Abstract
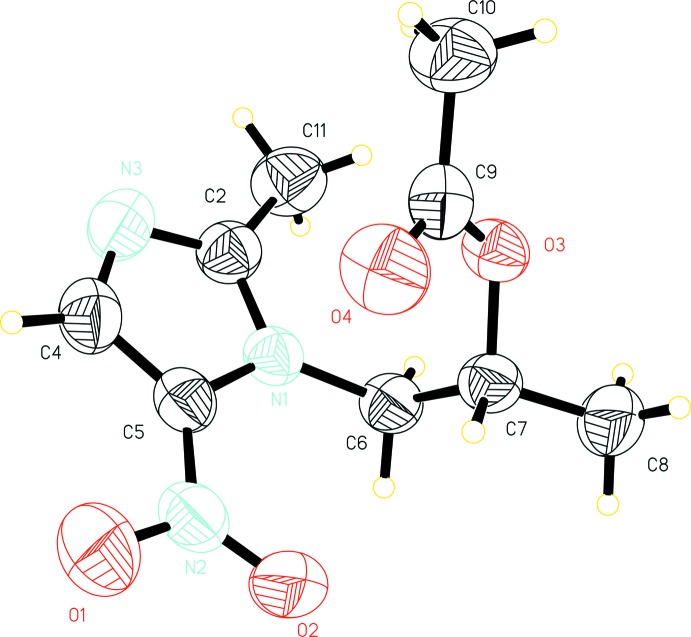
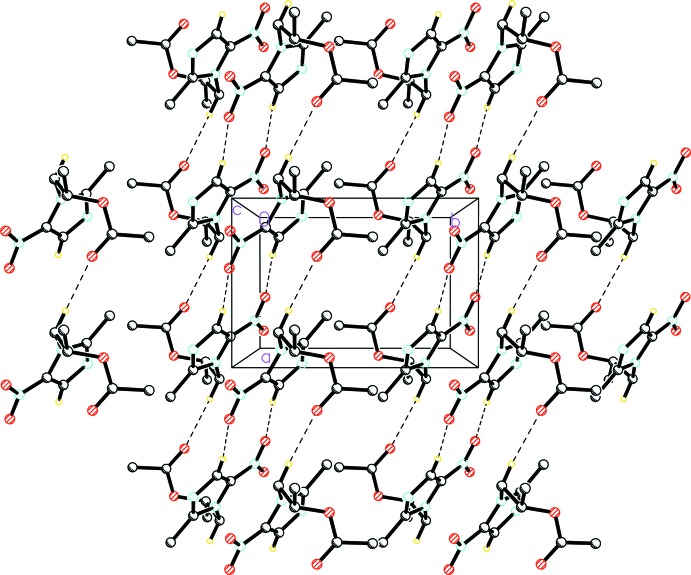
In the title compound, C9H13N3O4, an ester of the anti-infection drug secnidazole, the dihedral angle between the nitroimidazole mean plane (r.m.s. deviation = 0.028 Å) and the pendant acetate group is 43.17 (11)°. In the crystal, inversion dimers linked by pairs of C—H⋯O interactions generate R 2 2(10) loops and further C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the dimers into [100] chains. Weak aromatic π–π stacking interactions with a centroid–centroid distance of 3.7623 (11) Å are also observed.
