Abstract
Background: Melanoma is the most fatal form of skin cancer. Different signalling pathways and proteins will be differentially expressed to pace with the tumour growth. Thus, these signalling molecules and proteins are become potential targets to halt the progression of cancer. The present works were attempted to investigate the underlying molecular mechanisms of anticancer effects of Phyllanthus (P.amarus, P.niruri, P.urinaria and P.watsonii) on skin melanoma, MeWo cells. Methods: The ten cancer-related pathways reporter array was performed by transfection of plasmid construct of transcription factor-responsive reporter of each pathway in MeWo cells. The affected pathways in MeWo cells after treatment of Phyllanthus extracts were determined using luciferase assay. Western blot, 2D gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry analysis were performed to identity and confirm the affected proteins and signalling molecules in treated cells. Results: The ten-pathway reporter array revealed five different cancer-related signalling pathways were altered by Phyllanthus species in MeWo cells; NFκB, Myc/Max, Hypoxia, MAPK/ERK and MAPK/JNK (p<0.05). Western blot revealed that their intracellular signalling molecules including pan-Ras, c-Raf, RSK, phospho-Elk1, c-myc, Akt, HIF-1α, Bcl-2, and VEGF were down-regulated with concurrent of up-regulation; Bax, phospho-JNK-1/2 and phospho-GSK3β, in MeWo cells upon Phyllanthus treatment (p<0.05). Proteomics-based approach was performed and MS/MS results revealed that 52 differential expressed proteins were identified (p<0.05) and involved in tumour growth, metastasis, apoptosis, glycogenesis and glycolysis, angiogenesis, protein synthesis and energy metabolism. Conclusion: This study provides insight into the regulation on multiple survival signalling pathways by Phyllanthus in melanoma and might be a therapeutic target for cancer treatment.
Keywords: Phyllanthus, apoptosis, signaling, melanoma.
Introduction
Malignant melanoma is the most aggressive and life-threatening skin cancer with increasing incidences over the past decades. This disease is prevalent in faired-skin populations, and is easy to detect due to its abnormal colour, size and pigmentation. Despite accounting for only 4% of all skin cancers, melanoma confers 80% of skin cancer induced death 1. Although, melanoma has high recovery rates if detected early, it has a high tendency of metastasizing, dropping the 5-year survival rate less than 5% 2. The underlying cause of melanoma progression and metastasis is poorly understood, hence limiting the effectiveness of current treatments and contributing to increased cases of recurrence or refractory melanoma. Thus, it is vital that future anticancer agents can combat both local and metastatic melanoma.
Many vital biological processes are tightly regulated by complex signalling networks and signal transduction occurs when an external stimuli (e.g. stress, UV) initiate changes in a cell upon binding of ligand to surface receptor. This causes conformational changes to the intracellular signalling molecules, which in turn elicit cellular responses. Disruption of these pathways or intracellular communication can result in various diseases, including cancer 3, 4. Thus, signalling molecules have become potential targets to halt cancer progression by inducing apoptosis and/or inhibiting tumour metastasis and angiogenesis.
The mitogen activated protein kinase family members (MAPKs) are highly expressed in melanoma and it is believed this pathway mediates melanoma metastasis by inducing proteolytic enzymes (e.g. MMP) activation that leads to degradation of basement membrane, and also by regulating genes involved in cell migration, cell survival and growth 5. MAPK pathway also has been found in other cancers such as breast, colon, prostate and lung, suggesting a role for MAPK pathway in tumour progression and metastasis 6-9. Disrupting this pathway may halt cancer progression by inhibition of tumour angiogenesis, proliferation, invasion and metastasis. In melanoma, several other pathways have also been shown to be highly expressed including PI3K/Akt and NFκB signal transduction pathways and have been associated with tumour development and progression 10-12.
During tumour metastasis, high oxygen delivery and consumption requires activation of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), which induce transcription of growth-related genes such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The activation of VEGF can stimulate tumour angiogenesis and thereby increase the oxygen delivery 13. These changes in hypoxic cancer cells allow them to acquire invasive and metastatic properties as well as to develop resistance to chemotherapy 14.
The pharmacological effects of Phyllanthus, a widely distributed medicinal plant, are many including antiviral 15, anti-bacteria 16 and anti-hepatotoxic 17 as well as with anticancer properties 18. Previously, we reported four species of Phyllanthus to possess anti-proliferative effect and apoptosis inducing capabilities in melanoma cell 19. Currently, to understand the mechanism behind the anticancer properties of Phyllanthus on melanoma cells, we investigated the changes to intracellular signalling network upon treatment. At the same time, we also seek to identify potential new targets for therapeutic intervention in skin melanoma.
Materials and Methods
Preparation of Phyllanthus Extracts
P.amarus, P.niruri, P.urinaria, and P.watsonii were the four different species of Phyllanthus plant used in this study. Both aqueous and methanolic extracts of each Phyllanthus were prepared as described previously by Tang et al. 19. Briefly, plant samples were freshly harvested, washed, and freeze dried. For aqueous extract preparation, ultra-pure water was used to soak the dried plant samples and absolute methanol was used to prepare the methanolic extract. The samples then were homogenized with extraction buffer and the supernatant was collected after three rounds of extraction. Lyophilized forms of aqueous and methanolic extracts were obtained after evaporation and stored at -20ºC prior to experiments.
Chemicals and antibodies
EMEM (Eagle's minimum essential medium) was purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO). Foetal bovine serum (FBS) was obtained from Gibco. Antibodies; pan-Ras, c-Raf, RSK, phosopho-Elk1, c-Jun, phospho-JNK-1/2, c-myc, HIF-1α, Bcl-2, Bax, NFκB p50 and p52, VEGF, phospho-GSK3β, phospho-p38 MAPK and p53 were obtained from MERCK, San Diego, USA. While urea, CHAPS, DTT IPG buffer (pH 3-11NL), SDS, bromophenol blue Tris, glycine, acrylamide, bis-acrylamide were purchased from GE Healthcare.
Cell culture
Skin melanoma MeWo (HTB-65) cell line was purchased from American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, MD) and cultured with EMEM. This medium was supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated foetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco). Cells were maintained in culture at 37ºC with 5% CO2 and 95% humidity. Cells were harvested using 0.25% trypsin (Hyclone) when they reach 70-80% confluency in culture flasks. Cells undergoing exponential growth were used throughout the experiments.
Dual luciferase pathway reporter transient transfection
Ten different cancer-related pathways analysis was performed using the Cignal Finder 10-Pathway Reporter Arrays (SA Biosciences, Fredrick, MD). Optimization of the conditions, including amount and incubation time of plasmid construct of transcription factor-responsive reporter of each pathway into the cells, was performed to ensure highly transfection efficiency and inhibit transformation. After optimization, MeWo cells were seeded into a 96-well white plate and incubated overnight at 37°C. Transient transfection was conducted by adding plasmid construct of transcription factor-responsive reporter of each pathway and controls to cells and incubated overnight in a 37°C incubator. Then, cells were treated with Phyllanthus extracts at their respective IC50 values (Table 1) and further incubated for 48 hours. Each transfection condition was carried in triplicates. Each of the pathways/reporters consist an inducible transcription factor responsive firefly luciferase reporter and constitutively expressing Renilla construct. Renilla construct is to act as an internal control for normalizing transfection efficiencies and monitor cell viability. After 48h of Phyllanthus treatment, the changes in expression of each pathway in cells were determined by measuring the generated firefly and Renilla luminescent signals using the Dual-Glo Luciferase Assay system (Promega, Madison, WI) on the Glomax machine (Promega, USA). The relative luciferase units were determined by dividing the firefly to Renilla luciferase activity ratio.
Table 1.
