Abstract
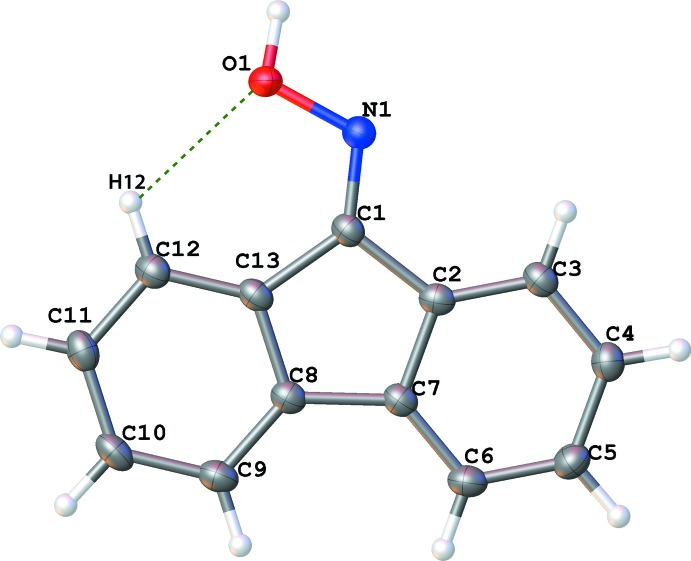
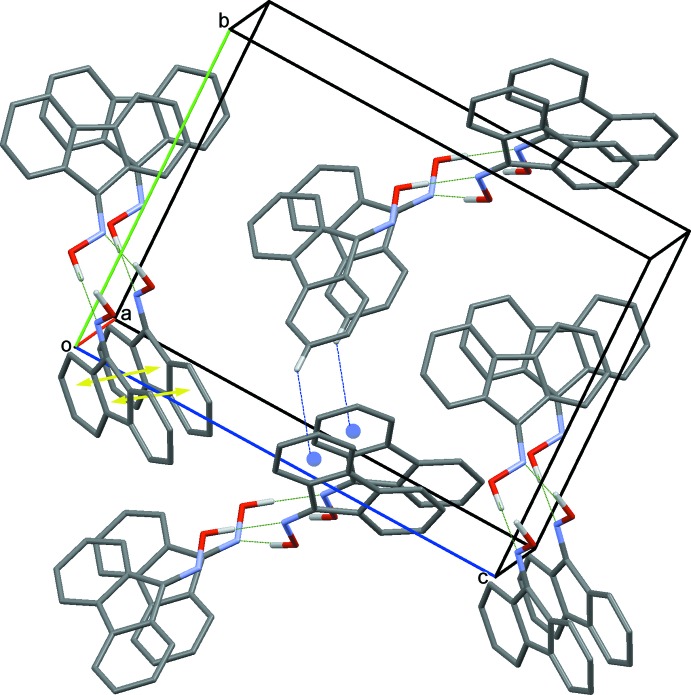
In the title molecule, C13H9NO, the fluorene system and the oxime group non-H atoms are essentially coplanar, with a maximum deviation from the fluorene mean plane of 0.079 (2) Å for the oxime O atom. A short intramolecular C—H⋯O generates an S(6) ring. In the crystal, molecules related by a twofold screw axis are connected by O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming [100] chains Within these chains, molecules related by a unit translation along [100] show π–π stacking interactions between their fluorene ring systems with an interplanar distance of 3.347 (2) Å. The dihedral angle between the fluorene units of adjacent molecules along the helix is 88.40 (2)°. There is a short C—H⋯π contact between the fluorene groups belonging to neighbouring chains.
