Abstract
We addressed the question as to which subtypes of G protein subunits mediate the activation of phospholipase C-beta by the muscarinic m1 receptor. We used the rat basophilic leukemia cell line RBL-2H3-hm1 stably transfected with the human muscarinic m1 receptor cDNA. We microinjected antisense oligonucleotides into the nuclei of the cells to inhibit selectively the expression of G protein subunits; 48 hr later muscarinic receptors were activated by carbachol, and the increase in free cytosolic calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) was measured. Antisense oligonucleotides directed against the mRNA coding for alpha(q) and alpha11 subunits both suppressed the carbachol-induced increase in [Ca2+]i. In cells injected with antisense oligonucleotides directed against alpha(o1) and alpha14 subunits, the carbachol effect was unchanged. A corresponding reduction of Galpha(q), and Galpha11 proteins by 70-80% compared to uninjected cells was immunochemically detected 2 days after injection of a mixture of alpha(q) and alpha11 antisense oligonucleotides. Expression of Galpha(q) and Galpha11 completely recovered after 4 days. Cells injected with antisense oligonucleotides directed against the mRNAs encoding for beta1, beta4, and gamma4 subunits showed a suppression of the carbachol-induced increase in [Ca2+]i compared to uninjected cells measured at the same time from the same coverslip, whereas in cells injected with antisense oligonucleotides directed against the beta2, beta3, gamma1, gamma2, gamma3, gamma5, and gamma7 subunits, no suppression of carbachol effect was observed. In summary, the results from RBL-2H3-hm1 cells indicate that the m1 receptor utilizes a G protein complex composed of the subunits alpha(q), alpha11, beta1, beta4, and gamma4 to activate phospholipase C.
Full text
PDF

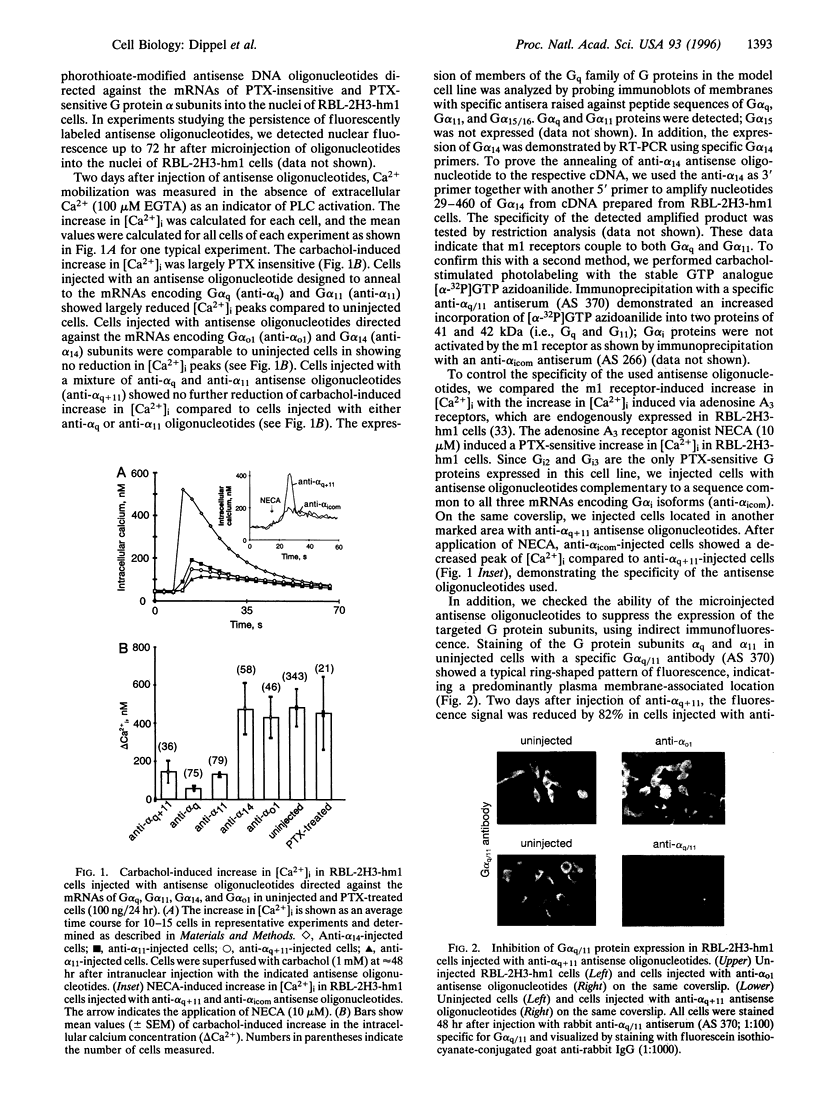
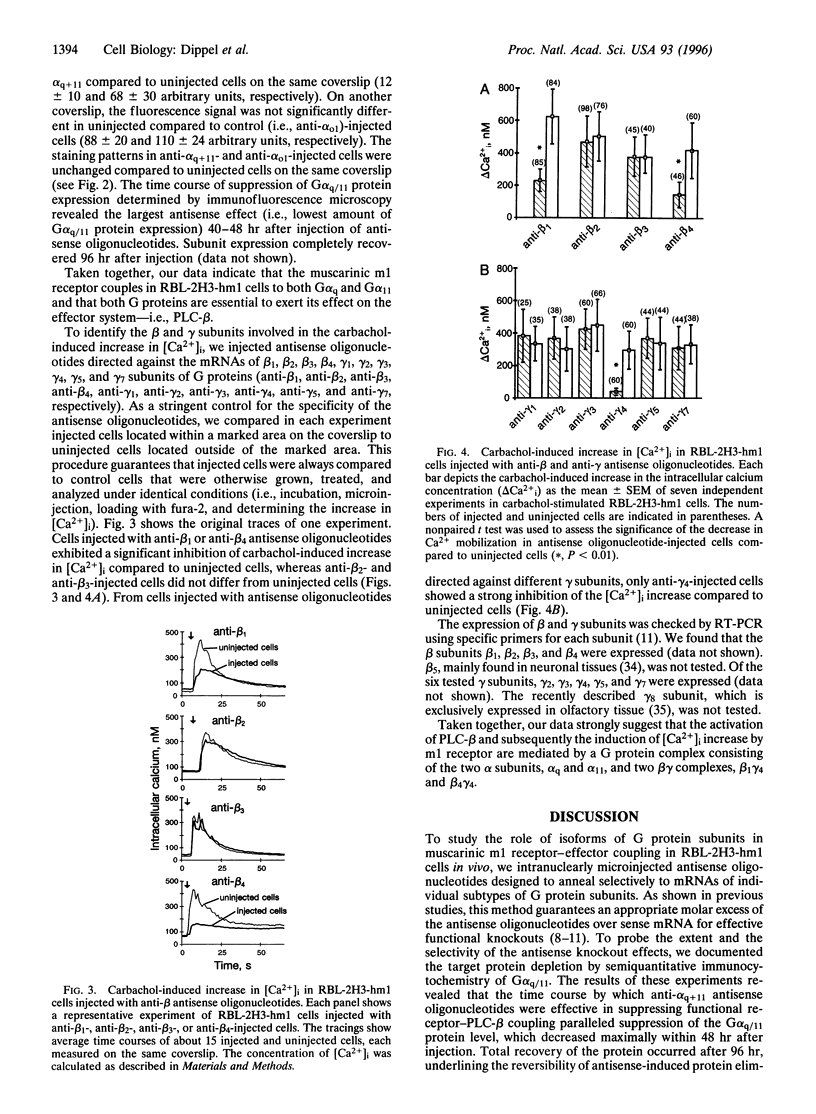


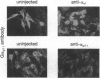
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashkenazi A., Peralta E. G., Winslow J. W., Ramachandran J., Capon D. J. Functionally distinct G proteins selectively couple different receptors to PI hydrolysis in the same cell. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90251-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashkenazi A., Winslow J. W., Peralta E. G., Peterson G. L., Schimerlik M. I., Capon D. J., Ramachandran J. An M2 muscarinic receptor subtype coupled to both adenylyl cyclase and phosphoinositide turnover. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):672–675. doi: 10.1126/science.2823384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berstein G., Blank J. L., Smrcka A. V., Higashijima T., Sternweis P. C., Exton J. H., Ross E. M. Reconstitution of agonist-stimulated phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis using purified m1 muscarinic receptor, Gq/11, and phospholipase C-beta 1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8081–8088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Birnbaumer M. Signal transduction by G proteins: 1994 edition. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 1995 Jan-Mar;15(1-4):213–252. doi: 10.3109/10799899509045218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L. Receptor-to-effector signaling through G proteins: roles for beta gamma dimers as well as alpha subunits. