Abstract
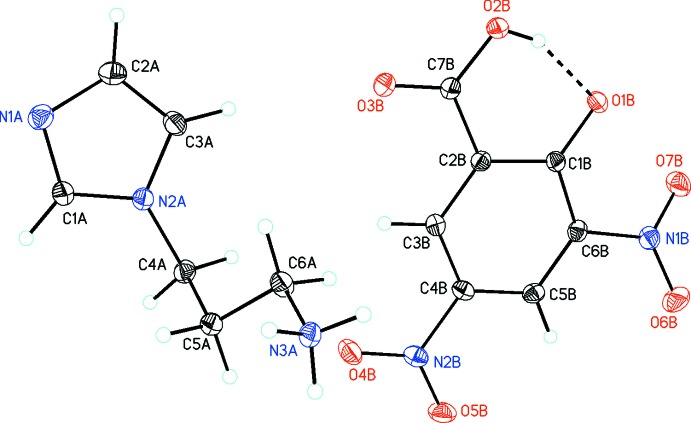
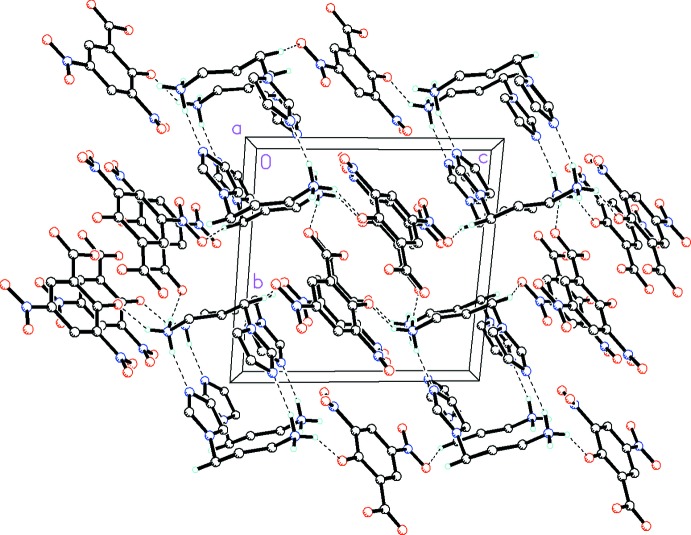
In the title salt, C6H12N3 +·C7H3N2O7 −, the imidazole ring is planar, with a maximum deviation of 0.0013 (14) Å for the N attached to the propanaminium group. In the anion, a single intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bond is observed. The mean planes of the nitro groups in the anion are twisted from the benzene ring mean plane making dihedral angles of 24.7 (9) and 3.9 (6)°. In the crystal, the ammonium H atoms form N—H⋯N and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, resulting in an infinite chain along [111]. In addition to the classical hydrogen bonds, weak C—H⋯O and π–π [centroid–centroid distance = 3.7124 (9) Å] interactions are also observed, which lead to the formation a three-dimensional supramolecular structure that links the chains into layers along the bc plane.
