Abstract
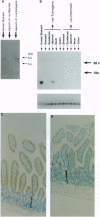
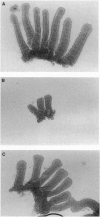
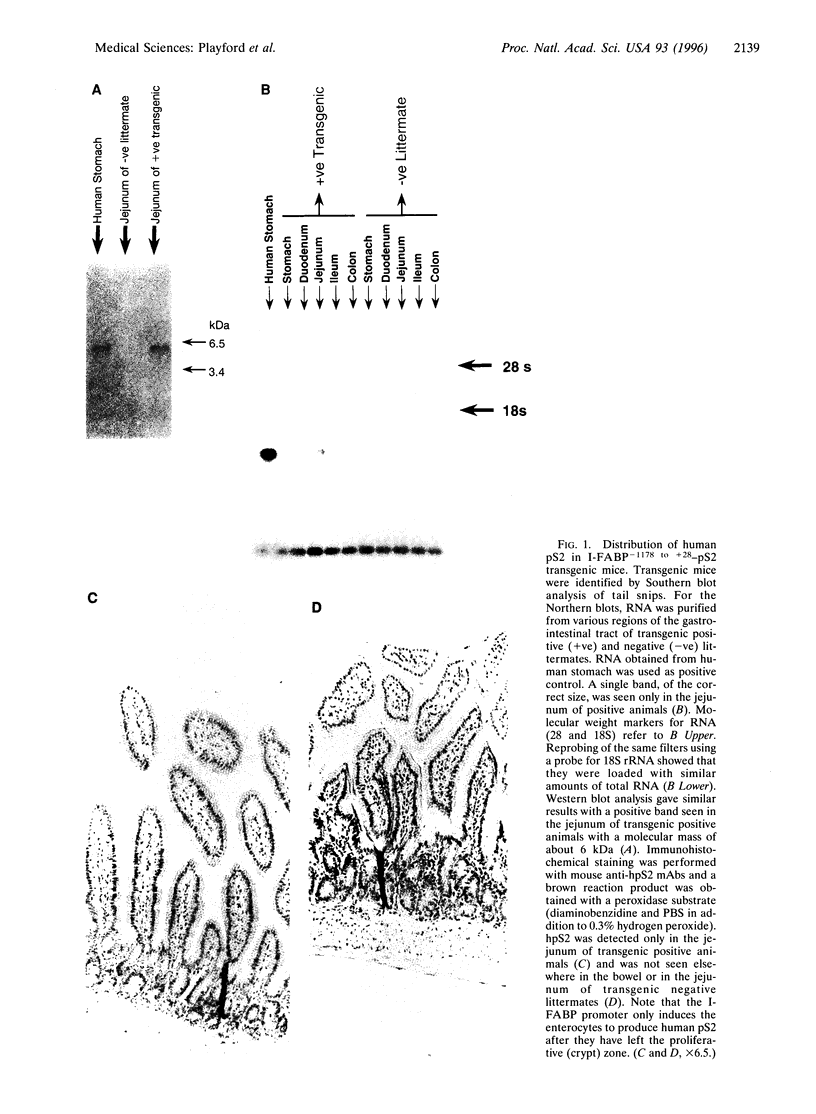
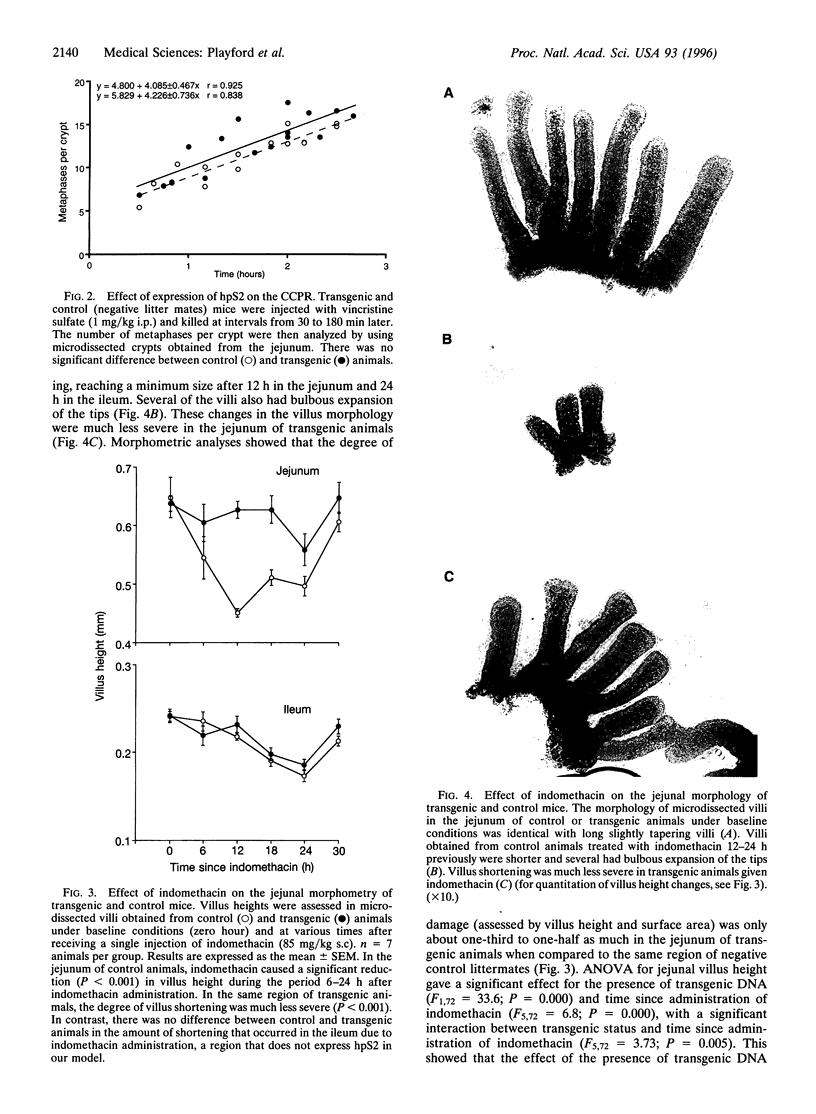
pS2 is a member of the trefoil peptide family, all of which are overexpressed at sites of gastrointestinal injury. We hypothesized that they are important in stimulating mucosal repair. To test this idea, we have produced a transgenic mice strain that expresses human pS2 (hpS2) specifically within the jejunum and examined the effect of this overexpression on proliferation and susceptibility to indomethacin-induced damage. A transgenic mouse was produced by microinjecting fertilized oocytes with a 1.7-kb construct consisting of rat intestinal fatty acid binding protein promoter (positions -1178 to +28) linked to full-length (490 bp) hpS2 cDNA. Screening for positive animals was by Southern blot analysis. Distribution of hpS2 expression was determined by using Northern and Western blot analyses and immunohistochemical staining. Proliferation of the intestinal mucosa was determined by assessing the crypt cell production rate. Differences in susceptibility to intestinal damage were analyzed in animals that had received indomethacin (85 mg/kg s.c.) 0-30 h previously. Expression of hpS2 was limited to the enterocytes of the villi within the jejunum. In the nondamaged intestine, villus height and crypt cell production rate were similar in transgenic and negative (control) litter mates. However, there was a marked difference in the amount of damage caused by indomethacin in control and transgenic animals in the jejunum (30% reduction in villus height in controls vs. 12% reduction in transgenic animals, P < 0.01) but the damage sustained in the non-hpS2-expressing ileal region was similar in control and transgenic animals. These studies support the hypothesis that trefoil peptides are important in stimulating gastrointestinal repair.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alison M. R., Chinery R., Poulsom R., Ashwood P., Longcroft J. M., Wright N. A. Experimental ulceration leads to sequential expression of spasmolytic polypeptide, intestinal trefoil factor, epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha mRNAs in rat stomach. J Pathol. 1995 Apr;175(4):405–414. doi: 10.1002/path.1711750408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinery R., Cox H. M. Immunoprecipitation and characterization of a binding protein specific for the peptide, intestinal trefoil factor. Peptides. 1995;16(4):749–755. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(95)00045-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinery R., Playford R. J. Combined intestinal trefoil factor and epidermal growth factor is prophylactic against indomethacin-induced gastric damage in the rat. Clin Sci (Lond) 1995 Apr;88(4):401–403. doi: 10.1042/cs0880401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn S. M., Simon T. C., Roth K. A., Birkenmeier E. H., Gordon J. I. Use of transgenic mice to map cis-acting elements in the intestinal fatty acid binding protein gene (Fabpi) that control its cell lineage-specific and regional patterns of expression along the duodenal-colonic and crypt-villus axes of the gut epithelium. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(1):27–44. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De A., Brown D. G., Gorman M. A., Carr M., Sanderson M. R., Freemont P. S. Crystal structure of a disulfide-linked "trefoil" motif found in a large family of putative growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):1084–1088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignass A., Lynch-Devaney K., Kindon H., Thim L., Podolsky D. K. Trefoil peptides promote epithelial migration through a transforming growth factor beta-independent pathway. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jul;94(1):376–383. doi: 10.1172/JCI117332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettarh R. R., Carr K. E. Structural and morphometric analysis of murine small intestine after indomethacin administration. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1993 Sep;28(9):795–802. doi: 10.3109/00365529309104012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helpap B., Hattori T., Gedigk P. Repair of gastric ulcer. A cell kinetic study. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1981;392(2):159–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00430818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoosein N. M., Thim L., Jørgensen K. H., Brattain M. G. Growth stimulatory effect of pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide on cultured colon and breast tumor cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):303–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81357-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakowlew S. B., Breathnach R., Jeltsch J. M., Masiakowski P., Chambon P. Sequence of the pS2 mRNA induced by estrogen in the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2861–2878. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre O., Wolf C., Kédinger M., Chenard M. P., Tomasetto C., Chambon P., Rio M. C. The mouse one P-domain (pS2) and two P-domain (mSP) genes exhibit distinct patterns of expression. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(1):191–198. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi S., Shaw-Smith C. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: how do they damage the gut? Br J Rheumatol. 1994 Jul;33(7):605–612. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/33.7.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggott N. H., Henry J. A., May F. E., Westley B. R. Antipeptide antibodies against the pNR-2 oestrogen-regulated protein of human breast cancer cells and detection of pNR-2 expression in normal tissues by immunohistochemistry. J Pathol. 