Abstract
Innate lymphoid cells (ILC) specialize in the rapid secretion of polarized sets of cytokines and chemokines to combat infection and promote tissue repair at mucosal barriers.1–9 Their diversity and similarities with previously characterized NK cells and lymphoid tissue inducers (LTi) have prompted a provisional classification of all innate lymphocytes into groups 1, 2 and 3 based solely on cytokine properties,10 but their developmental pathways and lineage relationships remain elusive. Using lineage tracing and transfer studies, we identified and characterized a novel subset of lymphoid precursors in fetal liver and adult bone marrow that transiently expressed high amounts of PLZF, a transcription factor previously associated with NKT cell development.11,12 PLZFhigh cells were committed ILC progenitors with multiple ILC1, ILC2 and ILC3 potential at the clonal level. They excluded classical LTi and NK cells, but included a peculiar subset of NK1.1+DX5− ‘NK-like’ cells residing in the liver. Deletion of PLZF markedly altered the development of several ILC subsets, but not LTi or NK cells. PLZFhigh precursors also expressed high amounts of Id2 and GATA3, as well as TOX, a known regulator of PLZF-independent NK and LTi lineages.13 These findings establish novel lineage relationships between ILC, NK and LTi cells, and identify the common precursor to ILC, termed ILCP. They also reveal the broad, defining role of PLZF in the differentiation of innate lymphocytes.
To study the expression pattern of Zbtb16 encoding the transcription factor PLZF, which directs the developmental acquisition of the innate effector program of NKT cells,11,12,14,15 we inserted a sequence coding for a fusion of eGFP and Cre downstream of an IRES after the last exon of Zbtb16 (Extended Data Fig. 1a). As expected, eGFP was selectively expressed in the NKT lineage, with early developmental stages 1 and 2 showing higher levels than mature stage 3 cells, but was not found in the bone marrow common lymphoid precursor (CLP), T or B cells of PLZFGFPcre+/− mice (Fig. 1a). In PLZFGFPcre+/− mice carrying the ROSA26-floxstop-YFP fate-mapping allele, nearly all NKT cells expressed YFP, as expected, although ~35% of cells in all lymphoid and myeloid lineages were also labeled (Extended Data Fig. 1b-c and data not shown). Since hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) did not express eGFP but were already labeled by YFP, this ‘background’ reflected some expression of PLZF prior to the HSC stage, probably in multipotent embryonic cells. Indeed, after transfer of FACS-sorted YFP-negative bone marrow cells into lethally irradiated recipients, 94% of NKT cells still expressed YFP, whereas donor-derived CLPs, B and T cells were unlabeled (Fig. 1a). Thus, the experiments shown in Fig. 1 were conducted with such bone marrow chimeras, although all results were confirmed in non-chimeric reporter mice. Intriguingly, several innate lymphoid lineages, which arise from CLP, were also specifically labeled by YFP despite absence of eGFP expression. Thus, ILC2 in the lungs, intestinal lamina propria (LP), peritoneal cavity and mesenteric lymph nodes were all fate-mapped (Fig. 1a, 1d, Extended Data Fig. 1b and data not shown). Immature ILC2 in the bone marrow (iILC2s) expressed very low amounts of eGFP, but were already maximally labeled by YFP, suggesting expression of higher level of PLZF at an earlier stage of their development (Fig. 1a, d). Group 1 innate lymphocyte subsets exhibited heterogeneous PLZF tracing: while few splenic NK cells expressed YFP, intestinal intraepithelial NK-like cells (termed ILC11) were prominently labeled (Fig. 1b). In the liver, the recently described non-recirculating DX5−CD49a+ subset of CD3ε−NK1.1+ cells,16 was heavily labeled, whereas classical recirculating DX5+CD49a− NK cells were mostly negative. Different subsets of group 3 innate lymphocytes in the LP also showed markedly different patterns of tracing (Fig. 1c and Extended Data Fig. 2). CD4+ and CD4− LTi were not labeled, whereas NCR+ ILC3 prominently expressed YFP. In summary, PLZF lineage-tracing labeled not only ILC2 but also the subsets of group 1 and group 3 cells that are most clearly distinguishable from classical NK and LTi cells, respectively, and will hereafter be termed ILC1 and ILC3.