Treatment of MeWo cells at different IC50 values of Phyllanthus extracts.
| IC50 ± SEM (µg/ml) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Phyllanthus species | Extracts | MeWo |
| P.amarus (PA) | Aqueous (H20) | 193.3 ± 1.3 |
| Methanolic (MeOH) | 133.3 ± 2.9 | |
| P.niruri (PN) | Aqueous (H20) | 260.0 ±2.4 |
| Methanolic (MeOH) | 153.3 ± 2.6 | |
| P.urinaria (PU) | Aqueous (H20) | 193.3 ± 1.1 |
| Methanolic (MeOH) | 56.2 ± 3.2 | |
| P.watsonii (PW) | Aqueous (H20) | 160.0 ± 3.2 |
| Methanolic (MeOH) | 100.7 ± 2.0 |
Western Blot analysis
The intracellular signalling molecules in MAPK (pan-Ras, c-Raf, phospho-Elk1, RSK, c-Jun, phospho-JNK-1/2, Akt and phospho-p38 MAPK), Myc/Max (c-myc) and Hypoxia (c-myc, HIF-1α, VEGF and GSK3β), NFκB (p50 and p52), as well as p53 (p53, Bcl-2, Bax) pathways were chosen for western blot analysis. Beta actin was used as a loading control. Briefly, protein lysates from Phyllanthus-treated (Table 1) and untreated groups after 48 hours of treatment were resolved on 12% SDS-PAGE gels. After electrophoresis, proteins were transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes, followed by blocking and incubation with primary antibodies overnight at 4°C. Subsequently, the membranes were incubated with appropriate secondary antibodies (horseradish-conjugated goat anti-mouse or anti-goat IgG) for 1h. Open-source software, ImageJ was used to measure band intensities. The percentage of protein expression was calculated by dividing the band intensity of treated group with the untreated group.
Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis
A total of 500mg protein was subjected to 2D gel electrophoresis according to the manufacturer's instructions (GE Healthcare). Briefly, total protein was extracted from cells (untreated and treated groups) after 48 hours of treatment (Table 1), by incubation with cold lysis buffer on ice for 30 minutes. The protein pellets were re-solubilized in rehydration solution (8 M urea, 2% CHAPS, 40 mM DTT, 0.5% IPG buffer pH3-11NL, bromophenol blue). A total of 500mg protein rehydrated into 13cm immobilized pH gradient (IPG) strips (pH 3-11 nonlinear) (GE Healthcare) overnight. The first dimension was run on the IPGphor III machine (GE Healthcare) at 20°C with the following settings: step 1 at 500V for 1h; step 2 at 500-1000V for 1h; step 3 at 1000-8000V for 2.5h, and step 4 at 8000V for 0.5h. Upon completion of first dimensional separation, the strip was equilibrated as following; first reduction with 64.8 mM of dithiothreitol-SDS equilibration buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 8.8], 6 M urea, 30% glycerol, 2% SDS, 0.002% bromophenol blue) for 15 minutes, followed by alkylation with 135.2 mM of iodoacetamide-SDS equilibration buffer for another 15 minutes. The second dimension electrophoresis was performed by electrophoresing the samples in 12.5% SDS acrylamide gels by using the SE600 Ruby system (GE Healthcare) at 25°C in an electrode buffer (25 mM Tris, 192 mM glycine, and 0.1% [wt/vol] SDS) with the following settings: step 1 at 100V/gel for 45 minutes; step 2 at 300V/gel until the run is completed. After electrophoresis, the gels were fixed with destaining solution for 30 minutes, followed by staining with hot Coomasie blue for 30 minutes. Lastly, the gels were scanned using Ettan DIGE Imager (GE Healthcare). Gel images were analyzed using PDQuest 2-D Analysis Software (Bio-Rad, USA) and only protein spots which showed significant differences (more than 1.0 fold) were selected for mass spectrometry analysis.
Protein Digestion, Desalting and MALDI-TOF/TOF Analysis
The significant differential expressed protein spots were excised from the polyacrylamide gels and kept in sterile 1.5ml eppendorf tubes. Excised spots (gel plugs) were washed with destaining solution (50 mM NH4HCO3) until the gel plugs were clear. The gel plugs were then incubated with reducing solution (100 mM NH4HCO3 containing 10 mM DTT) for 30 min at 60°C. The gel plugs were alkylated with 100 mM NH4HCO3 containing 55 mM of IAA for 20 min in the dark and followed with three times washed with 50% acetone in 100 mM NH4HCO3 for 20 min each. The gel plugs were then rehydrated with 100% ACN. In-gel digestion step, trypsin gold (Promega, Mass Spectrometry Grade) was used and added into gel plug and incubated overnight at 37°C. Proteins were extracted from gel plugs and purified by using Ziptip (Ziptip C18, Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA). The eluted proteins were mixed with MATRIX solution and spotted on MALDI plate using dry droplet method and analysed using Ab Sciex Tof/TofTM instrument. The generated peptides were blasted with MASCOT Search Algorithm (Version 2.1.0) to identify the possible proteins.
Statistical Analysis
For all experiments, results were expressed as the mean ± standard error (SEM) of data obtained from triplicate experiments using SPSS software. The Student's t-test was used where values of p < 0.05 were considered significant.
Results
Alteration in expression of several cancer pathways
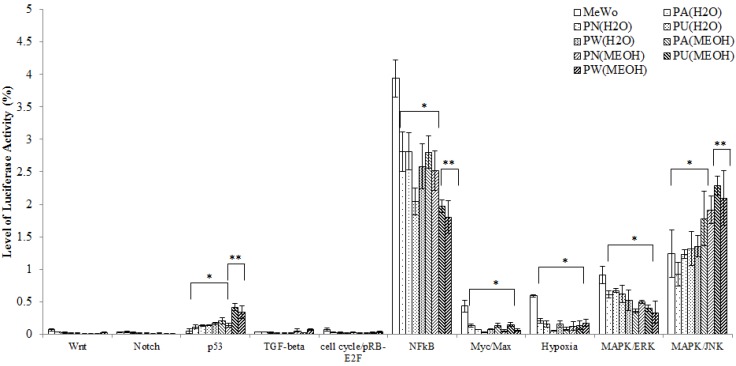
Ten cancer-related pathways including Wnt, Notch, p53, TGF-β, cell cycle/pRB-E2F, NFκB, Myc/Max, Hypoxia, MAPK/ERK and MAPK/JNK pathways were investigated. The differential expression of each of these pathways in treated and untreated MeWo cells is presented in Figure 1. From Figure 1, it was noted, that in the untreated MeWo cells, six (p53, NFκB, Myc/Max, Hypoxia and MAPK/ERK and MAPK/JNK) investigated pathways were expressed to regulate the cells growth and survival. However, the expressions of NFκB, Myc/Max, hypoxia and MAPK/ERK showed significant down-regulation in Phyllanthus treated MeWo cells (p<0.05). Contrarily, the expressions of p53 and MAPK/JNK pathways showed significant up-regulation in the treated cells (p<0.05). Other pathways investigated were found to be not significantly affected by Phyllanthus extracts (p>0.05).
Figure 1.
The expression of transcription activities in ten-cancer related pathways of untreated and treated MeWo. Four different pathways (NFκB, Myc/Max, Hypoxia, and MAPK/ERK) were significantly down-regulated (p<0.05) and two pathways (p53 and MAPK/JNK) were up-regulated (p<0.05). Other pathways showed no significant change. Bars show the mean percentage ± SEM. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs control.