Related literature
For general background and the pharmacological properties of imidazole compounds, see: ten Have et al. (1997 ▶); Lombardino & Wiseman (1974 ▶); Jackson et al. (2000 ▶); Krezel (1998 ▶); Maier et al. (1989 ▶). For the related structures of substituted imidazoles, see: Dayananda et al. (2012 ▶); Hemamalini & Fun (2010 ▶); Jasinski et al. (2011 ▶); Wei et al. (2012 ▶); Yamuna et al. (2013 ▶).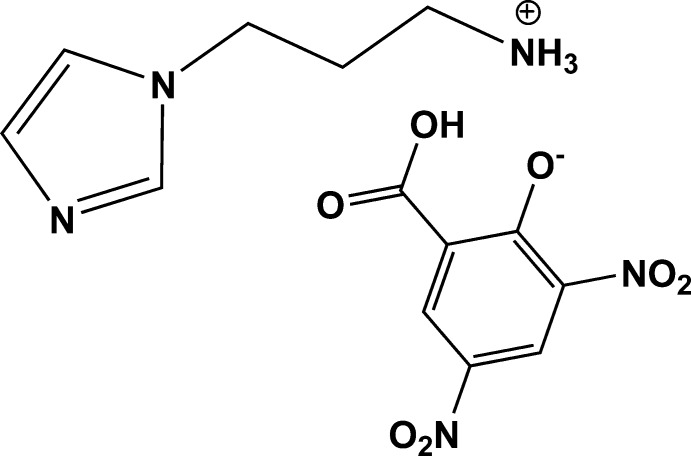
Experimental
Crystal data
C6H12N3 +·C7H3N2O7 −
M r = 353.30
Triclinic,
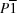
a = 7.0109 (4) Å
b = 10.6617 (8) Å
c = 10.7454 (7) Å
α = 93.075 (6)°
β = 95.863 (5)°
γ = 104.944 (6)°
V = 769.30 (9) Å3
Z = 2
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 1.09 mm−1
T = 173 K
0.22 × 0.14 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Agilent Xcalibur (Eos, Gemini) diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO and CrysAlis RED; Agilent, 2012 ▶) T min = 0.925, T max = 1.000
4664 measured reflections
2953 independent reflections
2582 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.026
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.042
wR(F 2) = 0.122
S = 1.04
2953 reflections
229 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.25 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2012 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis RED (Agilent, 2012 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SUPERFLIP (Palatinus & Chapuis, 2007 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2012 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: OLEX2.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814003146/fj2659sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814003146/fj2659Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814003146/fj2659Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 986378
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2B—H2B⋯O1B | 0.84 | 1.66 | 2.4484 (15) | 155 |
| N3A—H3AA⋯N1A i | 0.91 | 1.92 | 2.7987 (19) | 162 |
| N3A—H3AB⋯O1B ii | 0.91 | 2.03 | 2.8153 (17) | 144 |
| N3A—H3AC⋯O3B iii | 0.91 | 2.07 | 2.9546 (17) | 165 |
| C4A—H4AB⋯O4B iv | 0.99 | 2.53 | 3.3572 (19) | 142 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 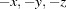 ; (ii)
; (ii) 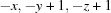 ; (iii)
; (iii) 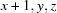 ; (iv)
; (iv) 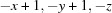 .
.
Acknowledgments
TSY thanks the University of Mysore for research facilities and is also grateful to the Principal, Maharani’s Science College for Women, Mysore, for giving permission to undertake research. JPJ acknowledges the NSF–MRI program (grant No. CHE-1039027) for funds to purchase the X-ray diffractometer.
supplementary crystallographic information
1. Comment
Imidazole rings appear frequently in biologically active compounds, both natural and man-made (ten Have et al., 1997). Compounds with an imidazole ring system have many pharmacological properties and play important roles in biochemical processes (Lombardino & Wiseman, 1974). Most of the imidazole compounds are known as inhibitors of fungicides and herbicides, plant growth regulators and therapeutic agents (Maier et al., 1989), anticancer agents (Krezel, 1998) and bactericidal effects (Jackson et al., 2000). The crystal structures of some related compounds, viz ; 2-amino-5-methylpyridinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (Hemamalini et al., 2010); Cinnarizinium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (Dayananda et al., 2012); Enrofloxacinium picrate (Jasinski et al., 2011); 3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propanaminium picrate (Yamuna et al., 2013); 3,5-dimethylpyrazolium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (Wei et al., 2012), have been reported. In view of the importance of substituted imidazoles and organic acid–base adducts based on hydrogen bonding and receiving great attention in recent years, this paper reports the crystal structure of the title salt, (I), C6H12N3+.C7H3N2O7-.
The title salt, (I), C6H12N3+.C7H3N2O7-, crystallizes with one independent monocation (A) and monoanion (B) in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 1). In the cation the protonated imidazol-1-ium ring is planar (maximum deviation = 0.0013 (14)Å for N2A). In the anion, a single O—H···O intramolecular hydrogen bond is observed. Bond lengths are in normal ranges. The mean planes of the nitro groups in the anion are twisted from the phenyl ring mean plane with maximun angles of 24.7 (9)° and 3.9 (6)°, respectively. The hydrogen atoms on the terminal N atom of the cation form N—H···N and N—H···O intermolecular hydrogen bonds resulting in an infinite 1D chain along [1 1 1]. In the crystal, in addition to the classical hydrogen bonds, weak C—H···O (Table 1) and Cg1—Cg2 π—π intermolecular interactions are observed with an intercentroid distance of 3.7125 (9)Å (symmetry operation -x,1-y,-z; Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C1B–C6B and N1A/C1A/N2A/C3A/C2A rings) which contribute to crystal packing stability (Fig. 2).
