Abstract
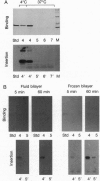
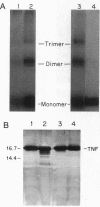
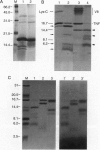
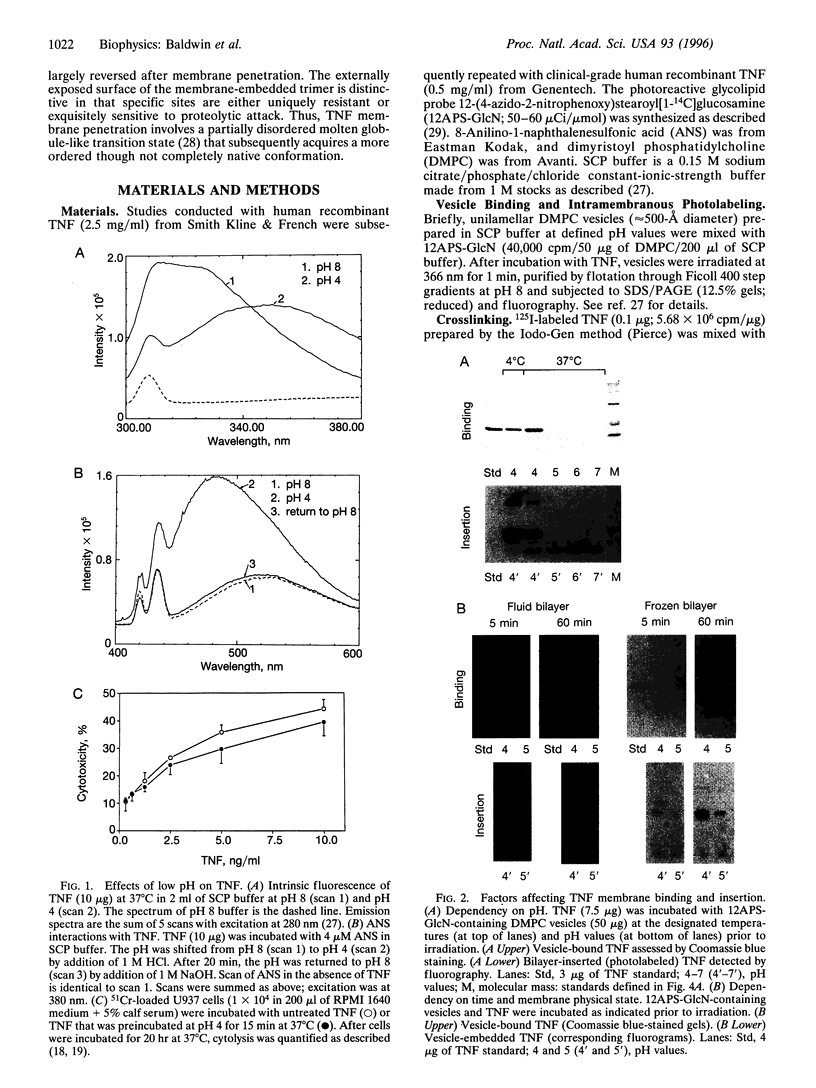
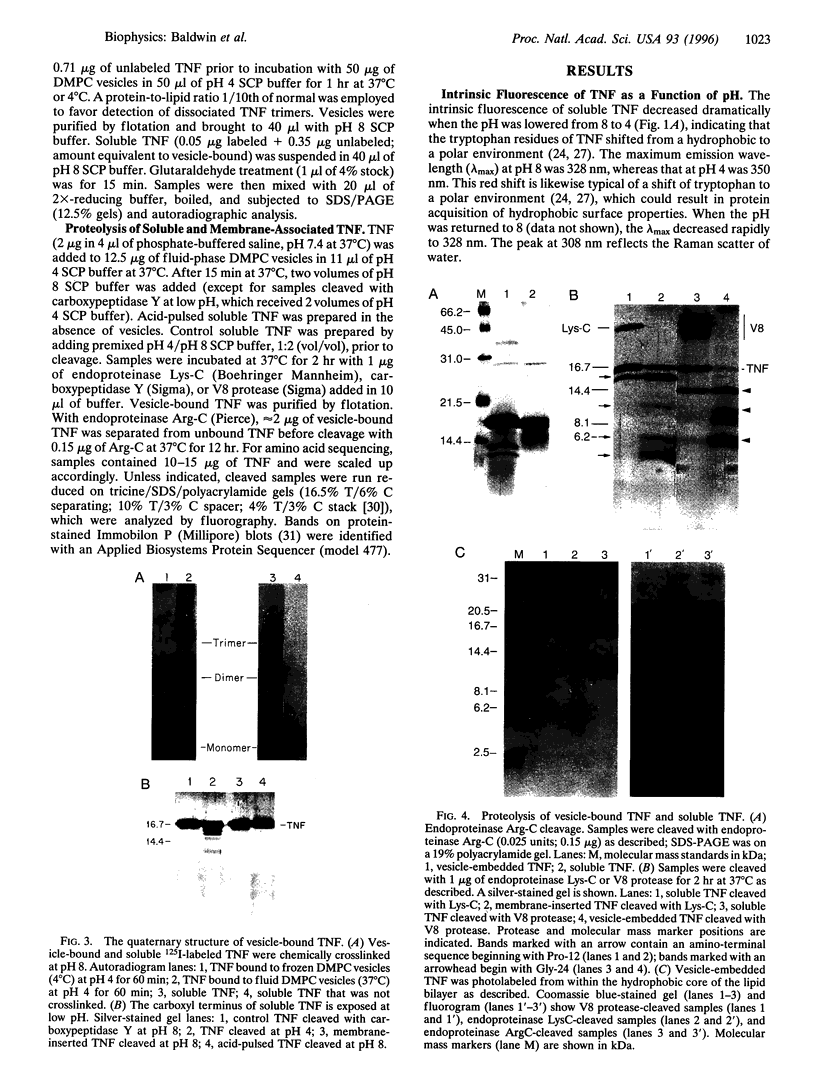
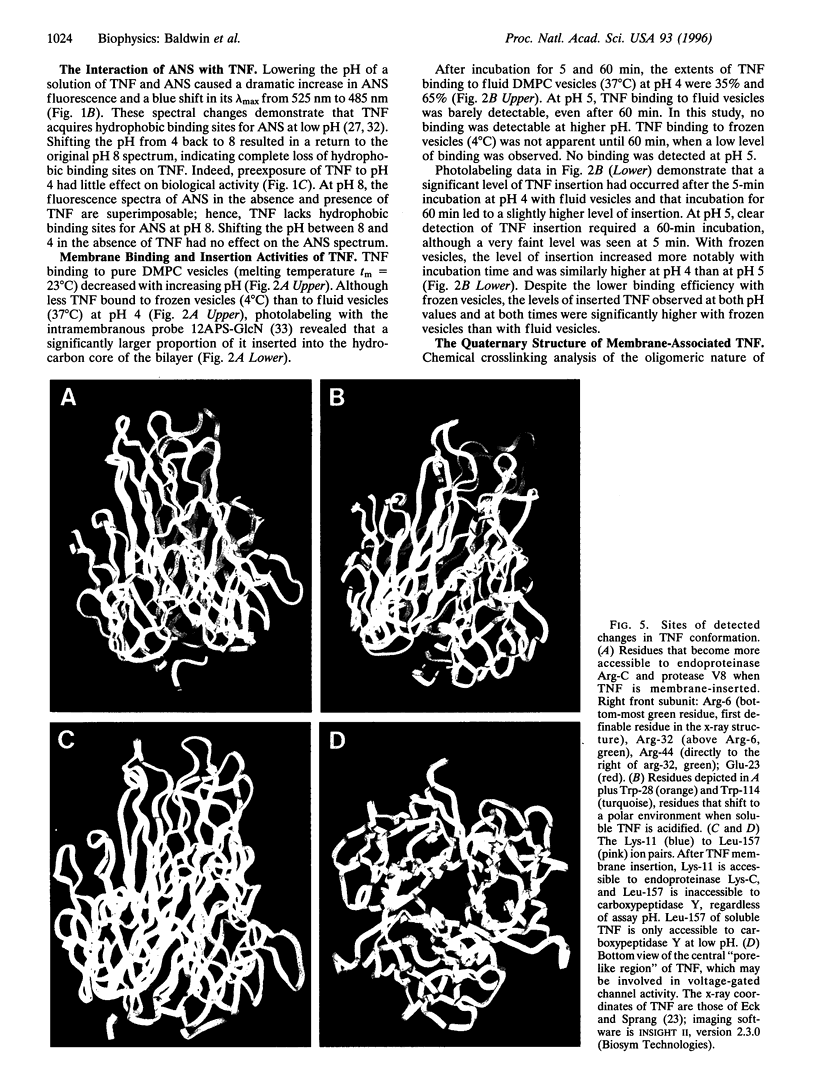
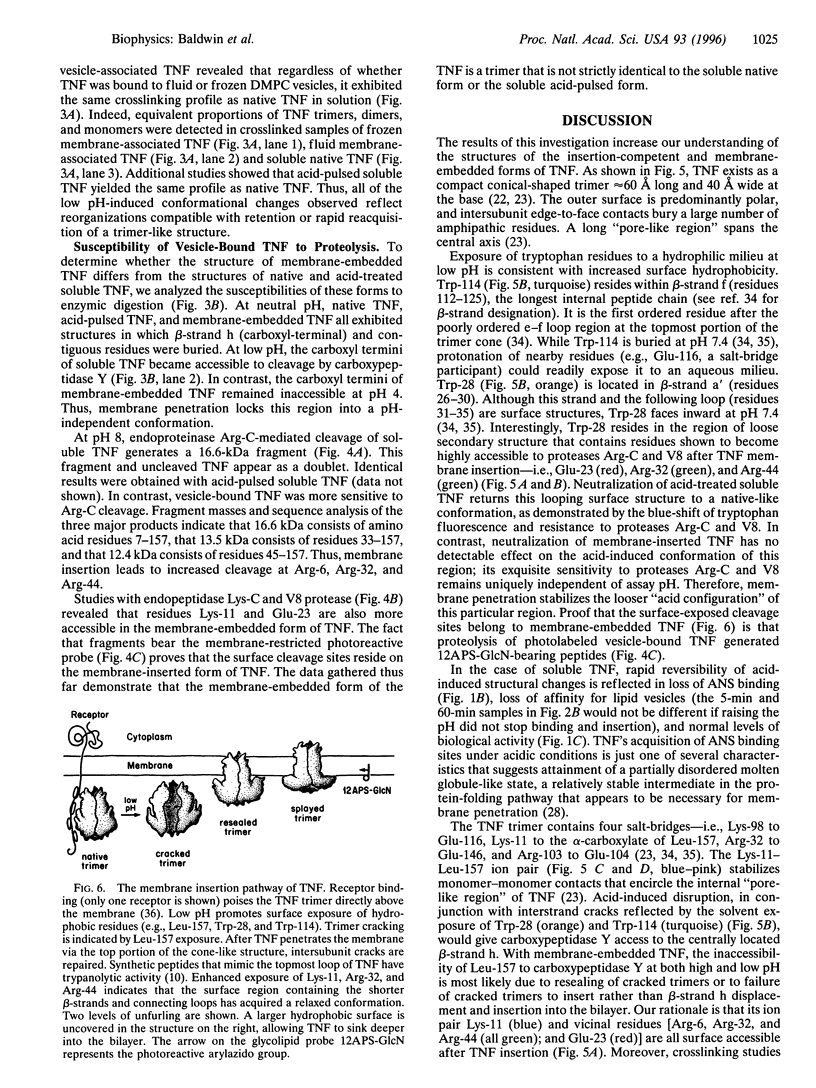
Low pH enhances tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF)-induced cytolysis of cancer cells and TNF-membrane interactions that include binding, insertion, and ion-channel formation. We have also found that TNF increases Na+ influx in cells. Here, we examined the structural features of the TNF-membrane interaction pathway that lead to channel formation. Fluorometric studies link TNF's acid-enhanced membrane interactions to rapid but reversible acquisition of hydrophobic surface properties. Intramembranous photolabeling shows that (i) protonation of TNF promotes membrane insertion, (ii) the physical state of the target bilayer affects the kinetics and efficiency of TNF insertion, and (iii) binding and insertion of TNF are two distinct events. Acidification relaxes the trimeric structure of soluble TNF so that the cryptic carboxyl termini, centrally located at the base of the trimer cone, become susceptible to carboxypeptidase Y. After membrane insertion, TNF exhibits a trimeric configuration in which the carboxyl termini are no longer exposed; however, the proximal salt-bridged Lys-11 residues as well as regional surface amino acids (Glu-23, Arg-32, and Arg-44) are notably more accessible to proteases. The sequenced cleavage products bear the membrane-restricted photoreactive probe, proof that surface-cleaved TNF has an intramembranous disposition. In summary, the trimer's structural plasticity is a major determinant of its channel-forming ability. Channel formation occurs when cracked or partially splayed trimers bind and penetrate the bilayer. Reannealing leads to a slightly relaxed trimeric structure. The directionality of bilayer penetration conforms with x-ray data showing that receptor binding to the monomer interfaces of TNF poises the tip of the trimeric cone directly above the target cell membrane.