Related literature
For background to the antibacterial properties of nitroimidazole and secnidazole-like compounds, see: Mital (2009 ▶); Edwards (1993 ▶); Crozet et al. (2009 ▶). For the crystal structures of related compounds, see: Yousuf et al. (2013 ▶); Tao et al. (2008 ▶);Zeb et al. (2012 ▶). 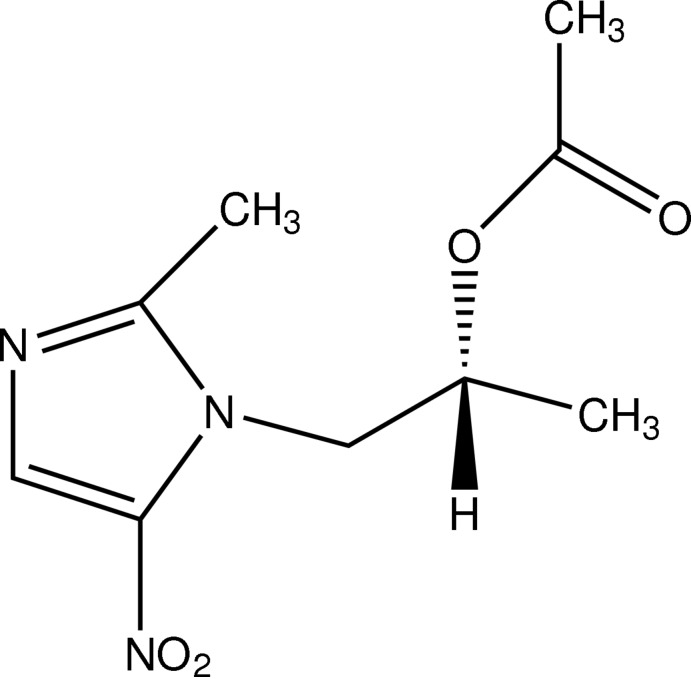
Experimental
Crystal data
C9H13N3O4
M r = 227.22
Monoclinic,
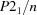
a = 6.1771 (5) Å
b = 8.9928 (7) Å
c = 20.3736 (16) Å
β = 90.978 (2)°
V = 1131.58 (16) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.11 mm−1
T = 273 K
0.45 × 0.27 × 0.06 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2000 ▶) T min = 0.954, T max = 0.994
6541 measured reflections
2042 independent reflections
1567 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.025
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.043
wR(F 2) = 0.119
S = 1.02
2042 reflections
145 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.12 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2000 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2000 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL, PARST (Nardelli, 1995 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002505/hb7195sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002505/hb7195Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002505/hb7195Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: http://scripts.iucr.org/cgi-bin/cr.cgi?rm=csd&csdid=984872
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4—H4A⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.45 | 3.369 (2) | 168 |
| C6—H6A⋯O4ii | 0.97 | 2.53 | 3.460 (2) | 161 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 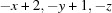 ; (ii)
; (ii) 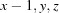 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Nabiqasim Pharmaceutical Industries (Pvt) Ltd for financial support during the research work.
supplementary crystallographic information
1. Comment
The title compound (I) is an ester derivative of well known 5-nitroimidazole drug i.e secnidazole. The worthwhile use of nitroimidazole derivatives is in the treatment of diseases caused by protozoa and anaerobic bacteria (Mital, 2009). Members of nitroimidazole drugs are pronounced in thier wide-range activities and in addition during their use the rate of resistance in anaerobes is still very low (Edwards, 1993). Antiprotozoal and bactericidal properties of nitroimidazoles are associated with their aromatic nitro group. The Secnidazole like chemotherapeutic agents inhibit the growth of both anaerobic bacteria and some anaerobic protozoa (Crozet et al. 2009).
The structure of the title compound (I) is similar to our previously reported compound 1-(2-Methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetone with the difference that acetone moiety is replaced by propyl acetate group (C6—C10/O3,O4)(Yousuf et al. 2013);. It also exhibits bond lengths and angles that are of normal range (Yousuf et al. 2013); A three dimensional consolidated architecture is formed by the non-covalent interactions of molecules in the crystal via C4– H4A···O1 [2.45 Å], and C6– H6A···O4 [2.53 Å] hydrogen bonding with R22(10) ring motifs. Possible weak pi-pi interactions (Cg1···Cg1) with minimum centroid-centroid distance of 3.7623 (11) Å are also observed.