Extended Data Figure 1. PLZF expression and lineage tracing in PLZFGFPcre mice.
a, A sequence encoding an IRES and an eGFP-cre fusion protein was inserted immediately after the Zbtb16 stop codon in C57BL/6J ES cells and knock-in mice were bred to ACTB-FLPe mice to excise the neomycin resistance cassette and generate the PLZFGFPcre allele. b, FACS analysis of the indicated populations from PLZFGFPcre+/− ROSA26-YFP mice. c, Summary of data (mean ± s.e.m.) from 2-5 mice analyzed in 2 or more independent experiments.
Figure 1. ILC lineage tracing in PLZFGFPcre reporter mice.
a-c, Top rows, expression of eGFP by indicated cell-types of PLZFGFPcre+/+ mice (filled grey) and WT (open); Bottom rows, YFP expression in radiation chimeras reconstituted with YFP−Lin−Sca-1+cKit+ (LSK) bone marrow cells from PLZFGFPcre+/− ROSA26-YFP mice. CLP and iILC2 from bone marrow (BM); B & T and NK from spleen; NKT from thymus (eGFP), divided in early stage 1-2 and late stage 3, and from spleen (YFP); ILC2 from lung; DX5+ and DX5− NK cells from liver; ILC1 from intestinal IEL; LTi and ILC3 from LPL. BM iILC2 and lung ILC2 were identified as Lin−CD25+IL-7Rα+Thy1.2+; LPL ILC2 as CD3ε−CD19−CD25+KLRG1+; LPL NCR+ ILC3 as CD3ε−CD19−NKp46+NK1.1−; LPL CD4− LTi cells as CD3ε−CD19−IL-7Rα+KLRG1−CCR6+CD4−; LPL CD4+ LTi cells as CD3ε−CD19−CCR6+CD4+; and IEL ILC1 as CD3ε−CD19−NKp46+NK1.1+CD160+. FACS identification of the remaining subsets is defined in the methods section. d, summary of results (mean ± s.e.m). Data representative of 3-9 individual mice analyzed in at least 2 independent experiments.
Extended Data Figure 2. Gating strategy for analysis of ILC and LTi among LPL.
ILC2 cells were identified as IL-7Rα+ KLRG1+ among CD3ε− CD19− LPL (top left), and then gated Thy1.2+ (not shown). CD3ε− CD19− LPL were gated as IL-7Rα+ KLRG1− (top left) and then subsetted into CCR6+ CD4+ (CD4+ LTi cells) and CCR6+ CD4− (CD4− LTi cells) (bottom left). NCR+ ILC3 were identified as CD3ε− CD19− LPL that expressed NKp46 but not NK1.1 (top right).
Searching for the PLZF-expressing precursor of ILCs, we identified a rare subset of PLZFhigh cells in fetal liver and adult bone marrow. They exhibited a homogeneous lineage−(Lin−)IL-7Rα+cKit+α4β7high phenotype (Fig. 2a-b), similar to the CLP-derived subset previously suggested to contain precursors for LTi.17–20 The PLZFhigh population represented ~5% of Lin−IL-7Rα+cKit+ cells and ~30% of the α4β7high fraction (Fig. 2bc). It expressed Thy1 but lacked expression of markers associated with mature ILCs, NK or LTis such as CD4, CXCR6, CD25, IL-17RB, T1/ST2, Sca-1, CD122, NK1.1, CCR6, and NKp46 (Fig. 2c-d and data not shown). Interestingly, the PLZFhigh cells included a fraction of CD62Lhigh ICOSlow cells, likely representing the earliest developmental stage after PLZF expression, because PLZF characteristically induces the downregulation of CD62L and upregulation of ICOS.15,21 Transcriptional analysis of purified PLZFhigh cells compared with bone marrow CLP, iILC2 and NK progenitors (NKP), and with ILC3-enriched LPL, confirmed the very high amounts of Zbtb16 mRNA encoding PLZF, as well as of other key transcription factors such as Id2, Gata3, and Rora, which are required for ILC2 development3,22–25 (Fig. 2e and Extended Data Fig. 3) and Tcf7, a target of Notch required for ILC2 and ILC3.26,27 Notably, they expressed very high amounts of Tox, which is required for the development of both NK and LTi cells,13 and low but detectable amounts of Tbx21 and Rorc, the transcription factors associated with ILC1 and ILC3, respectively.1,6 Single-cell analysis by intracellular flow cytometry was performed after MACS-depletion of Lin+ cells in fetal liver and adult bone marrow, gating on Lin−IL-7Rα+α4β7high cells (Fig. 2f). PLZFhigh cells, which represented up to 40% of this population, characteristically co-expressed high amounts of both GATA3 and TOX. Interestingly, a small fraction of these PLZFhigh cells also expressed RORγt, although these were mostly found in the fetal liver and were rare in adult bone marrow. A distinct population consisting of RORγthigh PLZF− cells, which was more abundant in the fetal liver, co-expressed high levels of TOX but not GATA3, likely representing LTi precursors. Finally, a fraction of Lin−IL-7Rα+α4β7high cells lacked both PLZF and RORγt, but expressed TOX. These may be earlier undifferentiated precursors to the ILC and LTi lineages, and may also include precursors to classical NK cells.