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin R. L., Chang M. P., Bramhall J., Graves S., Bonavida B., Wisnieski B. J. Capacity of tumor necrosis factor to bind and penetrate membranes is pH-dependent. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2352–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin R. L., Mirzabekov T., Kagan B. L., Wisnieski B. J. Conformation and ion channel activity of lymphotoxin at neutral and low pH. J Immunol. 1995 Jan 15;154(2):790–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banner D. W., D'Arcy A., Janes W., Gentz R., Schoenfeld H. J., Broger C., Loetscher H., Lesslauer W. Crystal structure of the soluble human 55 kd TNF receptor-human TNF beta complex: implications for TNF receptor activation. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):431–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90132-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF--a primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:625–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bychkova V. E., Pain R. H., Ptitsyn O. B. The 'molten globule' state is involved in the translocation of proteins across membranes? FEBS Lett. 1988 Oct 10;238(2):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80485-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. P., Wisnieski B. J. Comparison of the intoxication pathways of tumor necrosis factor and diphtheria toxin. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2644–2650. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2644-2650.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eck M. J., Sprang S. R. The structure of tumor necrosis factor-alpha at 2.6 A resolution. Implications for receptor binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17595–17605. doi: 10.2210/pdb1tnf/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farahbakhsh Z. T., Baldwin R. L., Wisnieski B. J. Effect of low pH on the conformation of Pseudomonas exotoxin A. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2256–2261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu V. W., Esser A. F., Podack E. R., Wisnieski B. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement: photolabeling reveals insertion of terminal proteins into target membrane. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):380–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida B., Cawley D. B., Reue K., Wisnieski B. J. Lipid-protein interactions during ricin toxin insertion into membranes. Evidence for A and B chain penetration. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5933–5937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. Y., Stuart D. I., Walker N. P. Structure of tumour necrosis factor. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):225–228. doi: 10.1038/338225a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan B. L., Baldwin R. L., Munoz D., Wisnieski B. J. Formation of ion-permeable channels by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Science. 1992 Mar 13;255(5050):1427–1430. doi: 10.1126/science.1371890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan B. L., Mirzabekov T., Munoz D., Baldwin R. L., Wisnieski B. The role of channel formation in the mechanism of action of tumor necrosis factors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Dec 20;707:317–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb38062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Besterman J. M. Drug-induced alterations of tumor necrosis factor-mediated cytotoxicity: discrimination of early versus late stage action. J Cell Biochem. 1990 Jan;42(1):1–12. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240420102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Cuatrecasas P. Possible requirement of internalization in the mechanism of in vitro cytotoxicity in tumor necrosis serum. Cancer Res. 1981 Dec;41(12 Pt 1):4885–4890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Cellular receptor for 125I-labeled tumor necrosis factor: specific binding, affinity labeling, and relationship to sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5756–5760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liddil J. D., Dorr R. T., Scuderi P. Association of lysosomal activity with sensitivity and resistance to tumor necrosis factor in