Abstract
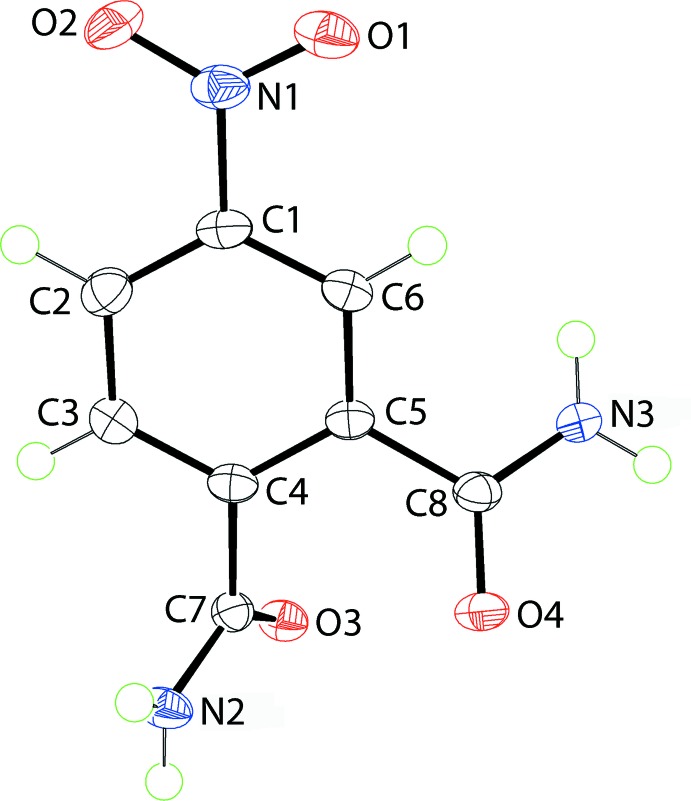
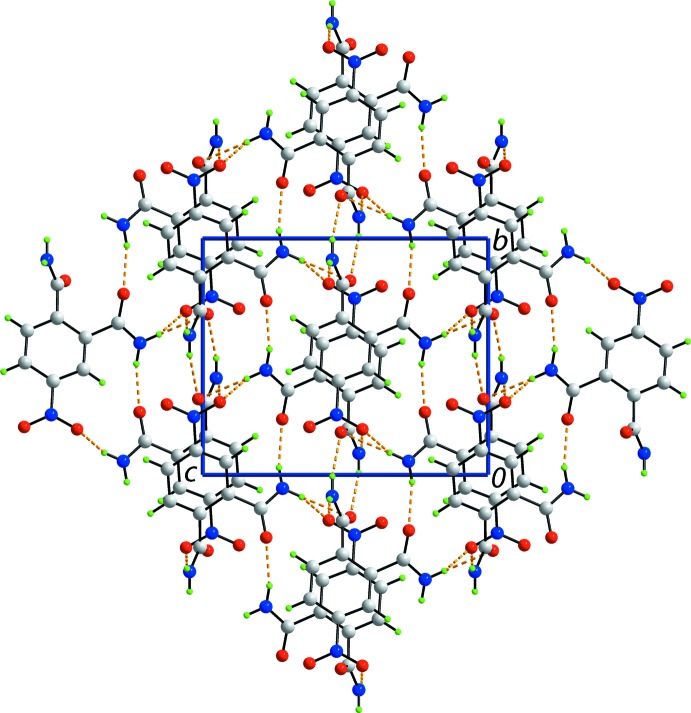
In the title compound, C8H7N3O4 (systematic name: 4-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxamide), each of the substituents is twisted out of the plane of the benzene ring to which it is attached [dihedral angles of 11.36 (2)° for the nitro group, and 60.89 (6) and 34.39 (6)° for the amide groups]. The amide groups are orientated to either side of the least-squares plane through the benzene ring with the amine groups being directed furthest apart. In the crystal, a three-dimensional architecture is established by a network of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For background to the synthesis of functional phthalocyanines, see: Chin et al. (2012 ▶). For the structure of the 1,2-dicarboxamide derivative, see: Hamada et al. (2012 ▶). For the synthesis, see: Rasmussen et al. (1978 ▶).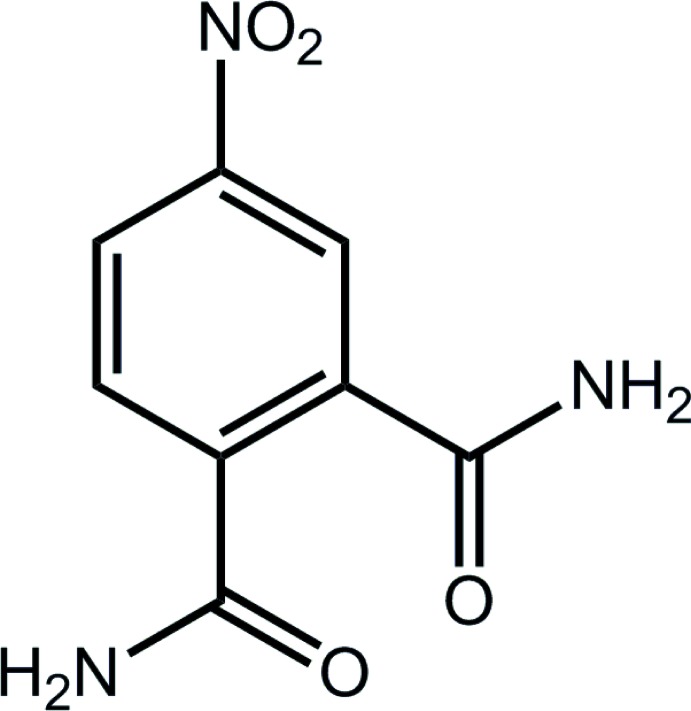
Experimental
Crystal data
C8H7N3O4
M r = 209.17
Monoclinic,
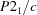
a = 7.7425 (2) Å
b = 9.6634 (2) Å
c = 12.1276 (3) Å
β = 106.008 (3)°
V = 872.19 (4) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 1.13 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.40 × 0.30 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Agilent SuperNova Dual diffractometer with an Atlas detector
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2013 ▶) T min = 0.668, T max = 1.000
7908 measured reflections
1821 independent reflections
1748 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.029
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.032
wR(F 2) = 0.090
S = 1.03
1821 reflections
164 parameters
4 restraints
All H-atom parameters refined
Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2013 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▶) and DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) general, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002955/hg5382sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002955/hg5382Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002955/hg5382Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 985960
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H21⋯O1i | 0.87 (1) | 2.22 (1) | 3.0718 (13) | 164 (2) |
| N2—H22⋯O3ii | 0.88 (1) | 2.10 (1) | 2.9628 (12) | 168 (2) |
| N3—H31⋯O1iii | 0.88 (1) | 2.42 (1) | 3.1288 (13) | 138 (1) |
| N3—H31⋯O3iv | 0.88 (1) | 2.35 (1) | 3.0979 (12) | 143 (1) |
| N3—H32⋯O4v | 0.87 (1) | 2.00 (1) | 2.8498 (13) | 167 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 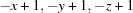 ; (ii)
; (ii) 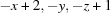 ; (iii)
; (iii) 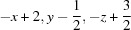 ; (iv)
; (iv) 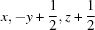 ; (v)
; (v) 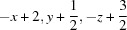 .
.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge funding from the Brunei Research Council, and thank the Ministry of Higher Education (Malaysia) and the University of Malaya for funding structural studies through the High-Impact Research scheme (UM.C/HIR-MOHE/SC/03).
supplementary crystallographic information
1. Chemical context
2. Structural commentary
As part of our on-going study of functional phthalocyanines, we have previously reported the synthesis and structure of 4-(prop-2-ylnyloxy)phthalonitrile, prepared from 4-nitrophthalonitrile (Chin et al. (2012). The latter, in turn, is prepared by dehydration of the title compound. As the structure of the title compound is not reported, herein its crystal structure determination is described.