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1069–1072. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell V., Berrow N., Dolphin A. C. GABAB receptor modulation of Ca2+ currents in rat sensory neurones by the G protein G(0): antisense oligonucleotide studies. J Physiol. 1993 Oct;470:1–11. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camps M., Carozzi A., Schnabel P., Scheer A., Parker P. J., Gierschik P. Isozyme-selective stimulation of phospholipase C-beta 2 by G protein beta gamma-subunits. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):684–686. doi: 10.1038/360684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield M. P. Muscarinic receptors--characterization, coupling and function. Pharmacol Ther. 1993 Jun;58(3):319–379. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(93)90027-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang W. J., Ying Y. S., Rothberg K. G., Hooper N. M., Turner A. J., Gambliel H. A., De Gunzburg J., Mumby S. M., Gilman A. G., Anderson R. G. Purification and characterization of smooth muscle cell caveolae. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):127–138. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C. A., Schroering A. G., Carey D. J., Robishaw J. D. Localization of a heterotrimeric G protein gamma subunit to focal adhesions and associated stress fibers. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(3):811–819. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.3.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Kozasa T., Smrcka A. V., Simon M. I., Rhee S. G., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Purification from Sf9 cells and characterization of recombinant Gq alpha and G11 alpha. Activation of purified phospholipase C isozymes by G alpha subunits. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14367–14375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhon D. Y., Lee H. H., Park D., Lee C. W., Lee K. H., Yoo O. J., Rhee S. G. Cloning, sequencing, purification, and Gq-dependent activation of phospholipase C-beta 3. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6654–6661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang H., Wu D., Simon M. I. Activation of phospholipase C beta 4 by heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7593–7596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. V., Choi O. H., Beaven M. A. Carbachol induces secretion in a mast cell line (RBL-2H3) transfected with the ml muscarinic receptor gene. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 2;289(1):47–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80905-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalkbrenner F., Degtiar V. E., Schenker M., Brendel S., Zobel A., Heschler J., Wittig B., Schultz G. Subunit composition of G(o) proteins functionally coupling galanin receptors to voltage-gated calcium channels. EMBO J. 1995 Oct 2;14(19):4728–4737. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00154.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Wu D., Simon M. I. Subunits beta gamma of heterotrimeric G protein activate beta 2 isoform of phospholipase C. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):686–689. doi: 10.1038/360686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Hescheler J., Ewel C., Rosenthal W., Schultz G., Wittig B. Assignment of G-protein subtypes to specific receptors inducing inhibition of calcium currents. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):43–48. doi: 10.1038/353043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Scherübl H., Hescheler J., Schultz G., Wittig B. Different beta-subunits determine G-protein interaction with transmembrane receptors. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):424–426. doi: 10.1038/358424a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Scherübl H., Hescheler J., Schultz G., Wittig B. Selectivity in signal transduction determined by gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):832–834. doi: 10.1126/science.8094261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozasa T., Hepler J. R., Smrcka A. V., Simon M. I., Rhee S. G., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Purification and characterization of recombinant G16 alpha from Sf9 cells: activation of purified phospholipase C isozymes by G-protein alpha subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):9176–9180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon G., Axelrod D., Neubig R. R. Lateral mobility of tetramethylrhodamine (TMR) labelled G protein alpha and beta gamma subunits in NG 108-15 cells. Cell Signal. 1994 Aug;6(6):663–679. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(94)90049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Park D., Wu D., Rhee S. G., Simon M. I. Members of the Gq alpha subunit gene family activate phospholipase C beta isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16044–16047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao C. F., Schilling W. P., Birnbaumer M., Birnbaumer L. Cellular responses to stimulation of the M5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor as seen in murine L cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11273–11284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura F., Kato M., Kameyama K., Nukada T., Haga T., Kato H., Takenawa T., Kikkawa U. Characterization of Gq family G proteins GL1 alpha (G14 alpha), GL2 alpha (G11 alpha), and Gq alpha expressed in the baculovirus-insect cell system. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 17;270(11):6246–6253. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.11.6246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J. Heterotrimeric G proteins: organizers of transmembrane signals. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90407-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubig R. R. Membrane organization in G-protein mechanisms. FASEB J. 1994 Sep;8(12):939–946. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.12.8088459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nürnberg B., Gudermann T., Schultz G. Receptors and G proteins as primary components of transmembrane signal transduction. Part 2. G proteins: structure and function. J Mol Med (Berl) 1995 Mar;73(3):123–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00198240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offermanns S., Schultz G. Complex information processing by the transmembrane signaling system involving G proteins. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1994 Oct;350(4):329–338. doi: 10.1007/BF00178947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offermanns S., Schultz G., Rosenthal W. Identification of receptor-activated G proteins with photoreactive GTP analog, [alpha-32P]GTP azidoanilide. Methods Enzymol. 1991;195:286–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)95174-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offermanns S., Wieland T., Homann D., Sandmann J., Bombien E., Spicher K., Schultz G., Jakobs K. H. Transfected muscarinic acetylcholine receptors selectively couple to Gi-type G proteins and Gq/11. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 May;45(5):890–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D., Jhon D. Y., Lee C. W., Lee K. H., Rhee S. G. Activation of phospholipase C isozymes by G protein beta gamma subunits. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4573–4576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar V., Stiles G. L., Beaven M. A., Ali H. The A3 adenosine receptor is the unique adenosine receptor which facilitates release of allergic mediators in mast cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):16887–16890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryba N. J., Tirindelli R. A novel GTP-binding protein gamma-subunit, G gamma 8, is expressed during neurogenesis in the olfactory and vomeronasal neuroepithelia. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 24;270(12):6757–6767. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.12.6757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargiacomo M., Sudol M., Tang Z., Lisanti M. P. Signal transducing molecules and glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-linked proteins form a caveolin-rich insoluble complex in MDCK cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):789–807. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Hescheler J., Offermanns S., Spicher K., Hinsch K. D., Klinz F. J., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Gausepohl H., Frank R. Involvement of pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins in the hormonal inhibition of dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ currents in an insulin-secreting cell line (RINm5F). J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18025–18033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicher K., Klinz F. J., Rudolph U., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Schultz G., Rosenthal W. Identification of the G-protein alpha-subunit encoded by alpha o2 cDNA as a 39 kDa pertussis toxin substrate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):473–479. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91588-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson A. J., Katz A., Simon M. I. A fifth member of the mammalian G-protein beta-subunit family. Expression in brain and activation of the beta 2 isotype of phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 2;269(35):22150–22156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wess J., Blin N., Mutschler E., Blüml K. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors: structural basis of ligand binding and G protein coupling. Life Sci. 1995;56(11-12):915–922. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(95)00028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]