an excess of lamina propria and dilated cystic glands; therefore, they are classified as hamartomatous polyps (Figure 4). Occasionally, they are referred to as inflammatory or retention polyps due to the appearance of distended, mucus-filled glands, inflammatory cells, and edema. Juvenile polyps are typically solitary pedunculated lesions in the antrum and range from 3 mm to 20 mm. When found alone, they are believed to be benign incidental lesions, unassociated with a syndrome. However, when multiple juvenile polyps are seen, a syndrome of juvenile polyposis should be considered. Since this is a clinical-pathologic diagnosis, the communication of a complete profile of endoscopic and clinical information is essential for the pathologist’s success. Juvenile polyposis is an autosomal dominant disorder that carries a lifetime gastric malignancy risk of greater than 50%.63 Thus, for juvenile polyposis syndrome, endoscopic screening is recommended beginning at age 18 years and every 3 years thereafter.7
Figure 4.
Juvenile polyps. A: Juvenile polyps are hamartomatous polyps and typically found in the antrum. Solitary polyps have hamartomatous or inflammatory components. B: Juvenile polyps are less specific in their histology than Peutz-Jeghers polyps and are sometimes referred to as inflammatory or retention polyps when unassociated with a syndrome. Their histologic features include dilated irregular glands (arrow), irregular rounded surface contour, lamina propria edema, and inflammation (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 40× magnification).
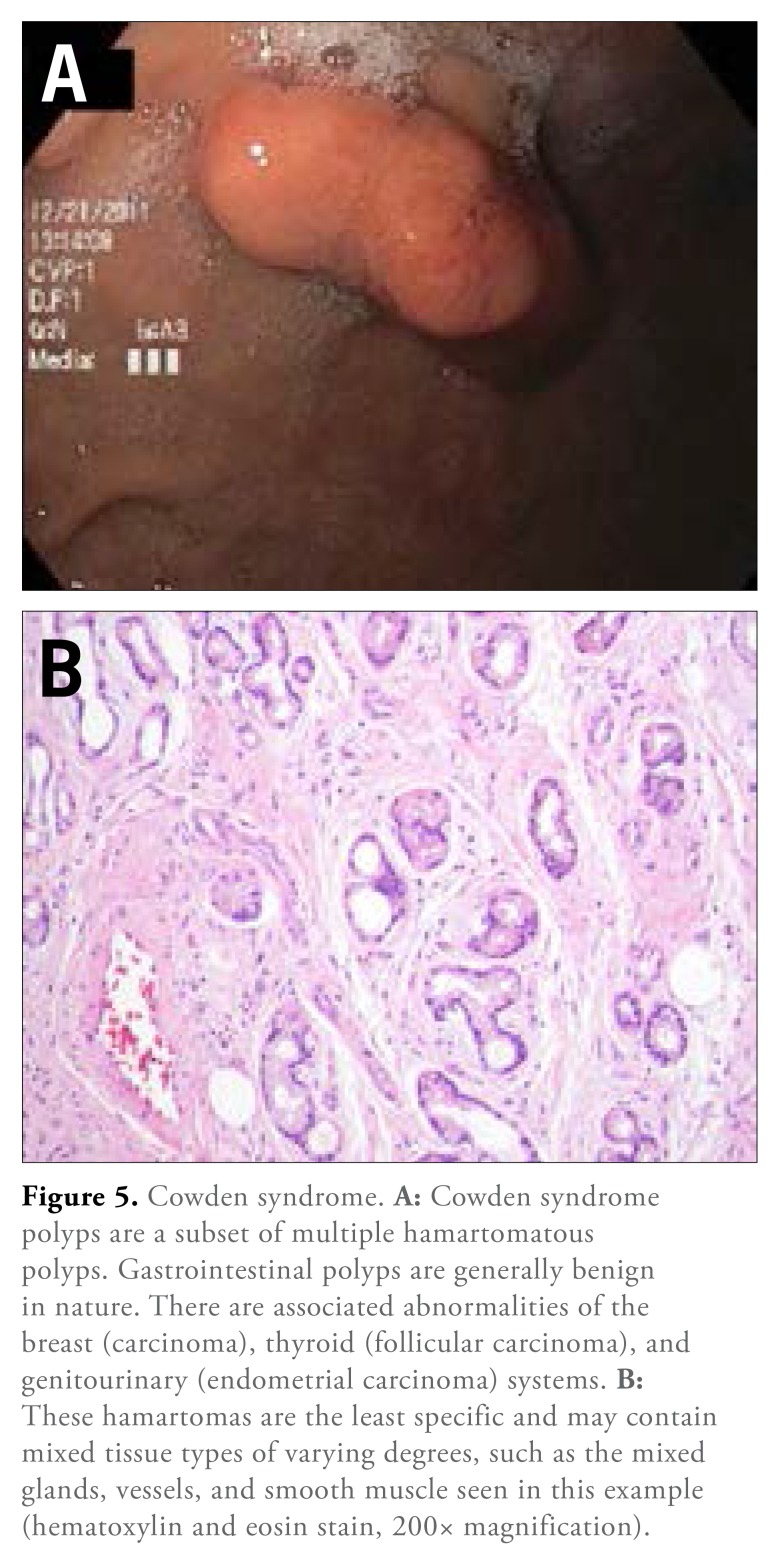
Cowden Syndrome
Cowden syndrome is another autosomal dominant, multisystem disorder characterized by hamartomatous tissue overgrowth of all 3 embryonic layers (Figure 5). Eighty percent of patients have a germline mutation of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene.64 There are several pathognomonic criteria for the diagnosis of this syndrome, including facial trichilemmomas, acral keratoses, and papillomatous papules. Just like other clinical-pathologic diagnoses, the importance of full communication between the endoscopist and the pathologist cannot be overemphasized. Cowden syndrome has a slight female preponderance, and the age of diagnosis ranges from 16 to 65 years. Transformation of gastrointestinal polyps to malignancy is thought to be extremely rare; thus, surveillance endoscopy has not been recommended by most. However, disorders and malignancy of the breast, thyroid, and genitourinary tract are more common; thus, further clinical investigation is warranted when this diagnosis is suggested on endoscopic biopsy.
