Abstract
The double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-dependent protein kinase PKR activates NF-κB via the IκB kinase (IKK) complex, but little is known about additional molecules that may be involved in this pathway. Analysis of the PKR sequence enabled us to identify two putative TRAF-interacting motifs. The viability of such an interaction was further suggested by computer modeling. Here, we present evidence of the colocalization and physical interaction between PKR and TRAF family proteins in vivo, as shown by immunoprecipitation and confocal microscopy experiments. This interaction is induced upon PKR dimerization. Most importantly, we show that the binding between PKR and TRAFs is functionally relevant, as observed by the absence of NF-κB activity upon PKR expression in cells genetically deficient in TRAF2 and TRAF5 or after expression of TRAF dominant negative molecules. On the basis of sequence information and mutational and computer docking analyses, we favored a TRAF-PKR interaction model in which the C-terminal domain of TRAF binds to a predicted TRAF interaction motif present in the PKR kinase domain. Altogether, our data suggest that TRAF family proteins are key components located downstream of PKR that have an important role in mediating activation of NF-κB by the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase.
Accumulation of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) is common in virus-infected cells as a by-product of viral replication. This dsRNA activates multiple signaling pathways (29). Among them, dsRNA induces NF-κB activity, which in turn is necessary for beta interferon (IFN-β) induction (8, 64). dsRNA engages two different pathways that induce NF-κB. On the one hand, dsRNA stimulates Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR-3) on the cell surface, triggering a signaling cascade activating NF-κB (2, 30). On the other hand, cytoplasmic dsRNA directly binds and activates the serine-threonine kinase PKR (39; for a review, see reference 10). PKR was initially described as a translational inhibitor located in an IFN-induced antiviral pathway. PKR inhibits translation through phosphorylation of the translational initiation factor eIF2α (37). More recently, it has been shown that PKR regulates other pathways, including those activating IRF-1, p53, p38, and NF-κB (11, 21, 31). The induction of NF-κB has a relevant role in mediating PKR functions. NF-κB activation by PKR is involved in IFN-β induction in response to dsRNA (8) and is also necessary for PKR-triggered cell death (18). It has been shown that NF-κB activation by PKR involves the IκB kinase (IKK) pathway (8, 19, 68), but the exact mechanism is unknown. The need for PKR kinase activity in this process remains controversial (5, 8, 20), and although an induced-proximity model of IKK activation has been proposed (16), the involvement of additional molecules in IKK activation by PKR remains unclear.
The main regulatory mechanism of NF-κB activation is mediated through its interaction with inhibitory molecules of the IκB family that retain NF-κB in the cytoplasm (63). IκB proteins are phosphorylated by the IKK complex at two serine residues in response to a variety of stimuli, thus tagging them for ubiquitin-proteasome-mediated degradation (51). This event allows NF-κB translocation to the nucleus, where it can regulate the transcription of different sets of genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses, cell differentiation, and control of apoptosis, among other processes (reviewed in reference 17). The IKK complex contains a structural protein termed IKKγ or NEMO and two kinase subunits, IKKα and IKKβ (16). Recently, a second conserved pathway for NF-κB activation has been described that involves NIK phosphorylation of a complex containing IKKα, which in turn phosphorylates p100, thus triggering its processing and finally activating p52/RelB target genes (48).
Since the IKK signalosome is the regulator of NF-κB activation in response to a plethora of stimuli, a general question to be addressed is how these stimuli converge in activating the IKK complex. Different studies have focused on IKK activation by cytokines such as interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α). It seems that MEKK3 and other kinases such as NAK or TAK1 are upstream regulators of these pathways resulting in IKKβ phosphorylation (16, 32, 44). However, kinases activating the IKK complex in other pathways have not been clearly identified. Conversely, several pathway-specific adapter proteins, such as members of the TRAF (TNF receptor-associated factor) family or MyD88 and TIRAP (Toll-interleukin-1 receptor adapter protein), play a role upstream of IKK activation (3, 27, 28, 66). For example, TRAF2 and TRAF5 have been shown to recruit the IKK complex to the TNF receptor (14), and this step is a prerequisite for IKK activation. TRAF proteins are widely conserved in mammals and other eukaryotes. They have emerged as key signal transducers, not only for the TNF receptor superfamily but also for other pathways (9). TRAF proteins control a wide range of biological functions, such as embryonic development or immune and stress responses. Structurally, TRAF proteins have a signature TRAF domain in the C terminus (52). This TRAF domain is necessary for self-association and also mediates its interaction with upstream molecules (58). Most TRAF proteins also contain a RING finger and several zing finger motifs in their N-terminal region that are involved in binding and activation of downstream effectors (53, 58).
