Abstract
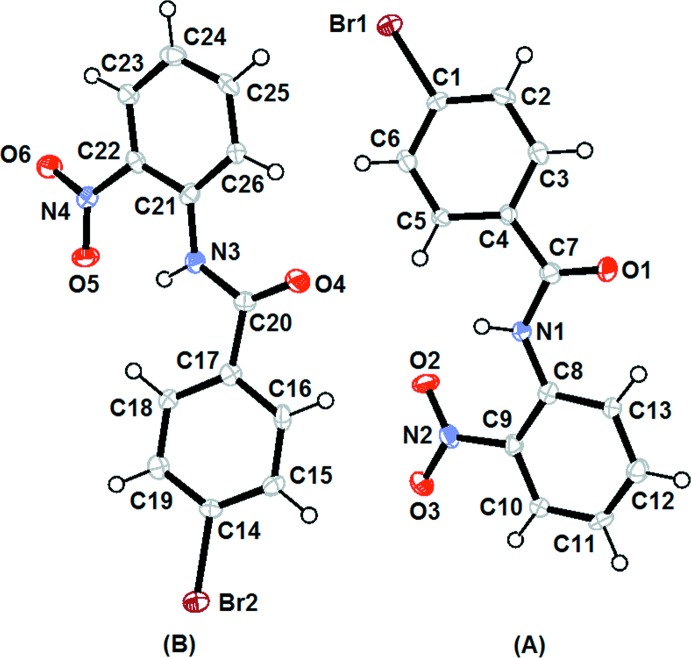
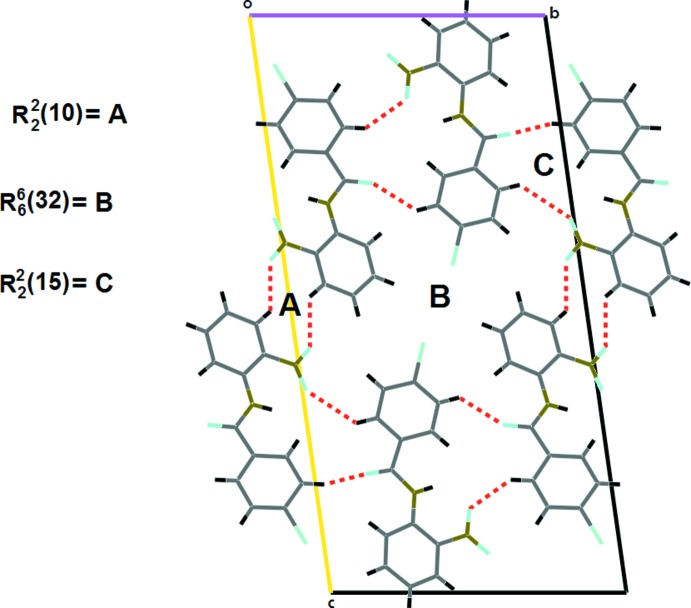
The title nitrophenyl benzamide, C13H9BrN2O3, with two molecules in the asymmetric unit, has dihedral angles of 16.78 (15) and 18.87 (14)° between the benzene rings. An intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond is observed in each molecule. In the crystal, the molecules are linked by weak C—H⋯O interactions; halogen–halogen interactions are also observed [Br⋯Br = 3.4976 (7) Å]. These interactions form R 2 2(10), R 2 2(15) and R 6 6(32) edge-fused rings along [010].