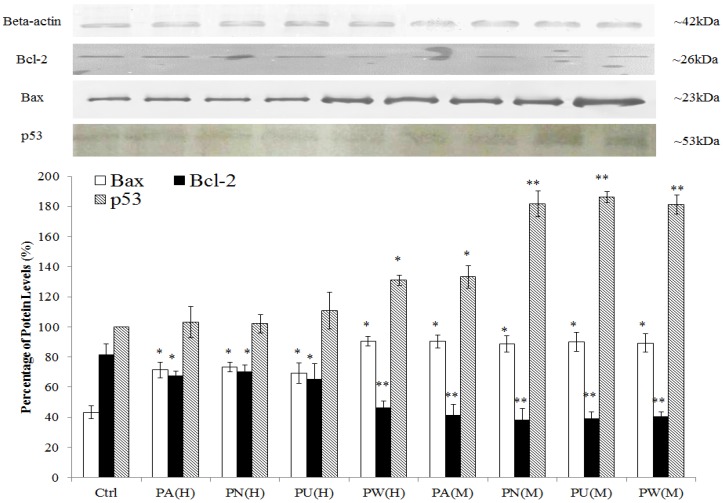
Induction of apoptosis through p53 protein and disruption in anti-apoptotic/pro-apoptotic balance
As shown in Figure 2, p53 protein was detected at 53 kDa and their expression was significantly up-regulated in Phyllanthus treated MeWo as compared to untreated MeWo cells (p<0.05). In addition, other apoptosis related proteins including Bcl-2 and Bax were detected at 23 kDa and 26 kDa, respectively. The graph shows a significant increase of pro-apoptoic protein, Bax in treated MeWo cells (p<0.05) with a concurrent decrease in anti-apoptotic protein, Bcl-2 (p<0.05) as compared to untreated MeWo cells. Among the species of Phyllanthus, both aqueous and methanolic extracts of P.watsonnii showed the most significant changes on p53, Bax and Bcl expression, followed by P.urinaria, P.niruri and P.amarus.
Figure 2.
Induction of apoptosis through p53 pathway and disruption in anti-apoptotic/pro-apoptotic balance. The expression of pro-apoptotic (Bax) was up-regulated and anti-apoptotic (Bcl-2) protein was down-regulated in MeWo cells after treatment with Phyllanthus extracts. Bars show the mean percentage ± SEM. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs control.
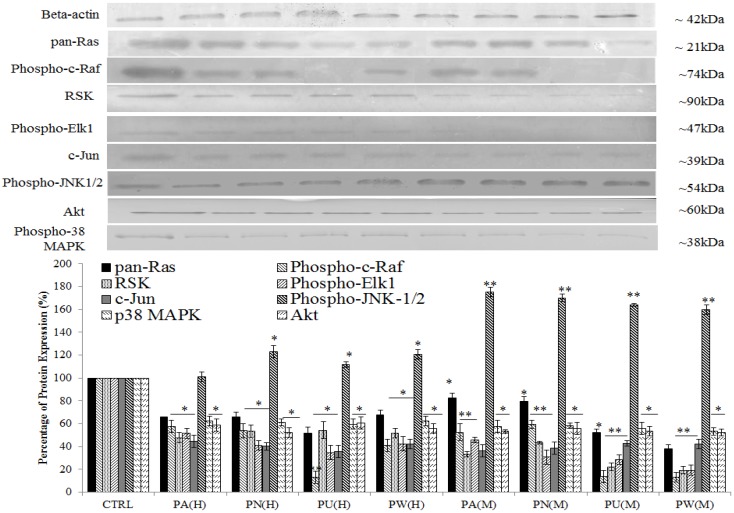
Phyllanthus alters activities of intracellular signalling molecules in affected pathways
Three up-stream activator molecules in MAPK pathway; pan-Ras, c-Raf and Akt were highly expressed in untreated MeWo cells (Figure 3). The constitutive activations of these molecules can activate their downstream targets including MAPK/ERK (RSK, phospho-Elk1, c-Jun/AP-1), MAPK/JNK (phospho-JNK-1/2) and p38 (phospho-p38 MAPK). As shown in Figure 3, the expressions of all these intracellular signalling molecules were detected in untreated MeWo cells indicating their involvement in regulating MeWo cells' growth. However, all these intracellular signalling molecules had notable down-regulated expression (p<0.05) except for phospho-JNK-1/2 protein, which showed a slight increase in expression in treated MeWo cells.
Figure 3.
Inhibition of MAPK/ERK and p38 MAPK but activation of MAPK/JNK pathways in MeWo cells. The expressions of Ras, Raf, phospho-Elk1, RSK, phospho-JNK-1/2, c-Jun, phospho-p38 MAPK and Akt in treated MeWo were significantly down-regulated. Bars show the mean percentage ± SEM. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs control.
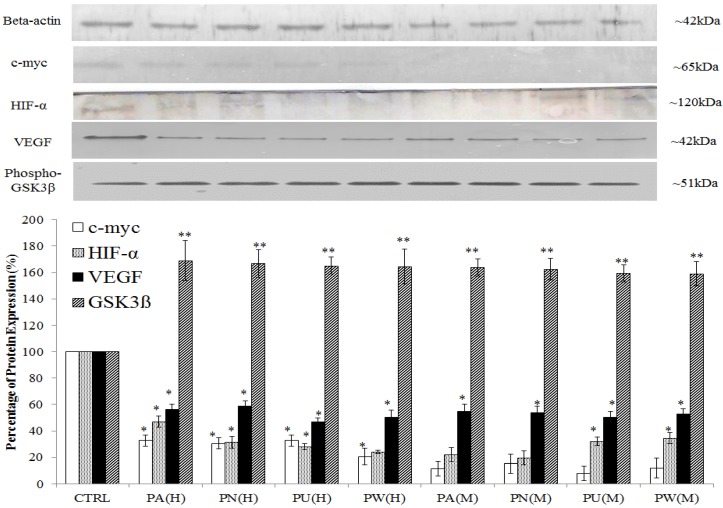
The expression of Myc/Max and hypoxia signalling pathway was detected at increased levels in MeWo cells (Figure 1) with a high percentage down-regulation after treatment with Phyllanthus. In these pathways, four intracellular signalling molecules were detected by western blot; c-myc, HIF-1α, VEGF and phospho-GSK3β. As shown in Figure 4, the expression of the c-myc was detected at 65 kDa and its expression was noticed significantly decreased by aqueous- (p<0.05) and methanolic-Phyllanthus (p<0.01) treated MeWo cells as compared to untreated cells. The downstream targets of c-myc; HIF-1α and VEGF were detected at 120 kDa and 50 kD, respectively. Their expressions were significantly down-regulated in treated MeWo cells as compared to untreated cells (p<0.05). A negative regulator of c-myc, phosphorylated glycogen synthase kinase 3-beta (phospho-GSK3β) was detected at 51 kDa and its expression was significantly up-regulated in treated cells as compared to untreated cells (p<0.01). Two intracellular signalling molecules in NFκB pathway; p50 and p52 were detected at 50 kDa and 52 kDa, respectively (Figure 5). Both NFκB proteins were significantly down-regulated in MeWo cells after treatment with Phyllanthus extracts (p<0.05).
Figure 4.
Phyllanthus alters expression in c-Myc and Hypoxia pathways of MeWo cells. The expressions of c-Myc, HIF-1α and VEGF were significantly down-regulated in conjunction with up-regulation of phospho-GSK3β. Bars show the mean percentage ± SEM. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs control.
Figure 5.
Inhibition of NFκB pathway in MeWo cells by Phyllanthus extracts. The expressions of p50 and p52 proteins were significantly down-regulated. Bars show the mean percentage ± SEM.*P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs control.
Among the Phyllanthus species, P.urinaria showed strongest effect on expression of intracellular signalling molecules in affected pathways, followed by P.watsonii, P.amarus and P.niruri for both aqueous and methanolic extracts.