Figure 5.
Cowden syndrome. A: Cowden syndrome polyps are a subset of multiple hamartomatous polyps. Gastrointestinal polyps are generally benign in nature. There are associated abnormalities of the breast (carcinoma), thyroid (follicular carcinoma), and genitourinary (endometrial carcinoma) systems. B: These hamartomas are the least specific and may contain mixed tissue types of varying degrees, such as the mixed glands, vessels, and smooth muscle seen in this example (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 200× magnification).
Mesenchymal Polyps
Mesenchymal lesions cover a broad spectrum of mesodermally derived tumors. These polyps can be mucosal or submucosal in location but are typically situated underneath the surface epithelium, imparting a more nodular than polypoid appearance. Given their deep location, these lesions should be further evaluated by endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and tissue acquisition. Select common mesenchymal polyps covered herein include IFPs, GISTs, leiomyomas, and granular cell tumors.
Inflammatory Fibroid Polyps
IFPs, or Vanek polyps/tumors, usually present as polypoid lesions or nodules. These histologically unique lesions, arising in the submucosa, were first described in 1949 by Vanek as gastric submucosal granulomas with eosinophilic infiltration.65 These lesions are characterized by CD34 immunoreactive spindle and stellate stromal cells mixed with inflammatory cells (predominantly eosinophils) and edema (Figure 6). Although once believed to be a reactive lesion, recent studies have proven that this lesion is neoplastic by identifying activating mutations in the platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRα). This mutation is also found in a subset of GISTs, typically the gastric benign epithelioid variant that does not have a CD117 (proto-oncogene c-Kit) mutation. IFPs are now viewed as PDGFRα-driven benign neoplasms.66
Figure 6.
Inflammatory fibroid polyps. A: Inflammatory polyps usually present as polypoid lesions or nodules that are sessile and small (<1.5 cm). They are wellcircumscribed lesions located in th antrum or prepyloric region. B: High-power magnification shows that this lesion is composed of vessels, small spindle cells (circled), and collagen fibers (arrows), as well as an inflammatory backdrop with numerous eosinophils (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 400× magnification).