Related literature
For properties of amide compounds, see: Bisson et al. (2000 ▶). For the antibacterial and antifungal activity of amide compounds, see: Aytemir et al. (2003 ▶). For similar compounds, see: Moreno-Fuquen et al. (2013 ▶); Sripet et al. (2012 ▶). For halogen–halogen interactions, see: Awwadi et al. (2006 ▶); For hydrogen-bonding information, see: Nardelli (1995 ▶). For hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Etter (1990 ▶).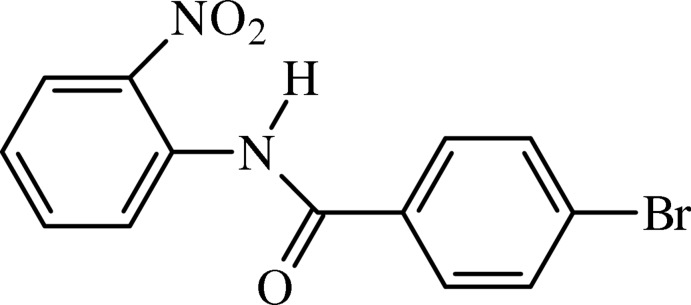
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H9BrN2O3
M r = 321.13
Triclinic,
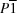
a = 3.8338 (4) Å
b = 12.6784 (13) Å
c = 24.918 (2) Å
α = 81.875 (8)°
β = 88.386 (7)°
γ = 85.460 (8)°
V = 1195.1 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 3.45 mm−1
T = 123 K
0.49 × 0.05 × 0.03 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur E diffractometer
Absorption correction: analytical [CrysAlis PRO (Oxford Diffraction, 2010 ▶; analytical numeric absorption correction using a multi-faceted crystal model (Clark & Reid, 1995 ▶)] T min = 0.380, T max = 0.914
9979 measured reflections
9979 independent reflections
7814 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.049
wR(F 2) = 0.135
S = 1.04
9979 reflections
344 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.62 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.77 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Oxford Diffraction, 2010 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 2012 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814003298/gg2134sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814003298/gg2134Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814003298/gg2134Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: http://scripts.iucr.org/cgi-bin/cr.cgi?rm=csd&csdid=986704
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6—H6⋯O4i | 0.95 | 2.65 | 3.378 (5) | 134 |
| C16—H16⋯O2ii | 0.95 | 2.64 | 3.349 (5) | 132 |
| C19—H19⋯O1iii | 0.95 | 2.52 | 3.262 (5) | 135 |
| C3—H3⋯O5iv | 0.95 | 2.58 | 3.299 (5) | 133 |
| C23—H23⋯O6v | 0.95 | 2.56 | 3.334 (5) | 139 |
| N1—H1N⋯O2 | 0.88 | 1.92 | 2.615 (5) | 134 |
| N3—H3N⋯O5 | 0.88 | 1.92 | 2.628 (5) | 136 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 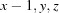 ; (ii)
; (ii) 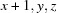 ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv) 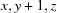 ; (v)
; (v) 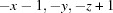 .
.
Acknowledgments
RMF thanks the Universidad del Valle, Colombia, for partial financial support.
supplementary crystallographic information
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Synthesis and crystallization
The reagents and solvents for the synthesis were obtained from the Aldrich Chemical Co., and were used without additional purification. The title molecule was synthesized using equimolar quantities of 4-bromobenzoyl chloride (0.328 g., 1.495 mmol) and 2-nitroaniline (0.206 g). The reagents were dissolved in 10 mL of acetonitrile and the solution was taken to reflux in constant stirring for 1 hour. Yellow crystals of good quality were obtained after leaving the solvent to evaporate. Yellow crystals of good quality were obtained with m.p of 423 (1)K.
2.2. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 1. All H-atoms were positioned at geometrically idealized positions with C—H distance of 0.95 Å and N—H distance of 0.88 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2 times Ueq of the atoms to which they were bonded.