Figure 2. PLZFhigh cells in fetal liver and bone marrow.
a, FACS analysis of total BM cells from adult WT littermate and PLZFGFPcre+/+ mice. Data representative of at least 3 independent experiments. b-c, eGFP expression is confined to the α4β7high population of indicated fractions in fetus and adult. Representative of at least 3 independent experiments. d, FACS analysis of PLZFhigh BM cells (solid line) and iILC2 (dashed line) compared with isotype controls (filled). iILC2 were gated as Lin−ICOS+T1/ST2+Sca-1+Thy1.2+ for CD25 profile, as CD25+CD62L−Sca-1+Thy1.2+ for CD44 profile, as CD25+CD44+Sca-1+Thy1.2+ for CD62L profile, as CD25+T1/ST2+Sca-1+Thy1.2+ for ICOS profile, as CD25+ICOS+Sca-1+Thy1.2+ for T1/ST2 profile, as CD25+Thy1.2+ for Sca-1 profile or as CD25+ICOS+Sca-1+ for Thy1.2 profile. Representative of at least 3 independent experiments. e, RT-qPCR analysis in bone marrow subsets as indicated. NKP are Lin−CD27+IL-7Rα−Flt3−CD122+ BM cells and ILC3-enriched LPL are CD3ε−CD19−IL-7Rα+Thy1.2+KLRG1−CD4− cells. Mean ± s.e.m of data from 2-3 independent experiments. f, Intracellular FACS analysis for transcription factors in cells as indicated. Representative of at least 3 independent experiments.
Extended Data Figure 3. Transcription factor expression by PLZFhigh bone marrow precursors.
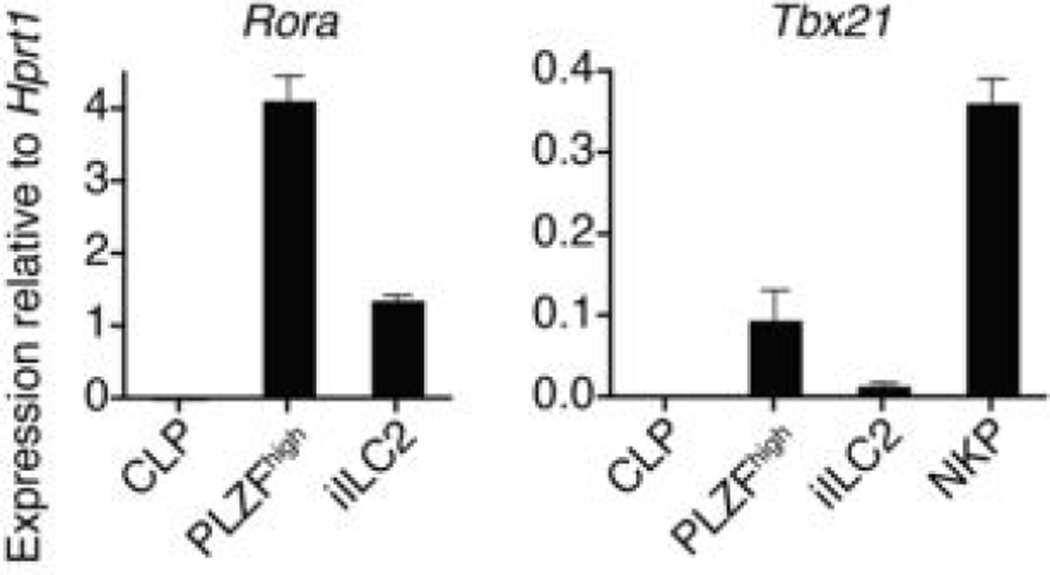
RT-qPCR analysis for Tbx21 and Rora as indicated. NKP are Lin− CD27+IL-7Rα− Flt3− CD122+ BM cells. Mean ± s.e.m of data from 2-3 independent experiments.