Related literature
For the original procedure for the preparation of the title compound, see: Moore & Huntress (1927 ▶). For the use of the title compound as a starting material for the synthesis of bioactive compounds, see: Amlaiky et al. (1983 ▶); Ni et al. (2009 ▶); Rad et al. (2012 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H9NO
M r = 195.21
Orthorhombic,
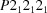
a = 4.8009 (1) Å
b = 12.2309 (2) Å
c = 16.0247 (3) Å
V = 940.96 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 0.70 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.16 × 0.13 × 0.13 mm
Data collection
Agilent SuperNova (Dual, Cu at zero, Atlas) diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2013 ▶) T min = 0.890, T max = 1.000
7588 measured reflections
1942 independent reflections
1865 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.029
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.029
wR(F 2) = 0.075
S = 1.05
1942 reflections
140 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.13 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack parameter determined using 735 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▶)
Absolute structure parameter: 0.16 (13)
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2013 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶) within OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002669/gk2601sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002669/gk2601Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002669/gk2601Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: http://scripts.iucr.org/cgi-bin/cr.cgi?rm=csd&csdid=985317
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of the C2–C7 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12—H12⋯O1 | 0.95 | 2.38 | 2.898 (2) | 114 |
| O1—H1⋯N1i | 0.98 (3) | 1.80 (3) | 2.7758 (18) | 169 (3) |
| C5—H5⋯Cg1ii | 0.95 | 3.08 | 3.873 | 142 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 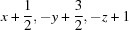 ; (ii)
; (ii) 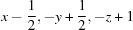 .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
1. Comment
The title compound, which was prepared according to a known procedure (Moore & Huntress, 1927) has found extensive use as a starting material for preparation of medicinal active compounds such as novel cyclophilin A inhibitors (Ni et al., 2009), novel analogs of beta-adrenoceptor antagonists (Rad et al., 2012) and beta-blocker (Amlaiky et al., 1983).
The ring atoms, N and O atoms in the title compound molecule, are essentially coplanar with a maximum deviation of 0.079 (2) Å for the O atom from the averaged ring plane (13 carbon atoms). The molecule in the crystal exhibits a C12—H12···O1 intramolecular interaction (Table 1), (Figure 1). The molecules related by a twofold screw axis are connected by O1—H1···N1 hydrogen bonds (Table 1) within a helical bonding network extending along the a axis (Figure 2). Within one helical bonding network, the neighboring molecules related by a unit translation along [100] show π–π stacking interactions between their fluorene ring systems with the interplanar distance of 3.347 (2) Å (Figure 2). The neighboring helical bonding networks in parallel alignment are linked to each other by C5—H5··· π (Cg1) (Table 1) close contact between their fluorene groups (Figure 3). The dihedral angle between the fluorene units of adjacent molecules along the helix is 88.40 (2)°.
2. Experimental
To a solution of fluoren-9-one (1.8 g, 10 mmol) in EtOH (47 ml) was given a solution of hydroxylamine hydrochloride (NH2OH.HCl, 2.75 g, 39.6 mmol) in water (7 ml), and the resulting mixture was stirred at 70 oC for 5 h. Thereafter, the reaction mixture was cooled and given into water (150 ml). The colorless precipitate was extracted with CH2Cl2 (2 × 75 ml). The organic phase was dried over anhydrous MgSO4 and concentrated in vacuo to give fluoren-9-one oxime (1.79 g, 92%) as a colorless solid, mp. 471 – 472 K; νmax (KBr/cm-1) 3500 – 2800 (bs, OH), 1604 (w), 1602, 1450, 1405, 1317, 1156, 1089, 998, 937, 780, 732, 640; δH (400 MHz, CDCl3) 7.28 – 7.47 (4H, m), 7.62 (1H, d, 3J = 7.6 Hz), 7.66 (1H, d, 3J = 7.2 Hz), 7.77 (1H, d, 3J = 7.2 Hz), 8.42 (1H, d, 3J = 7.6 Hz); δC (100.5 MHz, CDCl3) 119.8 (CH), 119.9 (CH), 121.7 (CH), 128.0 (CH), 128.4 (CH), 129.7 (CH), 130.2 (CH), 130.3 (Cquat), 131.3 (CH), 135.1 (Cquat), 140.5 (Cquat), 141.4 (Cquat), 153.6 (Cquat). Single crystals were obtained from cold CH2Cl2.