3. Results and discussion
The present compound forms part of a systematic work on N-aromatic amides. The formation of oligomers with properties of molecular zippers have been obtained using molecular templates which include amido ligands (Bisson et al., 2000). Antibacterial and antifungal activities of different carboxyamide derivatives have been reported (Aytemir et al., 2003). In the synthesis of amides in our group, the 2-nitroaniline is taken as a template, in order to study the structural changes and the supramolecular behavior by the reaction of different ligands with this precursor (Moreno-Fuquen et al., 2013). In the reactions involving the 2-nitroaniline, as precursor, we aimed to synthesize the N-(2-nitrophenyl)-4-bromobenzamide (I). A close structure, the 4-bromo-N-(4-methoxy-2-nitrophenyl)-benzamide, (4MNB), (Sripet et al., 2012), has been used as comparison with the structural parameters of the title compound. The title compound has two molecules (A and B) per asymmetric unit (see Fig. 1). The compound exhibits dihedral angles between the benzene rings, very similar: 16.78 (15)° and 18.87 (14)° for A and B molecules, respectively. These dihedral angles are somewhat different when compared with the related compound (4MNB) [2.90 (8)°]. In (I) the other bond lengths and bond angles agree closely with those values presented in its homologous amide (4MNB). The nitro groups form dihedral angles with the adjacent benzene ring of 6.7 (2)° and 9.9 (2)° for O2—N2—O3 and O5—N4—O6, respectively. The crystal packing shows no classical intermolecular hydrogen bonds and the molecules pack by forming weak C—H···O interactions that are propagated along [010] (see Fig. 2). According to the graph-set assignment, the intramolecular hydrogen-bond pattern generates a S(6) ring motif (Etter, 1990). The crystal packing is stabilized by weak C—H···O intermolecular interactions. The C6 and C3 atoms of the phenyl ring at (x,y,z) act as hydrogen-bond donors to carbonyl O4 atom at (x-1, +y, +z) and to nitro O5 atom at (x,+y+1,+z) respectively. The C16 and C19 atoms of the phenyl ring at (x, y, z) act as hydrogen-bond donors to nitro O2 atom at (x+1, y, z) and to carbonyl O1 atom at (x,y-1,z), respectively. Additionally the C23 atom at (x,y,z) acts as a hydrogen-bond donor to nitro O6 atom at (-x-1, -y, -z+1), (see Table 1; Nardelli, 1995). All these interactions form R22(10), R22(15) and R66(32) edge-fused rings along the [010] direction (see Fig. 2). Recent theoretical calculations show that halogen···halogen interactions are controlled by electrostatic forces and they display directional character (Awwadi et al., 2006). In the title structure, halogen···halogen interactions [Br···Br = 3.4976 (7) Å] within the chains stabilized by C—H···O interactions are observed. This Br···Br distance is much shorter than the sum of the van der Waals radii (3.70 Å).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular conformation and atom numbering scheme for the title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are shown as spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
Part of the crystal structure of (I), showing the formation of edge-fused R22(10), R22(15) and R22(32) rings running along [010].
Crystal data
| C13H9BrN2O3 | Z = 4 |
