Abstract
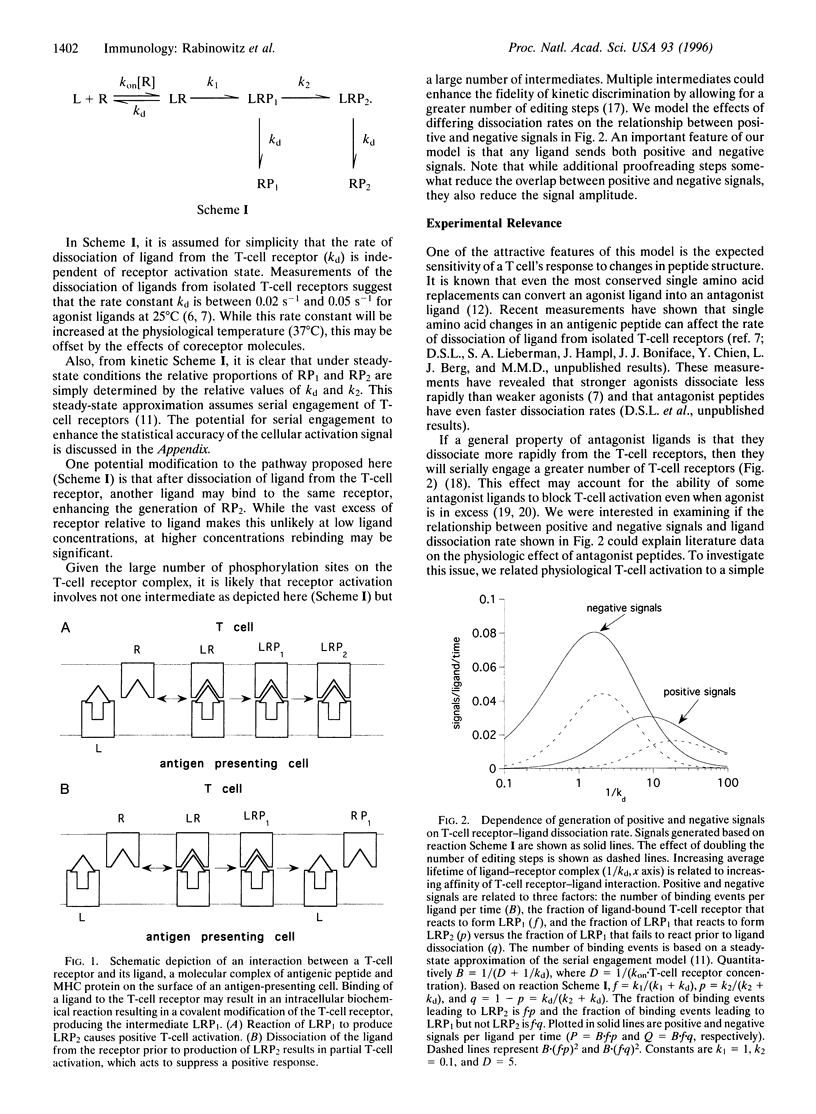
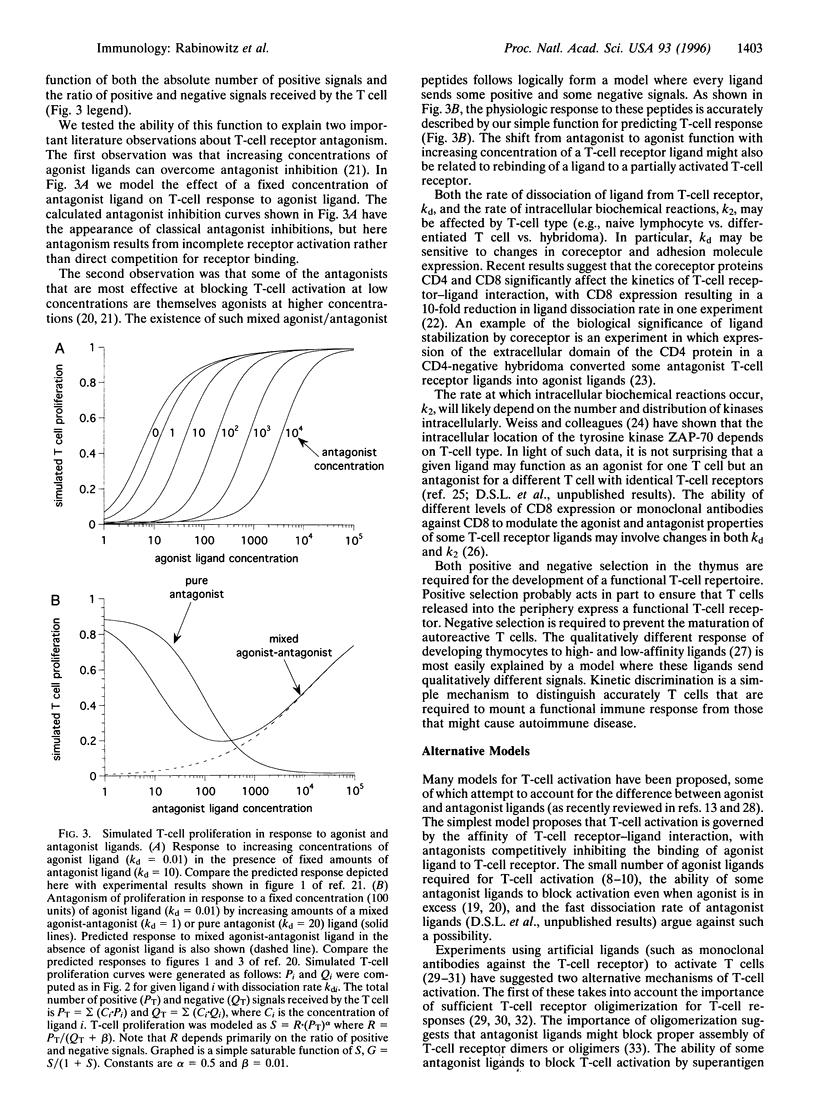
We propose a quantitative model for T-cell activation in which the rate of dissociation of ligand from T-cell receptors determines the agonist and antagonist properties of the ligand. The ligands are molecular complexes between antigenic peptides and proteins of the major histocompatibility complex on the surfaces of antigen-presenting cells. Binding of ligand to receptor triggers a series of biochemical reactions in the T cell. If the ligand dissociates after these reactions are complete, the T cell receives a positive activation signal. However, dissociation of ligand after completion of the first reaction but prior to generation of the final products results in partial T-cell activation, which acts to suppress a positive response. Such a negative signal is brought about by T-cell ligands containing the variants of antigenic peptides referred to as T-cell receptor antagonists. Results of recent experiments with altered peptide ligands compare favorably with T-cell responses predicted by this model.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J., Snoke K., Ruppert J., Sidney J., Wall M., Southwood S., Oseroff C., Arrhenius T., Gaeta F. C., Colón S. M. Functional consequences of engagement of the T cell receptor by low affinity ligands. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 1;150(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertoletti A., Sette A., Chisari F. V., Penna A., Levrero M., De Carli M., Fiaccadori F., Ferrari C. Natural variants of cytotoxic epitopes are T-cell receptor antagonists for antiviral cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1994 Jun 2;369(6479):407–410. doi: 10.1038/369407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christinck E. R., Luscher M. A., Barber B. H., Williams D. B. Peptide binding to class I MHC on living cells and quantitation of complexes required for CTL lysis. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):67–70. doi: 10.1038/352067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corr M., Slanetz A. E., Boyd L. F., Jelonek M. T., Khilko S., al-Ramadi B. K., Kim Y. S., Maher S. E., Bothwell A. L., Margulies D. H. T cell receptor-MHC class I peptide interactions: affinity, kinetics, and specificity. Science. 1994 Aug 12;265(5174):946–949. doi: 10.1126/science.8052850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M. T-cell receptors. Serial engagement proposed. Nature. 1995 May 11;375(6527):104–104. doi: 10.1038/375104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Magistris M. T., Alexander J., Coggeshall M., Altman A., Gaeta F. C., Grey H. M., Sette A. Antigen analog-major histocompatibility complexes act as antagonists of the T cell receptor. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):625–634. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demotz S., Grey H. M., Sette A. The minimal number of class II MHC-antigen complexes needed for T cell activation. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1028–1030. doi: 10.1126/science.2118680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evavold B. D., Allen P. M. Separation of IL-4 production from Th cell proliferation by an altered T cell receptor ligand. Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1308–1310. doi: 10.1126/science.1833816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evavold B. D., Sloan-Lancaster J., Allen P. M. Antagonism of superantigen-stimulated helper T-cell clones and hybridomas by altered peptide ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2300–2304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Unanue E. R. Quantitation of antigen-presenting cell MHC class II/peptide complexes necessary for T-cell stimulation. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):574–576. doi: 10.1038/346574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogquist K. A., Jameson S. C., Heath W. R., Howard J. L., Bevan M. J., Carbone F. R. T cell receptor antagonist peptides induce positive selection. Cell. 1994 Jan 14;76(1):17–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield J. J. Kinetic proofreading: a new mechanism for reducing errors in biosynthetic processes requiring high specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4135–4139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson S. C., Bevan M. J. T cell receptor antagonists and partial agonists. Immunity. 1995 Jan;2(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson S. C., Hogquist K. A., Bevan M. J. Specificity and flexibility in thymic selection. Nature. 1994 Jun 30;369(6483):750–752. doi: 10.1038/369750a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr Ligands for the T-cell receptor: hard times for avidity models. Immunol Today. 1995 May;16(5):223–225. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80163-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenerman P., Rowland-Jones S., McAdam S., Edwards J., Daenke S., Lalloo D., Köppe B., Rosenberg W., Boyd D., Edwards A. Cytotoxic T-cell activity antagonized by naturally occurring HIV-1 Gag variants. Nature. 1994 Jun 2;369(6479):403–407. doi: 10.1038/369403a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luescher I. F., Vivier E., Layer A., Mahiou J., Godeau F., Malissen B., Romero P. CD8 modulation of T-cell antigen receptor-ligand interactions on living cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1995 Jan 26;373(6512):353–356. doi: 10.1038/373353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madrenas J., Wange R. L., Wang J. L., Isakov N., Samelson L. E., Germain R. N. Zeta phosphorylation without ZAP-70 activation induced by TCR antagonists or partial agonists. Science. 1995 Jan 27;267(5197):515–518. doi: 10.1126/science.7824949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui K., Boniface J. J., Reay P. A., Schild H., Fazekas de St Groth B., Davis M. M. Low affinity interaction of peptide-MHC complexes with T cell receptors. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1788–1791. doi: 10.1126/science.1763329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui K., Boniface J. J., Steffner P., Reay P. A., Davis M. M. Kinetics of T-cell receptor binding to peptide/I-Ek complexes: correlation of the dissociation rate with T-cell responsiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12862–12866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeithan T. W. Kinetic proofreading in T-cell receptor signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):5042–5046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.5042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racioppi L., Ronchese F., Matis L. A., Germain R. N. Peptide-major histocompatibility complex class II complexes with mixed agonist/antagonist properties provide evidence for ligand-related differences in T cell receptor-dependent intracellular signaling. J Exp Med. 1993 Apr 1;177(4):1047–1060. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.4.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert J., Alexander J., Snoke K., Coggeshall M., Herbert E., McKenzie D., Grey H. M., Sette A. Effect of T-cell receptor antagonism on interaction between T cells and antigen-presenting cells and on T-cell signaling events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2671–2675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sette A., Alexander J., Ruppert J., Snoke K., Franco A., Ishioka G., Grey H. M. Antigen analogs/MHC complexes as specific T cell receptor antagonists. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:413–431. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.002213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan-Lancaster J., Evavold B. D., Allen P. M. Induction of T-cell anergy by altered T-cell-receptor ligand on live antigen-presenting cells. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):156–159. doi: 10.1038/363156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan-Lancaster J., Shaw A. S., Rothbard J. B., Allen P. M. Partial T cell signaling: altered phospho-zeta and lack of zap70 recruitment in APL-induced T cell anergy. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):913–922. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykulev Y., Brunmark A., Jackson M., Cohen R. J., Peterson P. A., Eisen H. N. Kinetics and affinity of reactions between an antigen-specific T cell receptor and peptide-MHC complexes. Immunity. 1994 Apr;1(1):15–22. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symer D. E., Dintzis R. Z., Diamond D. J., Dintzis H. M. Inhibition or activation of human T cell receptor transfectants is controlled by defined, soluble antigen arrays. J Exp Med. 1992 Nov 1;176(5):1421–1430. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.5.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahama Y., Suzuki H., Katz K. S., Grusby M. J., Singer A. Positive selection of CD4+ T cells by TCR ligation without aggregation even in the absence of MHC. Nature. 1994 Sep 1;371(6492):67–70. doi: 10.1038/371067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valitutti S., Müller S., Cella M., Padovan E., Lanzavecchia A. Serial triggering of many T-cell receptors by a few peptide-MHC complexes. Nature. 1995 May 11;375(6527):148–151. doi: 10.1038/375148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignali D. A., Strominger J. L. Amino acid residues that flank core peptide epitopes and the extracellular domains of CD4 modulate differential signaling through the T cell receptor. J Exp Med. 1994 Jun 1;179(6):1945–1956. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.6.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber S., Traunecker A., Oliveri F., Gerhard W., Karjalainen K. Specific low-affinity recognition of major histocompatibility complex plus peptide by soluble T-cell receptor. Nature. 1992 Apr 30;356(6372):793–796. doi: 10.1038/356793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windhagen A., Scholz C., Höllsberg P., Fukaura H., Sette A., Hafler D. A. Modulation of cytokine patterns of human autoreactive T cell clones by a single amino acid substitution of their peptide ligand. Immunity. 1995 Apr;2(4):373–380. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90145-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon S. T., Dianzani U., Bottomly K., Janeway C. A., Jr Both high and low avidity antibodies to the T cell receptor can have agonist or antagonist activity. Immunity. 1994 Oct;1(7):563–569. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oers N. S., Killeen N., Weiss A. ZAP-70 is constitutively associated with tyrosine-phosphorylated TCR zeta in murine thymocytes and lymph node T cells. Immunity. 1994 Nov;1(8):675–685. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Merwe P. A., Barclay A. N. Transient intercellular adhesion: the importance of weak protein-protein interactions. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Sep;19(9):354–358. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