3. Refinement
All carbon-bound hydrogen atoms, except the H of the OH group which was freely refined, were placed in calculated positions with C—H distance of 0.95 Å and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
A view of the title molecule with displacement ellipsoids shown at the 50% probability level, showing the intramolecular contact within the molecule.
Fig. 2.
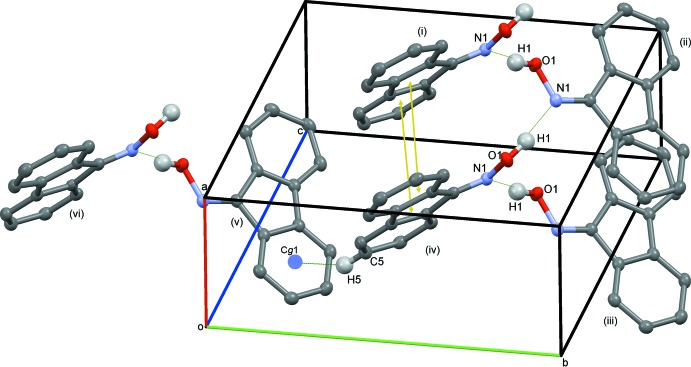
Intermolecular interactions between molecules of the title compound, including the π–π stacking interactions (represented by arrows in yellow). [Symmetry codes: i: 1 + x,y,z; ii: 1/2 + x,1.5 - y,1 - z; iii: -1/2 + x,1.5 - y,1 - z; iv: x, y, z; v: -1/2 + x, 1/2 - y, 1 - z; vi: x, -1 + y, z]
Fig. 3.
The crystal packing diagram showing the O—H···N close contacts (colored in green) between adjacent molecules in each helical bonding network, C—H···π intermolecular interaction between molecules within different helices (colored in blue) and π–π stacking interactions (arrows in yellow).
Crystal data
| C13H9NO | Dx = 1.378 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 195.21 | Melting point = 471–472 K |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.5418 Å |
| a = 4.8009 (1) Å | Cell parameters from 3850 reflections |
| b = 12.2309 (2) Å | θ = 4.5–76.1° |
| c = 16.0247 (3) Å | µ = 0.70 mm−1 |
| V = 940.96 (3) Å3 | T = 100 K |
| Z = 4 | Block, colourless |
| F(000) = 408 | 0.16 × 0.13 × 0.13 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent SuperNova (Dual, Cu at zero, Atlas) diffractometer | 1942 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: SuperNova (Cu) X-ray Source | 1865 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.029 |
| Detector resolution: 10.4127 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 76.3°, θmin = 4.6° |
| ω scans | h = −6→5 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2013) | k = −14→15 |
| Tmin = 0.890, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −19→20 |
| 7588 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.029 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0384P)2 + 0.1723P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.075 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.05 | Δρmax = 0.13 e Å−3 |
| 1942 reflections | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
| 140 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack parameter determined using 735 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure parameter: 0.16 (13) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.5506 (4) | 0.58330 (13) | 0.40422 (10) | 0.0189 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.8197 (4) | 0.44386 (15) | 0.17647 (10) | 0.0251 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.9543 (4) | 0.53953 (15) | 0.20052 (10) | 0.0242 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.8830 (4) | 0.59306 (14) | 0.27456 (10) | 0.0219 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.6741 (4) | 0.54803 (13) | 0.32367 (10) | 0.0196 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.3367 (4) | 0.50126 (13) | 0.42679 (10) | 0.0194 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.1613 (4) | 0.49391 (13) | 0.49503 (10) | 0.0209 (3) | |
| C4 | −0.0178 (4) | 0.40413 (13) | 0.50050 (11) | 0.0228 (4) | |
| C5 | −0.0177 (4) | 0.32387 (14) | 0.43891 (11) | 0.0246 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.1590 (4) | 0.33133 (14) | 0.37017 (11) | 0.0235 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.3353 (4) | 0.42037 (13) | 0.36414 (10) | 0.0195 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.5403 (4) | 0.45037 (13) | 0.30001 (10) | 0.0198 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.6112 (4) | 0.39797 (14) | 0.22607 (11) | 0.0239 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.898 (6) | 0.773 (2) | 0.4668 (17) | 0.068 (9)* | |
| H10 | 0.8703 | 0.4093 | 0.1256 | 0.030* | |
