Abstract
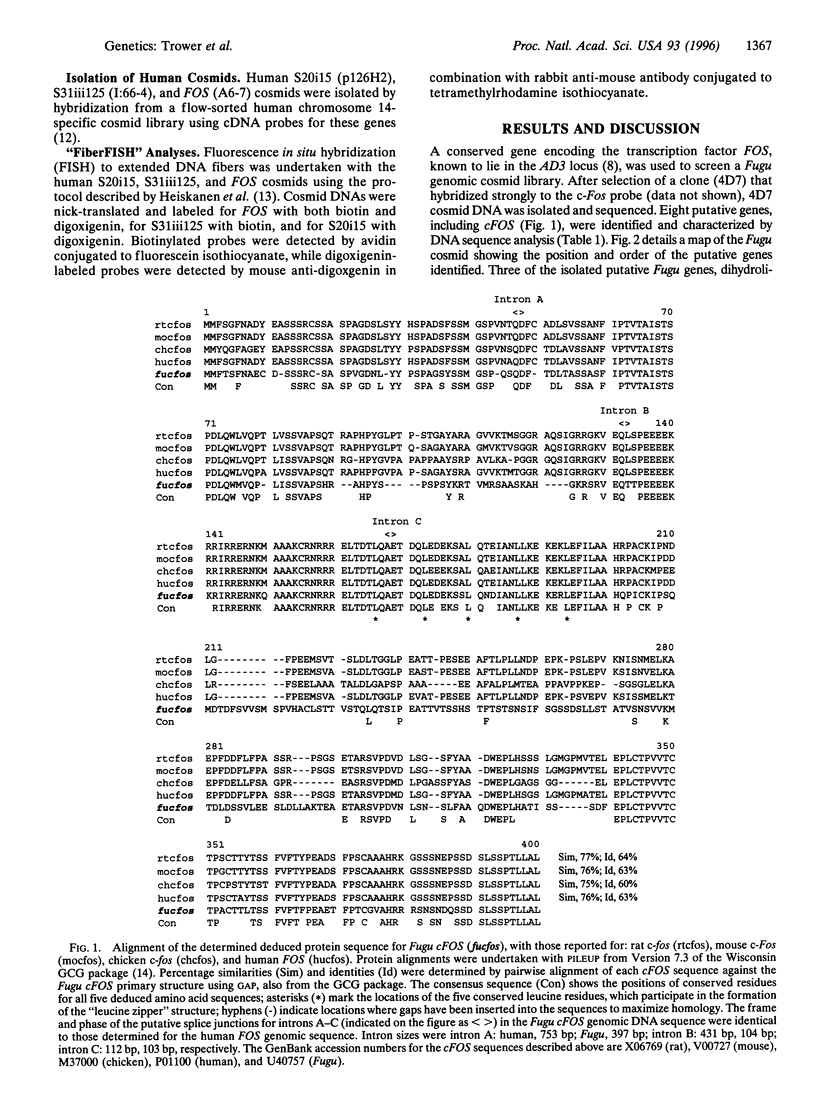
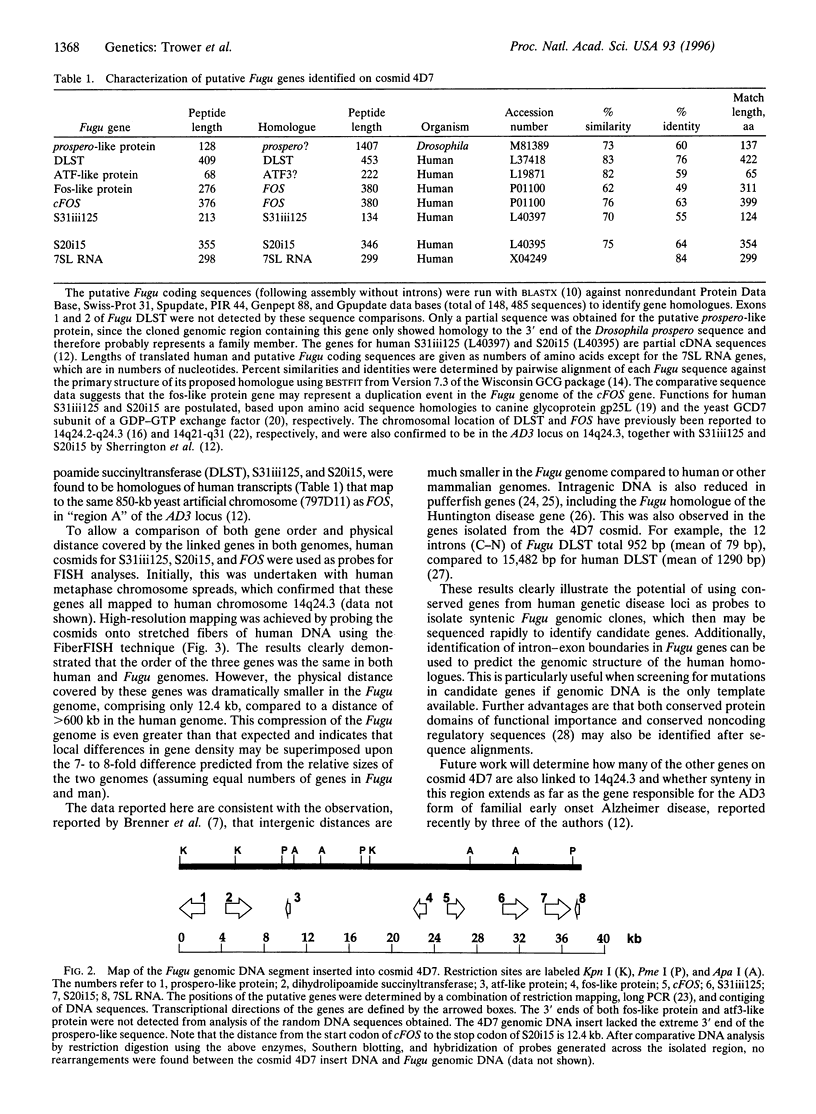
The genome of the pufferfish (Fugu rubripes) (400 Mb) is approximately 7.5 times smaller than the human genome, but it has a similar gene repertoire to that of man. If regions of the two genomes exhibited conservation of gene order (i.e., were syntenic), it should be possible to reduce dramatically the effort required for identification of candidate genes in human disease loci by sequencing syntenic regions of the compact Fugu genome. We have demonstrated that three genes (dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase, S31iii125, and S20i15), which are linked to FOS in the familial Alzheimer disease focus (AD3) on human chromosome 14, have homologues in the Fugu genome adjacent to Fugu cFOS. The relative gene order of cFOS, S31iii125, and S20i15 was the same in both genomes, but in Fugu these three genes lay within a 12.4-kb region, compared to >600 kb in the human AD3 locus. These results demonstrate the conservation of synteny between the genomes of Fugu and man and highlight the utility of this approach for sequence-based identification of genes in human disease loci.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aparicio S., Morrison A., Gould A., Gilthorpe J., Chaudhuri C., Rigby P., Krumlauf R., Brenner S. Detecting conserved regulatory elements with the model genome of the Japanese puffer fish, Fugu rubripes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1684–1688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker P. E., Rabin M., Watson M., Breg W. R., Ruddle F. H., Verma I. M. Human c-fos oncogene mapped within chromosomal region 14q21----q31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5826–5830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes W. M. PCR amplification of up to 35-kb DNA with high fidelity and high yield from lambda bacteriophage templates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2216–2220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxendale S., Abdulla S., Elgar G., Buck D., Berks M., Micklem G., Durbin R., Bates G., Brenner S., Beck S. Comparative sequence analysis of the human and pufferfish Huntington's disease genes. Nat Genet. 1995 May;10(1):67–76. doi: 10.1038/ng0595-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S., Elgar G., Sandford R., Macrae A., Venkatesh B., Aparicio S. Characterization of the pufferfish (Fugu) genome as a compact model vertebrate genome. Nature. 