In the title compound, Fig. 1, each of the nitro [the O1—N1—C1—C2 torsion angle is 168.48 (10)°], N2-amide [C3—C4—C7—O3 114.92 (12)°] and N3-amide [C6—C5—C8—O4 142.80 (11)°] groups are twisted out of the plane of the benzene ring to which they are attached. The relative orientation of the amide-O atoms places them in positions on either side of the benzene ring, with the amine groups similarly orientated but directed away from each other. As such, there are no intramolecular hydrogen bonding contacts. Very similar conformations were found for the two independent molecules comprising the asymmetric unit of the 1,2–dicarboxamide parent compound (Hamada et al., 2012).
In the crystal packing, each N—H H atoms forms a N—H···O hydrogen bond with H31 being bifurcated (Table 1); both O1 and O3 accept two hydrogen bonds. The result is a three-dimensional architecture that can be described globally as comprising columns of molecules aligned along the a axis (Fig. 2).
3. Supramolecular features
4. Database survey
5. Synthesis and crystallization
The title compound was prepared by modification of a literature procedure (Rasmussen et al., 1978). 4-Nitrophthalimide and concentrated NH4OH were stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The precipitate (an off-white powder) was filtered under vacuum and washed with cold water to provide the title compound in 0.68 g yield (63.8 %). M.pt: 465–469 K (literature: 462–464 K). Crystals for the X-ray study were grown from slow evaporation of its aqueous solution.
6. Refinement
All C-bound H atoms were refined freely. The N—H atoms were located from difference map and refined with N—H = 0.88±0.01 Å, and with unrestrained Uiso(H).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound showing the atom-labelling scheme and displacement ellipsoids at the 70% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A view of the unit-cell contents of (I) in projection down the a axis. The N—H···O hydrogen bonds are shown as orange dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C8H7N3O4 | F(000) = 432 |
| Mr = 209.17 | Dx = 1.593 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 4480 reflections |
| a = 7.7425 (2) Å | θ = 3.8–76.2° |
| b = 9.6634 (2) Å | µ = 1.13 mm−1 |
| c = 12.1276 (3) Å | T = 100 K |
| β = 106.008 (3)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 872.19 (4) Å3 | 0.40 × 0.30 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Agilent SuperNova Dual diffractometer with an Atlas detector | 1821 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: SuperNova (Cu) X-ray Source | 1748 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.029 |
| Detector resolution: 10.4041 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 76.4°, θmin = 6.0° |
| ω scan | h = −9→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2013) | k = −11→12 |
| Tmin = 0.668, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −14→15 |
| 7908 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.032 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.090 | All H-atom parameters refined |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0552P)2 + 0.2944P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1821 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 164 parameters | Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3 |
| 4 restraints | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.61481 (11) | 0.80745 (8) | 0.55898 (7) | 0.0202 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.54207 (13) | 0.79742 (9) | 0.37347 (8) | 0.0266 (2) | |
| O3 | 1.04596 (10) | 0.17952 (8) | 0.51619 (7) | 0.0160 (2) | |