These polyps also contain myxoid stroma and often thin-walled vessels. IFPs can occur in all ages but are most common at 50 to 60 years and have a slightly higher incidence in women.3 They are rare lesions, with an estimated relative prevalence of 0.09%.1,67
IFPs present most often as solitary lesions in the gastric pylorus or distal antrum and are typically small (<1.5 cm) and sessile.66 They rarely cause clinical symptoms; however, there have been reports of a few cases of large gastric IFPs causing gastric outlet obstruction.68 These lesions are believed to have no malignant potential; thus, no endoscopic follow-up is recommended after initial histologic confirmation. Larger and/or symptomatic lesions may require complete endoscopic resection by an experienced endoscopist.13
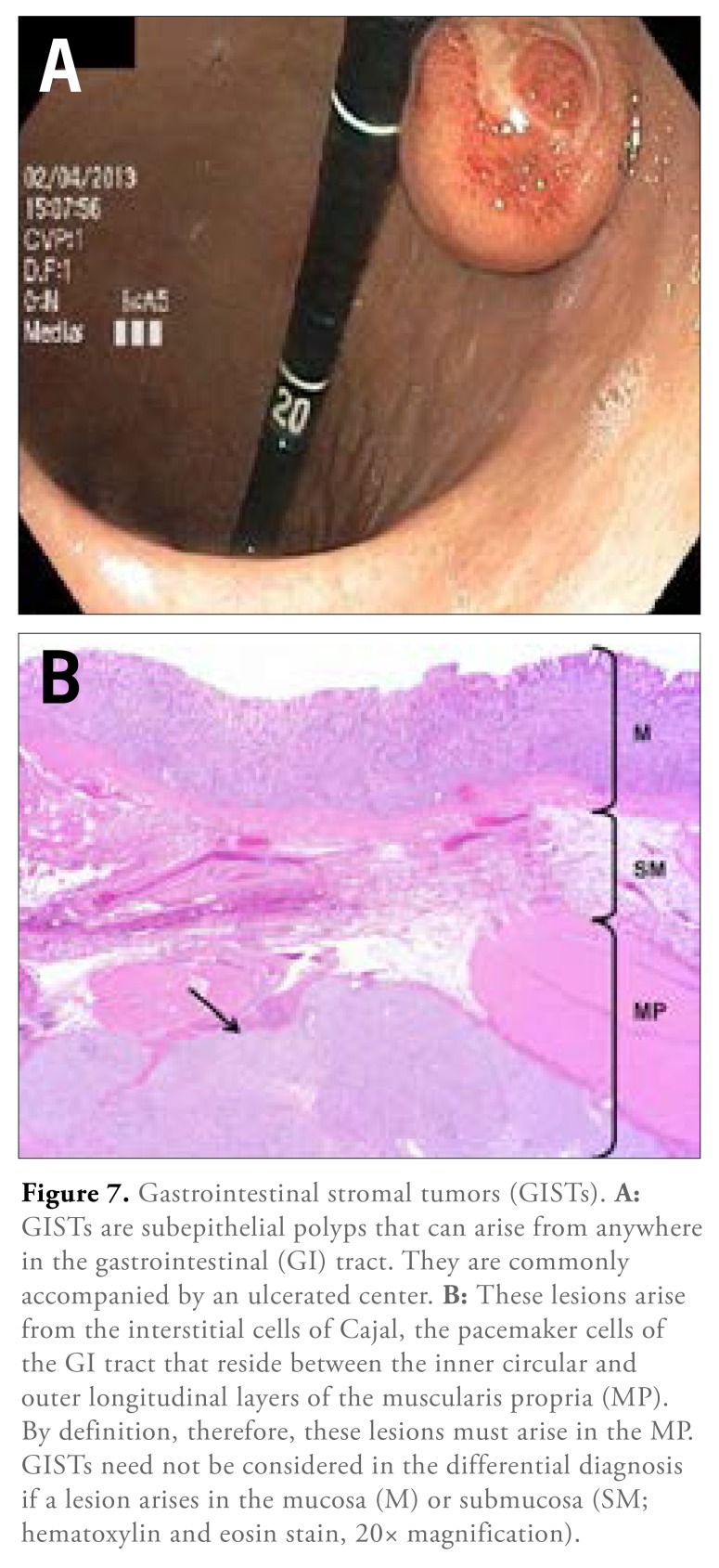
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
GISTs are rare connective tissue tumors originating in the muscularis propria and account for 1% to 3% of all malignant gastrointestinal tumors.69 Newer estimates show up to 5000 new cases per year in the United States.70,71 GISTs are often found incidentally during upper endoscopy performed for reasons or symptoms unrelated to the tumors.72 The clinical features can vary depending on the anatomic location, size, and aggressiveness of the tumor. Although these tumors may arise anywhere along the luminal gastrointestinal tract, the most common site is the stomach. These lesions are derived from the interstitial cells of Cajal (the pacemaker cells of the gastrointestinal tract), which reside between the inner circular and outer longitudinal layers of the muscularis propria. GISTs have a mutation of the proto-oncogenes c-Kit or PDGFR with known positivity for CD117 in 95% of the tumors.7 Although most GISTs (>90%) exhibit cytoplasmic immunoreactivity for CD117, a proportion can be CD117-negative. These particular GISTs will stain with DOG-1 immunohistochemistry, an equally sensitive and specific GIST marker.71,73,74 Additionally, a subset of lesions, particularly in the context of Carney-Stratakis syndrome, may have a mutation of the succinate-dehydrogenase gene.75 The most reliable prognostic factors for GISTs are the site and size of the primary tumor and mitotic index. EUS and computed tomography scan are important to determine local and metastatic spread.76-78
Treatment is dependent on the stage of the tumor. If localized to the stomach, the tumor can be surgically resected. If the tumor is metastatic or unresectable, imatinib is the first-line chemotherapeutic agent of choice in tumors expressing a c-Kit mutation (Figure 7). Additionally, genotyping GISTs has become an important therapeutic intervention for stratifying treatment options with neoadjuvant or adjuvant imatinib.79-81 Although patients with large (>2 cm) or symptomatic GISTs will need surgical interventions, many other patients may not. Unfortunately, there have been no large prospective studies to evaluate the use of routine EUS surveillance strategies.82 Nonetheless, case reports of adequate endoscopic resection of small GISTs using various techniques exist.83-89
Figure 7.