2. Experimental
The title compound was synthesized by adding acetic anhydride (1.2 ml, 12.70 mmol)to a hot (70 °C) stired solution of secnidazole (2 g m, 10.8 mmol) in pyridine (2 ml) and toluene (10 ml). The reaction mixture was further processed to refluxed for 5 hrs, cooled, treated with water and then organic phase was evaporated to obtain solid product which was recrystallized from chloroform and toluene solution to yield greenish plates in 81% yield. Melting point 346–348 K. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 8.006 (s, 1 H, imidazole H), 5.162–5.089 (m, 1 H, CH), 4.573–4.322 (m, 2 H, CH2), 3.300 (s, 3 H, CH3), 1.856 (s, 3 H CH3), 1.265–1.244 (d, J=6.3 Hz, 3 H, CH3). 13C NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 169.35 (C=O), 151.52 (N=C), 138.40 (C—NO2), 133.01 (N—CH), 68.64 (O—CH), 49.31 (N—CH2), 20.44 (CH3), 17.11 (CH3), 13.93 (CH3). IR (neat, cm-1): 3434, 3122, 2994, 1732, 1532, 1368, 1140, 1080.
3. Refinement
The hydrogen atoms are positioned at their calculated positions geometrically with C—H = 0.9300 Å, 0.9600 Å, 0.9700 Å, 0.9800 Å for aromatic, methyl, methylen, and methin H respectively. These are constrained to ride on their parent atoms during subsequent refinement with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for methyl, and Uiso(H) = 1.5eq(C) for rest of the H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Fig:1 The molecular structure of title compound I, showing displacement ellipsoids drawn at 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Fig: 2 Crystal packing diagram, showing intermolecular hydrogen bonding as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C9H13N3O4 | F(000) = 480 |
| Mr = 227.22 | Dx = 1.334 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.1771 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 1751 reflections |
| b = 8.9928 (7) Å | θ = 2.5–22.3° |
| c = 20.3736 (16) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| β = 90.978 (2)° | T = 273 K |
| V = 1131.58 (16) Å3 | Plate, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.45 × 0.27 × 0.06 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 2042 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1567 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.025 |
| ω scan | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 2.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2000) | h = −7→7 |
| Tmin = 0.954, Tmax = 0.994 | k = −10→10 |
| 6541 measured reflections | l = −23→24 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.119 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0605P)2 + 0.1628P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2042 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 145 parameters | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.12 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.9023 (2) | 0.57210 (19) | 0.08857 (8) | 0.0881 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.6626 (3) | 0.55701 (17) | 0.16347 (8) | 0.0834 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.48247 (17) | 0.11443 (13) | 0.18968 (6) | 0.0498 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.8273 (2) | 0.17014 (17) | 0.16857 (8) | 0.0744 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.7361 (3) | 0.51890 (17) | 0.11093 (9) | 0.0604 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.5484 (3) | 0.2475 (2) | −0.00606 (8) | 0.0658 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.4442 (2) | 0.33433 (15) | 0.09081 (7) | 0.0476 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.6300 (3) | 0.40876 (19) | 0.07274 (9) | 0.0497 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.6890 (3) | 0.3540 (2) | 0.01383 (10) | 0.0599 (5) | |
