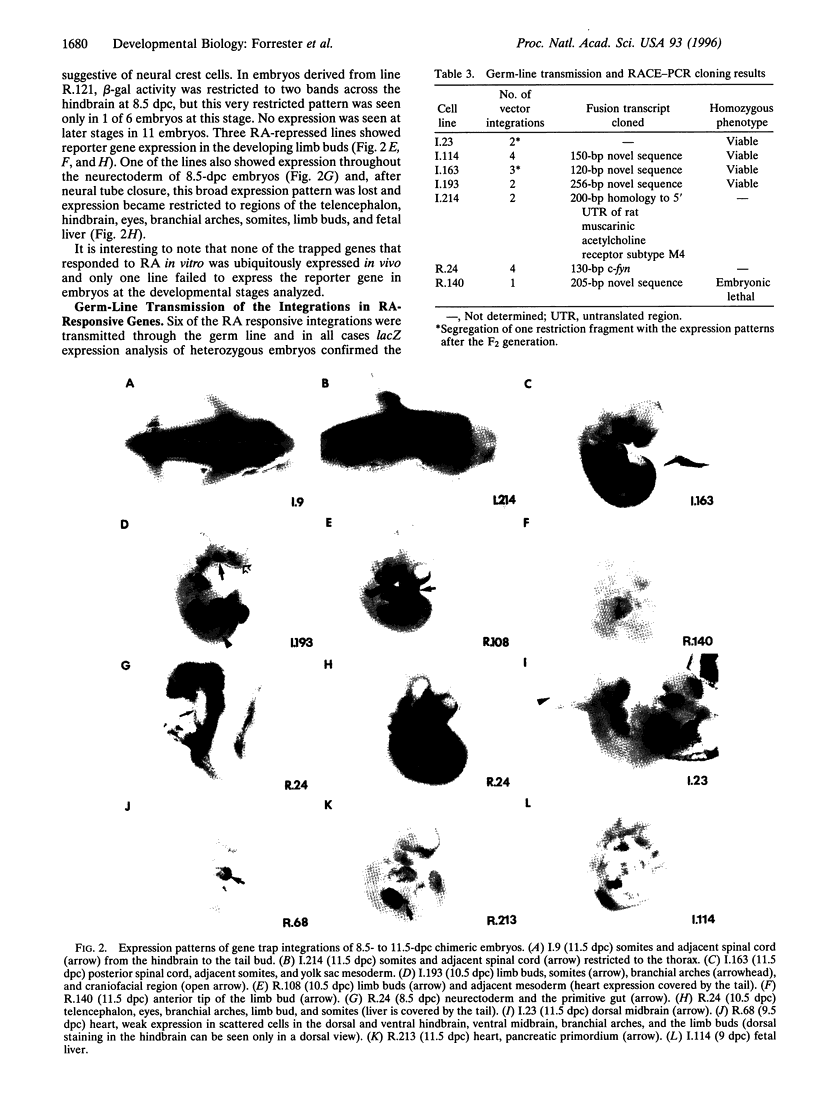
Abstract
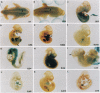
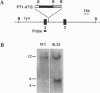
We have developed a novel induction gene trap approach that preselects in vitro for integrations into genes that lie downstream of receptor/ligand-mediated signaling pathways. Using this approach, we have identified 20 gene trap integrations in embryonic stem cells, 9 of which were induced and 11 of which were repressed after exposure to exogenous retinoic acid (RA). All but one of these integrations showed unique spatially restricted or tissue-specific patterns of expression between 8.5 and 11.5 days of embryogenesis. Interestingly, expression was observed in tissues that are affected by alterations in RA levels during embryogenesis. Sequence analysis of fusion transcripts from six integrations revealed five novel gene sequences and the previously identified protooncogene c-fyn. To date, germ-line transmission and breeding has uncovered one homozygous embryonic lethal and three homozygous viable insertions. These studies demonstrate the potential of this induction gene trap approach for identifying and mutating genes downstream of signal transduction pathways.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conlon R. A., Rossant J. Exogenous retinoic acid rapidly induces anterior ectopic expression of murine Hox-2 genes in vivo. Development. 1992 Oct;116(2):357–368. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.2.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke M. P., Perlmutter R. M. Expression of a novel form of the fyn proto-oncogene in hematopoietic cells. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):66–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichele G. Retinoids and vertebrate limb pattern formation. Trends Genet. 1989 Aug;5(8):246–251. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eustice D. C., Feldman P. A., Colberg-Poley A. M., Buckery R. M., Neubauer R. H. A sensitive method for the detection of beta-galactosidase in transfected mammalian cells. Biotechniques. 1991 Dec;11(6):739-40, 742-3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich G., Soriano P. Promoter traps in embryonic stem cells: a genetic screen to identify and mutate developmental genes in mice. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1513–1523. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossen M., Bujard H. Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5547–5551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossler A., Joyner A. L., Rossant J., Skarnes W. C. Mouse embryonic stem cells and reporter constructs to detect developmentally regulated genes. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):463–465. doi: 10.1126/science.2497519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. P., Wurst W. Gene and enhancer trapping: mutagenic strategies for developmental studies. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1993;28:181–206. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. P., Wurst W. Screening for novel pattern formation genes using gene trap approaches. Methods Enzymol. 1993;225:664–681. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(93)25043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner A. L. Gene targeting and gene trap screens using embryonic stem cells: new approaches to mammalian development. Bioessays. 1991 Dec;13(12):649–656. doi: 10.1002/bies.950131206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Gruss P. Homeotic transformations of murine vertebrae and concomitant alteration of Hox codes induced by retinoic acid. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):89–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90574-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langston A. W., Gudas L. J. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive enhancer 3' of the murine homeobox gene Hox-1.6. Mech Dev. 1992 Sep;38(3):217–227. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90055-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E. Retinoic acid receptors: transcription factors modulating gene regulation, development, and differentiation. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1992;27:309–350. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60538-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohnes D., Kastner P., Dierich A., Mark M., LeMeur M., Chambon P. Function of retinoic acid receptor gamma in the mouse. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):643–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90246-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall H., Nonchev S., Sham M. H., Muchamore I., Lumsden A., Krumlauf R. Retinoic acid alters hindbrain Hox code and induces transformation of rhombomeres 2/3 into a 4/5 identity. Nature. 1992 Dec 24;360(6406):737–741. doi: 10.1038/360737a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy A., Rossant J., Nagy R., Abramow-Newerly W., Roder J. C. Derivation of completely cell culture-derived mice from early-passage embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8424–8428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt S. C. Expression of Pax-3- and neuroectoderm-inducing activities during differentiation of P19 embryonal carcinoma cells. Development. 1992 Nov;116(3):573–583. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.3.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöpperl H., Featherstone M. S. Identification of a retinoic acid response element upstream of the murine Hox-4.2 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):257–265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Acampora D., Arcioni L., Andrews P. W., Boncinelli E., Mavilio F. Sequential activation of HOX2 homeobox genes by retinoic acid in human embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):763–766. doi: 10.1038/346763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Acampora D., Nigro V., Faiella A., D'Esposito M., Stornaiuolo A., Mavilio F., Boncinelli E. Differential regulation by retinoic acid of the homeobox genes of the four HOX loci in human embryonal carcinoma cells. Mech Dev. 1991 Mar;33(3):215–227. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarnes W. C., Auerbach B. A., Joyner A. L. A gene trap approach in mouse embryonic stem cells: the lacZ reported is activated by splicing, reflects endogenous gene expression, and is mutagenic in mice. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):903–918. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. L., Lee H. M., Rich S., Soriano P. pp59fyn mutant mice display differential signaling in thymocytes and peripheral T cells. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):741–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90308-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. L., Lee H. M., Rich S., Soriano P. pp59fyn mutant mice display differential signaling in thymocytes and peripheral T cells. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):741–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90308-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucov H. M., Dyson E., Gumeringer C. L., Price J., Chien K. R., Evans R. M. RXR alpha mutant mice establish a genetic basis for vitamin A signaling in heart morphogenesis. Genes Dev. 1994 May 1;8(9):1007–1018. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.9.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasios G., Mader S., Gold J. D., Leid M., Lutz Y., Gaub M. P., Chambon P., Gudas L. The late retinoic acid induction of laminin B1 gene transcription involves RAR binding to the responsive element. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1149–1158. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08055.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurst W., Rossant J., Prideaux V., Kownacka M., Joyner A., Hill D. P., Guillemot F., Gasca S., Cado D., Auerbach A. A large-scale gene-trap screen for insertional mutations in developmentally regulated genes in mice. Genetics. 1995 Feb;139(2):889–899. doi: 10.1093/genetics/139.2.889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi T., Shigetani Y., Furuta Y., Nada S., Okado N., Ikawa Y., Aizawa S. Fyn expression during early neurogenesis in mouse embryos. Oncogene. 1994 Sep;9(9):2433–2440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]