| Mr = 321.13 | F(000) = 640 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.785 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Melting point: 423(1) K |
| a = 3.8338 (4) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 12.6784 (13) Å | Cell parameters from 4010 reflections |
| c = 24.918 (2) Å | θ = 3.1–28.0° |
| α = 81.875 (8)° | µ = 3.45 mm−1 |
| β = 88.386 (7)° | T = 123 K |
| γ = 85.460 (8)° | Needle, yellow |
| V = 1195.1 (2) Å3 | 0.49 × 0.05 × 0.03 mm |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur E diffractometer | 9979 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 7814 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.000 |
| ω scans | θmax = 27.0°, θmin = 3.2° |
| Absorption correction: analytical [CrysAlis PRO (Oxford Diffraction, 2010; analytical numeric absorption correction using a multi-faceted crystal model (Clark & Reid, 1995)] | h = −4→4 |
| Tmin = 0.380, Tmax = 0.914 | k = −14→16 |
| 9979 measured reflections | l = −31→31 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.049 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.135 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0479P)2 + 3.1562P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 9979 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 344 parameters | Δρmax = 0.62 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −0.77 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | −0.49930 (10) | 0.56740 (4) | 0.433729 (18) | 0.02208 (13) | |
| Br2 | 0.96920 (10) | 0.05996 (4) | 0.084392 (18) | 0.02296 (13) | |
| O1 | 0.2537 (8) | 0.8253 (2) | 0.20551 (12) | 0.0270 (7) | |
| O2 | −0.0265 (8) | 0.4919 (3) | 0.14483 (13) | 0.0334 (8) | |
| O3 | 0.1224 (9) | 0.4476 (3) | 0.06706 (14) | 0.0384 (9) | |
| O4 | 0.4069 (8) | 0.3367 (3) | 0.29067 (13) | 0.0313 (8) | |
| O5 | −0.0468 (8) | −0.0126 (2) | 0.35060 (13) | 0.0312 (8) | |
| O6 | −0.3517 (8) | −0.0460 (2) | 0.42413 (13) | 0.0285 (8) | |
| N1 | 0.1677 (9) | 0.6691 (3) | 0.17304 (14) | 0.0202 (8) | |
| H1N | 0.0934 | 0.6052 | 0.1830 | 0.024* | |
| N2 | 0.1123 (9) | 0.5117 (3) | 0.09994 (16) | 0.0229 (9) | |
| N3 | 0.2077 (8) | 0.1750 (3) | 0.32592 (14) | 0.0197 (8) | |
| H3N | 0.1732 | 0.1120 | 0.3170 | 0.024* | |
| N4 | −0.1642 (9) | 0.0120 (3) | 0.39439 (15) | 0.0209 (8) | |
| C1 | −0.3041 (10) | 0.6174 (3) | 0.36484 (17) | 0.0168 (9) | |
| C2 | −0.2476 (11) | 0.7244 (3) | 0.35235 (18) | 0.0214 (10) | |
| H2 | −0.3098 | 0.7727 | 0.3775 | 0.026* | |
| C3 | −0.0988 (10) | 0.7599 (4) | 0.30253 (18) | 0.0215 (10) | |
| H3 | −0.0561 | 0.8331 | 0.2937 | 0.026* | |
| C4 | −0.0101 (10) | 0.6895 (3) | 0.26489 (17) | 0.0158 (9) | |
| C5 | −0.0678 (10) | 0.5813 (3) | 0.27900 (17) | 0.0180 (9) | |
| H5 | −0.0041 | 0.5321 | 0.2543 | 0.022* | |
| C6 | −0.2171 (10) | 0.5459 (3) | 0.32875 (17) | 0.0201 (10) | |
| H6 | −0.2598 | 0.4728 | 0.3381 | 0.024* | |
| C7 | 0.1510 (10) | 0.7357 (3) | 0.21253 (18) | 0.0194 (10) | |
| C8 | 0.2861 (10) | 0.6897 (3) | 0.11986 (17) | 0.0173 (9) | |
| C9 | 0.2622 (10) | 0.6145 (3) | 0.08342 (18) | 0.0186 (9) | |
| C10 | 0.3722 (10) | 0.6340 (3) | 0.02913 (17) | 0.0194 (10) | |
| H10 | 0.3486 | 0.5824 | 0.0056 | 0.023* | |
| C11 | 0.5139 (10) | 0.7282 (3) | 0.01035 (18) | 0.0212 (10) | |
| H11 | 0.5915 | 0.7424 | −0.0263 | 0.025* | |
| C12 | 0.5432 (10) | 0.8028 (4) | 0.04532 (18) | 0.0228 (10) | |
| H12 | 0.6411 | 0.8682 | 0.0321 | 0.027* | |
| C13 | 0.4345 (10) | 0.7847 (3) | 0.09874 (18) | 0.0193 (10) | |
| H13 | 0.4604 | 0.8375 | 0.1216 | 0.023* | |
| C14 | 0.7748 (10) | 0.1158 (3) | 0.14657 (17) | 0.0177 (9) | |