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs). A: GISTs are subepithelial polyps that can arise from anywhere in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. They are commonly accompanied by an ulcerated center. B: These lesions arise from the interstitial cells of Cajal, the pacemaker cells of the GI tract that reside between the inner circular and outer longitudinal layers of the muscularis propria (MP). By definition, therefore, these lesions must arise in the MP. GISTs need not be considered in the differential diagnosis if a lesion arises in the mucosa (M) or submucosa (SM; hematoxylin and eosin stain, 20× magnification).
Leiomyomas
Leiomyomas are benign smooth muscle tumors that were commonly categorized as GISTs in the past. GISTs are typically c-Kit–positive, whereas leiomyomas are desminpositive and c-Kit–negative.54 The size of the leiomyomas can vary greatly, ranging from less than 0.5 cm to 20 cm. Both GISTs and leiomyomas can grow inwardly and outwardly to form a dumbbell shape, although leiomyomas are more likely to grow intraluminally (vs GISTs, which expand predominantly in an extramural fashion).90
Leiomyomas are typically asymptomatic and found incidentally.91-93 Endoscopically, they appear as rounded submucosal lesions with intact overlying mucosa.90 When palpated, they feel rubbery. The histologic distinction between well-differentiated leiomyosarcomas and leiomyomas can be difficult with EUS fine-needle aspiration or true-cut biopsy, and the minimum diagnostic criteria for leiomyosarcomas are poorly defined.94-96 In a retrospective analysis of 53 EUS cases (7 leiomyomas and 46 GISTs), EUS features, such as inhomogeneity, hyperechoic foci, and a marginal halo, help to differentiate GISTs from leiomyomas.54
Granular Cell Tumors
Although commonly found in the esophagus, rare cases of granular cell tumors originating in the stomach have been reported.97 These tumors tend to occur equally in both sexes, usually in the fourth to sixth decade of life.98 For unknown reasons, approximately half of granular cell tumors occur synchronously with esophageal granular cell tumors.98 Granular cell tumors occur in the proximal stomach and range from a few millimeters in size up to 7 cm. Endoscopically, they are usually found incidentally and appear as yellow subepithelial masses or nodules, often mistaken for lipomas, although they are firmer on biopsy.98 Histologically, the tumors arise in the submucosa. Most are benign, but reports of malignancy exist.99
Conclusion
Gastric polyps are a common finding during routine endoscopy. Despite the fact that more than 90% are asymptomatic and do not have malignant potential, a subset of gastric polyps require further intervention, and histologic evaluation is necessary to determine the type of polyp and the presence of dysplasia. The identification of such polyps requires histologic evaluation and may involve additional diagnostic investigative techniques, such as tandem biopsies, immunohistochemistry staining, EUS, and EUS-assisted tissue acquisition. Furthermore, it is essential for gastroenterologists to provide full endoscopic and clinical information to the pathologist to reach a proper diagnosis, as many conditions have similar histologic characteristics.