Proteomic profiling of the differentially expressed proteins in Phyllanthus treated MeWo cells
Differentially expressed proteins in MeWo cells were statistically defined based on two criteria: 1) degree of intensity >1.0 fold (Protein scores greater than 52 are significant, p<0.05) and 2) reoccurrence in the three repeated experiments (Figure 6). According to these criteria, 52 proteins were identified by MS/MS and grouped in four biological processes based on their functions described in UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot protein database (Table 2).
Figure 6.
Proteomic profiling of the differentially expressed proteins in Phyllanthus extracts-treated MeWo cells. The differentially expressed proteins in (A) untreated, (B) aqueous- and (C) methanolic-treated of MeWo cells.
Table 2.
Fold changes of differential expressed proteins in aqueous- and methanolic-treated MeWo cells. Symbols“+” indicate up-regulation, and “-” indicate down-regulation. PA: P.amarus; PN: P.niruri; PU: P.urinaria and PW: P.watsonii.
| No | UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot (Accession number) | Protein | Phyllanthus | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA(H) | PN(H) | PU(H) | PW(H) | PA(M) | PN(M) | PU(M) | PW(M) | |||
| I | Cell Adhesion, Migration, Invasion and Metastasis and Angiogenesis | |||||||||
| 1 | P98172 | Ephrin-B1 | -1.46 | -1.47 | -1.53 | -1.48 | -1.59 | -1.58 | -1.57 | -1.65 |
| 2 | P61163 | Alpha-centractin | -1.42 | -1.33 | -1.57 | -1.45 | -1.58 | -1.75 | -1.58 | -1.74 |
| 3 | Q13895 | Bystin | -1.43 | -1.57 | -1.34 | -1.45 | -1.46 | -1.59 | -1.48 | -1.65 |
| 4 | P13646 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 13 | 1.42 | 1.47 | 1.46 | 1.57 | 1.74 | 1.58 | 1.57 | 1.64 |
| 5 | P08670 | Vimentin | -1.73 | -1.92 | -1.72 | -2.01 | -1.85 | -1.73 | -1.72 | -1.92 |
| 6 | P04179 | Superoxide dismutase [Mn], mitochondrial | -1.29 | -1.54 | -1.57 | -1.39 | -1.58 | -1.85 | -1.65 | -1.48 |
| 7 | P07437 | Tubulin beta chain | -1.42 | -1.48 | -1.67 | -1.97 | -1.57 | -1.58 | -1.59 | -1.54 |
| 8 | P47755 | F-actin-capping protein subunit alpha-2 | -1.34 | -1.33 | -1.63 | -1.58 | -1.68 | -1.58 | -1.53 | -1.63 |
| 9 | Q8TEW0 | Partitioning defective 3 homolog | -1.32 | -1.49 | -1.32 | -1.68 | -1.50 | -1.56 | -1.68 | -1.58 |
| II | Proliferation, Cell Cycle, and Apoptosis | |||||||||
| 10 | P68400 | Casein kinase II subunit alpha | -2.28 | -1.97 | -1.83 | -2.08 | -2.18 | -2.08 | -1.95 | -2.07 |
| 11 | P50583 | Bis(5'-nucleosyl)-tetraphosphatase [asymmetrical] | -1.47 | -1.53 | -1.48 | -1.37 | -1.58 | -1.74 | -1.63 | -1.75 |
| 12 | O60220 | Mitochondrial import inner membrane translocase subunit Tim8 | -1.56 | -1.35 | -1.64 | -1.62 | -1.63 | -1.65 | -1.68 | -1.58 |
| 13 | Q9BQ83 | Structure-specific endonuclease subunit SLX1 | -1.37 | -1.49 | -1.57 | -1.48 | -1.93 | -1.57 | -1.74 | -1.63 |
| 14 | Q6Q0C0 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRAF7 | 1.48 | 1.57 | 1.65 | 1.57 | 1.45 | 1.78 | -1.69 | -1.549 |
| 15 | P0CJ76 | Humanin-like protein 9 | -1.56 | -1.68 | -1.58 | -1.58 | -1.62 | 1.67 | 1.73 | 1.78 |
| 16 | P17931 | Galectin-3 | -1.58 | -1.75 | -1.63 | -1.69 | -1.68 | -1.68 | -1.64 | -1.78 |
| 17 | P31943 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H | -1.49 | -1.57 | -1.34 | -1.63 | -1.56 | -1.68 | -1.58 | -1.84 |
| 18 | P08758 | Annexin A5 | -1.42 | -1.57 | -1.73 | -1.57 | -1.57 | -1.47 | -1.59 | -1.47 |
| 19 | Q969E4 | Transcription elongation factor A protein-like 3 | -1.32 | -1.47 | -1.57 | -1.74 | -1.62 | -1.48 | -1.68 | -1.57 |
| 20 | Q9H930 | Nuclear body protein SP140-like protein | -1.32 | -1.38 | -1.55 | -1.57 | -1.58 | -1.58 | -1.57 | -1.58 |
| 21 | P27348 | 14-3-3 protein theta | -1.42 | -1.47 | -1.29 | -1.58 | -1.57 | -1.67 | -1.45 | -1.34 |
| 22 | P62937 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A | -1.54 | -1.23 | -1.47 | -1.54 | -1.58 | -1.62 | -1.57 | -1.46 |
| 23 | Q14929 | Zinc finger protein 169 | -1.69 | -1.57 | -1.33 | -1.84 | -1.75 | -1.55 | -1.47 | -1.56 |
| 24 | O75791 | GRB2-related adapter protein | -1.59 | -1.43 | -1.4 | -1.83 | -1.56 | -1.48 | -1.53 | -1.28 |
| 25 | O00165 | HCLS1-associated protein X-1 | -1.69 | -1.72 | -1.97 | -1.66 | -1.84 | -1.86 | -1.67 | -1.78 |
| 26 | O95243 | Methyl-CpG-binding domain protein 4 | -1.49 | -1.63 | -1.56 | -1.57 | -1.66 | -1.54 | -1.63 | -1.64 |
| 27 | P78417 | Glutathione transferase omega - 1 | -1.45 | -1.53 | -1.46 | -1.57 | -1.64 | -1.53 | -1.48 | -1.58 |
| 28 | Q06830 | Peroxiredoxin-1 | -1.45 | -1.42 | -1.46 | -1.47 | -1.64 | -1.74 | -1.53 | -1.48 |
| 29 | P50453 | Serpin B9 | -1.32 | -1.31 | -1.53 | -1.56 | -1.57 | -1.45 | -1.55 | -1.63 |
| 30 | Q8ND25 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ZNRF1 | -1.48 | -1.64 | -1.67 | -1.57 | -1.56 | -1.46 | -1.53 | -1.58 |
| 31 | Q06210 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ARIH2 | -1.48 | -1.58 | -1.64 | -1.6 | -1.57 | -1.65 | -1.45 | -1.64 |
| 32 | Q9Y4L5 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF115 | -1.56 | -1.43 | -1.66 | -1.73 | -1.69 | -1.58 | -1.58 | -1.56 |
| III | Glycogenesis and glycolysis | |||||||||
| 33 | Q969E3 | Glucosamine--fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase [isomerizing] 2 | -1.57 | -1.58 | -1.58 | -1.53 | -1.65 | -1.73 | 1.67 | -1.48 |
| 34 | P00558 | Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 3D | -1.33 | -1.58 | -1.53 | -1.64 | -1.56 | -1.37 | -1.57 | -1.74 |
| 35 | P06733 | Alpha-enolase | -1.42 | -1.57 | -1.74 | -1.73 | -1.58 | -1.57 | -1.65 | -1.69 |
| 36 | P04406 | Pyruvate kinase isozymes M1/M2 | -1.45 | -1.67 | -1.47 | -1.63 | -1.78 | -1.36 | -1.36 | -1.75 |
| 37 | P04075 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 | -1.57 | -1.58 | -1.61 | -1.64 | -1.48 | -1.53 | -1.52 | -1.58 |
| IV | Protein Synthesis and Energy Metabolism | |||||||||
| 38 | P17174 | Aspartate aminotransferase, cytoplasmic | -1.26 | -1.67 | -1.68 | -1.56 | -1.57 | -1.58 | -1.53 | -1.58 |
| 39 | Q9UBC9 | Small proline-rich protein 3 | -1.63 | -1.75 | -1.74 | -1.56 | -1.67 | -1.68 | -1.73 | -1.57 |
| 40 | P41247 | Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 4 | -1.63 | -1.32 | -1.49 | -1.66 | -1.53 | -1.53 | -1.58 | -1.64 |
| 41 | Q9HBU6 | Ethanolamine kinase 1 | -1.39 | -1.75 | -1.57 | -1.83 | -1.48 | -1.75 | -1.68 | -1.74 |
