Abstract
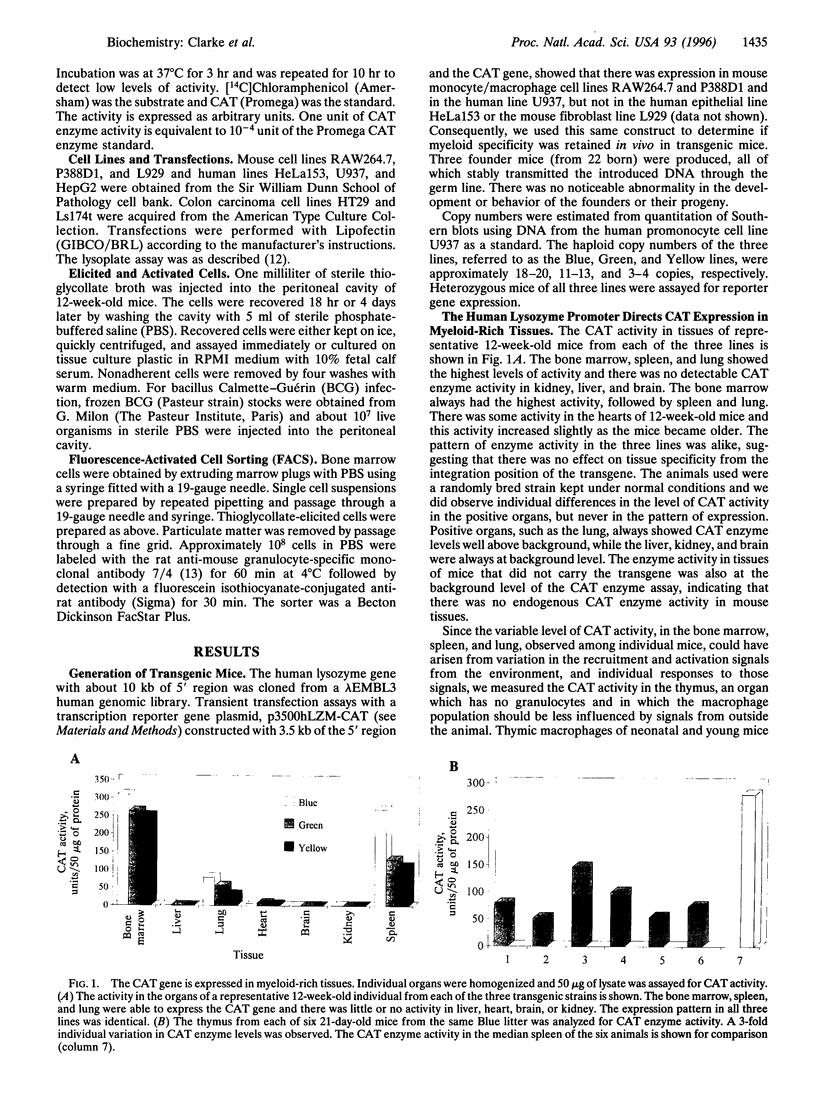
The 5' region of the human lysozyme gene from -3500 to +25 was fused to a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) reporter gene and three transgenic founder mice were obtained. All three transgenic lines showed the same pattern of CAT enzyme expression in adult mouse tissues that was consistent with the targeting of elicited, activated macrophages in tissues and developing and elicited granulocytes. In normal mice high CAT enzyme activity was found in the spleen, lung, and thymus, tissues rich in phagocytically active cells, but not in many other tissues, such as the gut and muscle, which contain resident macrophages. Cultured resident peritoneal macrophages and cells elicited 18 hr (granulocytes) and 4 days (macrophages) after injection of sterile thioglycollate broth expressed CAT activity. Bacillus Calmette-Guérin infection of transgenic mice resulted in CAT enzyme expression in the liver, which contained macrophage-rich granulomas, whereas the liver of uninfected mice did not have any detectable CAT enzyme activity. Although the Paneth cells of the small intestine in both human and mouse produce lysozyme, the CAT gene, under the control of the human lysozyme promoter, was not expressed in the mouse small intestine. These results indicate that the human lysozyme promoter region may be used to direct expression of genes to activated mouse myeloid cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Back A., East K., Hickstein D. Leukocyte integrin CD11b promoter directs expression in lymphocytes and granulocytes in transgenic mice. Blood. 1995 Feb 15;85(4):1017–1024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F., Farquhar M. G. Origin of granules in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Two types derived from opposite faces of the Golgi complex in developing granulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1966 Feb;28(2):277–301. doi: 10.1083/jcb.28.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifer C., Vidal M., Grosveld F., Sippel A. E. Tissue specific and position independent expression of the complete gene domain for chicken lysozyme in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2843–2848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07473.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung L. P., Keshav S., Gordon S. Cloning the human lysozyme cDNA: inverted Alu repeat in the mRNA and in situ hybridization for macrophages and Paneth cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6227–6231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A. Activation of mononuclear phagocytes: fact, fancy, and future. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):813–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker P. R., Morris L., Gordon S. Novel cell surface adhesion receptors involved in interactions between stromal macrophages and haematopoietic cells. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1988;9:185–206. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1988.supplement_9.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross M., Mangelsdorf I., Wedel A., Renkawitz R. Mouse lysozyme M gene: isolation, characterization, and expression studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6232–6236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross M., Renkawitz R. Repetitive sequence involvement in the duplication and divergence of mouse lysozyme genes. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1283–1288. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08237.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziennis S., Van Etten R. A., Pahl H. L., Morris D. L., Rothstein T. L., Blosch C. M., Perlmutter R. M., Tenen D. G. The CD11b promoter directs high-level expression of reporter genes in macrophages in transgenic mice. Blood. 1995 Jan 15;85(2):319–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett J. W., Strydom D. J., Lobb R. R., Alderman E. M., Vallee B. L., Artymiuk P. J., Collett S., Phillips D. C., Dobson C. M., Redfield C. Lysozyme: a major secretory product of a human colon carcinoma cell line. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 12;24(4):965–975. doi: 10.1021/bi00325a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S. Biology of the macrophage. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1986;4:267–286. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1986.supplement_4.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S., Clarke S., Greaves D., Doyle A. Molecular immunobiology of macrophages: recent progress. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995 Feb;7(1):24–33. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(95)80025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S., Perry V. H., Rabinowitz S., Chung L. P., Rosen H. Plasma membrane receptors of the mononuclear phagocyte system. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1988;9:1–26. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1988.supplement_9.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S., Todd J., Cohn Z. A. In vitro synthesis and secretion of lysozyme by mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1228–1248. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer P., Maltby V., Rossant J., Bernstein A., Pawson T. Myeloid expression of the human c-fps/fes proto-oncogene in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2521–2527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisolano J. L., Sclar G. M., Ley T. J. Early myeloid cell-specific expression of the human cathepsin G gene in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8989–8993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch S., Gordon S. Polymorphic expression of a neutrophil differentiation antigen revealed by monoclonal antibody 7/4. Immunogenetics. 1983;18(3):229–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00952962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvai A., Palinski W., Wu H., Moulton K. S., Kalla K., Glass C. K. Scavenger receptor A gene regulatory elements target gene expression to macrophages and to foam cells of atherosclerotic lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5391–5395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume D. A., Halpin D., Charlton H., Gordon S. The mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse defined by immunohistochemical localization of antigen F4/80: macrophages of endocrine organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4174–4177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshav S., Chung P., Milon G., Gordon S. Lysozyme is an inducible marker of macrophage activation in murine tissues as demonstrated by in situ hybridization. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1049–1058. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Sappino A. P., Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Starkey P. M., Gordon S. Quantitative analysis of total macrophage content in adult mouse tissues. Immunochemical studies with monoclonal antibody F4/80. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):475–489. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepay D. A., Nathan C. F., Steinman R. M., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Murine Kupffer cells. Mononuclear phagocytes deficient in the generation of reactive oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1079–1096. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. E., McCarthy S. P., Lorenzen J., McGee J. O. Differential effects of LPS, IFN-gamma and TNF alpha on the secretion of lysozyme by individual human mononuclear phagocytes: relationship to cell maturity. Immunology. 1990 Mar;69(3):402–408. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osserman E. F., Lawlor D. P. Serum and urinary lysozyme (muramidase) in monocytic and monomyelocytic leukemia. J Exp Med. 1966 Nov 1;124(5):921–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier M., Forget A., Bourassa D., Gros P., Skamene E. Immunopathology of BCG infection in genetically resistant and susceptible mouse strains. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2179–2185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters C. W., Kruse U., Pollwein R., Grzeschik K. H., Sippel A. E. The human lysozyme gene. Sequence organization and chromosomal localization. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jul 1;182(3):507–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pothier F., Ouellet M., Julien J. P., Guérin S. L. An improved CAT assay for promoter analysis in either transgenic mice or tissue culture cells. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Jan-Feb;11(1):83–90. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalnik D. G., Dorfman D. M., Perkins A. S., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Orkin S. H. Targeting of transgene expression to monocyte/macrophages by the gp91-phox promoter and consequent histiocytic malignancies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8505–8509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tom B. H., Rutzky L. P., Jakstys M. M., Oyasu R., Kaye C. I., Kahan B. D. Human colonic adenocarcinoma cells. I. Establishment and description of a new line. In Vitro. 1976 Mar;12(3):180–191. doi: 10.1007/BF02796440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]