| O4 | 0.91323 (12) | 0.23508 (8) | 0.72189 (7) | 0.0192 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.60572 (12) | 0.74606 (10) | 0.46837 (8) | 0.0177 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.76591 (13) | 0.09066 (10) | 0.45344 (8) | 0.0171 (2) | |
| H21 | 0.6511 (13) | 0.1037 (17) | 0.4443 (14) | 0.025 (4)* | |
| H22 | 0.809 (2) | 0.0070 (11) | 0.4535 (14) | 0.025 (4)* | |
| N3 | 1.04060 (14) | 0.44255 (10) | 0.77908 (8) | 0.0182 (2) | |
| H31 | 1.096 (2) | 0.4063 (17) | 0.8462 (10) | 0.027 (4)* | |
| H32 | 1.050 (2) | 0.5306 (10) | 0.7667 (13) | 0.025 (4)* | |
| C1 | 0.67444 (14) | 0.60364 (11) | 0.47498 (10) | 0.0154 (2) | |
| C2 | 0.63660 (14) | 0.52513 (12) | 0.37619 (10) | 0.0171 (2) | |
| H2 | 0.566 (2) | 0.5640 (18) | 0.3011 (14) | 0.030 (4)* | |
| C3 | 0.70007 (15) | 0.38986 (12) | 0.38425 (10) | 0.0164 (2) | |
| H3 | 0.677 (2) | 0.3367 (15) | 0.3164 (13) | 0.018 (3)* | |
| C4 | 0.80132 (14) | 0.33683 (11) | 0.48911 (9) | 0.0141 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.83839 (14) | 0.41940 (11) | 0.58825 (9) | 0.0137 (2) | |
| C6 | 0.77318 (15) | 0.55445 (11) | 0.58101 (10) | 0.0150 (2) | |
| H6 | 0.795 (2) | 0.6102 (16) | 0.6473 (13) | 0.019 (3)* | |
| C7 | 0.88135 (15) | 0.19421 (11) | 0.49017 (9) | 0.0137 (2) | |
| C8 | 0.93594 (14) | 0.35831 (11) | 0.70270 (9) | 0.0146 (2) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0180 (4) | 0.0139 (4) | 0.0287 (5) | 0.0015 (3) | 0.0063 (3) | −0.0027 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0284 (5) | 0.0171 (4) | 0.0269 (5) | 0.0051 (3) | −0.0047 (4) | 0.0061 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0152 (4) | 0.0130 (4) | 0.0202 (4) | 0.0004 (3) | 0.0053 (3) | −0.0006 (3) |
| O4 | 0.0283 (4) | 0.0105 (4) | 0.0193 (4) | 0.0000 (3) | 0.0076 (3) | 0.0020 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0128 (4) | 0.0128 (5) | 0.0258 (5) | −0.0002 (3) | 0.0024 (4) | 0.0013 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0153 (5) | 0.0111 (5) | 0.0246 (5) | 0.0009 (4) | 0.0049 (4) | −0.0017 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0265 (5) | 0.0115 (5) | 0.0147 (5) | −0.0005 (4) | 0.0021 (4) | 0.0017 (3) |
| C1 | 0.0135 (5) | 0.0105 (5) | 0.0221 (6) | 0.0003 (4) | 0.0050 (4) | 0.0024 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0148 (5) | 0.0169 (5) | 0.0187 (5) | 0.0003 (4) | 0.0032 (4) | 0.0029 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0170 (5) | 0.0149 (5) | 0.0170 (5) | −0.0009 (4) | 0.0045 (4) | −0.0012 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0136 (5) | 0.0109 (5) | 0.0185 (5) | −0.0012 (4) | 0.0057 (4) | 0.0003 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0138 (5) | 0.0113 (5) | 0.0167 (5) | −0.0008 (4) | 0.0053 (4) | 0.0012 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0157 (5) | 0.0118 (5) | 0.0180 (5) | −0.0017 (4) | 0.0058 (4) | −0.0011 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0177 (5) | 0.0118 (5) | 0.0124 (5) | 0.0002 (4) | 0.0055 (4) | −0.0002 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0177 (5) | 0.0112 (5) | 0.0161 (5) | 0.0018 (4) | 0.0069 (4) | −0.0002 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—N1 | 1.2336 (13) | C1—C2 | 1.3796 (16) |
| O2—N1 | 1.2252 (13) | C1—C6 | 1.3862 (15) |
| O3—C7 | 1.2338 (14) | C2—C3 | 1.3904 (16) |
| O4—C8 | 1.2351 (14) | C2—H2 | 0.997 (16) |
| N1—C1 | 1.4698 (14) | C3—C4 | 1.3945 (15) |
| N2—C7 | 1.3338 (14) | C3—H3 | 0.945 (15) |
| N2—H21 | 0.874 (9) | C4—C5 | 1.4050 (15) |
| N2—H22 | 0.875 (9) | C4—C7 | 1.5097 (14) |
| N3—C8 | 1.3280 (15) | C5—C6 | 1.3934 (15) |
| N3—H31 | 0.881 (9) | C5—C8 | 1.5058 (14) |
| N3—H32 | 0.870 (9) | C6—H6 | 0.943 (16) |
| O2—N1—O1 | 123.47 (10) | C4—C3—H3 | 121.1 (9) |
| O2—N1—C1 | 118.45 (10) | C3—C4—C5 | 120.16 (10) |
