Abstract
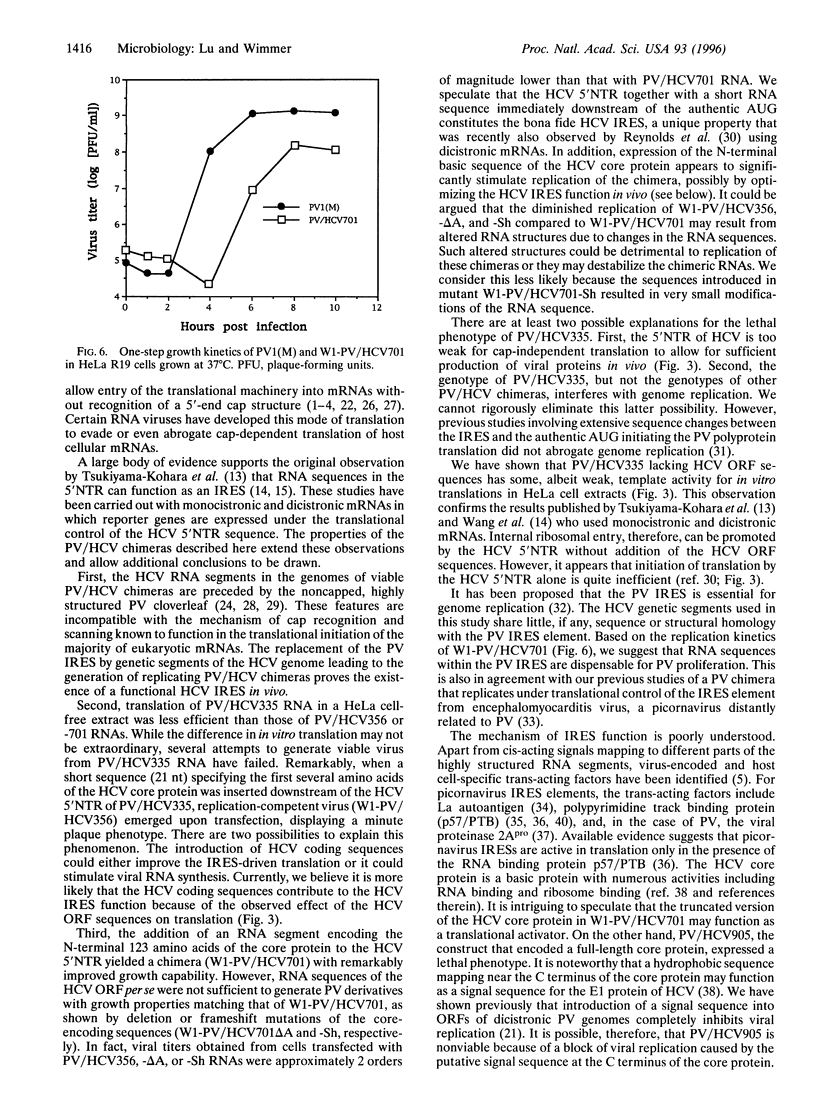
Chimeric genomes of poliovirus (PV) have been constructed in which the cognate internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) element was replaced by genetic elements of hepatitis C virus (HCV). Replacement of PV IRES with nt 9-332 of the genotype Ib HCV genome, a sequence comprising all but the first eight residues of the 5' nontranslated region (5'NTR) of HCV, resulted in a lethal phenotype. Addition of 366 nt of the HCV core-encoding sequence downstream of the HCV 5'NTR yielded a viable PV/HCV chimera, which expressed a stable, small-plaque phenotype. This chimeric genome encoded a truncated HCV core protein that was fused to the N terminus of the PV polyprotein via an engineered cleavage site for PV proteinase 3CPpro. Manipulation of the HCV core-encoding sequence of this viable chimera by deletion and frameshift yielded results suggesting that the 5'-proximal sequences of the HCV open reading frame were essential for viability of the chimera and that the N-terminal basic region of the HCV core protein is required for efficient replication of the chimeric virus. These data suggest that the bona fide HCV IRES includes genetic information mapping to the 5'NTR and sequences of the HCV open reading frame. PV chimeras replicating under translational control of genetic elements of HCV can serve to study HCV IRES function in vivo and to search for anti-HCV chemotherapeutic agents.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander L., Lu H. H., Wimmer E. Polioviruses containing picornavirus type 1 and/or type 2 internal ribosomal entry site elements: genetic hybrids and the expression of a foreign gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1406–1410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andino R., Rieckhof G. E., Baltimore D. A functional ribonucleoprotein complex forms around the 5' end of poliovirus RNA. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):369–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90170-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andino R., Silvera D., Suggett S. D., Achacoso P. L., Miller C. J., Baltimore D., Feinberg M. B. Engineering poliovirus as a vaccine vector for the expression of diverse antigens. Science. 1994 Sep 2;265(5177):1448–1451. doi: 10.1126/science.8073288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borman A. M., Deliat F. G., Kean K. M. Sequences within the poliovirus internal ribosome entry segment control viral RNA synthesis. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 1;13(13):3149–3157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06613.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. A., Zhang H., Ping L. H., Lemon S. M. Secondary structure of the 5' nontranslated regions of hepatitis C virus and pestivirus genomic RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 11;20(19):5041–5045. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.19.5041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruix J., Barrera J. M., Calvet X., Ercilla G., Costa J., Sanchez-Tapias J. M., Ventura M., Vall M., Bruguera M., Bru C. Prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis C virus in Spanish patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic cirrhosis. Lancet. 1989 Oct 28;2(8670):1004–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Weiner A. J., Overby L. R., Bradley D. W., Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):359–362. doi: 10.1126/science.2523562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambidge S. J., Sarnow P. Translational enhancement of the poliovirus 5' noncoding region mediated by virus-encoded polypeptide 2A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10272–10276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellen C. U., Witherell G. W., Schmid M., Shin S. H., Pestova T. V., Gil A., Wimmer E. A cytoplasmic 57-kDa protein that is required for translation of picornavirus RNA by internal ribosomal entry is identical to the nuclear pyrimidine tract-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7642–7646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka N., Najita L., Franzusoff A., Sarnow P. Cap-dependent and cap-independent translation by internal initiation of mRNAs in cell extracts prepared from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7322–7330. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Davies M. V., Kaufman R. J., Wimmer E. Initiation of protein synthesis by internal entry of ribosomes into the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vivo. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1651–1660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1651-1660.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C., Wimmer E. A segment of the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA directs internal entry of ribosomes during in vitro translation. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2636–2643. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2636-2643.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Wimmer E. Cap-independent translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: structural elements of the internal ribosomal entry site and involvement of a cellular 57-kD RNA-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1560–1572. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski A., Hunt S. L., Patton J. G., Jackson R. J. Direct evidence that polypyrimidine tract binding protein (PTB) is essential for internal initiation of translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. RNA. 1995 Nov;1(9):924–938. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuge S., Nomoto A. Construction of viable deletion and insertion mutants of the Sabin strain of type 1 poliovirus: function of the 5' noncoding sequence in viral replication. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1478–1487. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1478-1487.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo G., Choo Q. L., Alter H. J., Gitnick G. L., Redeker A. G., Purcell R. H., Miyamura T., Dienstag J. L., Alter M. J., Stevens C. E. An assay for circulating antibodies to a major etiologic virus of human non-A, non-B hepatitis. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):362–364. doi: 10.1126/science.2496467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen G. R., Semler B. L., Wimmer E. Stable hairpin structure within the 5'-terminal 85 nucleotides of poliovirus RNA. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):328–335. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.328-335.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H. H., Alexander L., Wimmer E. Construction and genetic analysis of dicistronic polioviruses containing open reading frames for epitopes of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120. J Virol. 1995 Aug;69(8):4797–4806. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.8.4797-4806.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H. H., Yang C. F., Murdin A. D., Klein M. H., Harber J. J., Kew O. M., Wimmer E. Mouse neurovirulence determinants of poliovirus type 1 strain LS-a map to the coding regions of capsid protein VP1 and proteinase 2Apro. J Virol. 1994 Nov;68(11):7507–7515. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.11.7507-7515.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macadam A. J., Ferguson G., Fleming T., Stone D. M., Almond J. W., Minor P. D. Role for poliovirus protease 2A in cap independent translation. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 15;13(4):924–927. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06336.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macejak D. G., Sarnow P. Internal initiation of translation mediated by the 5' leader of a cellular mRNA. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):90–94. doi: 10.1038/353090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBratney S., Chen C. Y., Sarnow P. Internal initiation of translation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;5(6):961–965. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90077-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerovitch K., Svitkin Y. V., Lee H. S., Lejbkowicz F., Kenan D. J., Chan E. K., Agol V. I., Keene J. D., Sonenberg N. La autoantigen enhances and corrects aberrant translation of poliovirus RNA in reticulocyte lysate. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):3798–3807. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.3798-3807.