| 42 | P62195 | 26S protease regulatory subunit 8 | -1.53 | -1.64 | -1.57 | -1.74 | -1.75 | -1.56 | -1.64 | -1.54 |
| 43 | Q5VTE0 | Putative elongation factor 1-alpha-like 3 | -1.48 | -1.64 | -1.64 | -1.57 | -1.57 | -1.64 | -1.58 | -1.85 |
| 44 | Q5TGZ0 | Mitochondrial inner membrane organizing system protein 1 | -1.53 | -1.63 | -1.74 | -1.56 | -1.67 | -1.68 | -1.64 | -1.75 |
| 45 | P07339 | Cathepsin D | -1.54 | -1.54 | -1.65 | -1.46 | -1.68 | -1.68 | -1.47 | -1.58 |
| 46 | Q9Y587 | AP-4 complex subunit sigma-1 | -1.33 | -1.57 | -1.56 | -1.36 | -1.68 | -1.74 | -1.58 | -1.67 |
| 47 | P00568 | Adenylate kinase | -1.58 | -1.39 | -1.53 | -1.57 | -1.56 | -1.63 | -1.68 | -1.58 |
| 48 | P80294 | Metallothionein-1H | -1.29 | -1.74 | -1.73 | -1.45 | -1.59 | -1.58 | -1.76 | -1.68 |
| 49 | Q76KX8 | Zinc finger protein 534 | -1.59 | -1.46 | -1.57 | -1.64 | -1.54 | -1.63 | -1.58 | -1.58 |
| 50 | Q9Y6H3 | Mitochondrial inner membrane protease ATP23 homolog | -1.59 | -1.56 | -1.57 | -1.67 | -1.68 | -1.67 | -1.68 | -1.63 |
| 51 | Q8WVM8 | Sec1 family domain-containing protein 1 | -1.44 | -1.56 | -1.64 | -1.54 | -1.76 | -1.65 | -1.75 | -1.64 |
| 52 | Q9NVH6 | Trimethyllysine dioxygenase, mitochondrial | -1.58 | -1.48 | -1.58 | -1.54 | -1.79 | -1.68 | -1.53 | -1.66 |
In Group I (cell adhesion, migration, invasion and metastasis), 8 proteins were found to be differentially expressed in treated MeWo cells. Of these, type I cytoskeletal 13 keratin was found to be up-regulated (p<0.05). Its expression was significantly up-regulated about 1.4-1.8 folds higher than untreated cells. The other identified proteins were down-regulated in treated cells; Ephrin-B1, alpha-centractin, bystin, superoxide dismutase, tubulin beta chain, F-actin-capping protein subunit alpha-2 and partitioning defective 3 homolog.
In Group II (proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis), 21 proteins were significantly down-regulated in MeWo cells after treatment with Phyllanthus extracts. Among these down-regulated proteins, HCLS1-associated protein X-1 and casein kinase II subunit alpha proteins showed the greatest reduction at 1.5-2.3 folds in their expression as compared to untreated cells (p<0.05).
In Group III (glycogenesis and glycolysis), 5 down-regulated enzymes were detected in treated MeWo cells. These identified enzymes were glucosamine--fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase, protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 3D, alpha-enolase, pyruvate kinase isozymes M1/M2 and phosphoglycerate kinase 1.
In Group IV (protein synthesis and energy metabolisms), 15 proteins were found to be down-regulated at the range of 1.3-1.9 in Phyllanthus treated MeWo cells as compared to untreated cells. Eight of these proteins; E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ARIH2 and RNF115, aspartate aminotransferase, 26S protease regulatory subunit 8, putative elongation factor 1-alpha-like 3, mitochondrial inner membrane organizing system protein 1 (MINOS), zinc finger protein, Sec1 and trimethyllysine dioxygenase, have been known to be involved in regulation of mitochondrial integrity and protein ubiquitination.
Discussion
Understanding cell signalling in cancer is of paramount importance and may provide potential targets for anticancer agents to induce apoptosis and/or inhibitions tumour metastasis and angiogenesis. Previously, we showed that Phyllanthus was capable of exhibiting selective cytotoxicity on melanoma cancer cells and apoptosis induction 19, was most likely attributed to the mixture bioactive compounds within the plant.
Bcl-2-family proteins play an important role in cell death regulation including apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy 26. Overexpression of the anti-apoptotic proteins (e.g. Bcl-2) and suppression of pro-apoptotic proteins (e.g. Bax) have been demonstrated to inhibit cell death leading to formation of cancer 26. In our study, the expression of Bax proteins was greatly up-regulated accompanied by down-regulation of Bcl-2 expression in Phyllanthus-treated MeWo cells (Figure 2). The highly expressed Bax protein could induce changes in mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP), causing the release of cytochrome c. This release will then induce caspase activation 27, 28 as detected in our previous report 19 and also inhibit the inhibitors of apoptosis (IAP) (e.g. SMAC and OMI/Htra2) 28, 29. Finally, this will leads to apoptosis induction in MeWo cells. In addition, another apoptotic protein, p53 was also found to be up-regulated in treated MeWo cells which could induce apoptosis through its transcription activity to produce pro-apoptotic proteins (e.g. Bid, Bax, Nova and PUMA) which in turn leads to cytochrome c release and activation of capases 30, 31.
Ras gene is frequently found high expressed in human cancers 32 whereby it triggers various other intracellular signalling cascades to regulate genes-driven malignancy of cancer including proliferation, evasion of apoptosis, metastasis and angiogenesis 33. When MeWo cells were treated with Phyllanthus, a down-regulation of Ras proteins was observed and this will eventually lead to suppression of its downstream targets; Raf and Akt as observed (Figure 3).
In melanoma, active ERK1/2 molecule has been shown to activate RSK and Elk molecules; subsequently activating c-Jun and c-Fos proteins. The combination of c-Jun and c-Fos will form activator protein 1 (AP-1), a transcription factor that translocates into nucleus and regulates cell survival genes 33. In addition, p38 MAPK also enhances AP-1 formation by producing c-Fos through activation on Elk protein 5. However, in Phyllanthus-treated MeWo cells, all the above-mentioned MAPK intracellular signalling molecules were noted to be down-regulated (Figure 3).
Tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) is a cytokine capable of activating multiple downstream signalling pathways, including caspases, IκB kinase (IKK) and JNK 34, 35. TNF-α does not usually induce apoptosis unless NFκB has been inactivated 35. During TNF-α induced apoptosis, caspases will be activated, and IKK will be inactivated causing NFκB to bind with its inhibitor; subsequently inhibiting the ability to regulate genes including inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) family.