Footnotes
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
- 1.Carmack SW, Genta RM, Graham DY, Lauwers GY. Management of gastric polyps: a pathology-based guide for gastroenterologists. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;6(6):331–341. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2009.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Carmack SW, Genta RM, Schuler CM, Saboorian MH. The current spectrum of gastric polyps: a 1-year national study of over 120,000 patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104(6):1524–1532. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2009.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stolte M, Sticht T, Eidt S, Ebert D, Finkenzeller G. Frequency, location, and age and sex distribution of various types of gastric polyp. Endoscopy. 1994;26(8):659–665. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1009061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Weston BR, Helper DJ, Rex DK. Positive predictive value of endoscopic features deemed typical of gastric fundic gland polyps. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003;36(5):399–402. doi: 10.1097/00004836-200305000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Abraham SC, Nobukawa B, Giardiello FM, Hamilton SR, Wu TT. Fundic gland polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis: neoplasms with frequent somatic adenomatous polyposis coli gene alterations. Am J Pathol. 2000;157(3):747–754. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64588-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jalving M, Koornstra JJ, Wesseling J, Boezen HM, De Jong S, Kleibeuker JH. Increased risk of fundic gland polyps during long-term proton pump inhibitor therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24(9):1341–1348. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.03127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Goddard AF, Badreldin R, Pritchard DM, Walker MM, Warren B. The management of gastric polyps. Gut. 2010;59(9):1270–1276. doi: 10.1136/gut.2009.182089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Burt RW. Gastric fundic gland polyps. Gastroenterology. 2003;125(5):1462–1469. doi: 10.1016/j.gastro.2003.07.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chandrasekhara V, Ginsberg GG. Endoscopic management of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011;13(6):532–539. doi: 10.1007/s11894-011-0224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Abraham SC, Nobukawa B, Giardiello FM, Hamilton SR, Wu TT. Sporadic fundic gland polyps: common gastric polyps arising through activating mutations in the beta-catenin gene. Am J Pathol. 2001;158(3):1005–1010. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64047-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Abraham SC, Singh VK, Yardley JH, Wu TT. Hyperplastic polyps of the stomach: associations with histologic patterns of gastritis and gastric atrophy. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001;25(4):500–507. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200104000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sekine S, Shibata T, Yamauchi Y, et al. Beta-catenin mutations in sporadic fundic gland polyps. Virchows Arch. 2002;440(4):381–386. doi: 10.1007/s004280100527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Stolte M. Clinical consequences of the endoscopic diagnosis of gastric polyps. Endoscopy. 1995;27(1):32–37. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005629. discussion 59-60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dickey W, Kenny BD, McConnell JB. Prevalence of fundic gland polyps in a western European population. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1996;23(1):73–75. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199607000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sakai N, Tatsuta M, Hirasawa R, et al. Low prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with hamartomatous fundic polyps. Dig Dis Sci. 1998;43(4):766–772. doi: 10.1023/a:1018814014139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Shand AG, Taylor AC, Banerjee M, et al. Gastric fundic gland polyps in south-east Scotland: absence of adenomatous polyposis coli gene mutations and a strikingly low prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;17(11):1161–1164. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2002.02863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Watanabe N, Seno H, Nakajima T, et al. Regression of fundic gland polyps following acquisition of Helicobacter pylori. Gut. 2002;51(5):742–745. doi: 10.1136/gut.51.5.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wu TT, Kornacki S, Rashid A, Yardley JH, Hamilton SR. Dysplasia and dysregulation of proliferation in foveolar and surface epithelia of fundic gland polyps from patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;22(3):293–298. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199803000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Stolte M, Vieth M, Ebert MP. High-grade dysplasia in sporadic fundic gland polyps: clinically relevant or not? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003;15(11):1153–1156. doi: 10.1097/00042737-200311000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jalving M, Koornstra JJ, Gotz JM, et al. High-grade dysplasia in sporadic fundic gland polyps: a case report and review of the literature. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003;15(11):1229–1233. doi: 10.1097/00042737-200311000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zelter A, Fernandez JL, Bilder C, et al. Fundic gland polyps and association with proton pump inhibitor intake: a prospective study in 1,780 endoscopies. Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56(6):1743–1748. doi: 10.1007/s10620-010-1493-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Choudhry U, Boyce HW, Jr, Coppola D. Proton pump inhibitor-associated gastric polyps: a retrospective analysis of their frequency, and endoscopic, histologic, and ultrastructural characteristics. Am J Clin Pathol. 1998;110(5):615–621. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/110.5.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bianchi LK, Burke CA, Bennett AE, Lopez R, Hasson H, Church JM. Fundic gland polyp dysplasia is common in familial adenomatous polyposis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6(2):180–185. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2007.11.