| C15 | 0.7605 (10) | 0.2246 (3) | 0.14817 (18) | 0.0200 (10) | |
| H15 | 0.8432 | 0.2718 | 0.1183 | 0.024* | |
| C16 | 0.6236 (10) | 0.2633 (3) | 0.19396 (18) | 0.0213 (10) | |
| H16 | 0.6128 | 0.3378 | 0.1957 | 0.026* | |
| C17 | 0.5013 (10) | 0.1945 (3) | 0.23763 (17) | 0.0184 (10) | |
| C18 | 0.5160 (10) | 0.0848 (3) | 0.23493 (18) | 0.0193 (10) | |
| H18 | 0.4291 | 0.0375 | 0.2644 | 0.023* | |
| C19 | 0.6571 (10) | 0.0450 (4) | 0.18936 (18) | 0.0202 (10) | |
| H19 | 0.6726 | −0.0296 | 0.1875 | 0.024* | |
| C20 | 0.3678 (11) | 0.2434 (4) | 0.28646 (18) | 0.0194 (10) | |
| C21 | 0.0933 (10) | 0.1912 (3) | 0.37755 (17) | 0.0180 (9) | |
| C22 | −0.0783 (10) | 0.1120 (3) | 0.41268 (18) | 0.0187 (10) | |
| C23 | −0.1763 (10) | 0.1250 (3) | 0.46513 (18) | 0.0204 (10) | |
| H23 | −0.2880 | 0.0701 | 0.4875 | 0.024* | |
| C24 | −0.1133 (11) | 0.2167 (4) | 0.48520 (18) | 0.0233 (10) | |
| H24 | −0.1778 | 0.2254 | 0.5215 | 0.028* | |
| C25 | 0.0461 (10) | 0.2968 (3) | 0.45179 (18) | 0.0198 (10) | |
| H25 | 0.0882 | 0.3608 | 0.4654 | 0.024* | |
| C26 | 0.1440 (10) | 0.2850 (3) | 0.39935 (18) | 0.0197 (10) | |
| H26 | 0.2486 | 0.3418 | 0.3773 | 0.024* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.0215 (2) | 0.0273 (3) | 0.0174 (3) | −0.00393 (18) | 0.00245 (17) | −0.00226 (19) |
| Br2 | 0.0207 (2) | 0.0277 (3) | 0.0208 (3) | −0.00279 (18) | 0.00324 (17) | −0.0047 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0428 (19) | 0.0170 (18) | 0.0223 (19) | −0.0113 (14) | 0.0046 (15) | −0.0028 (14) |
| O2 | 0.052 (2) | 0.031 (2) | 0.020 (2) | −0.0187 (16) | 0.0162 (16) | −0.0100 (15) |
| O3 | 0.067 (2) | 0.020 (2) | 0.032 (2) | −0.0136 (17) | 0.0130 (18) | −0.0141 (16) |
| O4 | 0.047 (2) | 0.021 (2) | 0.028 (2) | −0.0090 (15) | 0.0118 (15) | −0.0079 (15) |
| O5 | 0.049 (2) | 0.027 (2) | 0.020 (2) | −0.0157 (15) | 0.0125 (15) | −0.0091 (15) |
| O6 | 0.0359 (18) | 0.0234 (19) | 0.028 (2) | −0.0123 (14) | 0.0114 (15) | −0.0056 (15) |
| N1 | 0.029 (2) | 0.014 (2) | 0.018 (2) | −0.0049 (15) | 0.0032 (16) | −0.0033 (15) |
| N2 | 0.029 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.024 (2) | −0.0024 (16) | −0.0005 (17) | −0.0049 (17) |
| N3 | 0.0251 (19) | 0.014 (2) | 0.020 (2) | −0.0045 (15) | 0.0007 (15) | −0.0029 (16) |
| N4 | 0.0220 (19) | 0.021 (2) | 0.019 (2) | −0.0017 (15) | −0.0012 (16) | 0.0000 (17) |
| C1 | 0.014 (2) | 0.022 (3) | 0.014 (2) | −0.0017 (17) | 0.0008 (16) | −0.0008 (18) |
| C2 | 0.024 (2) | 0.023 (3) | 0.019 (3) | −0.0006 (19) | 0.0036 (18) | −0.010 (2) |
| C3 | 0.025 (2) | 0.017 (2) | 0.024 (3) | −0.0035 (18) | −0.0004 (19) | −0.0044 (19) |
| C4 | 0.018 (2) | 0.013 (2) | 0.016 (2) | −0.0002 (16) | −0.0023 (17) | −0.0016 (17) |
| C5 | 0.024 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.016 (2) | −0.0044 (17) | 0.0020 (18) | −0.0056 (18) |
| C6 | 0.022 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.022 (3) | −0.0012 (17) | −0.0036 (18) | −0.0041 (19) |
| C7 | 0.019 (2) | 0.019 (3) | 0.019 (3) | 0.0025 (18) | −0.0001 (17) | −0.0024 (19) |
| C8 | 0.013 (2) | 0.019 (2) | 0.019 (3) | −0.0009 (16) | −0.0022 (17) | −0.0006 (18) |
| C9 | 0.020 (2) | 0.015 (2) | 0.021 (3) | −0.0043 (17) | 0.0003 (18) | −0.0019 (18) |
| C10 | 0.022 (2) | 0.017 (2) | 0.019 (3) | −0.0009 (17) | 0.0042 (18) | −0.0031 (18) |
| C11 | 0.021 (2) | 0.029 (3) | 0.012 (2) | −0.0021 (18) | 0.0040 (17) | 0.0013 (19) |
| C12 | 0.021 (2) | 0.022 (3) | 0.025 (3) | −0.0058 (18) | 0.0020 (19) | −0.001 (2) |