| H11 | 1.0969 | 0.5689 | 0.1661 | 0.029* | |
| H12 | 0.9750 | 0.6584 | 0.2908 | 0.026* | |
| H3 | 0.1626 | 0.5485 | 0.5372 | 0.025* | |
| H4 | −0.1408 | 0.3978 | 0.5467 | 0.027* | |
| H5 | −0.1399 | 0.2631 | 0.4438 | 0.029* | |
| H6 | 0.1583 | 0.2764 | 0.3283 | 0.028* | |
| H9 | 0.5200 | 0.3325 | 0.2097 | 0.029* | |
| N1 | 0.6059 (3) | 0.66488 (11) | 0.45230 (8) | 0.0202 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.8178 (3) | 0.73127 (10) | 0.42014 (7) | 0.0233 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0217 (9) | 0.0194 (8) | 0.0158 (7) | 0.0029 (6) | −0.0016 (6) | 0.0013 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0300 (10) | 0.0290 (8) | 0.0164 (7) | 0.0078 (8) | −0.0003 (7) | −0.0031 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0257 (9) | 0.0289 (9) | 0.0179 (8) | 0.0060 (7) | 0.0018 (7) | 0.0038 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0266 (9) | 0.0206 (7) | 0.0186 (8) | 0.0025 (7) | −0.0013 (7) | 0.0015 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0228 (9) | 0.0204 (7) | 0.0155 (7) | 0.0050 (7) | −0.0024 (7) | −0.0007 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0216 (8) | 0.0185 (7) | 0.0181 (8) | 0.0028 (7) | −0.0048 (7) | 0.0005 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0233 (8) | 0.0219 (7) | 0.0174 (7) | 0.0043 (7) | −0.0018 (7) | 0.0005 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0223 (8) | 0.0248 (8) | 0.0214 (8) | 0.0028 (6) | 0.0007 (8) | 0.0042 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0259 (9) | 0.0210 (8) | 0.0268 (9) | −0.0024 (7) | −0.0015 (7) | 0.0030 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0277 (10) | 0.0200 (7) | 0.0228 (8) | 0.0012 (7) | −0.0040 (7) | −0.0025 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0209 (8) | 0.0200 (7) | 0.0177 (7) | 0.0037 (6) | −0.0021 (6) | −0.0002 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0212 (9) | 0.0202 (7) | 0.0181 (8) | 0.0034 (7) | −0.0032 (7) | −0.0001 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0287 (10) | 0.0220 (8) | 0.0209 (8) | 0.0030 (7) | −0.0039 (7) | −0.0034 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0236 (8) | 0.0184 (6) | 0.0185 (7) | 0.0010 (6) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0014 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0283 (6) | 0.0217 (5) | 0.0198 (6) | −0.0058 (5) | 0.0010 (5) | −0.0023 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C13 | 1.484 (2) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.481 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.393 (2) |
| C10—C11 | 1.391 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| C10—H10 | 0.9500 | C6—C7 | 1.383 (2) |
| C11—C12 | 1.398 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| C11—H11 | 0.9500 | C7—C8 | 1.469 (2) |
| C12—C13 | 1.389 (2) | C8—C13 | 1.408 (2) |
| C12—H12 | 0.9500 | C8—C9 | 1.389 (2) |
| C2—C7 | 1.410 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.396 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.383 (2) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.397 (2) | N1—C1 | 1.288 (2) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | O1—H1 | 0.98 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.392 (2) | O1—N1 | 1.4000 (19) |
| N1—O1—H1 | 107.7 (17) | C6—C7—C2 | 120.39 (16) |
| C1—N1—O1 | 112.25 (13) | C6—C7—C8 | 130.96 (16) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 121.43 (15) | C9—C8—C7 | 130.19 (16) |
| N1—C1—C13 | 131.53 (16) | C9—C8—C13 | 120.61 (16) |
| C2—C1—C13 | 107.00 (14) | C13—C8—C7 | 109.20 (14) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 131.26 (15) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.8 |
| C3—C2—C7 | 120.97 (15) | C8—C9—C10 | 118.41 (16) |