1993 Nov 18;366(6452):265–268. doi: 10.1038/366265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler A. J., Chang D. D., Graw S. L., Brook J. D., Haber D. A., Sharp P. A., Housman D. E. Exon amplification: a strategy to isolate mammalian genes based on RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):4005–4009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.4005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman J. L., Asuru A. I., Matts R. L., Hinnebusch A. G. Evidence that GCD6 and GCD7, translational regulators of GCN4, are subunits of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor for eIF-2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1920–1932. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen B. P., Liang G., Whelan J., Hai T. ATF3 and ATF3 delta Zip. Transcriptional repression versus activation by alternatively spliced isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 3;269(22):15819–15826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie J. M. A streamlined random sequencing strategy for finding coding exons. Genomics. 1994 Oct;23(3):575–581. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiskanen M., Karhu R., Hellsten E., Peltonen L., Kallioniemi O. P., Palotie A. High resolution mapping using fluorescence in situ hybridization to extended DNA fibers prepared from agarose-embedded cells. Biotechniques. 1994 Nov;17(5):928-9, 932-3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller T., Kaiser R. J., Koop B. F., Hood L. Large-scale and automated DNA sequence determination. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):59–67. doi: 10.1126/science.1925562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett M., Kere J., Hinton L. M. Direct selection: a method for the isolation of cDNAs encoded by large genomic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9628–9632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. J., Stevens D. J., Luzzatto L., Brenner S., Aparicio S. Genomic structure and sequence of the Fugu rubripes glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (G6PD). Genomics. 1995 Apr 10;26(3):587–591. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(95)80179-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano K., Matuda S., Sakamoto T., Takase C., Nakagawa S., Ohta S., Ariyama T., Inazawa J., Abe T., Miyata T. Human dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase: cDNA cloning and localization on chromosome 14q24.2-q24.3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Dec 14;1216(3):360–368. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90002-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano K., Takase C., Sakamoto T., Nakagawa S., Inazawa J., Ohta S., Matuda S. Isolation, characterization and structural organization of the gene and pseudogene for the dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase component of the human 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Aug 15;224(1):179–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb20010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parimoo