Abstract
Several enzymes involved in the formation of steroids of the pregnene and pregnane series have been identified in the brain, but the biosynthesis of testosterone has never been reported in the central nervous system. In the present study, we have investigated the distribution and bioactivity of 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (17beta-HSD) (EC 1.1.1.62; a key enzyme that is required for the formation of testosterone and estradiol) in the brain of the male frog Rana ridibunda. By using an antiserum against human type I placental 17beta-HSD, immunoreactivity was localized in a discrete group of ependymal glial cells bordering the telencephalic ventricles. HPLC analysis of telencephalon and hypothalamus extracts combined with testosterone radioimmunoassay revealed the existence of two peaks coeluting with testosterone and 5alpha-dihydrotestosterone. After HPLC purification, testosterone was identified by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Incubation of telencephalon slices with [3H]pregnenolone resulted in the formation of metabolites which coeluted with progesterone, 17alpha-hydroxyprogesterone, dehydroepiandrosterone, androstenedione, testosterone, and 5alpha-dihydrotestosterone. The newly synthesized steroid comigrating with testosterone was selectively immunodetected by using testosterone antibodies. These data indicate that 17beta-HSD is expressed in a subpopulation of gliocytes in the frog telencephalon and that telencephalic cells are capable of synthesizing various androgens, including dehydroepiandrosterone, androstenedione, testosterone, and 5alpha-dihydrotestosterone.
Full text
PDF
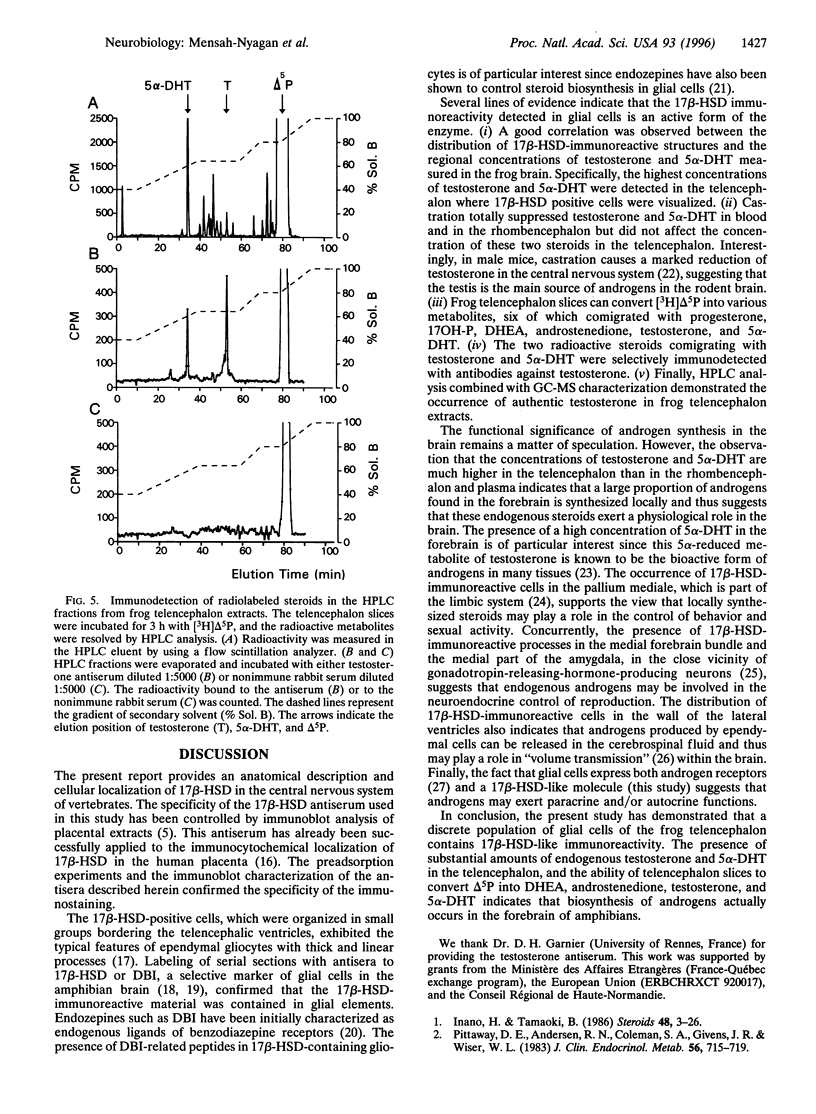

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akwa Y., Young J., Kabbadj K., Sancho M. J., Zucman D., Vourc'h C., Jung-Testas I., Hu Z. Y., Le Goascogne C., Jo D. H. Neurosteroids: biosynthesis, metabolism and function of pregnenolone and dehydroepiandrosterone in the brain. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;40(1-3):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(91)90169-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen A. C., Tonon M. C., Pelletier G., Conlon J. M., Fasolo A., Vaudry H. Neuropeptides in the amphibian brain. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;138:89-210, 315-26. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61588-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney D. L., Uzunov D., Costa E., Guidotti A. Gas chromatographic-mass fragmentographic quantitation of 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 alpha-pregnan-20-one (allopregnanolone) and its precursors in blood and brain of adrenalectomized and castrated rats. J Neurosci. 1995 Jun;15(6):4641–4650. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-06-04641.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corpéchot C., Robel P., Axelson M., Sjövall J., Baulieu E. E. Characterization and measurement of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4704–4707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont E., Labrie F., Luu-The V., Pelletier G. Localization of 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase throughout gestation in human placenta. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Oct;39(10):1403–1407. doi: 10.1177/39.10.1940311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Glaister D., Seeburg P. H., Guidotti A., Costa E. Cloning and expression of cDNA for human diazepam binding inhibitor, a natural ligand of an allosteric regulatory site of the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7547–7551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inano H., Tamaoki B. Testicular 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: molecular properties and reaction mechanism. Steroids. 1986 Jul-Aug;48(1-2):1–26. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(86)90038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung-Testas I., Renoir M., Bugnard H., Greene G. L., Baulieu E. E. Demonstration of steroid hormone receptors and steroid action in primary cultures of rat glial cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992 Mar;41(3-8):621–631. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(92)90394-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrie F., Luu-The V., Labrie C., Bérubé D., Couet J., Zhao H. F., Gagné R., Simard J. Characterization of two mRNA species encoding human estradiol 17 beta-dehydrogenase and assignment of the gene to chromosome 17. J Steroid Biochem. 1989;34(1-6):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(89)90082-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lihrmann I., Plaquevent J. C., Tostivint H., Raijmakers R., Tonon M. C., Conlon J. M., Vaudry H. Frog diazepam-binding inhibitor: peptide sequence, cDNA cloning, and expression in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):6899–6903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luu The V., Labrie C., Zhao H. F., Couët J., Lachance Y., Simard J., Leblanc G., Côté J., Bérubé D., Gagné R. Characterization of cDNAs for human estradiol 17 beta-dehydrogenase and assignment of the gene to chromosome 17: evidence of two mRNA species with distinct 5'-termini in human placenta. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1301–1309. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-8-1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luu-The V., Labrie C., Zhao H. F., Couët J., Lachance Y., Simard J., Côté J., Leblanc G., Lagacé L., Bérubé D. Purification, cloning, complementary DNA structure, and predicted amino acid sequence of human estradiol 17 beta-dehydrogenase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;595:40–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb34281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martel C., Rhéaume E., Takahashi M., Trudel C., Couët J., Luu-The V., Simard J., Labrie F. Distribution of 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase gene expression and activity in rat and human tissues. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992 Mar;41(3-8):597–603. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(92)90390-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini L. The 5alpha-reduction of testosterone in the neuroendocrine structures. Biochemical and physiological implications. Endocr Rev. 1982 Winter;3(1):1–25. doi: 10.1210/edrv-3-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon S. H. Neurosteroids: biochemistry, modes of action, and clinical relevance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 May;78(5):1003–1008. doi: 10.1210/jcem.78.5.8175951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mensah-Nyagan A. G., Feuilloley M., Dupont E., Do-Rego J. L., Leboulenger F., Pelletier G., Vaudry H. Immunocytochemical localization and biological activity of 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in the central nervous system of the frog. J Neurosci. 1994 Dec;14(12):7306–7318. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-12-07306.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos V., Guarneri P., Kreuger K. E., Guidotti A., Costa E. Pregnenolone biosynthesis in C6-2B glioma cell mitochondria: regulation by a mitochondrial diazepam binding inhibitor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5113–5117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittaway D. E., Andersen R. N., Coleman S. A., Jr, Givens J. R., Wiser W. L. Human ovarian 17 beta-hydroxysteroid oxidoreductase activity: a comparison of normal and polycystic ovarian tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Apr;56(4):715–719. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-4-715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. V. Estrogen metabolism in neural tissues of rabbits: 17 beta - hydroxysteroid oxidoreductase activity. Steroids. 1979 Aug;34(2):207–215. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(79)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada M., Urano A., Gorbman A. A stereotaxic atlas for diencephalic nuclei of the frog, Rana pipiens. Arch Histol Jpn. 1980 May;43(2):157–173. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.43.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]