| H4A | 0.8088 | 0.3851 | −0.0095 | 0.072* | |
| C2 | 0.4036 (3) | 0.2373 (2) | 0.04109 (10) | 0.0552 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.2199 (3) | 0.1309 (3) | 0.03950 (12) | 0.0744 (6) | |
| H11A | 0.2237 | 0.0738 | −0.0003 | 0.112* | |
| H11B | 0.0859 | 0.1848 | 0.0412 | 0.112* | |
| H11C | 0.2312 | 0.0654 | 0.0766 | 0.112* | |
| C6 | 0.3239 (3) | 0.3431 (2) | 0.15215 (9) | 0.0517 (5) | |
| H6A | 0.1826 | 0.2979 | 0.1455 | 0.062* | |
| H6B | 0.3018 | 0.4468 | 0.1633 | 0.062* | |
| C7 | 0.4387 (3) | 0.26641 (19) | 0.20886 (9) | 0.0489 (5) | |
| H7A | 0.5748 | 0.3178 | 0.2193 | 0.059* | |
| C8 | 0.2980 (4) | 0.2624 (2) | 0.26847 (10) | 0.0674 (6) | |
| H8A | 0.3741 | 0.2134 | 0.3038 | 0.101* | |
| H8B | 0.1670 | 0.2092 | 0.2583 | 0.101* | |
| H8C | 0.2633 | 0.3622 | 0.2814 | 0.101* | |
| C9 | 0.6837 (3) | 0.0809 (2) | 0.17030 (9) | 0.0514 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.7003 (3) | −0.0780 (2) | 0.15128 (12) | 0.0731 (6) | |
| H10A | 0.8452 | −0.0989 | 0.1377 | 0.110* | |
| H10B | 0.6007 | −0.0982 | 0.1157 | 0.110* | |
| H10C | 0.6658 | −0.1395 | 0.1882 | 0.110* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0725 (10) | 0.0951 (12) | 0.0972 (12) | −0.0330 (9) | 0.0186 (9) | −0.0015 (10) |
| O2 | 0.1073 (12) | 0.0620 (9) | 0.0817 (11) | −0.0251 (8) | 0.0283 (10) | −0.0176 (8) |
| O3 | 0.0430 (6) | 0.0450 (7) | 0.0615 (8) | −0.0013 (5) | 0.0057 (6) | 0.0015 (6) |
| O4 | 0.0452 (7) | 0.0801 (10) | 0.0982 (12) | −0.0049 (7) | 0.0122 (7) | 0.0021 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0624 (10) | 0.0496 (9) | 0.0693 (12) | −0.0064 (8) | 0.0080 (9) | 0.0057 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0700 (11) | 0.0718 (11) | 0.0558 (11) | 0.0022 (9) | 0.0071 (9) | −0.0034 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0473 (8) | 0.0420 (7) | 0.0536 (9) | 0.0043 (6) | 0.0056 (7) | 0.0033 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0488 (9) | 0.0452 (10) | 0.0551 (12) | 0.0015 (8) | 0.0040 (9) | 0.0065 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0565 (11) | 0.0639 (12) | 0.0595 (13) | 0.0037 (10) | 0.0109 (10) | 0.0096 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0551 (11) | 0.0536 (11) | 0.0570 (12) | 0.0043 (8) | 0.0002 (9) | −0.0004 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0676 (13) | 0.0759 (14) | 0.0794 (16) | −0.0104 (11) | −0.0022 (12) | −0.0129 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0461 (9) | 0.0476 (10) | 0.0618 (12) | 0.0042 (8) | 0.0119 (9) | −0.0012 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0482 (9) | 0.0444 (9) | 0.0544 (11) | −0.0031 (8) | 0.0073 (8) | −0.0037 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0717 (13) | 0.0701 (13) | 0.0609 (13) | −0.0068 (10) | 0.0190 (11) | −0.0045 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0445 (9) | 0.0612 (11) | 0.0486 (11) | 0.0040 (9) | 0.0015 (8) | 0.0070 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0706 (13) | 0.0668 (13) | 0.0820 (16) | 0.0185 (11) | 0.0043 (12) | −0.0038 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—N2 | 1.2276 (19) | C11—H11B | 0.9600 |
| O2—N2 | 1.219 (2) | C11—H11C | 0.9600 |
| O3—C9 | 1.3447 (19) | C6—C7 | 1.512 (3) |
| O3—C7 | 1.448 (2) | C6—H6A | 0.9700 |
| O4—C9 | 1.197 (2) | C6—H6B | 0.9700 |
| N2—C5 | 1.414 (2) | C7—C8 | 1.506 (2) |
| N3—C2 | 1.327 (2) | C7—H7A | 0.9800 |
| N3—C4 | 1.351 (3) | C8—H8A | 0.9600 |
| N1—C2 | 1.357 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.9600 |
| N1—C5 | 1.384 (2) | C8—H8C | 0.9600 |
| N1—C6 | 1.467 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.485 (3) |
| C5—C4 | 1.353 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| C2—C11 | 1.484 (3) | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| C11—H11A | 0.9600 | ||