To determine precursor-product relationships, we injected a 1:1 mixture of PLZFhigh cells and CLP cells into Rag2−/−Il2rg−/− mice. The PLZFhigh cells, which were purified from a ROSA-floxstop-tdTomato x PLZFGFPcre+/− background to further ascertain their history of PLZF expression based on tdTomato expression, gave rise to a diversity of innate lineages, with the notable exception of CD4+ LTi (Fig. 3a). Significantly more peripheral ILC2 were derived from the PLZFhigh fraction at 5–7 weeks post-injection (Fig. 3a, c). Both progenitors gave rise to similar amounts of CD3ε−NK1.1+ group 1 cells, but CLP mostly generated the classical DX5+CD49a−NK1.1+ NK cells, whereas the PLZFhigh cells primarily generated a distinct DX5–CD49a+NK1.1+ ILC1 subset in the liver (Fig. 3b-c). PLZFhigh-derived NK1.1+CD3ε–TCRβ– cells were observed in the spleen and lungs, and expressed significantly more NKp46 than CLP-derived NK cells (Extended Data Fig. 4). Unlike CLP, PLZFhigh cells did not generate B cells consistent with their expression of Tcf7, suggesting that they had already received a Notch signal in vivo. They also gave rise to far fewer T cells than CLP after transfer into Rag2−/−Il2rg−/− mice in vivo (Fig. 3a, c) or after co-culture with fetal thymic stroma in vitro (Extended Data Fig. 5), indicating that PLZFhigh cells had also largely lost T cell potential. Thus, the PLZFhigh cell is an ILC precursor (ILCP) heavily committed to innate lymphoid lineages, excluding classical NK and LTi cells.
Figure 3. PLZFhigh cells are ILC progenitors.
a-c, CD45.2 Rag2−/−Il2rg−/− mice were injected with equivalent numbers of tdTomato+ PLZFhigh cells and CD45.1 CLP (800-1200 of each) and the progeny of these populations analyzed 5-7 weeks later by FACS, as indicated. Summary bar graph of mean percentages ± s.e.m. in c, with significant differences between PLZFhigh- (black bar) and CLP-derived (white bar) shown by *. LPL RORγt+ NCR+ cells were identified as CD3ε−CD19−RORγt+NKp46+CD4−; LPL RORγt+NCR− cells as CD3ε−CD19−RORγt+NKp46−CD4−; and LPL RORγt+CD4+ cells as CD3ε−CD19−RORγt+CD4+. Remaining populations were gated as indicated in Fig. 1. Data representative of 6-9 chimeras analyzed in at least 2 independent experiments. d, FACS analysis of Lin−IL-7Rα+α4β7higheGFP−CXCR6− cells sorted from PLZFGFPcre+/− BM and cultured on OP9 or OP9-DL1 for 48 h. Data representative of 3 independent experiments. e, FACS analysis of sorted PLZFhigh BM cells cultured on OP9 for indicated periods. Data representative of at least 4 replicate cultures for each time point from 2 or more independent experiments. f, FACS analysis of PLZFhigh or CLP cells from adult BM or fetal liver cultured on OP9 for 4 days. Data representative of at least 4 replicate cultures from 2 or more independent experiments. g, FACS analysis of representative colonies originating from single fetal liver PLZFhigh cells that were sorted and cultured into 96-well plates containing irradiated OP9 stromal cells for 5-6 days. ILC1 were characterized as ICOSlowα4β7− NK1.1+ populations, ILC2 as ICOShighα4β7−NK1.1−, and ILC3 as ICOSint/highα4β7+NK1.1−. The table summarizes the analysis of thirteen 96-well plates analyzed in four independent experiments (three plates in experiments 1, 2, and 4; four plates in experiment 3), with the average colony size ± s.e.m. as indicated. In experiment 4, we mixed 1:1 CD45.1/5.2 and CD45.2 PLZFGFPcre+/− fetal liver cells prior to single-cell sorting. All 122 colonies were either CD45.1/5.2 (n=59) or CD45.2 (n=63) ruling out doublet contamination as an explanation for the presence of mixed ILC colonies (p<0.01 Chi-Square). The cloning efficiency was 40% on average, with all but 17 colonies (not shown in the table) unambiguously assigned to defined ILC lineages.