The aims of this investigation were to analyze whether PKR can interact with TRAFs and to define the role of this interaction in the process of NF-κB activation triggered by PKR. Here, we present evidence that members of the TRAF family of proteins interact with PKR in vivo and that this association is needed for NF-κB activation by PKR. Thus, TRAF proteins are universal adapters linking NF-κB activation not only to membrane receptor-triggered pathways but also to dsRNA-dependent NF-κB activation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Antibodies.
Anti-hemagglutinin (HA) antibody was from Roche. Rabbit anti-eIF2α phosphorylated antibody was from Biosource. Rabbit anti-TRAF2 was from Santa Cruz. For PKR immunoprecipitation, a PKR polyclonal antibody raised against PKR expressed in Escherichia coli was used. Detection of PKR by Western blotting and immunofluorescence analysis was performed with a polyclonal antibody previously described (18). Monoclonal antibody AC-74 for mouse β-actin and anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody M2 were from Sigma. IκBα antibodies were from Cell Signaling Technologies. Rhodamine-conjugated goat anti-mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG) was from Jackson Laboratory. Horseradish peroxidase-conjugated antibodies were purchased from Cappel.
Plasmids.
Plasmids pCDNA3-HA-TRAF2, pCR-Flag-TRAF6, and pCR-Flag-TRAF5 (encoding the full-length protein or deletion mutant forms) have been previously described (1, 54) and were kindly provided by Jorge Moscat (Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa, Madrid, Spain). Deletion mutant forms PKR-N (amino acids [aa] 1 to 265) and PKR-C (aa 266 to 551), cloned into the BamHI and XhoI sites of plasmid pcDNA1/Amp, were kindly provided by Elaine Meurs (Pasteur Institute, Paris, France). Plasmid pcDNA3FLAG-CYLD (6) was provided by Rene Bernards (NKI, Amsterdam, The Netherlands). A plasmid encoding Gyr-PKR (60) was provided by Tom Dever (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md.).
Cells and viruses.
HeLa cells were grown in Dulbecco modified Eagle medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% newborn calf serum. 293T cells were grown in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (FCS). 3T3 cells derived from homozygous PKR knockout (PKR0/0) mice or wild-type (WT) animals with the same genetic background (PKR+/+) (both a generous gift of C. Weissmann, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland) were grown in DMEM supplemented with 10% FCS. 3T3 cells derived from mice doubly deficient in TRAF2 and TRAF5 (DKO 3T3) or WT animals with the same genetic background (WT 3T3) (57) were grown in DMEM supplemented with 10% FCS. After mock treatment or viral adsorption, cells were maintained with DMEM supplemented with 2% serum. A recombinant vaccinia virus (VV) expressing isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside-inducible PKR (VV PKR) or mutant PKR (K296R) and a VV expressing T7 polymerase (VT7) have been previously described (15, 36). VV TRAF5 DN and VV TRAF6 DN were generated by recombination of the pHLZ-based vectors pTRAF5DN and pTRAF6DN, respectively, with VV in accordance with standard procedures (38).
pIC treatment.
Polyriboinosinic polyribocytidylic acid (pIC; Roche) was prepared in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions as a 10-mg/ml stock solution and stored at −20°C. Semiconfluent cells seeded the night before were serum starved for 2 h, and 10 μg of pIC per ml was transfected for the time indicated with Lipofectamine (Gibco) in accordance with the supplier's instructions.
Immunoblotting.
For immunoblot analysis, total cell extracts were fractionated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and proteins were transferred onto nitrocellulose paper. Filters were incubated with antiserum overnight at 4°C and then incubated with a secondary antibody, and proteins were detected with ECL reagents (Amersham).
Confocal microscopy.
HeLa cells cultured on coverslips were infected with the indicated recombinant viruses. At 16 h postinfection (hpi), cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, and permeabilized for 10 min at room temperature with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS. After washing, coverslips were blocked with 20% bovine serum albumin in PBS. Cells were incubated with antibodies against PKR and FLAG (1 h, 37°C). Coverslips were washed extensively with PBS and further incubated with To-Pro (Molecular Probes) and appropriate isotype-specific secondary antibodies conjugated to fluorescein or Texas Red (1 h at 37°C). After several washes with PBS, coverslips were mounted on microscope slides with Mowiol (Calbiochem). Images were obtained with a Bio-Rad Radiance 2100 confocal laser microscope.
Immunoprecipitation analysis.
Confluent PKR0/0 cells grown in 60-mm-diameter plates were infected for 20 h with the recombinant viruses indicated, cells were collected and lysed, and the clarified supernatant was incubated overnight with 150 μl of protein A-Sepharose previously incubated with specific antibodies. For the experiments showing inducible binding between PKR and TRAFs, 293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids for 48 h, treated with pIC or coumermycin as described, and processed as described above. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.
Transfection of 293T cells.
Semiconfluent 293T cells growing in 10-cm-diameter dishes were transfected by the calcium phosphate method with a total of 20 μg of plasmid DNA. The medium was changed 16 h after transfection. Similar results were obtained with Lipofectamine (Gibco) in accordance with the supplier's instructions.