The inhibition of NFκB was observed in Phyllanthus-treated MeWo cells by measurements of NFkB-1 (p50) and NFkB -2 (p52). Furthermore, we believed that the down-regulation of NFkB pathway in treated MeWo cells can inhibit proliferation, metastasis and angiogenesis by suppressing the MMP, VEGF, and IL-8, and anti-apoptotic proteins (bcl-xl, cIAP) as well as inducing programmed cell death in MeWo cells 37, 42.
The PI3K/Akt pathway is found highly expressed in advanced melanoma and inhibits apoptosis 43-45. However, the suppression of Akt protein in treated MeWo could induce apoptosis by the activation pro-apoptotic factors (Bad, GSK3ß, procaspase-9 and TRAIL/APO-2L (TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand) 46, 47 and inhibition of anti-apoptotic factors (cyclic AMP response element-binding protein (CREB) and the IκB kinase (IKK) 47. The up-regulation of phosphorylated GSK3β was detected in treated MeWo cells can further degrade c-myc as was observed; possibly halting tumour growth with induction of S-phase arrest as we report previously 19. In addition, the cell cycle arrest at S-phase could be due to the activation of p53 as p21 is a major target for transactivation by p53 51 which will then induce cell cycle arrest at S-phase through two mechanisms; (1) interaction of p21 with the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) 52 and/or (2) p21 directly inhibiting the activity of cyclin E/CDK2 complexes 53.
According to Warburg effect, the microenvironment surrounding a solid tumour is an anaerobic/ hypoxia state. This will lead cancer cells to up-regulate the expression of intracellular signalling molecules and enzymes that involved anaerobic glycolytic pathway 54-56. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) is an important protein activated upon hypoxic condition or low oxygen level 13. The target genes of HIF are involved in angiogenesis (e.e VEGF), cell survival (e.g. IGF-1) and metastasis (e.g. LOX, PAI-1) and all these process can drive tumour progression 14. In our study, Phyllanthus extracts were noted to inhibit the glycolytic pathway and ATP production in melanoma cells by down-regulating the HIF-1α protein and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) (Figure 5). In addition, several of glycolytic enzymes were found to be down-regulated in MeWo cells after treatment with Phyllanthus extracts such as glucosamine--fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase, protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 3D, alpha-enolase, pyruvate kinase isozymes M1/M2 and phosphoglycerate kinase 1. The down-regulation in PI3K/Akt and Ras/MAPK pathways in treated MeWo cells are believed to be involved in the inhibition of hypoxia pathway 14.
The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a cellular process that allows immotile epithelial cells to become motile mesenchymal cells, promoting carcinoma invasion and metastasis as well as resistance to apoptosis 57. Several signalling networks including Ras/MAPK-, PI3K/Akt-, Wnt- and NFκB-dependent pathways in EMT were found to be down regulated in treated MeWo cells, and thus were believed to inhibit metastasis of melanoma 58. The inhibition on melanoma metastasis was further imposed with the up-regulation of type I cytoskeletal 13 keratin and concurrent down-regulation of vimentin in MeWo cells after treatment with Phyllanthus. Despite the exact mechanism of up-regulation of keratin during EMT being unclear but its down-regulation in treated cells can restrict the motility of cells, thus halting metastasis 59, 60. Vimentin also plays an important role in cell survival by stabilizing the ERK protein and governing its translocation into the nucleus 61 and by preventing assembly of Raf-14-3-3 complex enabling Ras protein to be continuously expressed 62. Therefore, the down regulation of vimentin could induce apoptosis via suppression on ERK- and Ras-dependent survival pathways in MeWo cells.
Following the treatment of Phyllanthus, many tightly regulated proteins were found to be altered in MeWo cells. Of these, two proteins, HCLS1-associated protein X-1 (HAX1) and casein kinase II subunit alpha. HAX-1 interacts with HS1 and α-subunit of Gα13 heterotrimeric G protein for cell migration 63, 64 and is highly expressed in hypoxic tumor progression 65, 66. Protein kinase casein kinase II (CK2) is a highly conserved protein serine/threonine kinase and is found highly expressed in cancers 67-70. CK2 can be anti-apoptotic via (1) inhibition on Max, a transcriptional partner of the c-myc, from caspase-mediated degradation 71, (2) activation of Bid, a pro-apoptotic protein 72, and (3) confer protection from Fas- and drug-triggered apoptosis 72, 73. Therefore, down-regulation of CK2 in treated MeWo cells could elicit apoptosis induction and could increase the susceptibility of MeWo cells to apoptotic inducer chemotherapeutic agents 74-76.
Mitochondrion is involved in protein synthesis and energy metabolism for cancer cell survival, transformation, invasion, and metastasis. The alteration in mitochondrial integrity and ubiquitination components such as E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ARIH2 and RNF115, aspartate aminotransferase, 26S protease regulatory subunit 8, putative elongation factor 1-alpha-like 3, mitochondrial inner membrane organizing system protein 1 (MINOS), zinc finger protein, Sec1 and trimethyllysine dioxygenase, by Phyllanthus in MeWo cells could inhibit ATP production and stability of proteins, therefore halting cancer growth. In addition, disruption on mitochondria stability could elicit apoptosis in MeWo by releasing its components, cytochrome c 36.
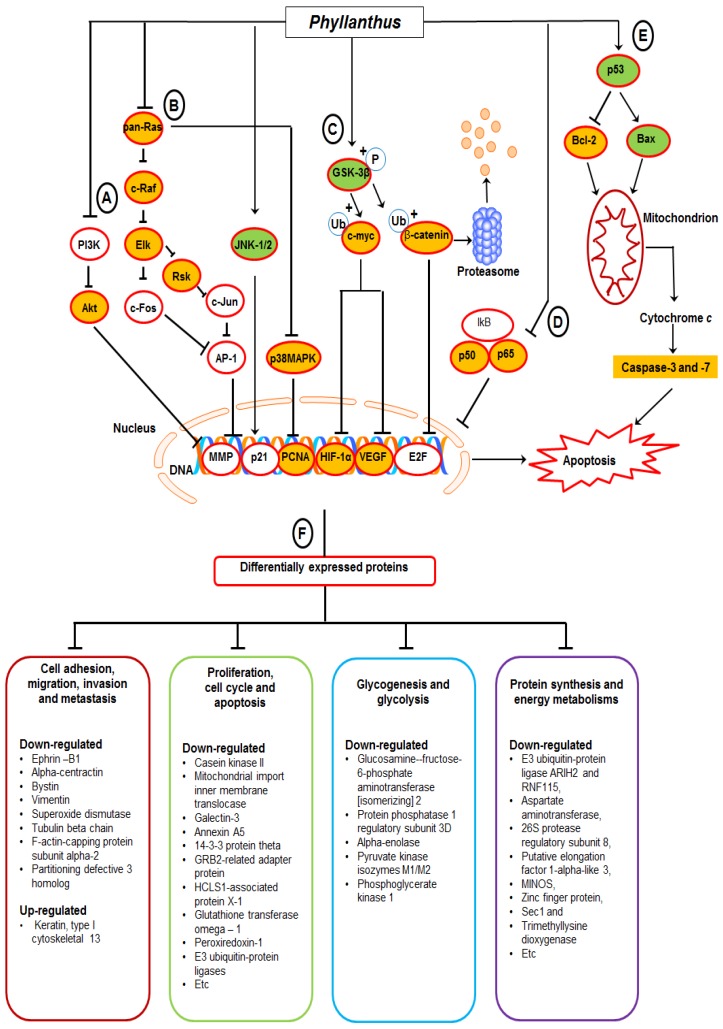
Based on the findings, we proposed a schematic presentation of the possible mechanism behind the anti-cancer activity of Phyllanthus extracts in MeWo cells (Figure 7). In conclusion, this study revealed a comprehensive perspective of the possible mechanism behind the anti-cancer activity of Phyllanthus extracts by inspection of their regulation in multiple signalling pathways and protein-protein interaction in melanoma MeWo cells. In addition, the identified differentially expressed proteins could become potential targets for new anticancer agent development.
