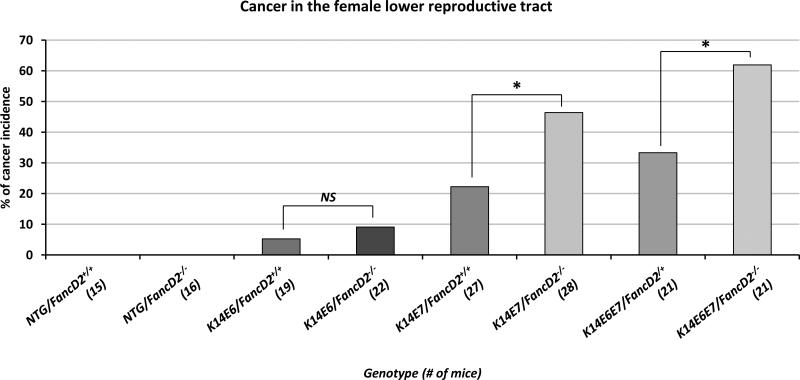
Figure 1. HPV-associated cancer incidence in the lower reproductive tract.
Mice were treated with 17β-estradiol which is predominant estrogen for a period of 6 months to achieve a state of persistent estrus. After the estrogen treatment, the female lower reproductive tract was harvested, fixed and sectioned. Every tenth, 5 μm section was stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and histopathologically evaluated the worst lesion scored as the final diagnosis. Cervical and/or vaginal cancers were scored in each genotype of mice. The cancer incidence in K14E7/FancD2+/+ is significantly higher than it in NTG/FancD2+/+ (P=0.03) or K14E6/FancD2+/+ mice (P=0.07). fancD2 deficiency significantly increased cancer incidence in K14E7 and K14E6E7 mice. Asterisk (*) means significant difference (P<0.05). NS means no significant difference. All statistical analyses were performed using a one-sided Barnard's exact test.