| C13 | 0.023 (2) | 0.015 (2) | 0.019 (3) | −0.0040 (17) | 0.0042 (18) | −0.0027 (18) |
| C14 | 0.015 (2) | 0.021 (3) | 0.017 (2) | −0.0007 (17) | 0.0004 (17) | −0.0050 (18) |
| C15 | 0.019 (2) | 0.023 (3) | 0.017 (3) | −0.0059 (18) | 0.0026 (18) | −0.0010 (19) |
| C16 | 0.021 (2) | 0.012 (2) | 0.029 (3) | −0.0024 (17) | −0.0003 (19) | 0.0019 (19) |
| C17 | 0.016 (2) | 0.020 (3) | 0.020 (3) | −0.0047 (17) | −0.0015 (17) | −0.0037 (19) |
| C18 | 0.021 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.018 (3) | −0.0022 (17) | 0.0030 (18) | −0.0002 (19) |
| C19 | 0.018 (2) | 0.019 (3) | 0.024 (3) | −0.0033 (17) | −0.0022 (18) | −0.0030 (19) |
| C20 | 0.022 (2) | 0.020 (3) | 0.017 (3) | −0.0017 (18) | −0.0008 (18) | −0.0041 (19) |
| C21 | 0.015 (2) | 0.020 (3) | 0.018 (2) | 0.0002 (17) | −0.0015 (17) | 0.0011 (18) |
| C22 | 0.016 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.025 (3) | 0.0016 (16) | −0.0027 (18) | −0.0042 (19) |
| C23 | 0.022 (2) | 0.019 (3) | 0.020 (3) | 0.0008 (18) | 0.0001 (18) | −0.0035 (19) |
| C24 | 0.021 (2) | 0.030 (3) | 0.018 (3) | 0.0067 (19) | −0.0013 (18) | −0.006 (2) |
| C25 | 0.020 (2) | 0.017 (2) | 0.024 (3) | 0.0017 (17) | −0.0022 (18) | −0.0094 (19) |
| C26 | 0.024 (2) | 0.015 (2) | 0.020 (3) | −0.0010 (17) | 0.0020 (18) | −0.0014 (18) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br1—C1 | 1.898 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.400 (6) |
| Br2—C14 | 1.902 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.368 (6) |
| O1—C7 | 1.219 (5) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| O2—N2 | 1.227 (5) | C11—C12 | 1.386 (6) |
| O3—N2 | 1.230 (5) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| O4—C20 | 1.223 (5) | C12—C13 | 1.377 (6) |
| O5—N4 | 1.239 (5) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| O6—N4 | 1.227 (4) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C7 | 1.382 (5) | C14—C15 | 1.383 (6) |
| N1—C8 | 1.385 (5) | C14—C19 | 1.383 (6) |
| N1—H1N | 0.8800 | C15—C16 | 1.378 (6) |
| N2—C9 | 1.467 (5) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C20 | 1.380 (5) | C16—C17 | 1.390 (6) |
| N3—C21 | 1.385 (5) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| N3—H3N | 0.8800 | C17—C18 | 1.399 (6) |
| N4—C22 | 1.470 (5) | C17—C20 | 1.502 (6) |
| C1—C6 | 1.381 (6) | C18—C19 | 1.386 (6) |
| C1—C2 | 1.382 (6) | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.383 (6) | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C21—C26 | 1.404 (6) |
| C3—C4 | 1.401 (6) | C21—C22 | 1.425 (6) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C22—C23 | 1.378 (6) |
| C4—C5 | 1.400 (6) | C23—C24 | 1.370 (6) |
| C4—C7 | 1.491 (6) | C23—H23 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.382 (6) | C24—C25 | 1.388 (6) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C24—H24 | 0.9500 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C25—C26 | 1.374 (6) |
| C8—C13 | 1.402 (6) | C25—H25 | 0.9500 |
| C8—C9 | 1.415 (6) | C26—H26 | 0.9500 |
| C7—N1—C8 | 128.5 (4) | C13—C12—C11 | 121.9 (4) |
| C7—N1—H1N | 115.8 | C13—C12—H12 | 119.1 |
| C8—N1—H1N | 115.8 | C11—C12—H12 | 119.1 |
| O2—N2—O3 | 121.3 (4) | C12—C13—C8 | 120.9 (4) |
| O2—N2—C9 | 120.5 (4) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.5 |
| O3—N2—C9 | 118.1 (4) | C8—C13—H13 | 119.5 |
| C20—N3—C21 | 129.4 (4) | C15—C14—C19 | 122.1 (4) |
| C20—N3—H3N | 115.3 | C15—C14—Br2 | 119.6 (3) |
| C21—N3—H3N | 115.3 | C19—C14—Br2 | 118.3 (3) |