2. Experimental
Commercially available 1-(3-aminopropyl)imidazole (0.5 g, 3.99 mmol) and 3,5 dinitrosalicylic acid (0.909 g, 3.99 mmol) were dissolved in 10 ml of methanol and stirred for 15 minutes at 308 K. X-ray quality crystals were formed on slow evaporation of methanol. (m.p.: 468- 475K).
3. Refinement
All of the H atoms were placed in their calculated positions and then refined using the riding model with Atom—H lengths of 0.95Å (CH); 0.99Å (CH2); 0.84Å (OH) or 0.91Å (NH3) . Isotropic displacement parameters for these atoms were set to 1.2 (CH, CH2, NH3) or 1.5 (OH) times Ueq of the parent atom. Idealised ammonium and tetrahedral OH were refined as rotating groups.
Figures
Fig. 1.
ORTEP drawing of (I) ( C6H12N3+.C7H3N2O7-) showing the labeling scheme with 30% probability displacement ellipsoids. Dashed lines indicate a O2B—H2B···O1B intramolecular hydrogen bond in the anion within the asymmetric unit.
Fig. 2.
Molecular packing for (I) viewed along the a axis. Dashed lines indicate N—H···O, N—H···N intermolecular hydrogen bonds and weak C—H···O intermolecular interactions. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been removed for clarity.
Crystal data
| C6H12N3+·C7H3N2O7− | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 353.30 | F(000) = 368 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.525 Mg m−3 |
| a = 7.0109 (4) Å | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| b = 10.6617 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 2218 reflections |
| c = 10.7454 (7) Å | θ = 4.2–72.3° |
| α = 93.075 (6)° | µ = 1.09 mm−1 |
| β = 95.863 (5)° | T = 173 K |
| γ = 104.944 (6)° | Irregular, yellow |
| V = 769.30 (9) Å3 | 0.22 × 0.14 × 0.12 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur (Eos, Gemini) diffractometer | 2953 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Cu) X-ray Source | 2582 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.026 |
| Detector resolution: 16.0416 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 72.5°, θmin = 4.2° |
| ω scans | h = −8→5 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO and CrysAlis RED; Agilent, 2012) | k = −12→13 |
| Tmin = 0.925, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −13→13 |
| 4664 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0682P)2 + 0.1101P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.122 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.04 | Δρmax = 0.25 e Å−3 |
| 2953 reflections | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
| 229 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL2012 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.0087 (12) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1B | −0.19166 (16) | 0.67530 (11) | 0.52669 (10) | 0.0288 (3) | |