| C7—C2—C1 | 107.75 (14) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.8 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.8 | C9—C10—H10 | 119.6 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 118.38 (15) | C11—C10—C9 | 120.89 (16) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.8 | C11—C10—H10 | 119.6 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C10—C11—H11 | 119.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.63 (16) | C10—C11—C12 | 121.04 (17) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C12—C11—H11 | 119.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.5 | C11—C12—H12 | 120.9 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.97 (17) | C13—C12—C11 | 118.17 (17) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 | C13—C12—H12 | 120.9 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.7 | C8—C13—C1 | 107.38 (15) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 118.66 (16) | C12—C13—C1 | 131.75 (16) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 120.7 | C12—C13—C8 | 120.87 (15) |
| C2—C7—C8 | 108.64 (14) | ||
| O1—N1—C1—C2 | 178.85 (14) | C5—C6—C7—C2 | 0.5 (3) |
| O1—N1—C1—C13 | 1.2 (2) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −179.68 (17) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 1.5 (3) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 1.3 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C7 | −177.14 (15) | C6—C7—C8—C13 | −178.35 (18) |
| N1—C1—C13—C8 | 177.82 (17) | C7—C2—C3—C4 | 0.0 (2) |
| N1—C1—C13—C12 | −1.4 (3) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −178.93 (17) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −178.52 (16) | C7—C8—C13—C1 | −0.88 (18) |
| C1—C2—C7—C6 | 178.38 (15) | C7—C8—C13—C12 | 178.46 (15) |
| C1—C2—C7—C8 | −1.52 (18) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.3 (3) |
| C2—C1—C13—C8 | −0.04 (18) | C9—C8—C13—C1 | 179.46 (15) |
| C2—C1—C13—C12 | −179.28 (17) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | −1.2 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.4 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.6 (3) |
| C2—C7—C8—C9 | −178.86 (18) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.1 (3) |
| C2—C7—C8—C13 | 1.53 (18) | C11—C12—C13—C1 | 179.97 (17) |
| C3—C2—C7—C6 | −0.5 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | 0.8 (2) |
| C3—C2—C7—C8 | 179.64 (15) | C13—C1—C2—C3 | 179.66 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.4 (3) | C13—C1—C2—C7 | 0.98 (18) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 0.0 (3) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | 0.6 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the C2–C7 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C12—H12···O1 | 0.95 | 2.38 | 2.898 (2) | 114 |
| O1—H1···N1i | 0.98 (3) | 1.80 (3) | 2.7758 (18) | 169 (3) |
| C5—H5···Cg1ii | 0.95 | 3.08 | 3.873 | 142 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1/2, −y+3/2, −z+1; (ii) x−1/2, −y+1/2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: GK2601).
References
- Agilent (2013). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Amlaiky, N., Leclerc, G., Decker, N. & Schwartz, J. (1983). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 18, 437–439.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Moore, F. J. & Huntress, E. H. (1927). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 49, 2618–, 2624.
- Ni, S., Yuan, Y., Huang, J., Mao, X., Lu, M., Zhu, J., Shen, X., Pei, J., Lai, L., Jiang, H. & Li, J. (2009). J. Med. Chem. 52, 5295–5298. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rad, M. N. S., Behrouz, S., Karimitabar, F. & Khalafi-Nezhad, A. (2012). Helv. Chim. Acta, 95, 491–501.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002669/gk2601sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002669/gk2601Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002669/gk2601Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: http://scripts.iucr.org/cgi-bin/cr.cgi?rm=csd&csdid=985317
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report