| O6—N4—O5 | 121.7 (4) | C16—C15—C14 | 118.6 (4) |
| O6—N4—C22 | 117.7 (4) | C16—C15—H15 | 120.7 |
| O5—N4—C22 | 120.6 (4) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.7 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 121.5 (4) | C15—C16—C17 | 120.8 (4) |
| C6—C1—Br1 | 119.4 (3) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.6 |
| C2—C1—Br1 | 119.0 (3) | C17—C16—H16 | 119.6 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 118.7 (4) | C16—C17—C18 | 119.5 (4) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.6 | C16—C17—C20 | 117.1 (4) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.6 | C18—C17—C20 | 123.4 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.0 (4) | C19—C18—C17 | 120.1 (4) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.5 | C19—C18—H18 | 120.0 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.5 | C17—C18—H18 | 120.0 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.8 (4) | C14—C19—C18 | 118.8 (4) |
| C5—C4—C7 | 124.4 (4) | C14—C19—H19 | 120.6 |
| C3—C4—C7 | 116.7 (4) | C18—C19—H19 | 120.6 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.1 (4) | O4—C20—N3 | 123.4 (4) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.9 | O4—C20—C17 | 121.5 (4) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.9 | N3—C20—C17 | 115.1 (4) |
| C1—C6—C5 | 119.7 (4) | N3—C21—C26 | 122.7 (4) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.1 | N3—C21—C22 | 121.8 (4) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.1 | C26—C21—C22 | 115.4 (4) |
| O1—C7—N1 | 123.6 (4) | C23—C22—C21 | 122.3 (4) |
| O1—C7—C4 | 122.3 (4) | C23—C22—N4 | 116.4 (4) |
| N1—C7—C4 | 114.2 (4) | C21—C22—N4 | 121.4 (4) |
| N1—C8—C13 | 122.8 (4) | C24—C23—C22 | 120.3 (4) |
| N1—C8—C9 | 121.2 (4) | C24—C23—H23 | 119.8 |
| C13—C8—C9 | 116.0 (4) | C22—C23—H23 | 119.8 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 122.5 (4) | C23—C24—C25 | 119.1 (4) |
| C10—C9—N2 | 115.5 (4) | C23—C24—H24 | 120.4 |
| C8—C9—N2 | 122.0 (4) | C25—C24—H24 | 120.4 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 119.3 (4) | C26—C25—C24 | 121.2 (4) |
| C11—C10—H10 | 120.4 | C26—C25—H25 | 119.4 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 120.4 | C24—C25—H25 | 119.4 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 119.4 (4) | C25—C26—C21 | 121.7 (4) |
| C10—C11—H11 | 120.3 | C25—C26—H26 | 119.2 |
| C12—C11—H11 | 120.3 | C21—C26—H26 | 119.2 |
| O2—O2—N2—O3 | 0.0 (3) | N1—C8—C13—C12 | −178.8 (3) |
| O2—O2—N2—C9 | 0.0 (4) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 1.0 (5) |
| O5—O5—N4—O6 | 0.0 (12) | C19—C14—C15—C16 | −0.1 (6) |
| O5—O5—N4—C22 | 0.0 (13) | Br2—C14—C15—C16 | −179.0 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.3 (6) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −0.2 (6) |
| Br1—C1—C2—C3 | 178.7 (3) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | −0.3 (6) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.8 (6) | C15—C16—C17—C20 | 178.0 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.4 (6) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 1.1 (6) |
| C2—C3—C4—C7 | −179.6 (3) | C20—C17—C18—C19 | −177.1 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.5 (6) | C15—C14—C19—C18 | 0.9 (6) |
| C7—C4—C5—C6 | 179.6 (3) | Br2—C14—C19—C18 | 179.8 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.4 (6) | C17—C18—C19—C14 | −1.4 (5) |
| Br1—C1—C6—C5 | −178.6 (3) | C21—N3—C20—O4 | −6.5 (6) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −1.0 (6) | C21—N3—C20—C17 | 172.1 (3) |