murine L929 cells. Cancer Res. 1989 May 15;49(10):2722–2728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher H., Pan Y. C., Lahm H. W., Gentz R., Brockhaus M., Tabuchi H., Lesslauer W. Molecular cloning and expression of the human 55 kd tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90815-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas R., Magez S., De Leys R., Fransen L., Scheerlinck J. P., Rampelberg M., Sablon E., De Baetselier P. Mapping the lectin-like activity of tumor necrosis factor. Science. 1994 Feb 11;263(5148):814–817. doi: 10.1126/science.8303299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishige H., Ohkuma T., Kaji A. In vitro cytostatic effect of TNF (tumor necrosis factor) entrapped in immunoliposomes on cells normally insensitive to TNF. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Sep 5;1151(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muchmore A., Decker J., Shaw A., Wingfield P. Evidence that high mannose glycopeptides are able to functionally interact with recombinant tumor necrosis factor and recombinant interleukin 1. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 1;50(19):6285–6290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nii A., Fan D., Fidler I. J. Cytotoxic potential of liposomes containing tumor necrosis factor-alpha against sensitive and resistant target cells. J Immunother (1991) 1991 Feb;10(1):13–19. doi: 10.1097/00002371-199102000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niitsu Y., Watanabe N., Sone H., Neda H., Yamauchi N., Urushizaki I. Mechanism of the cytotoxic effect of tumor necrosis factor. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1985 Dec;76(12):1193–1197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall T. J., Lewis M., Koller K. J., Lee A., Rice G. C., Wong G. H., Gatanaga T., Granger G. A., Lentz R., Raab H. Molecular cloning and expression of a receptor for human tumor necrosis factor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90816-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver I. A., Murrills R. J., Etherington D. J. Microelectrode studies on the acid microenvironment beneath adherent macrophages and osteoclasts. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Apr;175(2):266–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90191-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Davis T., Anderson D., Solam L., Beckmann M. P., Jerzy R., Dower S. K., Cosman D., Goodwin R. G. A receptor for tumor necrosis factor defines an unusual family of cellular and viral proteins. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1019–1023. doi: 10.1126/science.2160731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Munger W. E., Kung H. F., Takacs L., Durum S. K. Direct evidence for an intracellular role for tumor necrosis factor-alpha 1. Microinjection of tumor necrosis factor kills target cells. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):162–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis factor, other cytokines and disease. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:317–343. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor: specific binding and internalization in sensitive and resistant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7626–7630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli P. The pathophysiology of tumor necrosis factors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:411–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.002211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisnieski B. J., Bramhall J. S. Photolabelling of cholera toxin subunits during membrane penetration. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):319–321. doi: 10.1038/289319a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalman L. S., Wisnieski B. J. Characterization of the insertion of Pseudomonas exotoxin A into membranes. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):630–635. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.630-635.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalman L. S., Wisnieski B. J. Mechanism of insertion of diphtheria toxin: peptide entry and pore size determinations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3341–3345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]