| C9—O3—C7 | 117.93 (13) | C7—C6—H6A | 109.0 |
| O2—N2—O1 | 122.85 (18) | N1—C6—H6B | 109.0 |
| O2—N2—C5 | 120.29 (15) | C7—C6—H6B | 109.0 |
| O1—N2—C5 | 116.86 (17) | H6A—C6—H6B | 107.8 |
| C2—N3—C4 | 105.66 (17) | O3—C7—C8 | 107.95 (14) |
| C2—N1—C5 | 104.86 (14) | O3—C7—C6 | 108.15 (14) |
| C2—N1—C6 | 125.45 (14) | C8—C7—C6 | 110.95 (15) |
| C5—N1—C6 | 129.44 (15) | O3—C7—H7A | 109.9 |
| C4—C5—N1 | 107.28 (17) | C8—C7—H7A | 109.9 |
| C4—C5—N2 | 127.87 (17) | C6—C7—H7A | 109.9 |
| N1—C5—N2 | 124.84 (16) | C7—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| N3—C4—C5 | 110.04 (17) | C7—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| N3—C4—H4A | 125.0 | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 125.0 | C7—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| N3—C2—N1 | 112.15 (17) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| N3—C2—C11 | 123.62 (19) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—C11 | 124.23 (17) | O4—C9—O3 | 123.20 (17) |
| C2—C11—H11A | 109.5 | O4—C9—C10 | 125.65 (18) |
| C2—C11—H11B | 109.5 | O3—C9—C10 | 111.14 (16) |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 | C9—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C2—C11—H11C | 109.5 | C9—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 | C9—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| N1—C6—C7 | 112.86 (13) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| N1—C6—H6A | 109.0 | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C2—N1—C5—C4 | 0.4 (2) | C5—N1—C2—N3 | −0.6 (2) |
| C6—N1—C5—C4 | 174.87 (16) | C6—N1—C2—N3 | −175.27 (16) |
| C2—N1—C5—N2 | −178.36 (17) | C5—N1—C2—C11 | 179.00 (18) |
| C6—N1—C5—N2 | −3.9 (3) | C6—N1—C2—C11 | 4.3 (3) |
| O2—N2—C5—C4 | 179.99 (19) | C2—N1—C6—C7 | 100.0 (2) |
| O1—N2—C5—C4 | −0.1 (3) | C5—N1—C6—C7 | −73.4 (2) |
| O2—N2—C5—N1 | −1.5 (3) | C9—O3—C7—C8 | −139.19 (17) |
| O1—N2—C5—N1 | 178.41 (17) | C9—O3—C7—C6 | 100.71 (17) |
| C2—N3—C4—C5 | −0.1 (2) | N1—C6—C7—O3 | −55.09 (18) |
| N1—C5—C4—N3 | −0.2 (2) | N1—C6—C7—C8 | −173.30 (14) |
| N2—C5—C4—N3 | 178.55 (18) | C7—O3—C9—O4 | 0.4 (3) |
| C4—N3—C2—N1 | 0.4 (2) | C7—O3—C9—C10 | −178.99 (16) |
| C4—N3—C2—C11 | −179.12 (19) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4—H4A···O1i | 0.93 | 2.45 | 3.369 (2) | 168 |
| C6—H6A···O4ii | 0.97 | 2.53 | 3.460 (2) | 161 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z; (ii) x−1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB7195).
References
- Bruker (2000). SADABS, SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Crozet, M. D., Botta, C., Gasquet, M., Curti, C., Rémusat, V., Hutter, S., Chapelle, O., Azas, N., De Méo, M. & Vanelle, P. (2009). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44, 653–659. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Edwards, D. I. (1993). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 31, 9–20. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mital, A. (2009). Sci. Pharm. 77, 497–520.
- Nardelli, M. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst. 28, 659.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tao, X., Yuan, L., Zhang, X.-Q. & Wang, J.-T. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Yousuf, S., Khan, K. M., Naz, F., Perveen, S. & Miana, G. A. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zeb, A., Yousuf, S. & Basha, F. Z. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002505/hb7195sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002505/hb7195Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002505/hb7195Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: http://scripts.iucr.org/cgi-bin/cr.cgi?rm=csd&csdid=984872
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report