| O2B | −0.38294 (16) | 0.47146 (11) | 0.40815 (11) | 0.0309 (3) | |
| H2B | −0.3493 | 0.5402 | 0.4563 | 0.046* | |
| O3B | −0.25490 (16) | 0.37708 (11) | 0.26154 (11) | 0.0308 (3) | |
| O4B | 0.41267 (18) | 0.58644 (12) | 0.16868 (12) | 0.0360 (3) | |
| O5B | 0.59770 (17) | 0.75622 (12) | 0.28233 (13) | 0.0378 (3) | |
| O6B | 0.34447 (19) | 0.93705 (13) | 0.62652 (14) | 0.0466 (4) | |
| O7B | 0.02866 (19) | 0.91669 (12) | 0.61489 (13) | 0.0407 (3) | |
| N1B | 0.1720 (2) | 0.88464 (13) | 0.58134 (13) | 0.0293 (3) | |
| N2B | 0.43937 (19) | 0.67328 (13) | 0.25380 (13) | 0.0277 (3) | |
| C1B | −0.0459 (2) | 0.68012 (14) | 0.46271 (13) | 0.0220 (3) | |
| C2B | −0.0571 (2) | 0.57869 (14) | 0.36592 (13) | 0.0216 (3) | |
| C3B | 0.0986 (2) | 0.57928 (14) | 0.29803 (13) | 0.0224 (3) | |
| H3B | 0.0860 | 0.5126 | 0.2331 | 0.027* | |
| C4B | 0.2742 (2) | 0.67709 (15) | 0.32417 (14) | 0.0235 (3) | |
| C5B | 0.2969 (2) | 0.77675 (14) | 0.41652 (14) | 0.0242 (3) | |
| H5B | 0.4187 | 0.8428 | 0.4339 | 0.029* | |
| C6B | 0.1396 (2) | 0.77858 (15) | 0.48287 (14) | 0.0240 (3) | |
| C7B | −0.2410 (2) | 0.46764 (15) | 0.34003 (14) | 0.0240 (3) | |
| N1A | −0.2236 (2) | 0.05132 (13) | −0.17302 (13) | 0.0301 (3) | |
| N2A | −0.01482 (18) | 0.22563 (12) | −0.06974 (12) | 0.0236 (3) | |
| N3A | 0.34673 (18) | 0.20535 (12) | 0.28180 (12) | 0.0247 (3) | |
| H3AA | 0.3273 | 0.1193 | 0.2584 | 0.030* | |
| H3AB | 0.3097 | 0.2146 | 0.3598 | 0.030* | |
| H3AC | 0.4776 | 0.2474 | 0.2829 | 0.030* | |
| C1A | −0.0393 (2) | 0.12597 (15) | −0.15759 (15) | 0.0267 (3) | |
| H1A | 0.0635 | 0.1112 | −0.2029 | 0.032* | |
| C2A | −0.3211 (2) | 0.10673 (16) | −0.08994 (16) | 0.0311 (4) | |
| H2A | −0.4575 | 0.0745 | −0.0793 | 0.037* | |
| C3A | −0.1954 (2) | 0.21366 (16) | −0.02562 (15) | 0.0290 (4) | |
| H3A | −0.2257 | 0.2692 | 0.0372 | 0.035* | |
| C4A | 0.1721 (2) | 0.32486 (15) | −0.02842 (14) | 0.0265 (3) | |
| H4AA | 0.1419 | 0.4032 | 0.0094 | 0.032* | |
| H4AB | 0.2423 | 0.3502 | −0.1023 | 0.032* | |
| C5A | 0.3076 (2) | 0.27761 (16) | 0.06655 (14) | 0.0270 (3) | |
| H5AA | 0.3236 | 0.1929 | 0.0335 | 0.032* | |
| H5AB | 0.4405 | 0.3407 | 0.0792 | 0.032* | |
| C6A | 0.2253 (2) | 0.26209 (16) | 0.19094 (14) | 0.0276 (3) | |
| H6AA | 0.2200 | 0.3483 | 0.2271 | 0.033* | |
| H6AB | 0.0877 | 0.2051 | 0.1769 | 0.033* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1B | 0.0263 (6) | 0.0300 (6) | 0.0273 (6) | 0.0012 (5) | 0.0097 (4) | −0.0047 (4) |
| O2B | 0.0247 (6) | 0.0304 (6) | 0.0321 (6) | −0.0027 (4) | 0.0082 (5) | −0.0070 (5) |
| O3B | 0.0276 (6) | 0.0282 (6) | 0.0318 (6) | 0.0003 (5) | 0.0045 (5) | −0.0081 (5) |
| O4B | 0.0360 (6) | 0.0319 (6) | 0.0414 (7) | 0.0081 (5) | 0.0168 (5) | −0.0040 (5) |
