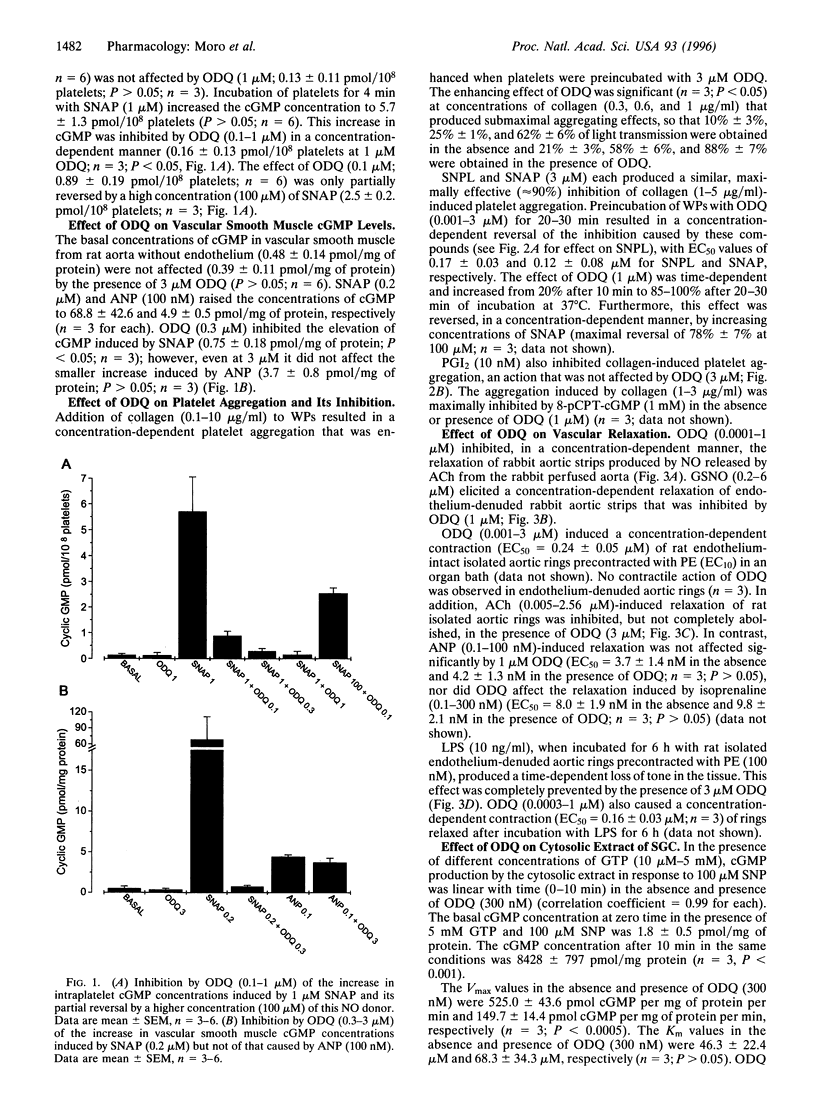
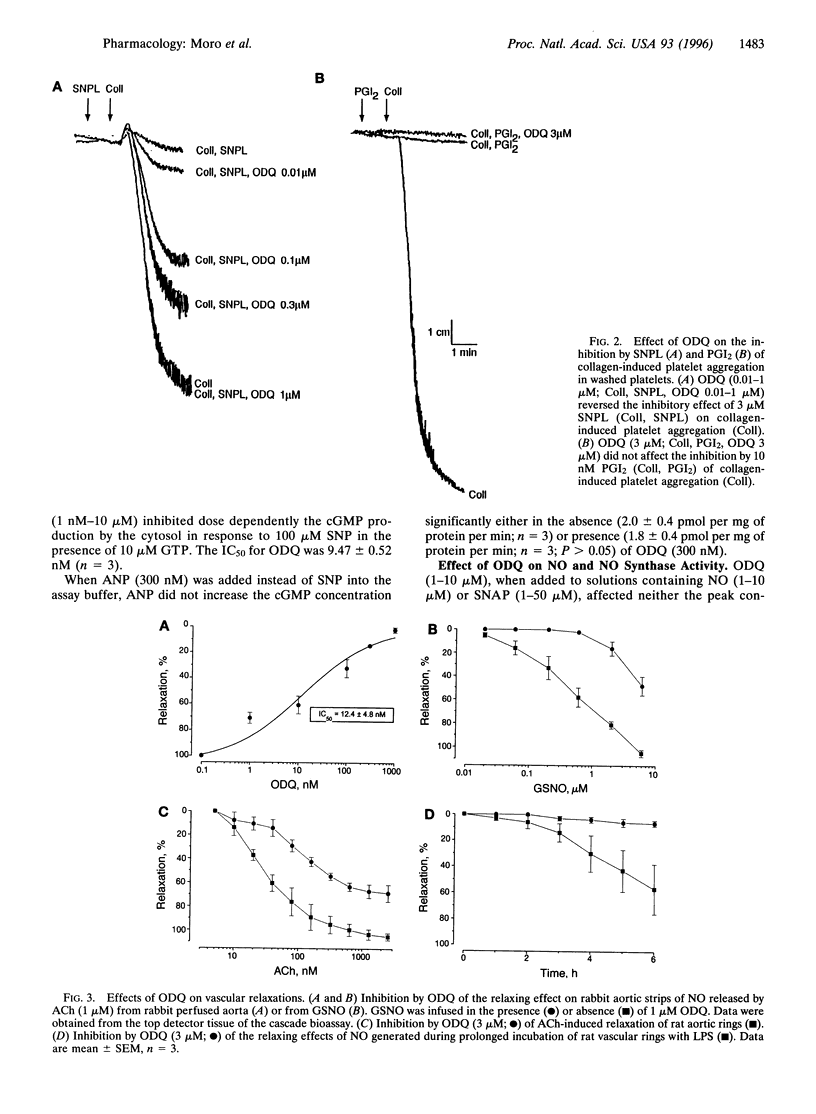
Abstract
The L-arginine:nitric oxide (NO) pathway is believed to exert many of its physiological effects via stimulation of the soluble guanylyl cyclase (SGC); however, the lack of a selective inhibitor of this enzyme has prevented conclusive demonstration of this mechanism of action. We have found that the compound 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo[4,3,-a]quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ) inhibits the elevation of cGMP induced by the NO donor S-nitroso-DL-penicillamine in human platelets and rat vascular smooth muscle (IC50 = 10-60 nM and <10 nM, respectively) and that this is accompanied by prevention of the platelet inhibitory and vasodilator actions of NO donors. ODQ also inhibited the antiaggregatory action of NO generated by the platelets but did not affect the action of prostacyclin or that of a cGMP mimetic. In addition, ODQ inhibited the vasodilator actions of endogenously released NO and of NO generated after induction of NO synthase in vascular preparations. It did not, however, affect the increase in vascular smooth muscle cGMP or the dilatation induced by atrial natriuretic factor. ODQ had no effect on NO synthase activity, nor did it react with NO. It did, however, potently (IC50 approximately 10 nM) inhibit the activity of the SGC in cytosol obtained from crude extract of rat aortic smooth muscle. Thus ODQ prevents the actions of NO on platelets and vascular smooth muscle through its potent inhibitory effect on the SGC.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolotina V. M., Najibi S., Palacino J. J., Pagano P. J., Cohen R. A. Nitric oxide directly activates calcium-dependent potassium channels in vascular smooth muscle. Nature. 1994 Apr 28;368(6474):850–853. doi: 10.1038/368850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüne B., Lapetina E. G. Activation of a cytosolic ADP-ribosyltransferase by nitric oxide-generating agents. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8455–8458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Gardner F. H. Thrombocytopenia as a laboratory sign and complication of gram-negative bacteremic infection. Arch Intern Med. 1966 Jan;117(1):113–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrigan J. J., Jr, Ray W. L., May N. Changes in the blood coagulation system associated with septicemia. N Engl J Med. 1968 Oct 17;279(16):851–856. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196810172791603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. A., DeRubertis F. R. Restoration of the responsiveness of purified guanylate cyclase to nitrosoguanidine, nitric oxide, and related activators by heme and hemeproteins. Evidence for involvement of the paramagnetic nitrosyl-heme complex in enzyme activation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8433–8443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. Effects of LY83583, nordihydroguaiaretic acid, and quinacrine on cyclic GMP elevation and inhibition of tension by muscarinic agonists in rabbit aorta and left atrium. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;65(9):1913–1917. doi: 10.1139/y87-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmeler S., Lottspeich F., Brüne B. Nitric oxide causes ADP-ribosylation and inhibition of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16771–16774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feelisch M., Noack E. A. Correlation between nitric oxide formation during degradation of organic nitrates and activation of guanylate cyclase. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul 2;139(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis S. H., Noblett B. D., Todd B. W., Wells J. N., Corbin J. D. Relaxation of vascular and tracheal smooth muscle by cyclic nucleotide analogs that preferentially activate purified cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;34(4):506–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J., Southam E., Boulton C. L., Nielsen E. B., Schmidt K., Mayer B. Potent and selective inhibition of nitric oxide-sensitive guanylyl cyclase by 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one. Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Aug;48(2):184–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Moncada S., Palmer R. M. Bioassay of prostacyclin and endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF) from porcine aortic endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;87(4):685–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb14586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova K., Schaefer M., Drummer C., Gerzer R. Effects of nitric oxide-containing compounds on increases in cytosolic ionized Ca2+ and on aggregation of human platelets. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan 4;244(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(93)90057-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marczin N., Ryan U. S., Catravas J. D. Methylene blue inhibits nitrovasodilator- and endothelium-derived relaxing factor-induced cyclic GMP accumulation in cultured pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells via generation of superoxide anion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Oct;263(1):170–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. J., Wei E. P., Kontos H. A. Independent blockade of cerebral vasodilation from acetylcholine and nitric oxide. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):H847–H854. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.4.H847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Drazan K. M., Newby A. C. Methylene blue but not changes in cyclic GMP inhibits resting and bradykinin-stimulated production of prostacyclin by pig aortic endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):51–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurice D. H., Haslam R. J. Molecular basis of the synergistic inhibition of platelet function by nitrovasodilators and activators of adenylate cyclase: inhibition of cyclic AMP breakdown by cyclic GMP. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 May;37(5):671–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B., Brunner F., Schmidt K. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis by methylene blue. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Jan 26;45(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellion B. T., Ignarro L. J., Ohlstein E. H., Pontecorvo E. G., Hyman A. L., Kadowitz P. J. Evidence for the inhibitory role of guanosine 3', 5'-monophosphate in ADP-induced human platelet aggregation in the presence of nitric oxide and related vasodilators. Blood. 1981 May;57(5):946–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menshikov MYu, Ivanova K., Schaefer M., Drummer C., Gerzer R. Influence of the cGMP analog 8-PCPT-cGMP on agonist-induced increases in cytosolic ionized Ca2+ and on aggregation of human platelets. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 May 15;245(3):281–284. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(93)90108-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina y Vedia L., McDonald B., Reep B., Brüne B., Di Silvio M., Billiar T. R., Lapetina E. G. Nitric oxide-induced S-nitrosylation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase inhibits enzymatic activity and increases endogenous ADP-ribosylation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):24929–24932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murad F. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate as a mediator of vasodilation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):1–5. doi: 10.1172/JCI112536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mülsch A., Lückhoff A., Pohl U., Busse R., Bassenge E. LY 83583 (6-anilino-5,8-quinolinedione) blocks nitrovasodilator-induced cyclic GMP increases and inhibition of platelet activation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;340(1):119–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00169217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura T., Yoshida K., Toda N. Suppression by methylene blue of prostaglandin I2 synthesis in isolated dog renal arteries. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Jul;254(1):198–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petros A., Bennett D., Vallance P. Effect of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors on hypotension in patients with septic shock. Lancet. 1991 Dec 21;338(8782-8783):1557–1558. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92376-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. The anti-aggregating properties of vascular endothelium: interactions between prostacyclin and nitric oxide. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;92(3):639–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11367.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Rees D. D., Dutra A., Moncada S. S-nitroso-glutathione inhibits platelet activation in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):745–749. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Vallance P., Whitley G., Foxwell N., Moncada S. Platelet adhesion to human vascular endothelium is modulated by constitutive and cytokine induced nitric oxide. Cardiovasc Res. 1993 Jul;27(7):1380–1382. doi: 10.1093/cvr/27.7.1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M., Moncada S. An improved method for washing of human platelets with prostacyclin. Thromb Res. 1983 May 15;30(4):383–389. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90230-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. A specific inhibitor of nitric oxide formation from L-arginine attenuates endothelium-dependent relaxation. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;96(2):418–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11833.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt K., Klatt P., Mayer B. Reaction of peroxynitrite with oxyhaemoglobin: interference with photometrical determination of nitric oxide. Biochem J. 1994 Aug 1;301(Pt 3):645–647. doi: 10.1042/bj3010645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tare M., Parkington H. C., Coleman H. A., Neild T. O., Dusting G. J. Hyperpolarization and relaxation of arterial smooth muscle caused by nitric oxide derived from the endothelium. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):69–71. doi: 10.1038/346069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateson J. E., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Effects of prostacyclin (PGX) on cyclic AMP concentrations in human platelets. Prostaglandins. 1977 Mar;13(3):389–397. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Atrial natriuretic factor selectively activates particulate guanylate cyclase and elevates cyclic GMP in rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14332–14334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. J., Warren J. B. Adenylate cyclase-mediated vascular responses of rabbit aorta, mesenteric artery and skin microcirculation. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;110(2):633–638. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13858.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe L., Corbin J. D., Francis S. H. Characterization of a novel isozyme of cGMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine aorta. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7734–7741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin M. S., Cherry P. D., Rodenburg J. M., Messina E. J., Kaley G. Methylene blue inhibits vasodilation of skeletal muscle arterioles to acetylcholine and nitric oxide via the extracellular generation of superoxide anion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Sep;254(3):872–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. E., Rees D. D., Moncada S. Protective and pathological roles of nitric oxide in endotoxin shock. Cardiovasc Res. 1992 Jan;26(1):48–57. doi: 10.1093/cvr/26.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide stimulates auto-ADP-ribosylation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9382–9385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