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.el-Zimaity HM, Jackson FW, Graham DY. Fundic gland polyps developing during omeprazole therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997;92(10):1858–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ohkusa T, Miwa H, Hojo M, et al. Endoscopic, histological and serologic findings of gastric hyperplastic polyps after eradication of Helicobacter pylori: comparison between responder and non-responder cases. Digestion. 2006;68(2-3):57–62. doi: 10.1159/000074516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ohkusa T, Takashimizu I, Fujiki K, et al. Disappearance of hyperplastic polyps in the stomach after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. A randomized, clinical trial. Ann Intern Med. 1998;129(9):712–715. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-129-9-199811010-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ji F, Wang ZW, Ning JW, Wang QY, Chen JY, Li YM. Effect of drug treatment on hyperplastic gastric polyps infected with Helicobacter pylori: a randomized, controlled trial. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12(11):1770–1773. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i11.1770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ljubicic N, Banic M, Kujundzic M, et al. The effect of eradicating Helicobacter pylori infection on the course of adenomatous and hyperplastic gastric polyps. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999;11(7):727–730. doi: 10.1097/00042737-199907000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dirschmid K, Platz-Baudin C, Stolte M. Why is the hyperplastic polyp a marker for the precancerous condition of the gastric mucosa? Virchows Arch. 2006;448(1):80–84. doi: 10.1007/s00428-005-0068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ginsberg GG, Al-Kawas FH, Fleischer DE, Reilly HF, Benjamin SB. Gastric polyps: relationship of size and histology to cancer risk. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996;91(4):714–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Daibo M, Itabashi M, Hirota T. Malignant transformation of gastric hyper-plastic polyps. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987;82(10):1016–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rattan J, Arber N, Tiomny E, et al. Gastric polypoid lesions—an eight-year study. Hepatogastroenterology. 1993;40(2):107–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hizawa K, Fuchigami T, Iida M, et al. Possible neoplastic transformation within gastric hyperplastic polyp. Application of endoscopic polypectomy. Surg Endosc. 1995;9(6):714–718. doi: 10.1007/BF00187948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zea-Iriarte WL, Sekine I, Itsuno M, et al. Carcinoma in gastric hyperplastic polyps. A phenotypic study. Dig Dis Sci. 1996;41(2):377–386. doi: 10.1007/BF02093832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cristallini EG, Ascani S, Bolis GB. Association between histologic type of polyp and carcinoma in the stomach. Gastrointest Endosc. 1992;38(4):481–484. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(92)70481-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Harju E. Gastric polyposis and malignancy. Br J Surg. 1986;73(7):532–533. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800730705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hirota WK, Zuckerman MJ, Adler DG, et al. ASGE guideline: the role of endoscopy in the surveillance of premalignant conditions of the upper GI tract. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;63(4):570–580. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2006.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Saito K, Arai K, Mori M, Kobayashi R, Ohki I. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on malignant transformation of gastric adenoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000;52(1):27–32. doi: 10.1067/mge.2000.106112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tomasulo J. Gastric polyps. Histologic types and their relationship to gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 1971;27(6):1346–1355. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197106)27:6<1346::aid-cncr2820270612>3.0.co;2-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nakamura T, Nakano G. Histopathological classification and malignant change in gastric polyps. J Clin Pathol. 1985;38(7):754–764. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.7.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Schmitz JM, Stolte M. Gastric polyps as precancerous lesions. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 1997;7(1):29–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lanza FL, Graham DY, Nelson RS, Godines R, McKechnie JC. Endoscopic upper gastrointestinal polypectomy. Report of 73 polypectomies in 63 patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 1981;75(5):345–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Rugge M, Correa P, Di Mario F, et al. OLGA staging for gastritis: a tutorial. Dig Liver Dis. 2008;40(8):650–658. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2008.02.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Orlowska J, Jarosz D, Pachlewski J, Butruk E. Malignant transformation of benign epithelial gastric polyps. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995;90(12):2152–2159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Paski SC, Semrad CE. Small bowel tumors. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2009;19(3):461–479. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2009.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Borch K, Ahren B, Ahlman H, Falkmer S, Granerus G, Grimelius L. Gastric carcinoids: biologic behavior and prognosis after differentiated treatment in relation to type. Ann Surg. 2005;242(1):64–73. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000167862.52309.7d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Burkitt MD, Pritchard DM. Review article: pathogenesis and management of gastric carcinoid tumours. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24(9):1305–1320. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.03130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rorstad O. Prognostic indicators for carcinoid neuroendocrine tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. J Surg Oncol. 2005;89(3):151–160. doi: 10.1002/jso.20179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bordi C, Falchetti A, Azzoni C, et al. Aggressive forms of gastric neuroendocrine tumors in multiple endocrine neoplasia type I. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997;21(9):1075–1082. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199709000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Scherubl H, Faiss S, Jahn HU, et al. Neuroendocrine tumors of the stomach (gastric carcinoids) are on the rise: good prognosis with early detection [in German] Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2009;134(30):1529–1535. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1233975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kloppel G. Classification and pathology of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2011;18(suppl 1):S1–S16. doi: 10.1530/ERC-11-0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Grendell JH, Ermak TH. Anatomy, histology, embryology, and developmental anomalies of the pancreas. In: Felman M, Friedman L, Brandt L, editors. Sleisenger & Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 1998. pp. 761–771. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kopelman HR. The pancreas: congenital anomalies. In: Walker WA, Durie PR, Hamilton RJ, Walker-Smith JW, Watkins JB, editors. Pediatric Gastrointestinal Disease. St. Louis, Mo: Mosby; 1996. pp. 1427–1436. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kim JY, Lee JM, Kim KW, et al. Ectopic pancreas: CT findings with emphasis on differentiation from small gastrointestinal stromal tumor and leiomyoma. Radiology. 2009;252(1):92–100. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2521081441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ura H, Denno R, Hirata K, Saeki A, Natori H. Carcinoma arising from ectopic pancreas in the stomach: endosonographic detection of malignant change. J Clin Ultrasound. 1998;26(5):265–268. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0096(199806)26:5<265::aid-jcu7>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Jeong HY, Yang HW, Seo SW, et al. Adenocarcinoma arising from an ectopic pancreas in the stomach. Endoscopy. 2002;34(12):1014–1017. doi: 10.1055/s-2002-35836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Vieth M, Kushima R, de Jonge JP, Borchard F, Oellig F, Stolte M. Adenoma with gastric differentiation (so-called pyloric gland adenoma) in a heterotopic gastric corpus mucosa in the rectum. Virchows Arch. 2005;446(5):542–545. doi: 10.1007/s00428-005-1242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Chen ZM, Scudiere JR, Abraham SC, Montgomery E. Pyloric gland adenoma: an entity distinct from gastric foveolar type adenoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33(2):186–193. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31817d7ff4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Vieth M, Kushima R, Borchard F, Stolte M. Pyloric gland adenoma: a clinicopathological analysis of 90 cases. Virchows Arch. 2003;442(4):317–321. doi: 10.1007/s00428-002-0750-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Beggs AD, Latchford AR, Vasen HF, et al. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: a systematic review and recommendations for management. Gut. 2010;59(7):975–986. doi: 10.1136/gut.2009.198499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Latchford AR, Phillips RK. Gastrointestinal polyps and cancer in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: clinical aspects. Fam Cancer. 2011;10(3):455–461. doi: 10.1007/s10689-011-9442-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Lam-Himlin D, Park JY, Cornish TC, Shi C, Montgomery E. Morphologic characterization of syndromic gastric polyps. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34(11):1656–1662. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181f2b1f1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Howe JR, Mitros FA, Summers RW. The risk of gastrointestinal carcinoma in familial juvenile polyposis. Ann Surg Oncol. 1998;5(8):751–756. doi: 10.1007/BF02303487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Farooq A, Walker LJ, Bowling J, Audisio RA. Cowden syndrome. Cancer Treat Rev. 2010;36(8):577–583. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Vanek J. Gastric submucosal granuloma with eosinophilic infiltration. Am J Pathol. 1949;25(3):397–411. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Rittershaus AC, Appelman HD. Benign gastrointestinal mesenchymal BUMPS: a brief review of some spindle cell polyps with published names. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135(10):1311–1319. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2011-0038-RA. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Rossi P, Montuori M, Balassone V, et al. Inflammatory fibroid polyp. A case report and review of the literature. Ann Ital Chir. 2012;83(4):347–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Morandi E, Pisoni L, Castoldi M, Tavani E, Trabucchi E. Gastric outlet obstruction due to inflammatory fibroid polyp. Ann Ital Chir. 2006;77(1):59–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Cassier PA, Ducimetiere F, Lurkin A, et al. A prospective epidemiological study of new incident GISTs during two consecutive years in Rhone Alpes region: incidence and molecular distribution of GIST in a European region. Br J Cancer. 2010;103(2):165–170. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Fletcher CD, Berman JJ, Corless C, et al. Diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a consensus approach. Hum Pathol. 2002;33(5):459–465. doi: 10.1053/hupa.2002.123545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Miettinen M, El-Rifai W, Sobin LH, Lasota J. Evaluation of malignancy and prognosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a review. Hum Pathol. 2002;33(5):478–483. doi: 10.1053/hupa.2002.124123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Miettinen M, Sarlomo-Rikala M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: recent advances in understanding of their biology. Hum Pathol. 1999;30(10):1213–1220. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(99)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Dei Tos AP, Laurino L, Bearzi I, Messerini L, Farinati F. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: the histology report. Dig Liver Dis. 2011;43(suppl 4):S304–S309. doi: 10.1016/S1590-8658(11)60586-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Liegl-Atzwanger B, Fletcher JA, Fletcher CD. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Virchows Arch. 2010;456(2):111–127. doi: 10.1007/s00428-010-0891-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Pasini B, McWhinney SR, Bei T, et al. Clinical and molecular genetics of patients with the Carney-Stratakis syndrome and germline mutations of the genes coding for the succinate dehydrogenase subunits SDHB, SDHC, and SDHD. Eur J Hum Genet. 2008;16(1):79–88. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Caletti G, Deviere J, Fockens P, et al. Guidelines of the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Part II: Retroperitoneum and large bowel, training. The European Endosonography Club Working Party. Endoscopy. 1996;28(7):626–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Van Dam J, Brady PG, Freeman M, et al. Guidelines for training in electronic ultrasound: guidelines for clinical application. From the ASGE. American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999;49(6):829–833. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(99)70312-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Nesje LB, Laerum OD, Svanes K, Odegaard S. Subepithelial masses of the gastrointestinal tract evaluated by endoscopic ultrasonography. Eur J Ultrasound. 2002;15(1-2):45–54. doi: 10.1016/s0929-8266(01)00166-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Casali PG, Jost L, Reichardt P, Schlemmer M, Blay JY. Gastrointestinal stromal tumours: ESMO clinical recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2009;20(suppl 4):64–67. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdp131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Casali PG, Verweij J, Kotasek D, LeCesne A, Reichardt P, Blay JY. Imatinib mesylate in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST): survival analysis of the intergroup EORTC/ISG/AGITG randomized trial in 946 patients. Eur J Cancer. 2005;3:201. [Google Scholar]
- 81.Debiec-Rychter M, Sciot R, Le Cesne A, et al. KIT mutations and dose selection for imatinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42(8):1093–1103. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2006.01.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Hwang JH, Rulyak SD, Kimmey MB. American Gastroenterological Association Institute technical review on the management of gastric subepithelial masses. Gastroenterology. 2006;130(7):2217–2228. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.04.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Huang WH, Feng CL, Lai HC, et al. Endoscopic ligation and resection for the treatment of small EUS-suspected gastric GI stromal tumors. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;71(6):1076–1081. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2009.12.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Lee IL, Lin PY, Tung SY, Shen CH, Wei KL, Wu CS. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for the treatment of intraluminal gastric subepithelial tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer. Endoscopy. 2006;38(10):1024–1028. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-944814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Park YS, Park SW, Kim TI, et al. Endoscopic enucleation of upper-GI submu-cosal tumors by using an insulated-tip electrosurgical knife. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;59(3):409–415. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(03)02717-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Sun S, Ge N, Wang C, Wang M, Lu Q. Endoscopic band ligation of small gastric stromal tumors and follow-up by endoscopic ultrasonography. Surg Endosc. 2007;21(4):574–578. doi: 10.1007/s00464-006-9028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Zhou PH, Yao LQ, Qin XY, et al. Endoscopic full-thickness resection without laparoscopic assistance for gastric submucosal tumors originated from the muscularis propria. Surg Endosc. 2011;25(9):2926–2931. doi: 10.1007/s00464-011-1644-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Ledo-Rodriguez A, Ulla-Rocha JL, Baltar-Arias R, et al. Endoscopic resection of rectal gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) using band ligation. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2009;101(12):870–871. doi: 10.4321/s1130-01082009001200007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Katoh T, Itoh Y, Mohri T, Suzuki H. Endoscopic enucleation of gastrointestinal stromal tumors of the stomach: report of five cases. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(16):2609–2611. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Davis GB, Blanchard DK, Hatch GF, 3rd, et al. Tumors of the stomach. World J Surg. 2000;24(4):412–420. doi: 10.1007/s002689910066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Miettinen M, Sarlomo-Rikala M, Sobin LH, Lasota J. Esophageal stromal tumors: a clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic study of 17 cases and comparison with esophageal leiomyomas and leiomyosarcomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24(2):211–222. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200002000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Hyun JH, Jeen YT, Chun HJ, et al. Endoscopic resection of submucosal tumor of the esophagus: results in 62 patients. Endoscopy. 1997;29(3):165–170. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Pidhorecky I, Cheney RT, Kraybill WG, Gibbs JF. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: current diagnosis, biologic behavior, and management. Ann Surg Oncol. 2000;7(9):705–712. doi: 10.1007/s10434-000-0705-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Williams DB, Sahai AV, Aabakken L, et al. Endoscopic ultrasoundguided fine-needle aspiration biopsy: a large single centre experience. Gut. 1999;44(5):720–726. doi: 10.1136/gut.44.5.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Fritscher-Ravens A, Sriram PV, Schroder S, Topalidis T, Bohnacker S, Soehendra N. Stromal tumor as a pitfall in EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000;51(6):746–749. doi: 10.1067/mge.2000.105730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Varadarajulu S, Fraig M, Schmulewitz N, et al. Comparison of EUS-guided 19-gauge Trucut needle biopsy with EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration. Endoscopy. 2004;36(5):397–401. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-814316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.White JG, el-Newihi HM, Hauser CJ. Granular cell tumor of the stomach presenting as gastric outlet obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994;89(12):2259–2260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Wang LM, Chetty R. Selected unusual tumors of the stomach: a review. Int J Surg Pathol. 2012;20(1):5–14. doi: 10.1177/1066896911429300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Matsumoto H, Kojima Y, Inoue T, et al. A malignant granular cell tumor of the stomach: report of a case. Surg Today. 1996;26(2):119–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00311775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]