| O5B | 0.0229 (6) | 0.0376 (7) | 0.0501 (8) | 0.0011 (5) | 0.0111 (5) | 0.0012 (6) |
| O6B | 0.0351 (7) | 0.0402 (8) | 0.0540 (8) | −0.0004 (6) | −0.0049 (6) | −0.0192 (6) |
| O7B | 0.0393 (7) | 0.0324 (7) | 0.0472 (8) | 0.0026 (5) | 0.0160 (6) | −0.0121 (6) |
| N1B | 0.0319 (7) | 0.0233 (7) | 0.0293 (7) | 0.0012 (5) | 0.0057 (6) | −0.0025 (5) |
| N2B | 0.0253 (7) | 0.0258 (7) | 0.0339 (7) | 0.0072 (5) | 0.0088 (5) | 0.0060 (5) |
| C1B | 0.0230 (7) | 0.0232 (7) | 0.0194 (7) | 0.0049 (6) | 0.0033 (5) | 0.0023 (6) |
| C2B | 0.0215 (7) | 0.0215 (7) | 0.0207 (7) | 0.0035 (6) | 0.0021 (5) | 0.0028 (6) |
| C3B | 0.0255 (7) | 0.0216 (7) | 0.0210 (7) | 0.0072 (6) | 0.0043 (6) | 0.0016 (5) |
| C4B | 0.0220 (7) | 0.0248 (7) | 0.0258 (7) | 0.0076 (6) | 0.0066 (6) | 0.0059 (6) |
| C5B | 0.0215 (7) | 0.0221 (7) | 0.0268 (7) | 0.0017 (6) | 0.0023 (6) | 0.0051 (6) |
| C6B | 0.0270 (8) | 0.0208 (7) | 0.0226 (7) | 0.0041 (6) | 0.0017 (6) | 0.0002 (6) |
| C7B | 0.0240 (7) | 0.0253 (7) | 0.0213 (7) | 0.0047 (6) | 0.0016 (5) | 0.0001 (6) |
| N1A | 0.0291 (7) | 0.0246 (7) | 0.0347 (7) | 0.0050 (5) | 0.0016 (6) | −0.0005 (6) |
| N2A | 0.0241 (6) | 0.0230 (6) | 0.0229 (6) | 0.0049 (5) | 0.0032 (5) | 0.0002 (5) |
| N3A | 0.0258 (6) | 0.0224 (6) | 0.0241 (6) | 0.0041 (5) | 0.0025 (5) | −0.0028 (5) |
| C1A | 0.0273 (8) | 0.0256 (8) | 0.0277 (8) | 0.0078 (6) | 0.0050 (6) | −0.0019 (6) |
| C2A | 0.0262 (8) | 0.0311 (8) | 0.0354 (9) | 0.0045 (6) | 0.0070 (6) | 0.0059 (7) |
| C3A | 0.0293 (8) | 0.0308 (8) | 0.0286 (8) | 0.0093 (6) | 0.0093 (6) | 0.0013 (6) |
| C4A | 0.0268 (8) | 0.0245 (7) | 0.0248 (7) | 0.0007 (6) | 0.0048 (6) | −0.0001 (6) |
| C5A | 0.0237 (7) | 0.0293 (8) | 0.0258 (8) | 0.0029 (6) | 0.0054 (6) | −0.0020 (6) |
| C6A | 0.0301 (8) | 0.0301 (8) | 0.0256 (8) | 0.0124 (6) | 0.0060 (6) | 0.0017 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1B—C1B | 1.2803 (18) | N1A—C2A | 1.375 (2) |
| O2B—H2B | 0.8400 | N2A—C1A | 1.3472 (19) |
| O2B—C7B | 1.3019 (18) | N2A—C3A | 1.3748 (19) |
| O3B—C7B | 1.2249 (18) | N2A—C4A | 1.4660 (19) |
| O4B—N2B | 1.2303 (18) | N3A—H3AA | 0.9100 |
| O5B—N2B | 1.2261 (18) | N3A—H3AB | 0.9100 |
| O6B—N1B | 1.2300 (18) | N3A—H3AC | 0.9100 |
| O7B—N1B | 1.2224 (18) | N3A—C6A | 1.4844 (19) |
| N1B—C6B | 1.4629 (19) | C1A—H1A | 0.9500 |
| N2B—C4B | 1.4540 (18) | C2A—H2A | 0.9500 |
| C1B—C2B | 1.441 (2) | C2A—C3A | 1.352 (2) |
| C1B—C6B | 1.433 (2) | C3A—H3A | 0.9500 |
| C2B—C3B | 1.373 (2) | C4A—H4AA | 0.9900 |
| C2B—C7B | 1.498 (2) | C4A—H4AB | 0.9900 |
| C3B—H3B | 0.9500 | C4A—C5A | 1.517 (2) |
| C3B—C4B | 1.385 (2) | C5A—H5AA | 0.9900 |
| C4B—C5B | 1.381 (2) | C5A—H5AB | 0.9900 |
| C5B—H5B | 0.9500 | C5A—C6A | 1.510 (2) |
| C5B—C6B | 1.377 (2) | C6A—H6AA | 0.9900 |
| N1A—C1A | 1.320 (2) | C6A—H6AB | 0.9900 |