Extended Data Figure 4. PLZFhigh-derived NK1.1+ cells are distinct from CLP-derived NK1.1+ cells.
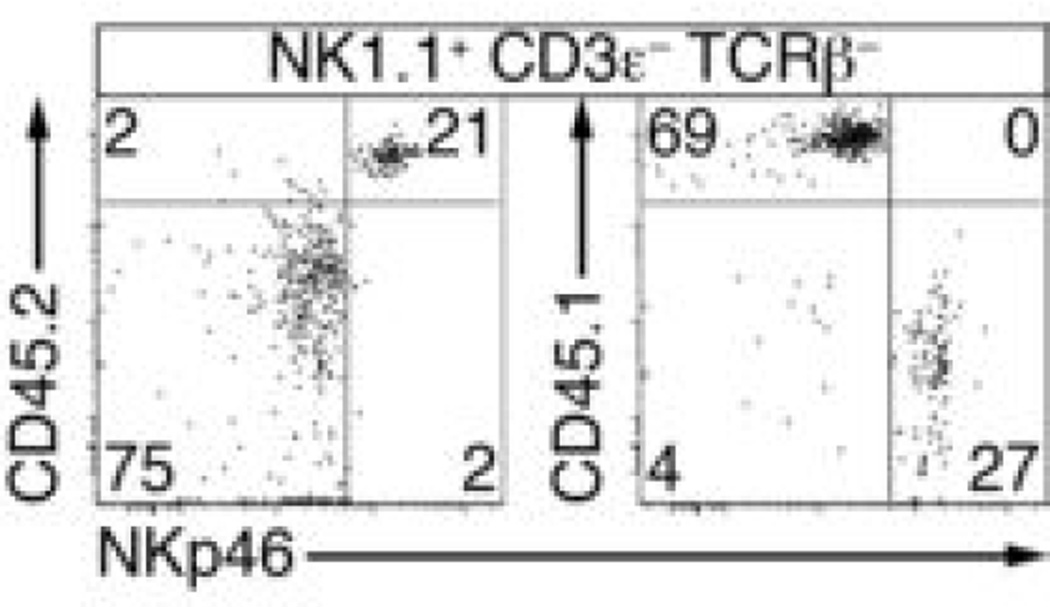
CD45.2 Rag2−/−Il2rg−/− mice were injected with equivalent numbers of CD45.2 PLZFhigh cells and CD45.1 CLP (800 of each) and the resulting NK1.1+ CD3ε− TCRβ− cells present in the spleen were analyzed 5-7 weeks later by FACS, as indicated. Note that PLZFhigh-derived cells expressed higher amount of surface NKp46, whether they were identified as CD45.2+ or as CD45.1− in reciprocal staining experiments. Similar results were obtained for lung NK1.1+ cells. Data representative of 5 chimeras from 2 independent experiments.
Extended Data Figure 5. FTOC of PLZFhigh cells.
FACS analysis of PLZFhigh and CLP cells (100 of each) co-cultured for 15 days in FTOC. The percentages of PLZFhigh- or CLP-derived cells that are CD3ε+ are summarized in the bar graph. Data representative of 7 independent cultures.