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H., Purcell R. H. Hepatitis C virus shares amino acid sequence similarity with pestiviruses and flaviviruses as well as members of two plant virus supergroups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2057–2061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molla A., Jang S. K., Paul A. V., Reuer Q., Wimmer E. Cardioviral internal ribosomal entry site is functional in a genetically engineered dicistronic poliovirus. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):255–257. doi: 10.1038/356255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molla A., Paul A. V., Wimmer E. Cell-free, de novo synthesis of poliovirus. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1647–1651. doi: 10.1126/science.1661029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Kurai K., Okada S., Yamamoto K., Lizuka H., Tanaka T., Fukuda S., Tsuda F., Mishiro S. Full-length sequence of a hepatitis C virus genome having poor homology to reported isolates: comparative study of four distinct genotypes. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):331–341. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90762-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Internal binding of eucaryotic ribosomes on poliovirus RNA: translation in HeLa cell extracts. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):441–444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.441-444.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):320–325. doi: 10.1038/334320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilipenko E. V., Blinov V. M., Romanova L. I., Sinyakov A. N., Maslova S. V., Agol V. I. Conserved structural domains in the 5'-untranslated region of picornaviral genomes: an analysis of the segment controlling translation and neurovirulence. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. E., Kaminski A., Kettinen H. J., Grace K., Clarke B. E., Carroll A. R., Rowlands D. J., Jackson R. J. Unique features of internal initiation of hepatitis C virus RNA translation. EMBO J. 1995 Dec 1;14(23):6010–6020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijnbrand R., Bredenbeek P., van der Straaten T., Whetter L., Inchauspé G., Lemon S., Spaan W. Almost the entire 5' non-translated region of hepatitis C virus is required for cap-independent translation. FEBS Lett. 1995 May 29;365(2-3):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00458-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera V. M., Welsh J. D., Maizel J. V., Jr Comparative sequence analysis of the 5' noncoding region of the enteroviruses and rhinoviruses. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):42–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90656-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito I., Miyamura T., Ohbayashi A., Harada H., Katayama T., Kikuchi S., Watanabe Y., Koi S., Onji M., Ohta Y. Hepatitis C virus infection is associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6547–6549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santolini E., Migliaccio G., La Monica N. Biosynthesis and biochemical properties of the hepatitis C virus core protein. J Virol. 1994 Jun;68(6):3631–3641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.6.3631-3641.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukiyama-Kohara K., Iizuka N., Kohara M., Nomoto A. Internal ribosome entry site within hepatitis C virus RNA. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1476–1483. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1476-1483.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Sarnow P., Siddiqui A. Translation of human hepatitis C virus RNA in cultured cells is mediated by an internal ribosome-binding mechanism. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3338–3344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3338-3344.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E., Hellen C. U., Cao X. Genetics of poliovirus. Annu Rev Genet. 1993;27:353–436. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.27.120193.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Bradley J., Wimmer E., Studier F. W., Dunn J. J. Synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA by purified T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]