Figure 7.
A proposed schematic diagram of (A) PI3K/Akt, (B) MAPKs, (C) Myc/Max and Hypoxia, (D) NFκB, and (E) p53 apoptosis signalling pathways as well as (F) multiple proteins regulations in Phyllanthus-treated MeWo cells. See the text for discussion.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Postgraduate Research Grant, University of Malaya (PV053/2011B), University of Malaya Research Grant (UMRG) (RG391-11HTM) and Malaysian Agricultural and Research Development Institute (MARDI) (53-02-03-1002).
Abbreviations
- NFκB
Nuclear Factor-kappa B
- MAPK
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
- ERK
Extracellular signal-regulated kinases
- JNK
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- RSK
Ribosomal s6 kinase
- Elk1
E twenty-six (ETS)-like transcription factor 1
- HIF-1α
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha
- VEGF
vascular endothelial growth factor
- GSK3β
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta
- MMP
matrix metalloproteinase
- PI3K
Phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase.
References
- 1.Miller AJ, Mihm Jr MC. Melanoma. New England Journal of Medicine. 2006;355:51–65. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra052166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tsao H, Sober AJ. Melanoma treatment update. Dermatologic clinics. 2005;23:323. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2004.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Anagnostopoulos K, Tentes I, Kortsaris A. Cell signaling in cancer. Journal of BU ON: official journal of the Balkan Union of Oncology. 2008;13:17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Martin GS. Cell signaling and cancer. Cancer cell. 2003;4:167–74. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dhillon A, Hagan S, Rath O, Kolch W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:3279–90. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Oh AS, Lorant LA, Holloway JN, Miller DL, Kern FG, El-Ashry D. Hyperactivation of MAPK induces loss of ERα expression in breast cancer cells. Molecular Endocrinology. 2001;15:1344–59. doi: 10.1210/mend.15.8.0678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Barault L, Veyrie N, Jooste V, Lecorre D, Chapusot C, Ferraz JM. et al. Mutations in the RAS-MAPK, PI (3) K (phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase) signaling network correlate with poor survival in a population-based series of colon cancers. International journal of cancer. 2008;122:2255–9. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fecher LA, Amaravadi RK, Flaherty KT. The MAPK pathway in melanoma. Current opinion in oncology. 2008;20:183–9. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0b013e3282f5271c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chen KH, Weng MS, Lin JK. Tangeretin suppresses IL-1β-induced cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 expression through inhibition of p38 MAPK, JNK, and AKT activation in human lung carcinoma cells. Biochemical pharmacology. 2007;73:215–27. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.09.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Polakis P. The many ways of Wnt in cancer. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 2007;17:45–51. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2006.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.McNulty SE, Tohidian NB, Meyskens FL. RelA, p50 and inhibitor of kappa B alpha are elevated in human metastatic melanoma cells and respond aberrantly to ultraviolet light B. Pigment Cell Research. 2001;14:456–65. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0749.2001.140606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dhawan P, Singh AB, Ellis DL, Richmond A. Constitutive activation of Akt/protein kinase B in melanoma leads to up-regulation of nuclear factor-κB and tumor progression. Cancer research. 2002;62:7335–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ziello JE, Jovin IS, Huang Y. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF)-1 regulatory pathway and its potential for therapeutic intervention in malignancy and ischemia. The Yale Journal of Biology and Medicine. 2007;80:51. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Poon E, Harris AL, Ashcroft M. Targeting the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) pathway in cancer. Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine. 2009. 11. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 15.Lam WY, Leung KT, Law PTW, Lee SMY, Chan HLY, Fung KP. et al. Antiviral effect of Phyllanthus nanus ethanolic extract against hepatitis B virus (HBV) by expression microarray analysis. Journal of cellular biochemistry. 2006;97:795–812. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Doughari J, Sunday D. Antibacterial Activity of Phyllanthus muellerianus. Pharmaceutical biology. 2008;46:400–5. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ahmed B, Al-Howiriny A, Mathew R. Anti-hepatotoxic activity of Phyllanthus fraternus. Pharmazie. 2002;57:855–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Huang ST, Pang JHS, Yang RC. Anti-cancer effects of Phyllanthus urinaria and relevant mechanisms. Chang Gung Med J. 2010. 33. [PubMed]
- 19.Tang YQ, Jaganath IB, Sekaran SD. Phyllanthus spp. induces selective growth inhibition of PC-3 and MeWo human cancer cells through modulation of cell cycle and induction of apoptosis. PLoS One. 2010;5:e12644.. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012644. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kasibhatla S, Tseng B. Why target apoptosis in cancer treatment? Molecular cancer therapeutics. 2003;2:573–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lowe SW, Lin AW. Apoptosis in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:485–95. doi: 10.1093/carcin/21.3.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ho HH, Chang CS, Ho WC, Liao SY, Wu CH, Wang CJ. Anti-metastasis effects of gallic acid on gastric cancer cells involves inhibition of NF-κB activity and downregulation of PI3K/AKT/small GTPase signals. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2010;48:2508–16. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2010.06.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Huang ST, Yang RC, Pang JHS. Aqueous extract of Phyllanthus urinaria induces apoptosis in human cancer cells. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine. 2004;32:175–83. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X04001849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sun J, Hai Liu R. Cranberry phytochemical extracts induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cancer letters. 2006;241:124–34. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.10.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gross A, McDonnell JM, Korsmeyer SJ. BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes & Development. 1999;13:1899–911. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.15.1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Coultas L, Strasser A. The role of the Bcl-2 protein family in cancer. Seminars in cancer biology: Elsevier. 2003:115–23. doi: 10.1016/s1044-579x(02)00129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yip K, Reed J. Bcl-2 family proteins and cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27:6398–406. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chang HY, Yang X. Proteases for cell suicide: functions and regulation of caspases. Microbiology and molecular biology reviews. 2000;64:821–46. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.64.4.821-846.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Fridman JS, Lowe SW. Control of apoptosis by p53. Oncogene. 2003;22:9030–40. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schuler M, Bossy-Wetzel E, Goldstein JC, Fitzgerald P, Green DR. p53 induces apoptosis by caspase activation through mitochondrial cytochrome c release. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2000;275:7337–42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.10.7337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bos JL. Ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer research. 1989;49:4682–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Roberts P, Der C. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:3291–310. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lin A. Activation of the JNK signaling pathway: breaking the brake on apoptosis. Bioessays. 2002;25:17–24. doi: 10.1002/bies.10204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Karin M, Lin A. NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nature immunology. 2002;3:221–7. doi: 10.1038/ni0302-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Debatin KM. Apoptosis pathways in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy. 2004;53:153–9. doi: 10.1007/s00262-003-0474-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Aggarwal BB. Nuclear factor-κB: the enemy within. Cancer cell. 2004;6:203–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Baldwin Jr AS. The NF-κB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annual review of immunology. 1996;14:649–81. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.14.1.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wang CY, Mayo MW, Korneluk RG, Goeddel DV, Baldwin Jr AS. NF-κB antiapoptosis: induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science. 1998;281:1680–3. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5383.1680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Farina AR, Cappabianca L, DeSantis G, Ianni ND, Ruggeri P, Ragone M. et al. Thioredoxin stimulates MMP-9 expression, de-regulates the MMP-9/TIMP-1 equilibrium and promotes MMP-9 dependent invasion in human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. FEBS letters. 2011;585:3328–36. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.09.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bond M, Chase AJ, Baker AH, Newby AC. Inhibition of transcription factor NF-κB reduces matrix metalloproteinase-1,-3 and-9 production by vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovascular research. 