When cultured on OP9 stromal cells, the eGFP− fraction of Lin−IL-7Rα+cKit+α4β7high cells generated a small fraction of eGFP+ cells within two days of culture, which was increased upon culture on OP9-DL1 cells (Fig. 3d), confirming the precursor-product relationship and its promotion by Notch signals. To study the short-term fate of ILCP in vitro, we sorted Lin−IL-7Rα+cKit+α4β7high PLZFhigh cells from either adult bone marrow or fetal liver and cultured them on OP9 stromal cells, without Notch ligands, in the presence of non-polarizing IL-7 and stem cell factor (SCF). By 24 hours, a substantial fraction of the PLZFhigh population had already begun to downregulate eGFP and to upregulate either ICOS or CD122 (Fig. 3e), and by four days, the cells had resolved into three separate populations of ILC1 (ICOS−IL-17RB−T1/ST2−CD25−RORγt−GATA3−α4β7−CD122+NK1.1+NKp46+), ILC2 (ICOShighIL-17RB+T1/ST2+CD25+RORγt−GATA3+α4β7−CD122−NK1.1−NKp46−), and ILC3(ICOSintIL17RB−T1/ST2−CD25−RORγt+GATA3−α4β7+CD122−NK1.1−NKp46−/low) (Fig. 3f and Extended Data Fig. 6). This transient expression of PLZF prior to ILC differentiation may explain why fate-mapping by the ROSA-YFP allele in Fig. 1 did not quite reach 100% for these populations as in NKT cells where PLZF expression is permanent. Notably, ILC3 cells consistently arose with higher frequency from fetal liver than from adult bone marrow cells (Fig. 3f). In single-cell cultures with OP9 stromal cells, fetal PLZFhigh cells generated mixtures of ILC lineages, including triple and double ILC1, 2 and 3, in 58/500 wells (12%) as well as single ILC1, ILC2 or ILC3 populations in the remaining wells (Fig. 3g). Mixing CD45 allele-marked fetal liver cells prior to single-cell sorting confirmed that the mixed ILC colonies did not result from cell aggregates escaping exclusion during cell-sorting (Fig. 3g, expt 4) and post-sorting microscopic assessment confirmed single-cell seeding in each of 96 wells. These results indicated that the PLZFhigh cells contained a common ILC progenitor characterized by multiple ILC lineage potential at the clonal level, and that subsequent commitment to individual ILC1, 2 or 3 lineages occurred rapidly during the PLZFhigh stage of ILC development. Wells containing mixtures of ILC lineages were routinely larger than those with single lineages, suggesting that multipotent ILC progenitors retained greater proliferative capacity.
Extended Data Figure 6. Additional characterization of PLZFhigh cells after culture on OP9 cells.
a, FACS analysis of PLZFhigh or CLP cells from adult BM cultured on OP9 for 4 days showing expression of T1/ST2 on ICOShigh cells. Data representative of 4 replicate cultures from 2 independent experiments. b, FACS analysis of fetal liver PLZFhigh cells after culture on OP9 for 7 days, showing expression of GATA3 by ICOShigh cells and RORγt by ICOSint cells. Data representative of 2 independent experiments.
We then assessed the contribution of PLZF to ILC development in lethally irradiated recipients of a mixture of bone marrow from congenically labeled Zbtb16−/− and Zbtb16+/+ littermate donors (Fig. 4a). The production of ILC2 was markedly decreased in the PLZF-deficient compartment of all tissues, demonstrating a cell-intrinsic requirement of PLZF. Furthermore, residual immature ILC2 in the bone marrow expressed significantly less ICOS and more CD62L in the absence of PLZF (Fig. 4b-c), a phenotype entirely consistent with that of PLZF-deficient NKT cells,11,12,15 which accounts for altered recirculating properties and reduced frequencies in peripheral tissues. LTi cells were unaffected by the genetic deletion of PLZF, as expected (Fig. 4a). Other ILC3 cells, including NCR+ ILC3 were unaffected, despite their expression of PLZF during development. However, liver ILC1 (DX5−CD49a+) were profoundly affected, similar to ILC2, whereas classical (DX5+CD49a−) NK cells were not (Fig. 4a).
Figure 4. PLZF is required for ILC development.
a, Lethally irradiated CD45.1/2 mice were reconstituted with a mixture of CD45.2 Zbtb16−/− and CD45.1 WT BM and analyzed as indicated 5-7 weeks later. a, representative FACS analysis of LPL gated as indicated, and summary bar graph of mean percentages ± s.e.m for indicated populations, with significant variation from 1.00 indicated by *. Populations were gated as indicated in Fig. 3. Data representative of 6-10 chimeras analyzed in at least 2 independent experiments. b-c, FACS analysis of iILC2 from Zbtb16−/− mice and Zbtb16+/+ littermates, representative of 5 (b) and 8 (c) mice of each genotype analyzed in 3 or more independent experiments.