Transactivation assays.
To measure NF-κB transcriptional activity, we used the p3κB-Luc vector containing three human immunodeficiency virus κB sites upstream of the thymidine kinase minimal reporter and the luciferase cDNA and a control vector containing mutations impairing NF-κB binding. At 36 h after transfection (with Lipofectamine; Gibco), cells were treated with pIC for 6 h and luciferase activity was measured with the luciferase assay system (Promega) in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations.
Gel retardation assay.
Nuclear extracts from HeLa cells were prepared as previously described (4). Three micrograms of nuclear extracts was analyzed with [α32-P]dCTP-labeled double-stranded synthetic WT human immunodeficiency virus enhancer oligonucleotide 5′-AGCTTACAAGGGACTTTCCGCTGGGGACTTTCCAGGGA-3′ containing the two κB consensus motifs.
NF-κB activation enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
The Trans AM assay kit (Active Motif) was used in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. This DNA-binding assay is based on the use of multiwell plates coated with an unlabeled oligonucleotide containing the consensus-binding site for NF-κB. The presence of the DNA-bound transcription factor is then detected by anti-NF-κB antibodies coupled to colorimetric detection (49).
Measurement of the extent of apoptosis.
The cell death detection ELISA kit (Roche) was used in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
Modeling of the three-dimensional structure of PKR.
The atomic coordinates for the PKR dsRBD domain were obtained from Protein Data Bank (PDB [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb]) entry 1qu6 (41). The atomic coordinates for the TRAF2 trimer structure were taken from PDB entry 1ca9 (45). The program Swiss-PdbViewer and the SWISS-MODEL server facilities (22, 23) (http://www.expasy.ch/swissmod/SWISS-MODEL.html) were used to model the structure of the human PKR kinase domain (aa 231 to 551). The template structure used to model the kinase domain was the one corresponding to PDB entry 1fmo (43), following the subdomain alignment proposed by Hanks and Quinn (24) (http://www.sdsc.edu/kinases/pkr/pk_catalytic/pk_hanks_seq_align_long.html). The structure model was built with the program ProMod II (46, 47), and the quality of the model was analyzed with the WHAT-CHECK routines (26) from the WHAT IF program (65). Briefly, the overall quality values of the model are poorer than the usual ones for experimental X-ray or nuclear magnetic resonance structures but acceptable in the expected region for protein structure models. The proposed docking structures between the dsRBD domain and the kinase active site, as well as the docking between the dsRNA binding motif 2 (dsRBM2) subdomain and the TRAF2 ligand groove, were obtained with the geometric docking program GRAMM (62) and the macromolecular docking program Hex (50) on the basis of spherical polar Fourier correlations, evaluating the docking score at more than 40,000 distinct rotational orientations at each of 10 different intermolecular distances (at increments of 1 Å) between both kinase or dsRDB2 domains of the PKR and TRAF three-dimensional structures. The InsightII (Biosym/MSI, San Diego, Calif.), Rasmol (55), and Swiss PDBViewer molecular visualization programs were used to graphically display and manipulate the biomolecular structures and generate the figures.
RESULTS
A structural model of PKR-TRAF interaction.
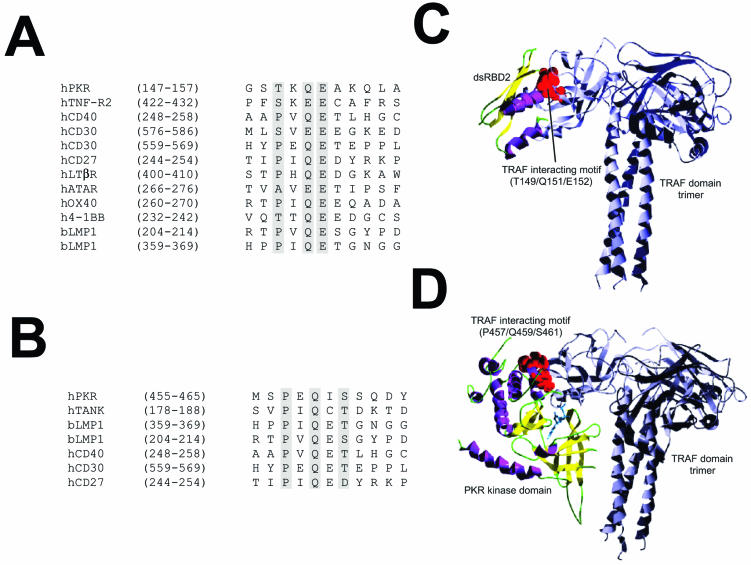
TRAF proteins act as adapters linking extracellular receptors with several signal transduction pathways, among them the NF-κB pathway (7, 40, 53). TRAFs binds to a conserved amino acid sequence, termed the TRAF-interacting motif (13, 67). Analysis of the PKR sequence allowed us to identify two TRAF binding motifs in PKR (one in the dsRBD2 subdomain comprising aa 149 to 152, which match the consensus P/S/A/T × Q/E E, and the other in the kinase domain comprising aa 457 to 461, matching the consensus P × Q × S/T/D; Fig. 1). To investigate the feasibility of these interactions, we built a structural model of PKR by homology modeling based on the structure obtained experimentally for the dsRBD domain (PDB entry 1qu6) (41, 42) and the homology between known structures for several serine/threonine protein kinases as shown in the Hanks classification (24). We used the structural model of PKR to assess the interaction between the putative TRAF-interacting motifs of PKR and the TRAF domain of TRAF trimers by computer docking analysis. Thus, we modeled the interaction between the TRAF peptide recognition region and (i) the dsRBD2 subdomain (Fig. 1C) and (ii) the PKR kinase domain-interacting motif (Fig. 1D). Bioinformatic analysis suggested that both interactions are structurally possible and that the one involving the PKR kinase domain is energetically more feasible, as it involves the interaction of larger surfaces, including the ATP binding pocket, the putative substrate site, and part of the small lobe of the modeled kinase domain of PKR.