2001;50:556–65. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(01)00220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Shishodia S, Aggarwal BB. Guggulsterone inhibits NF-κB and IκBα kinase activation, suppresses expression of anti-apoptotic gene products, and enhances apoptosis. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2004;279:47148–58. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408093200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Majewski N, Nogueira V, Bhaskar P, Coy PE, Skeen JE, Gottlob K. et al. Hexokinase-mitochondria interaction mediated by Akt is required to inhibit apoptosis in the presence or absence of Bax and Bak. Molecular cell. 2004;16:819–30. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.11.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rathmell JC, Fox CJ, Plas DR, Hammerman PS, Cinalli RM, Thompson CB. Akt-directed glucose metabolism can prevent Bax conformation change and promote growth factor-independent survival. Molecular and cellular biology. 2003;23:7315–28. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.20.7315-7328.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Dai DL, Martinka M, Li G. Prognostic significance of activated Akt expression in melanoma: a clinicopathologic study of 292 cases. Journal of clinical oncology. 2005;23:1473–82. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.07.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Majumder PK, Sellers WR. Akt-regulated pathways in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2005;24:7465–74. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Vara JÁF, Casado E, de Castro J, Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C, González-Barón M. PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treatment Reviews. 2004;30:193–204. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2003.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Dang CV, O'Donnell KA, Zeller KI, Nguyen T, Osthus RC, Li F. The c-Myc target gene network. Seminars in cancer biology: Elsevier. 2006:253–64. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2006.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Dominguez-Sola D, Ying CY, Grandori C, Ruggiero L, Chen B, Li M. et al. Non-transcriptional control of DNA replication by c-Myc. Nature. 2007;448:445–51. doi: 10.1038/nature05953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Robinson K, Asawachaicharn N, Galloway DA, Grandori C. c-Myc accelerates S-phase and requires WRN to avoid replication stress. PLoS One. 2009;4:e5951. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Radhakrishnan SK, Feliciano CS, Najmabadi F, Haegebarth A, Kandel ES, Tyner AL. et al. Constitutive expression of E2F-1 leads to p21-dependent cell cycle arrest in S phase of the cell cycle. Oncogene. 2004;23:4173–6. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Waga S, Hannon GJ, Beach D, Stillman B. The p21 inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases controls DNA replication by interaction with PCNA. Nature. 1994;369:574–8. doi: 10.1038/369574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Shishodia S, Sethi G, Ahn KS, Aggarwal BB. Guggulsterone inhibits tumor cell proliferation, induces S-phase arrest, and promotes apoptosis through activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase, suppression of Akt pathway, and downregulation of antiapoptotic gene products. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2007;74:118–30. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.03.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science. 1956;123:309–14. doi: 10.1126/science.123.3191.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Xu R, Pelicano H, Zhou Y, Carew JS, Feng L, Bhalla KN. et al. Inhibition of glycolysis in cancer cells: a novel strategy to overcome drug resistance associated with mitochondrial respiratory defect and hypoxia. Cancer Research. 2005;65:613–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Guppy M. The hypoxic core: a possible answer to the cancer paradox. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2002;299:676–80. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(02)02710-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Voulgari A, Pintzas A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis: mechanisms, markers and strategies to overcome drug resistance in the clinic. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Reviews on Cancer. 2009;1796:75–90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2009.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Yilmaz M, Christofori G. EMT, the cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews. 2009;28:15–33. doi: 10.1007/s10555-008-9169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Stockinger A, Eger A, Wolf J, Beug H, Foisner R. E-cadherin regulates cell growth by modulating proliferation-dependent β-catenin transcriptional activity. The Journal of cell biology. 2001;154:1185–96. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200104036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Valdés F, Murillo MM, Valverde ÁM, Herrera B, Sánchez A, Benito M. et al. Transforming growth factor-beta activates both pro-apoptotic and survival signals in fetal rat hepatocytes. Experimental cell research. 2004;292:209–18. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2003.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Perlson E, Michaelevski I, Kowalsman N, Ben-Yaakov K, Shaked M, Seger R. et al. Vimentin binding to phosphorylated Erk sterically hinders enzymatic dephosphorylation of the kinase. Journal of Molecular Biology. 2006;364:938–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.09.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Tzivion G, Gupta VS, Kaplun L, Balan V. 14-3-3 proteins as potential oncogenes. Seminars in Cancer Biology: Elsevier. 2006:203–13. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2006.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Suzuki Y, Demoliere C, Kitamura D, Takeshita H, Deuschle U, Watanabe T. HAX-1, a novel intracellular protein, localized on mitochondria, directly associates with HS1, a substrate of Src family tyrosine kinases. The Journal of Immunology. 1997;158:2736–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Radhika V, Onesime D, Ha JH, Dhanasekaran N. Gα13 stimulates cell migration through cortactin-interacting protein Hax-1. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2004;279:49406–13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408836200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Ramsay AG, Keppler MD, Jazayeri M, Thomas GJ, Parsons M, Violette S. et al. HS1-associated protein X-1 regulates carcinoma cell migration and invasion via clathrin-mediated endocytosis of integrin αvβ6. Cancer Research. 2007;67:5275–84. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Klein C, Grudzien M, Appaswamy G, Germeshausen M, Sandrock I, Schäffer AA. et al. HAX1 deficiency causes autosomal recessive severe congenital neutropenia (Kostmann disease) Nature Genetics. 2006;39:86–92. doi: 10.1038/ng1940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Litchfield DW. Protein kinase CK2: structure, regulation and role in cellular decisions of life and death. Biochemical Journal. 2003;369:1. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.MÜNSTERMANN U, FRITZ G, SEITZ G, YIPING L, SCHNEIDER HR, ISSINGER OG. Casein kinase II is elevated in solid human tumours and rapidly proliferating non-neoplastic tissue. European Journal of Biochemistry. 2005;189:251–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Landesman-Bollag E, Romieu-Mourez R, Song DH, Sonenshein GE, Cardiff RD, Seldin DC. Protein kinase CK2 in mammary gland tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2001;20:3247–57. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Faust RA, Niehans G, Gapany M, Hoistad D, Knapp D, Cherwitz D. et al. Subcellular immunolocalization of protein kinase CK2 in normal and carcinoma cells. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. 1999;31:941–9. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(99)00050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Krippner-Heidenreich A, Talanian RV, Sekul R, Kraft R, Thole H, Ottleben H. et al. Targeting of the transcription factor Max during apoptosis: phosphorylation-regulated cleavage by caspase-5 at an unusual glutamic acid residue in position P1. Biochemical Journal. 2001;358:705. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3580705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Desagher S, Osen-Sand A, Montessuit S, Magnenat E, Vilbois F, Hochmann A. et al. Phosphorylation of bid by casein kinases I and II regulates its cleavage by caspase 8. Molecular Cell. 2001;8:601–11. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Guo C, Yu S, Davis AT, Wang H, Green JE, Ahmed K. A potential role of nuclear matrix-associated protein kinase CK2 in protection against drug-induced apoptosis in cancer cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2001;276:5992–9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M004862200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ruzzene M, Penzo D, Pinna LA. Protein kinase CK2 inhibitor 4, 5, 6, 7-tetrabromobenzotriazole (TBB) induces apoptosis and caspase-dependent degradation of haematopoietic lineage cell-specific protein 1 (HS1) in Jurkat cells. Biochemical Journal. 2002;364:41. doi: 10.1042/bj3640041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Ravi R, Bedi A. Sensitization of tumor cells to Apo2 ligand/TRAIL-induced apoptosis by inhibition of casein kinase II. Cancer Research. 2002;62:4180–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Ahmad KA, Wang G, Unger G, Slaton J, Ahmed K. Protein kinase CK2-a key suppressor of apoptosis. Advances in enzyme regulation. 2008;48:179. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2008.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]