Our studies have identified the elusive CLP-derived common progenitor to the ILC1, ILC2, and ILC3 lineages and demonstrated close but distinct lineage relationships with classical NK and LTi cells. We have shown that a committed PLZFhigh ILCP emerges from within the same IL-7Rα+α4β7high population that includes precursors to LTi and possibly also to NK cells (Extended Data Fig. 7). It is uniquely distinguished and impacted by the rapid and transient upregulation of PLZF, whereas TOX is more broadly induced and reciprocally controls classical NK and LTi cells. The concomitant induction of GATA3, RORα, Tbet, and RORγt, which govern the polarization of ILC, parallels the sequence during PLZF-dependent NKT cell differentiation,28 indicating a broad and defining role of PLZF in the differentiation of innate lymphocyte lineages.
Extended Data Figure 7. Proposed model of ILC development.
A CLP-derived IL-7Rα+ α4β7+ population bifurcates into RORγthigh LTi precursors (LTiP) and PLZFhigh ILCP, the latter of which gives rise to all ILC lineages. Whether NKP develop directly from CLPs or progress through an IL-7Rα+ α4β7+ stage has yet to be determined.
Method Summary
PLZFGFPcre mice were generated by inserting a sequence encoding an IRES and eGFP-cre fusion protein immediately after the Zbtb16 stop codon through homologous recombination in C57BL/6J embryonic stem cells. For fate-mapping, they were crossed to mice carrying a ROSA26-fl-STOP-fl-YFP or a ROSA26-fl-STOP-fl-tdTomato allele. Bone marrow chimeras were generated by reconstituting lethally irradiated recipients with purified Lin− Sca-1+ cKit+ (LSK) bone marrow cells. PLZFhigh ILC precursors were purified from bone marrow or fetal liver and cultured in bulk or as single-cells deposited by flow cytometry in 96-well plates with irradiated OP9 or OP9-DL1 stromal cells and mIL-7 and mSCF. For in vivo transfers, PLZFhigh ILC precursors and CLP were purified from bone marrow and injected into Rag2−/−IL2rg−/− mice. Quantitative RT-PCR for transcription factors was performed using TaqMan primers.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank. W. Yokoyama for discussion; F. Gounari, and R. de Pooter for advice on OP9 cultures; H. Gudjonson for statistical advice; D. Leclerc, J. Cao, M. Olsen and R. Duggan for help with cell sorting; V. Bindokas and R. Mathew for help with fluorescence microscopy. This work was supported by NIH grants R01HL118092, R01AI038339, and P30DK42086 and by HHMI (A.B.).
Footnotes
Author Contributions
M.G.C, B.D.M, and P.A.V. designed research, performed experiments, and analyzed data. M.G.C. and A.B. wrote the paper. A.B. supervised the research.
Author Information
Reprints and permissions information is available at www.nature.com/reprints. The authors declare no competing financial interests. Readers are welcome to comment on the online version of the paper.