FIG. 1.
Model predicting TRAF-PKR interaction. (A) Sequence alignment of the putative TRAF-interacting motif present in the dsRBD2 subdomain of PKR with those from different TRAF binding domains. (B) Sequence alignment of the putative TRAF-interacting motif present in the kinase domain of PKR with those from different TRAF binding domains. (C) Putative model of the interaction between dsRDB2 and TRAF. A ribbon plot of the structure obtained through docking procedures for the interaction between the TRAF-interacting motif (T149/Q151/E152; red spheres) of the dsRDB2 subdomain of PKR and TRAF. TRAF trimer secondary-structure elements are depicted in grey. The dsRBD amino-terminal domain of PKR is shown as a ribbon plot (α helices, magenta; β strands, yellow). (D) Model of the PKR (kinase domain)-TRAF interaction. A docking model of the putative interaction between the TRAF-interacting motif (P457/Q459/S46; red spheres) of the kinase domain of PKR and the TRAF domain. TRAF trimer secondary-structure elements are depicted in grey. In the kinase domain of PKR, α helices are in magenta and β strands are in yellow. A molecule of ATP has been included solely to indicate the position of the putative ATP binding pocket.
PKR interacts with TRAFs.
In view of the models shown in Fig. 1, we decided to investigate the potential interaction between TRAFs and PKR by coimmunoprecipitation. For that purpose, we expressed epitope-tagged versions of different TRAFs together with a noncatalytic mutant form of PKR in HeLa cells. We used the VT7 transfection-infection system (15) for protein expression as this provides the correct environment for PKR activation. We have previously used a similar system based on VV recombinants capable of expressing PKR and other proteins and have shown that expression of PKR in an activated form triggers apoptosis, induces antiviral activity against VV and VSV, inhibits translation, and activates NF-κB through the IKK complex (18-20, 33-36). Results obtained with this inducible virus-cell system have been confirmed by others with transfected cells or with cells derived from PKR gene knockout mice (12, 56).
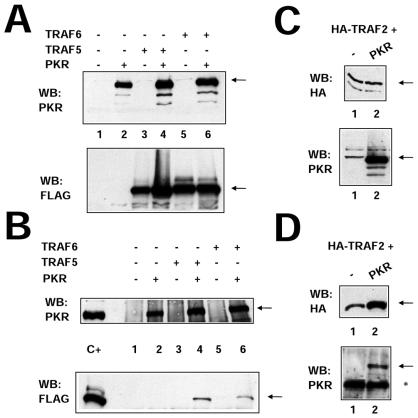
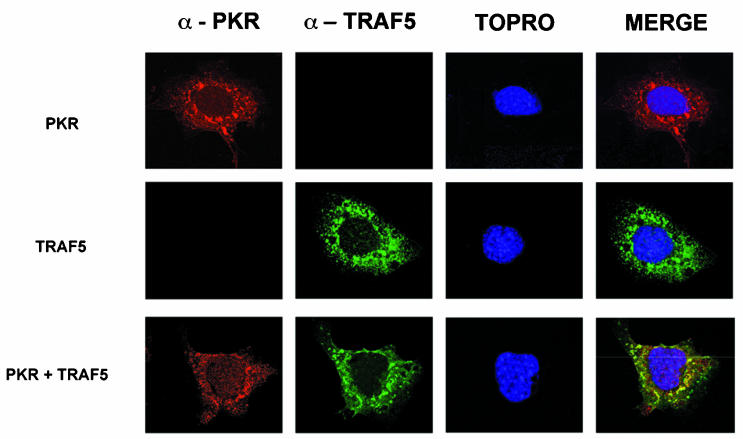
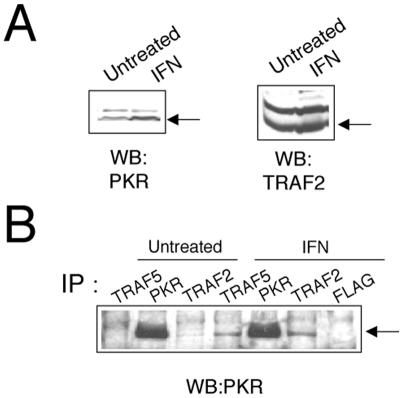
Expression of TRAF2, TRAF5, or TRAF6 together with PKR (K296R, Fig. 2), followed by immunoprecipitation of PKR with PKR-specific antibodies, resulted in coimmunoprecipitation of TRAF proteins, thus demonstrating an interaction between PKR and TRAFs. In order to confirm the PKR-TRAF association in vivo, we infected HeLa cells with VV PKR and VV FLAG-tagged TRAF5. Cells were then analyzed by triple confocal laser scanning microscopy with a rabbit polyclonal anti-PKR antibody (red fluorescence), an anti-mouse antibody to detect FLAG-tagged TRAF5 (green fluorescence), and To-Pro to detect DNA (blue fluorescence). TRAF5 expression results in a characteristic punctate cytosolic staining (Fig. 3). PKR expression is mainly cytoplasmic, with strong perinuclear localization. When PKR and TRAF5 were expressed together, we observed clear colocalization of PKR and TRAF5. Next, we determined whether we could observe binding between endogenous TRAF proteins and PKR. HeLa cells were treated with or without 300 U of IFN per ml in order to induce PKR (Fig. 4A). Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with antibodies directed against TRAF2, TRAF5, and PKR or anti-FLAG antibodies (as a negative control). Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-PKR antibodies. Treatment with IFN resulted in an association between TRAF proteins and PKR (Fig. 4B). No unspecific PKR binding was observed when we used the anti-FLAG antibody as a control.
FIG. 2.
PKR interacts with TRAF family proteins in vivo. (A) HeLa cells were infected with 10 PFU of VT7 per cell. After 1 h, plasmids encoding FLAG-tagged TRAF5 and TRAF6 proteins or the empty vector were transfected together with the empty vector or a plasmid encoding PKR (K296R mutant form). Cell extracts were collected 20 hpi and analyzed by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblot (Western blot [WB]) analysis with anti-PKR or anti-FLAG antiserum. (B) Extracts prepared as described for panel A were immunoprecipitated with anti-PKR serum and thoroughly washed, and immunocomplexes were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblotting with antiserum to PKR or FLAG. (C) HeLa cells in 10-cm-diameter plates were infected with 10 PFU of VT7 per cell. After 1 h, a plasmid (10 μg) encoding HA-tagged TRAF2 was transfected together with 10 μg of the empty vector (lane 1) or with 10 μg of a plasmid encoding PKR (K296R mutant form, lane 2). Cells extracts were collected at 20 hpi and analyzed by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblot analysis with anti-PKR or anti-HA antiserum. (D) Extracts prepared as described for panel C were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA serum and thoroughly washed, and immunocomplexes were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblotting with antiserum to PKR or HA. The asterisk denotes IgGs, and the arrows indicate the specific proteins.
FIG. 3.
PKR and TRAF5 colocalize in HeLa cells. HeLa cells were infected at 3 PFU per cell with VV PKR K296R (upper panels), VV FLAG-tagged TRAF5 (middle panels), or both (lower panels). Cells were fixed at 16 hpi and processed for immunofluorescence analysis by confocal microscopy with antibodies directed against PKR (red), FLAG (green), and To-Pro for nuclear staining (blue). Merged images are presented on the right.
FIG. 4.
Interaction between PKR and endogenous TRAF proteins. (A) Extracts (50 μg) from HeLa cells left untreated or treated with IFN-α/β for 16 h were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting (Western blotting [WB]) with anti-PKR or anti-TRAF2 antibodies. (B) Extracts (1 mg) were immunoprecipitated (IP) with antibodies against TRAF2, TRAF5, PKR, or FLAG and thoroughly washed, and immunocomplexes were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblotting with antiserum to PKR.