| C7B—O2B—H2B | 109.5 | H3AA—N3A—H3AC | 109.5 |
| O6B—N1B—C6B | 117.54 (13) | H3AB—N3A—H3AC | 109.5 |
| O7B—N1B—O6B | 123.30 (14) | C6A—N3A—H3AA | 109.5 |
| O7B—N1B—C6B | 119.17 (13) | C6A—N3A—H3AB | 109.5 |
| O4B—N2B—C4B | 118.05 (13) | C6A—N3A—H3AC | 109.5 |
| O5B—N2B—O4B | 123.43 (13) | N1A—C1A—N2A | 111.69 (13) |
| O5B—N2B—C4B | 118.52 (13) | N1A—C1A—H1A | 124.2 |
| O1B—C1B—C2B | 120.31 (13) | N2A—C1A—H1A | 124.2 |
| O1B—C1B—C6B | 124.78 (14) | N1A—C2A—H2A | 124.8 |
| C6B—C1B—C2B | 114.84 (13) | C3A—C2A—N1A | 110.33 (14) |
| C1B—C2B—C7B | 119.59 (13) | C3A—C2A—H2A | 124.8 |
| C3B—C2B—C1B | 121.69 (14) | N2A—C3A—H3A | 127.0 |
| C3B—C2B—C7B | 118.70 (13) | C2A—C3A—N2A | 105.94 (14) |
| C2B—C3B—H3B | 120.0 | C2A—C3A—H3A | 127.0 |
| C2B—C3B—C4B | 120.03 (14) | N2A—C4A—H4AA | 109.1 |
| C4B—C3B—H3B | 120.0 | N2A—C4A—H4AB | 109.1 |
| C3B—C4B—N2B | 119.02 (13) | N2A—C4A—C5A | 112.48 (12) |
| C5B—C4B—N2B | 119.37 (13) | H4AA—C4A—H4AB | 107.8 |
| C5B—C4B—C3B | 121.60 (13) | C5A—C4A—H4AA | 109.1 |
| C4B—C5B—H5B | 120.7 | C5A—C4A—H4AB | 109.1 |
| C6B—C5B—C4B | 118.69 (14) | C4A—C5A—H5AA | 109.3 |
| C6B—C5B—H5B | 120.7 | C4A—C5A—H5AB | 109.3 |
| C1B—C6B—N1B | 120.14 (13) | H5AA—C5A—H5AB | 108.0 |
| C5B—C6B—N1B | 116.69 (13) | C6A—C5A—C4A | 111.50 (12) |
| C5B—C6B—C1B | 123.12 (14) | C6A—C5A—H5AA | 109.3 |
| O2B—C7B—C2B | 116.03 (13) | C6A—C5A—H5AB | 109.3 |
| O3B—C7B—O2B | 121.99 (14) | N3A—C6A—C5A | 112.37 (12) |
| O3B—C7B—C2B | 121.96 (13) | N3A—C6A—H6AA | 109.1 |
| C1A—N1A—C2A | 105.07 (13) | N3A—C6A—H6AB | 109.1 |
| C1A—N2A—C3A | 106.97 (13) | C5A—C6A—H6AA | 109.1 |
| C1A—N2A—C4A | 125.58 (13) | C5A—C6A—H6AB | 109.1 |
| C3A—N2A—C4A | 127.43 (13) | H6AA—C6A—H6AB | 107.9 |
| H3AA—N3A—H3AB | 109.5 | ||
| O1B—C1B—C2B—C3B | −178.23 (13) | C3B—C2B—C7B—O2B | 179.26 (13) |
| O1B—C1B—C2B—C7B | 0.3 (2) | C3B—C2B—C7B—O3B | 1.0 (2) |
| O1B—C1B—C6B—N1B | −0.9 (2) | C3B—C4B—C5B—C6B | −0.6 (2) |
| O1B—C1B—C6B—C5B | 176.43 (14) | C4B—C5B—C6B—N1B | 178.87 (13) |
| O4B—N2B—C4B—C3B | 3.8 (2) | C4B—C5B—C6B—C1B | 1.5 (2) |
| O4B—N2B—C4B—C5B | −177.14 (13) | C6B—C1B—C2B—C3B | −0.9 (2) |
| O5B—N2B—C4B—C3B | −176.02 (14) | C6B—C1B—C2B—C7B | 177.58 (12) |
| O5B—N2B—C4B—C5B | 3.0 (2) | C7B—C2B—C3B—C4B | −176.73 (13) |
| O6B—N1B—C6B—C1B | 154.04 (15) | N1A—C2A—C3A—N2A | 0.13 (18) |
| O6B—N1B—C6B—C5B | −23.4 (2) | N2A—C4A—C5A—C6A | −69.71 (16) |
| O7B—N1B—C6B—C1B | −25.8 (2) | C1A—N1A—C2A—C3A | 0.02 (18) |
| O7B—N1B—C6B—C5B | 156.73 (14) | C1A—N2A—C3A—C2A | −0.23 (17) |
| N2B—C4B—C5B—C6B | −179.60 (13) | C1A—N2A—C4A—C5A | −80.85 (18) |
| C1B—C2B—C3B—C4B | 1.8 (2) | C2A—N1A—C1A—N2A | −0.17 (18) |
| C1B—C2B—C7B—O2B | 0.7 (2) | C3A—N2A—C1A—N1A | 0.26 (18) |
| C1B—C2B—C7B—O3B | −177.60 (13) | C3A—N2A—C4A—C5A | 97.42 (17) |