1991 Feb;163(2):95–104. doi: 10.1002/path.1711630204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playford R. J., Marchbank T., Chinery R., Evison R., Pignatelli M., Boulton R. A., Thim L., Hanby A. M. Human spasmolytic polypeptide is a cytoprotective agent that stimulates cell migration. Gastroenterology. 1995 Jan;108(1):108–116. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio M. C., Bellocq J. P., Daniel J. Y., Tomasetto C., Lathe R., Chenard M. P., Batzenschlager A., Chambon P. Breast cancer-associated pS2 protein: synthesis and secretion by normal stomach mucosa. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):705–708. doi: 10.1126/science.3041593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio M. C., Chenard M. P., Wolf C., Marcellin L., Tomasetto C., Lathe R., Bellocq J. P., Chambon P. Induction of pS2 and hSP genes as markers of mucosal ulceration of the digestive tract. Gastroenterology. 1991 Feb;100(2):375–379. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90205-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svanes K., Ito S., Takeuchi K., Silen W. Restitution of the surface epithelium of the in vitro frog gastric mucosa after damage with hyperosmolar sodium chloride. Morphologic and physiologic characteristics. Gastroenterology. 1982 Jun;82(6):1409–1426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D. A., Birkenmeier E. H., Klisak I. J., Zollman S., Sparkes R. S., Mohandas T., Lusis A. J., Gordon J. I. The human and rodent intestinal fatty acid binding protein genes. A comparative analysis of their structure, expression, and linkage relationships. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16060–16071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thim L. A surprising sequence homology. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 1;253(1):309–309. doi: 10.1042/bj2530309a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasetto C., Wolf C., Rio M. C., Mehtali M., LeMeur M., Gerlinger P., Chambon P., Lathe R. Breast cancer protein PS2 synthesis in mammary gland of transgenic mice and secretion into milk. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1579–1584. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-10-1579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright N. A., Poulsom R., Stamp G. W., Hall P. A., Jeffery R. E., Longcroft J. M., Rio M. C., Tomasetto C., Chambon P. Epidermal growth factor (EGF/URO) induces expression of regulatory peptides in damaged human gastrointestinal tissues. J Pathol. 1990 Dec;162(4):279–284. doi: 10.1002/path.1711620402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright N. A., Poulsom R., Stamp G., Van Noorden S., Sarraf C., Elia G., Ahnen D., Jeffery R., Longcroft J., Pike C. Trefoil peptide gene expression in gastrointestinal epithelial cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jan;104(1):12–20. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90830-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]