| O1—N1—C1 | 118.09 (9) | C3—C4—C7 | 118.00 (9) |
| C7—N2—H21 | 119.9 (11) | C5—C4—C7 | 121.64 (9) |
| C7—N2—H22 | 118.1 (11) | C6—C5—C4 | 119.54 (10) |
| H21—N2—H22 | 120.6 (15) | C6—C5—C8 | 120.41 (10) |
| C8—N3—H31 | 116.6 (11) | C4—C5—C8 | 119.89 (9) |
| C8—N3—H32 | 122.9 (10) | C1—C6—C5 | 118.50 (10) |
| H31—N3—H32 | 120.4 (15) | C1—C6—H6 | 121.1 (9) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 123.21 (10) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.4 (9) |
| C2—C1—N1 | 118.72 (10) | O3—C7—N2 | 123.29 (10) |
| C6—C1—N1 | 118.06 (10) | O3—C7—C4 | 119.99 (9) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 118.01 (10) | N2—C7—C4 | 116.51 (9) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 121.2 (10) | O4—C8—N3 | 123.42 (10) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.8 (10) | O4—C8—C5 | 119.37 (10) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.57 (10) | N3—C8—C5 | 117.20 (9) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 118.2 (9) | ||
| O2—N1—C1—C2 | −11.31 (15) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.37 (17) |
| O1—N1—C1—C2 | 168.48 (10) | N1—C1—C6—C5 | 179.78 (9) |
| O2—N1—C1—C6 | 169.25 (10) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.61 (16) |
| O1—N1—C1—C6 | −10.96 (15) | C8—C5—C6—C1 | −176.01 (10) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.44 (17) | C3—C4—C7—O3 | 114.92 (12) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −178.96 (10) | C5—C4—C7—O3 | −60.00 (14) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.02 (16) | C3—C4—C7—N2 | −60.02 (13) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.79 (16) | C5—C4—C7—N2 | 125.05 (11) |
| C2—C3—C4—C7 | −174.21 (10) | C6—C5—C8—O4 | 142.80 (11) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.05 (16) | C4—C5—C8—O4 | −32.58 (15) |
| C7—C4—C5—C6 | 174.86 (9) | C6—C5—C8—N3 | −35.96 (14) |
| C3—C4—C5—C8 | 175.47 (10) | C4—C5—C8—N3 | 148.66 (11) |
| C7—C4—C5—C8 | −9.71 (15) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H21···O1i | 0.87 (1) | 2.22 (1) | 3.0718 (13) | 164 (2) |
| N2—H22···O3ii | 0.88 (1) | 2.10 (1) | 2.9628 (12) | 168 (2) |
| N3—H31···O1iii | 0.88 (1) | 2.42 (1) | 3.1288 (13) | 138 (1) |
| N3—H31···O3iv | 0.88 (1) | 2.35 (1) | 3.0979 (12) | 143 (1) |
| N3—H32···O4v | 0.87 (1) | 2.00 (1) | 2.8498 (13) | 167 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) −x+2, −y, −z+1; (iii) −x+2, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (iv) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (v) −x+2, y+1/2, −z+3/2.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HG5382).
References
- Agilent (2013). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA.
- Brandenburg, K. (2006). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Chin, Y. J., Tan, A. L., Wimmer, F. L., Mirza, A. H., Young, D. J., Ng, S. W. & Tiekink, E. R. T. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o2293–o2294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Hamada, A., Boudinar, Y., Beghidja, A. & Boutebdja, M. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o2710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, C. R., Gardocki, J. F., Plampin, J. N., Twardzik, B. L., Reynolds, B. E., Molinari, A. J., Schwartz, N., Bennetts, W. W., Price, B. E. & Marakowski, J. (1978). J. Med. Chem. 21, 1044–1054. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) general, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002955/hg5382sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002955/hg5382Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814002955/hg5382Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 985960
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report