Abstract
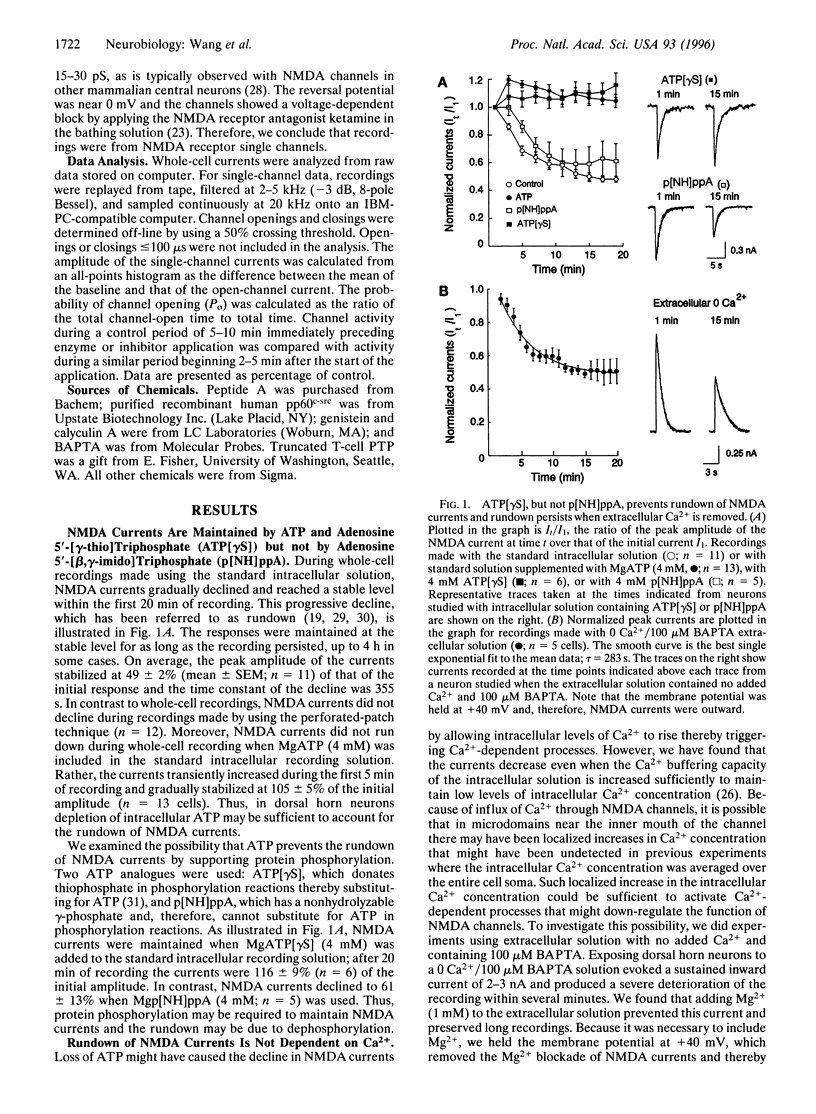
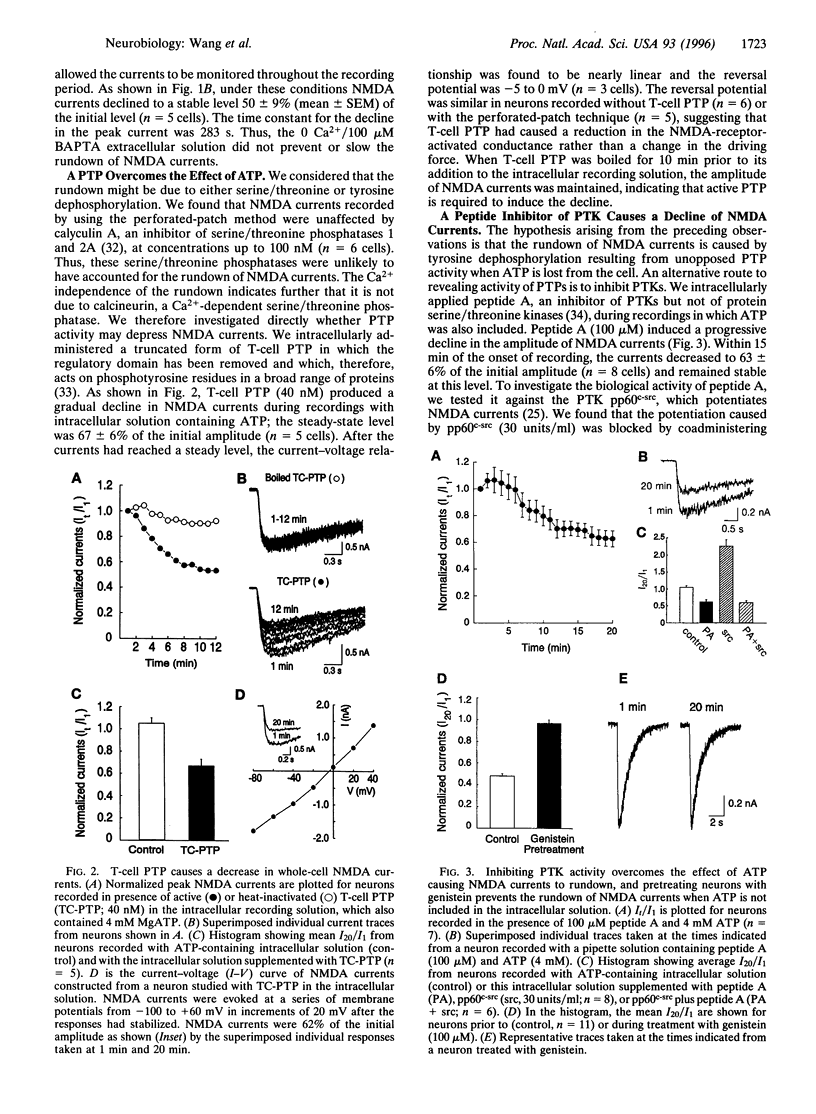
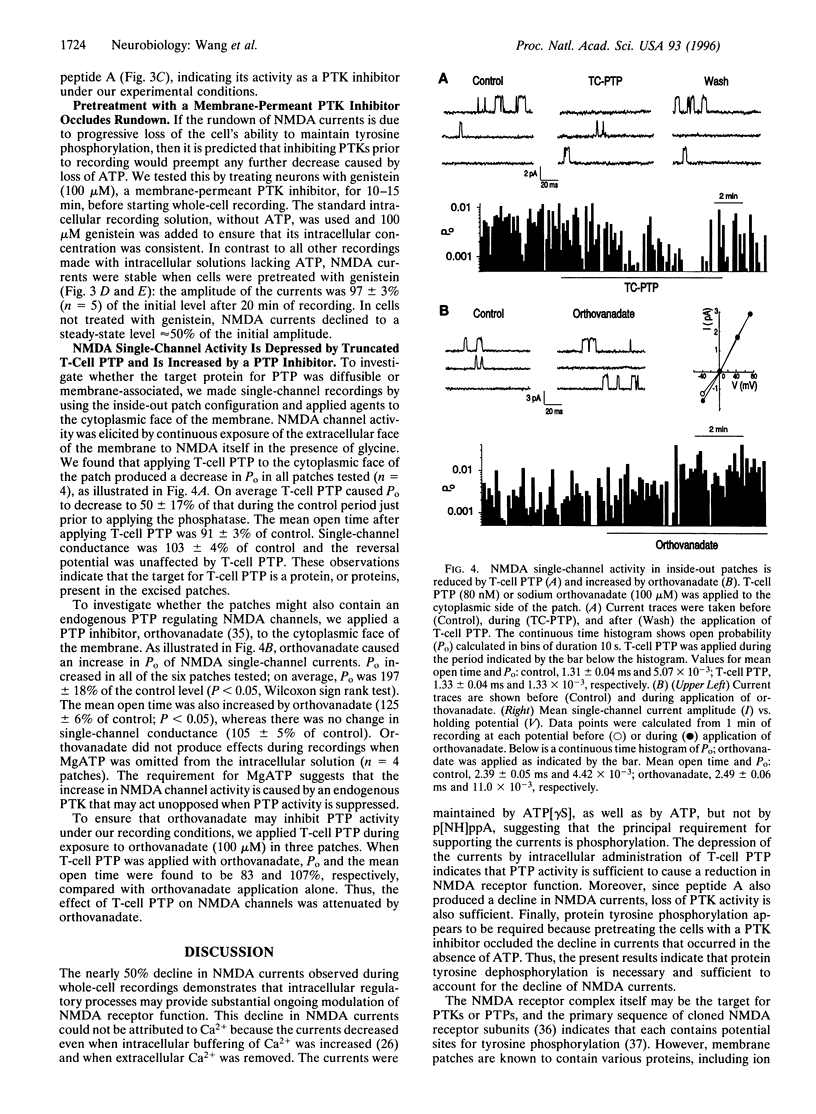
Regulation of ion channel function by intracellular processes is fundamental for controlling synaptic signaling and integration in the nervous system. Currents mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors decline during whole-cell recordings and this may be prevented by ATP. We show here that phosphorylation is necessary to maintain NMDA currents and that the decline is not dependent upon Ca2+. A protein tyrosine phosphatase or a peptide inhibitor of protein tyrosine kinase applied intracellularly caused a decrease in NMDA currents even when ATP was included. On the other hand, pretreating the neurons with a membrane-permeant tyrosine kinase inhibitor occluded the decline in NMDA currents when ATP was omitted. In inside-out patches, applying a protein tyrosine phosphatase to the cytoplasmic face of the patch caused a decrease in probability of opening of NMDA channels. Conversely, open probability was increased by a protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor. These results indicate that NMDA channel activity is reduced by a protein tyrosine phosphatase associated with the channel complex.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bading H., Greenberg M. E. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by NMDA receptor activation. Science. 1991 Aug 23;253(5022):912–914. doi: 10.1126/science.1715095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brautigan D. L. Great expectations: protein tyrosine phosphatases in cell regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Sep 14;1114(1):63–77. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(92)90007-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Cotton P. C., Queral A. E., Barrett J. N., Nonner D., Keane R. W. Neurones express high levels of a structurally modified, activated form of pp60c-src. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):554–557. doi: 10.1038/316554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catarsi S., Drapeau P. Tyrosine kinase-dependent selection of transmitter responses induced by neuronal contact. Nature. 1993 May 27;363(6427):353–355. doi: 10.1038/363353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K. 1002 protein phosphatases? Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:463–493. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Huang L. Y. Protein kinase C reduces Mg2+ block of NMDA-receptor channels as a mechanism of modulation. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):521–523. doi: 10.1038/356521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba T., Nagata Y., Machide M., Kishi A., Amanuma H., Sugiyama M., Todokoro K. Tyrosine kinase activation through the extracellular domains of cytokine receptors. Nature. 1993 Apr 15;362(6421):646–648. doi: 10.1038/362646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christine C. W., Choi D. W. Effect of zinc on NMDA receptor-mediated channel currents in cortical neurons. J Neurosci. 