References
- 1.Fuchs A, et al. Intraepithelial type 1 innate lymphoid cells are a unique subset of IL-12- and IL-15-responsive IFN-gamma-producing cells. Immunity. 2013;38:769–781. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.02.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Neill DR, et al. Nuocytes represent a new innate effector leukocyte that mediates type-2 immunity. Nature. 2010;464:1367–1370. doi: 10.1038/nature08900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Moro K, et al. Innate production of T(H)2 cytokines by adipose tissue-associated c-Kit(+)Sca-1(+) lymphoid cells. Nature. 2010;463:540–544. doi: 10.1038/nature08636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Price AE, et al. Systemically dispersed innate IL-13-expressing cells in type 2 immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:11489–11494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1003988107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Monticelli LA, et al. Innate lymphoid cells promote lung-tissue homeostasis after infection with influenza virus. Nat Immunol. 2011;12:1045–1054. doi: 10.1031/ni.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Satoh-Takayama N, et al. Microbial flora drives interleukin 22 production in intestinal NKp46+ cells that provide innate mucosal immune defense. Immunity. 2008;29:958–970. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sanos SL, et al. RORgammat and commensal microflora are required for the differentiation of mucosal interleukin 22-producing NKp46+ cells. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:83–91. doi: 10.1038/ni.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Luci C, et al. Influence of the transcription factor RORgammat on the development of NKp46+ cell populations in gut and skin. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:75–82. doi: 10.1038/ni.1681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cella M, et al. A human natural killer cell subset provides an innate source of IL-22 for mucosal immunity. Nature. 2009;457:722–725. doi: 10.1038/nature07537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Spits H, et al. Innate lymphoid cells--a proposal for uniform nomenclature. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13:145–149. doi: 10.1038/nri3365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Savage AK, et al. The transcription factor PLZF directs the effector program of the NKT cell lineage. Immunity. 2008;29:391–403. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.07.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kovalovsky D, et al. The BTB-zinc finger transcriptional regulator PLZF controls the development of invariant natural killer T cell effector functions. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:1055–1064. doi: 10.1038/ni.1641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Aliahmad P, de la Torre B, Kaye J. Shared dependence on the DNA-binding factor TOX for the development of lymphoid tissue-inducer cell and NK cell lineages. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:945–952. doi: 10.1038/ni.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Savage AK, Constantinides MG, Bendelac A. Promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger turns on the effector T cell program without requirement for agonist TCR signaling. J Immunol. 2011;186:5801–5806. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Constantinides MG, Picard D, Savage AK, Bendelac A. A naive-like population of human CD1d-restricted T cells expressing intermediate levels of promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger. J Immunol. 2011;187:309–315. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Peng H, et al. Liver-resident NK cells confer adaptive immunity in skin-contact inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:1444–1456. doi: 10.1172/JCI66381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yoshida H, et al. Expression of alpha(4)beta(7) integrin defines a distinct pathway of lymphoid progenitors committed to T cells, fetal intestinal lymphotoxin producer, NK, and dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2001;167:2511–2521. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.5.2511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sawa S, et al. Lineage relationship analysis of RORgammat+ innate lymphoid cells. Science. 2010;330:665–669. doi: 10.1126/science.1194597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Possot C, et al. Notch signaling is necessary for adult, but not fetal, development of RORgammat(+) innate lymphoid cells. Nat Immunol. 2011;12:949–958. doi: 10.1038/ni.2105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cherrier M, Sawa S, Eberl G. Notch, Id2, and RORgammat sequentially orchestrate the fetal development of lymphoid tissue inducer cells. J Exp Med. 2012;209:729–740. doi: 10.1084/jem.20111594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gleimer M, von Boehmer H, Kreslavsky T. PLZF Controls the Expression of a Limited Number of Genes Essential for NKT Cell Function. Front Immunol. 2012;3:374. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hoyler T, et al. The transcription factor GATA-3 controls cell fate and maintenance of type 2 innate lymphoid cells. Immunity. 2012;37:634–648. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.06.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mjosberg J, et al. The transcription factor GATA3 is essential for the function of human type 2 innate lymphoid cells. Immunity. 2012;37:649–659. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wong SH, et al. Transcription factor RORalpha is critical for nuocyte development. Nat Immunol. 2012;13:229–236. doi: 10.1038/ni.2208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Halim TY, et al. Retinoic-acid-receptor-related orphan nuclear receptor alpha is required for natural helper cell development and allergic inflammation. Immunity. 2012;37:463–474. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.06.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yang Q, et al. T cell factor 1 is required for group 2 innate lymphoid cell generation. Immunity. 2013;38:694–704. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.12.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mielke LA, et al. TCF-1 Controls ILC2 and NKp46+RORgammat+ Innate Lymphocyte Differentiation and Protection in Intestinal Inflammation. J Immunol. 2013;191:4383–4391. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Constantinides MG, Bendelac A. Transcriptional regulation of the NKT cell lineage. Curr Opin Immunol. 2013;25:161–167. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2013.01.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 1.Lee EC, et al. A highly efficient Escherichia coli-based chromosome engineering system adapted for recombinogenic targeting and subcloning of BAC DNA. Genomics. 2001;73:56–65. doi: 10.1006/geno.2000.6451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.