| C2B—C1B—C6B—N1B | −178.03 (12) | C4A—N2A—C1A—N1A | 178.83 (13) |
| C2B—C1B—C6B—C5B | −0.7 (2) | C4A—N2A—C3A—C2A | −178.77 (14) |
| C2B—C3B—C4B—N2B | 177.99 (13) | C4A—C5A—C6A—N3A | 175.16 (12) |
| C2B—C3B—C4B—C5B | −1.0 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2B—H2B···O1B | 0.84 | 1.66 | 2.4484 (15) | 155 |
| N3A—H3AA···N1Ai | 0.91 | 1.92 | 2.7987 (19) | 162 |
| N3A—H3AB···O1Bii | 0.91 | 2.03 | 2.8153 (17) | 144 |
| N3A—H3AC···O3Biii | 0.91 | 2.07 | 2.9546 (17) | 165 |
| C4A—H4AB···O4Biv | 0.99 | 2.53 | 3.3572 (19) | 142 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y, −z; (ii) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) x+1, y, z; (iv) −x+1, −y+1, −z.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FJ2659).
References
- Agilent (2012). CrysAlis PRO and CrysAlis RED Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Dayananda, A. S., Yathirajan, H. S., Gerber, T., Hosten, E. & Betz, R. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o1165–o1166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Have, R. ten, Huisman, M., Meetsma, A. & van Leusen, A. M. (1997). Tetrahedron, 53, 11355–11368.
- Hemamalini, M. & Fun, H.-K. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o1194–o1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C. J., Lamb, D. C., Kelly, D. E. & Kelly, S. L. (2000). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 192, 159–162. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Jasinski, J. P., Butcher, R. J., Siddegowda, M. S., Yathirajan, H. S. & Siddaraju, B. P. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o432–o433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Krezel, I. (1998). Il Farmaco, 53, 342–345. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lombardino, J. G. & Wiseman, E. H. (1974). J. Med. Chem. 17, 1182–1188. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Maier, T., Schmierer, R., Bauer, K., Bieringer, H., Buerstell, H. & Sachse, B. (1989). US Patent No. 4 820 335.
- Palatinus, L. & Chapuis, G. (2007). J. Appl. Cryst. 40, 786–790.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wei, S., Jin, S., Hu, Z., Zhou, Y. & Zhou, Y. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o3117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Yamuna, T. S., Jasinski, J. P., Duff, C. E., Yathirajan, H. S. & Kaur, M. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o1572–o1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814003146/fj2659sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814003146/fj2659Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814003146/fj2659Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 986378
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report