1990 Jan;10(1):108–116. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-01-00108.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand G. M., Gregor P., Zheng X., Bennett M. V., Uhl G. R., Zukin R. S. Cloning of an apparent splice variant of the rat N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NMDAR1 with altered sensitivity to polyamines and activators of protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9359–9363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer E. H., Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: a diverse family of intracellular and transmembrane enzymes. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):401–406. doi: 10.1126/science.1650499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami Y., Sato K., Ikeda K., Kamisango K., Koizumi K., Matsuno T. Evidence for autoinhibitory regulation of the c-src gene product. A possible interaction between the src homology 2 domain and autophosphorylation site. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1132–1140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibb A. J., Colquhoun D. Activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by L-glutamate in cells dissociated from adult rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:143–179. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelso S. R., Nelson T. E., Leonard J. P. Protein kinase C-mediated enhancement of NMDA currents by metabotropic glutamate receptors in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:705–718. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legendre P., Rosenmund C., Westbrook G. L. Inactivation of NMDA channels in cultured hippocampal neurons by intracellular calcium. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):674–684. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00674.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman D. N., Mody I. Regulation of NMDA channel function by endogenous Ca(2+)-dependent phosphatase. Nature. 1994 May 19;369(6477):235–239. doi: 10.1038/369235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Mody I., Salter M. W. Regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors revealed by intracellular dialysis of murine neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1989 Jul;414:17–34. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Guthrie P. B. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):261–263. doi: 10.1038/309261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBain C. J., Mayer M. L. N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor structure and function. Physiol Rev. 1994 Jul;74(3):723–760. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1994.74.3.