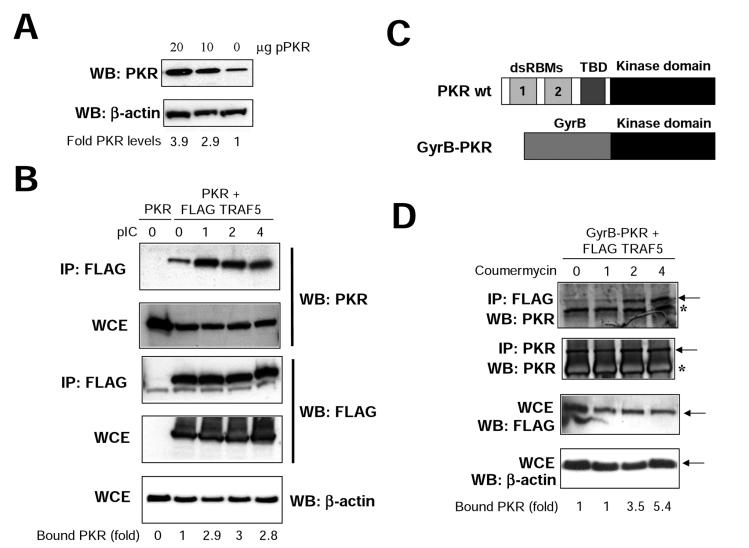
To further confirm and characterize the binding between PKR and TRAFs, we decided to use two different systems. Both were based on the use of transient transfection in 293T cells (thus avoiding VV infection). Transfection of PKR in 293T cells resulted in a dose-dependent increase in PKR of up to 3.9 times compared with endogenous levels (Fig. 5A). First, we transfected PKR alone or together with FLAG-TRAF5 and analyzed the interaction between them upon pIC treatment (Fig. 5B). Although a certain amount of PKR interacted with TRAF prior to pIC treatment, a significant increase in the interaction (up to threefold) was observed upon pIC treatment. Since plasmid transfection is known to increase intracellular dsRNA levels, we sought another system that could provide us with further insights into the inducibility of the binding observed. We transfected cells with FLAG-TRAF5 and with a plasmid encoding a GyrB-PKR fusion protein. This chimeric protein consists of the N-terminal 220 aa of E. coli GyrB fused to the kinase domain (aa 258 to 551) of human PKR (Fig. 5C). After coumermycin addition, the GyrB-PKR protein dimerizes and becomes activated (60). We found that TRAF-PKR binding is dependent on PKR dimerization, observing an increase of more than fivefold in the PKR-TRAF interaction upon coumermycin addition (Fig. 5D). It is noteworthy that since the fusion protein contains the kinase domain and lacks the dsRNA binding domain of PKR, this experiment indicates that the PKR-TRAF interaction involves the PKR kinase domain; in addition, these findings are not affected by potential pitfalls caused by increased dsRNA levels associated with plasmid transfection. Together, these data suggest that PKR and TRAF proteins are able to form complexes in vivo.
FIG. 5.
TRAF-PKR interaction is inducible. (A) 293T cells growing in 10-cm-diameter dishes were transfected with 10 or 20 μg of a plasmid coding for PKR, and at 48 h after transfection, cell extracts were collected and analyzed by immunoblotting (Western blotting [WB]) with antiserum to PKR or actin. Signals were quantitated with NIH Image software. (B) 293T cells were transfected with 20 μg of a plasmid coding for PKR (lane 0) or with 10 μg each of plasmids encoding for PKR and FLAG-TRAF5, as indicated. At 48 h after transfection, cells were treated with 10 μg of pIC per ml. At the noted times, cell extracts were collected, immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG serum, and thoroughly washed and immunocomplexes or whole-cell extracts (WCE) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblotting with antiserum to PKR, FLAG, or actin. Signals were quantitated with NIH Image software. (C) Schematic representation of PKR and the GyrB-PKR chimera. The different domains of PKR are shown (dsRBMs, the third basic domain [TBD], and the kinase domain). The chimera consists of the N-terminal 220 aa of E. coli GyrB fused to the kinase domain (aa 258 to 551) of human PKR. (D) 293T cells were transfected with 10 μg each of plasmids encoding Gyr-PKR and FLAG-TRAF5 as indicated. At 48 h after transfection, cells were treated with coumermycin. At the indicated times posttreatment, cell extracts were collected, immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG or anti-PKR serum, and thoroughly washed and immunocomplexes or whole-cell extracts (WCE) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblotting with antiserum to PKR, FLAG, or actin. Asterisks denote IgGs, and arrows indicate the specific proteins. Signals were quantitated with NIH Image software.
Domains involved in PKR-TRAF interaction.
