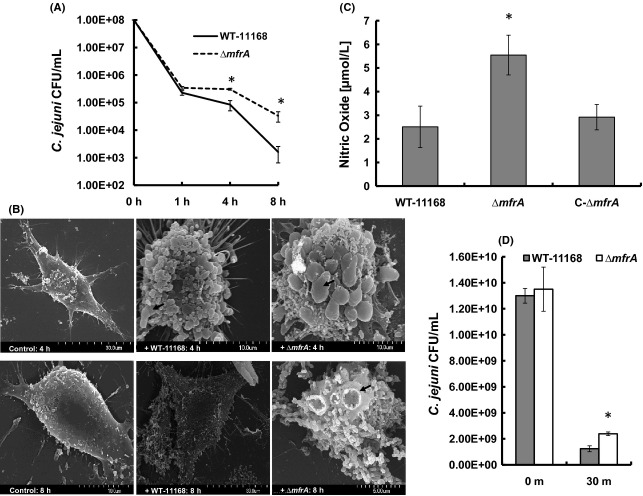
Figure 6.
The interaction of Campylobacter jejuni strains with murine macrophages (RAW 264.7 cells). (A) Enumeration of C. jejuniCFUs that survived inside the macrophages using the gentamicin protection assay. (B) Scanning electron microscopy showing macrophages infected with the C. jejuni strains. Monolayers that were not infected are labeled as control. Note the ruffled surface of infected macrophages and the black arrows show budding bodies and craters on the surface of the macrophages. At 8 h, macrophages challenged with the wildtype showed a decrease in ruffled surface and budding structures. (C) The production of nitric oxide in macrophage cultures challenged with the C. jejuni strains. (D) Quantification of C. jejuniCFUs that survived exposure to sodium nitroprusside (10 mmol/L) for 30 min. Survival in macrophages, NO production, and resistance to nitroprusside assays were repeated three times independently and samples were tested in three replicates per experiment. The SEM assay was repeated twice and the samples were analyzed in duplicate. Statistically significant (P < 0.05) differences are highlighted with “*” and data are presented as mean ± standard deviation.