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGurk J. F., Bennett M. V., Zukin R. S. Polyamines potentiate responses of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors expressed in xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9971–9974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mody I., Salter M. W., MacDonald J. F. Requirement of NMDA receptor/channels for intracellular high-energy phosphates and the extent of intraneuronal calcium buffering in cultured mouse hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Oct 31;93(1):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monyer H., Sprengel R., Schoepfer R., Herb A., Higuchi M., Lomeli H., Burnashev N., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. Heteromeric NMDA receptors: molecular and functional distinction of subtypes. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1217–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon I. S., Apperson M. L., Kennedy M. B. The major tyrosine-phosphorylated protein in the postsynaptic density fraction is N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 2B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3954–3958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dell T. J., Kandel E. R., Grant S. G. Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus is blocked by tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):558–560. doi: 10.1038/353558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan M. G., Florio T., Stork P. J. G protein activation of a hormone-stimulated phosphatase in human tumor cells. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1215–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenmund C., Westbrook G. L. Calcium-induced actin depolymerization reduces NMDA channel activity. Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):805–814. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90197-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenmund C., Westbrook G. L. Rundown of N-methyl-D-aspartate channels during whole-cell recording in rat hippocampal neurons: role of Ca2+ and ATP. J Physiol. 1993 Oct;470:705–729. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahin M., Hockfield S. Protein tyrosine phosphatases expressed in the developing rat brain. J Neurosci. 1993 Nov;13(11):4968–4978. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-11-04968.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter M. W., Hicks J. L. ATP-evoked increases in intracellular calcium in neurons and glia from the dorsal spinal cord. J Neurosci. 1994 Mar;14(3 Pt 2):1563–1575. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-03-01563.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Growth factor signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90177-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokabe M., Sachs F. The structure and dynamics of patch-clamped membranes: a study using differential interference contrast light microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):599–606. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker A. W. Isoforms of a novel cell adhesion molecule-like protein tyrosine phosphatase are implicated in neural development. Mech Dev. 1994 Jun;46(3):201–217. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(94)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suganuma M., Fujiki H., Okabe S., Nishiwaki S., Brautigan D., Ingebritsen T. S., Rosner M. R. Structurally different members of the okadaic acid class selectively inhibit protein serine/threonine but not tyrosine phosphatase activity. Toxicon. 1992 Aug;30(8):873–878. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(92)90385-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarup G., Cohen S., Garbers D. L. Inhibition of membrane phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase activity by vanadate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1104–1109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traynelis S. F., Cull-Candy S. G. Proton inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in cerebellar neurons. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):347–350. doi: 10.1038/345347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner K. R., Mei L., Huganir R. L. Protein tyrosine kinases and phosphatases in the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1991 Jun;1(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(91)90011-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. Y., Orser B. A., Brautigan D. L., MacDonald J. F. Regulation of NMDA receptors in cultured hippocampal neurons by protein phosphatases 1 and 2A. Nature. 1994 May 19;369(6477):230–232. doi: 10.1038/369230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. T., Pak Y. S., Salter M. W. Rundown of NMDA-receptor mediated currents is resistant to lowering intracellular [Ca2+] and is prevented by ATP in rat spinal dorsal horn neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Jul 23;157(2):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90732-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. T., Salter M. W. Regulation of NMDA receptors by tyrosine kinases and phosphatases. Nature. 1994 May 19;369(6477):233–235. doi: 10.1038/369233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. C., Krause G. S., O'Neil B. J., DeGracia D. J., Tiffany B. R., Grossman L. I., Grunberger G. Potential role of growth factors in global brain ischemia and reperfusion. Observation of insulin-driven tyrosine phosphorylation of a 90-kDa protein during reperfusion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Aug 27;692:281–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb26234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount R. G. ATP analogs. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1975;43:1–56. doi: 10.1002/9780470122884.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zander N. F., Lorenzen J. A., Cool D. E., Tonks N. K., Daum G., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H. Purification and characterization of a human recombinant T-cell protein-tyrosine-phosphatase from a baculovirus expression system. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 16;30(28):6964–6970. doi: 10.1021/bi00242a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