S., Patanjali S. R., Shukla H., Chaplin D. D., Weissman S. M. cDNA selection: efficient PCR approach for the selection of cDNAs encoded in large chromosomal DNA fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9623–9627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setoyama C., Frunzio R., Liau G., Mudryj M., de Crombrugghe B. Transcriptional activation encoded by the v-fos gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3213–3217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrington R., Rogaev E. I., Liang Y., Rogaeva E. A., Levesque G., Ikeda M., Chi H., Lin C., Li G., Holman K. Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1995 Jun 29;375(6534):754–760. doi: 10.1038/375754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George-Hyslop P., Haines J., Rogaev E., Mortilla M., Vaula G., Pericak-Vance M., Foncin J. F., Montesi M., Bruni A., Sorbi S. Genetic evidence for a novel familial Alzheimer's disease locus on chromosome 14. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):330–334. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J., Du Z., Thomas K., Wilson R., Hillier L., Staden R., Halloran N., Green P., Thierry-Mieg J., Qiu L. The C. elegans genome sequencing project: a beginning. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):37–41. doi: 10.1038/356037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trower M. K., Burt D., Purvis I. J., Dykes C. W., Christodoulou C. Fluorescent dye-primer cycle sequencing using unpurified PCR products as templates; development of a protocol amenable to high-throughput DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Jun 25;23(12):2348–2349. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.12.2348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaessin H., Grell E., Wolff E., Bier E., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. prospero is expressed in neuronal precursors and encodes a nuclear protein that is involved in the control of axonal outgrowth in Drosophila. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):941–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90367-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada I., Rindress D., Cameron P. H., Ou W. J., Doherty J. J., 2nd, Louvard D., Bell A. W., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y., Bergeron J. J. SSR alpha and associated calnexin are major calcium binding proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19599–19610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Signal recognition particle contains a 7S RNA essential for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):691–698. doi: 10.1038/299691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