| C8—N1—C7—O1 | −2.2 (6) | C16—C17—C20—O4 | −9.4 (6) |
| C8—N1—C7—C4 | 176.8 (3) | C18—C17—C20—O4 | 168.8 (4) |
| C5—C4—C7—O1 | −166.6 (4) | C16—C17—C20—N3 | 172.0 (3) |
| C3—C4—C7—O1 | 11.5 (6) | C18—C17—C20—N3 | −9.8 (5) |
| C5—C4—C7—N1 | 14.3 (5) | C20—N3—C21—C26 | −3.4 (6) |
| C3—C4—C7—N1 | −167.5 (3) | C20—N3—C21—C22 | 178.0 (4) |
| C7—N1—C8—C13 | 4.4 (6) | N3—C21—C22—C23 | 176.4 (3) |
| C7—N1—C8—C9 | −175.5 (4) | C26—C21—C22—C23 | −2.3 (5) |
| N1—C8—C9—C10 | 178.5 (3) | N3—C21—C22—N4 | −4.3 (5) |
| C13—C8—C9—C10 | −1.4 (6) | C26—C21—C22—N4 | 177.0 (3) |
| N1—C8—C9—N2 | −0.1 (6) | O6—N4—C22—C23 | 8.7 (5) |
| C13—C8—C9—N2 | −179.9 (3) | O5—N4—C22—C23 | −170.6 (3) |
| O2—N2—C9—C10 | −172.0 (4) | O5—N4—C22—C23 | −170.6 (3) |
| O2—N2—C9—C10 | −172.0 (4) | O6—N4—C22—C21 | −170.6 (3) |
| O3—N2—C9—C10 | 6.2 (5) | O5—N4—C22—C21 | 10.1 (5) |
| O2—N2—C9—C8 | 6.7 (6) | O5—N4—C22—C21 | 10.1 (5) |
| O2—N2—C9—C8 | 6.7 (6) | C21—C22—C23—C24 | 0.7 (6) |
| O3—N2—C9—C8 | −175.1 (4) | N4—C22—C23—C24 | −178.6 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 1.1 (6) | C22—C23—C24—C25 | 0.8 (6) |
| N2—C9—C10—C11 | 179.8 (3) | C23—C24—C25—C26 | −0.6 (6) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.5 (6) | C24—C25—C26—C21 | −1.1 (6) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.2 (6) | N3—C21—C26—C25 | −176.2 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13—C8 | −0.5 (6) | C22—C21—C26—C25 | 2.5 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C6—H6···O4i | 0.95 | 2.65 | 3.378 (5) | 134 |
| C16—H16···O2ii | 0.95 | 2.64 | 3.349 (5) | 132 |
| C19—H19···O1iii | 0.95 | 2.52 | 3.262 (5) | 135 |
| C3—H3···O5iv | 0.95 | 2.58 | 3.299 (5) | 133 |
| C23—H23···O6v | 0.95 | 2.56 | 3.334 (5) | 139 |
| N1—H1N···O2 | 0.88 | 1.92 | 2.615 (5) | 134 |
| N3—H3N···O5 | 0.88 | 1.92 | 2.628 (5) | 136 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y, z; (ii) x+1, y, z; (iii) x, y−1, z; (iv) x, y+1, z; (v) −x−1, −y, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: GG2134).
References
- Awwadi, F. F., Willett, R. D., Peterson, K. A. & Twamley, B. (2006). Chem. Eur. J. 12, 8952–8960. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Aytemir, M. D., Hider, R. C., Erol, D. D., Ozalp, M. & Ekizoglu, M. (2003). Turk. J. Chem. 27, 445–452.
- Bisson, A. P., Carver, F. J., Eggleston, D. S., Haltiwanger, R. C., Hunter, C. A., Livingstone, D. L., McCabe, J. F., Rotger, C. & Rowan, A. E. (2000). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 8856–8868.
- Clark, R. C. & Reid, J. S. (1995). Acta Cryst. A51, 887–897.
- Etter, M. (1990). Acc. Chem. Res. 23, 120–126.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Moreno-Fuquen, R., Azcárate, A., Kennedy, A. R., Gilmour, D. & De Almeida Santos, R. H. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o1592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, M. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst. 28, 659.
- Oxford Diffraction (2010). CrysAlis PRO Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sripet, W., Chantrapromma, S., Ruanwas, P. & Fun, H.-K. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814003298/gg2134sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814003298/gg2134Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814003298/gg2134Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: http://scripts.iucr.org/cgi-bin/cr.cgi?rm=csd&csdid=986704
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report