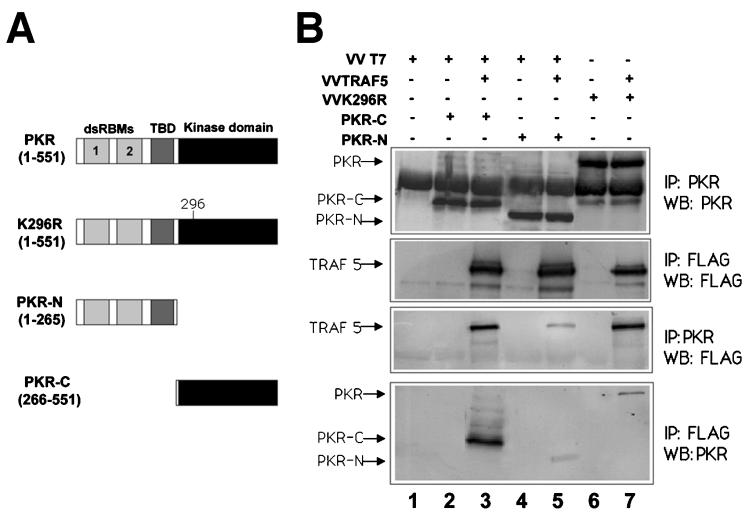
As TRAF proteins are modular proteins with distinct domains involved in mediating interactions with upstream or downstream molecules (52, 58), we reasoned that mapping the domains involved in PKR-TRAF binding will help us to further understand the nature of the interaction. In order to determine which region of PKR is required for the interaction with TRAF5, deletion mutant PKRs encompassing the kinase or the regulatory domain (Fig. 6A) were expressed in HeLa cells together with FLAG-tagged TRAF5, and their association was determined by immunoprecipitation studies. A deletion mutant form containing the kinase domain, encompassing aa 266 to 551 of PKR, showed that this domain is sufficient to bind to TRAF5, thus confirming the data shown in Fig. 5B. A minor association was also observed between TRAF5 and the PKR regulatory domain.
FIG. 6.
TRAF5 preferentially interacts with the PKR kinase domain. (A) Schematic representation of PKR and the different mutant proteins used. Domains are as in Fig. 5C. (B) HeLa cells grown in 10-cm-diameter plates were infected with 5 PFU of VT7 per cell plus 5 PFU of VV per cell (lanes 1, 2, and 4), 5 PFU of VT7 per cell plus 5 PFU of VV TRAF5 per cell (lanes 3 and 5), 5 PFU of VV per cell plus 5 PFU of VV K296R per cell (lane 6), or 5 PFU of VV TRAF5 per cell plus 5 PFU of VV K296R per cell (lane 7). After 1 h, plasmids encoding PKR-C (10 μg) or PKR-N (10 μg) were transfected as indicated. Cell extracts were collected at 20 hpi, immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-PKR or anti-FLAG serum, and thoroughly washed, and immunocomplexes were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblotting (Western blotting [WB]) with antiserum to PKR or FLAG. TBD, third basic domain.
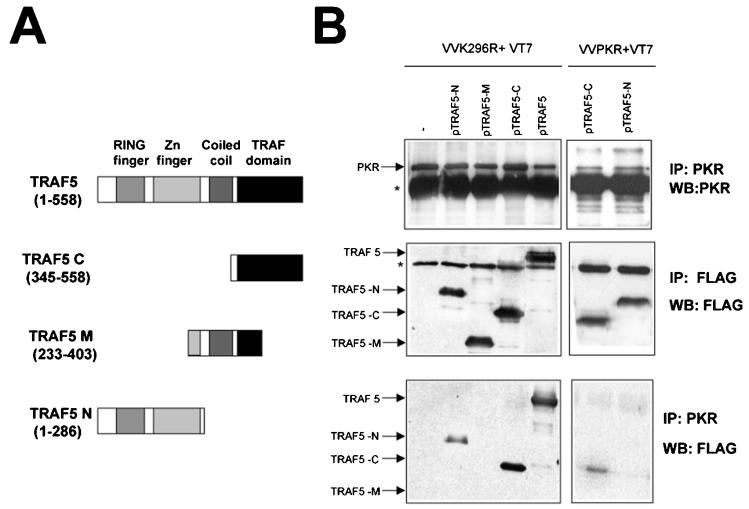
We also analyzed the domains of TRAF necessary for interaction with PKR with different deletion mutant TRAFs. As shown in Fig. 7, a mutant form of TRAF5 encompassing the C-terminal TRAF domain (aa 345 to 558) was able to bind PKR K296R to an extent similar to that of full-length TRAF5. A mutant encompassing the central region of TRAF5 (aa 233 to 403) showed no binding with PKR, while an N-terminal mutant form encompassing the RING finger and Zn finger domains (aa 1 to 286) showed reduced binding to PKR. When binding of the mutant TRAFs to WT PKR was analyzed, it was apparent that PKR preferentially binds to the C-terminal domain of TRAF proteins (Fig. 7B and data not shown). This is the same region responsible for the binding of TRAF molecules to the TRAF-interacting motif of their different upstream activators (45).
FIG. 7.
PKR preferentially interacts with the TRAF domain of TRAF5. (A) Schematic representation of TRAF5 and the different mutant proteins used. (B) HeLa cells grown in 10-cm-diameter plates were infected with 5 PFU of VT7 per cell and 5 PFU of VV K296R or VV PKR per cell as indicated. After 1 h, 10 μg of a plasmid encoding FLAG-tagged TRAF5 (full-length protein or deletion mutant forms) or 10 μg of the empty vector was transfected. Cell extracts were collected at 20 hpi, immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-PKR or anti-FLAG serum, and thoroughly washed, and immunocomplexes were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblotting (Western blotting [WB]) with antiserum to PKR or FLAG. The asterisks indicate IgGs.
Activation of NF-κB by PKR is dependent on TRAFs.
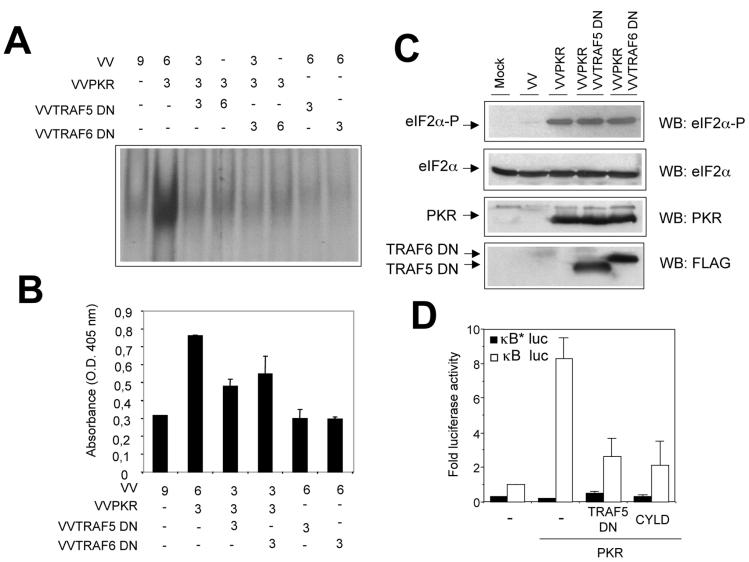
TRAF proteins truncated at the N-terminal domain function as dominant negative inhibitors of TRAF signaling (52). To evaluate the functional impact of the interaction between TRAF and PKR, we generated VV expressing dominant negative forms of both TRAF5 and TRAF6. We coexpressed mutant TRAF5 or TRAF6 together with PKR and then measured NF-κB activation in nuclear cell extracts. In the absence of the TRAF dominant negative proteins, PKR activated NF-κB, as measured by both gel shift assay and ELISA (Fig. 8A and B). Increased expression of mutant TRAF proteins led to progressive reduction of NF-κB activity (up to 70%). However, expression of dominant negative TRAF proteins had no effect on PKR protein levels or eIF-2α phosphorylation (Fig. 8C), eliminating the possibility that they can act as PKR inhibitors.
FIG. 8.
Dominant negative TRAF proteins inhibit PKR-induced NF-κB activity. (A) HeLa cells were infected with VV recombinants at the numbers of PFU per cell indicated. Nuclear extracts were prepared at 20 hpi and analyzed by gel shift assay with a probe specific for NF-κB. This experiment was performed in duplicate. (B) NF-κB activation was measured in HeLa cells infected with the indicated VV recombinants by using an ELISA as described in Materials and Methods. O.D., optical density. (C) Western blot (WB) analysis of cell extracts from HeLa cells mock infected (first lane) or infected with the indicated viruses was performed with antibodies directed against total or phosphorylated eIF-2a, PKR, or FLAG. (D) 293T cells grown in 10-cm-diameter plates were transfected with equal amounts (10 μg each) of the indicated plasmids together with 0.5 μg of the p3κB-Luc vector (white bars) or the p3κB*Luc vector (with mutated κB sites, black bars). At 36 h after transfection, cells were treated with 10 μg of pIC per ml for 6 h. Luciferase activity was measured, and fold luciferase activity is shown (readings from cells transfected with the empty vector were used as a reference).
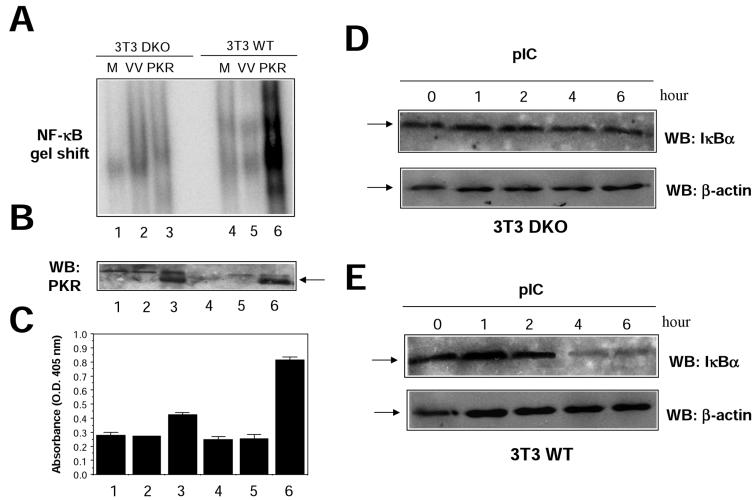
In order to confirm these results in a virus-free environment, we analyzed transcriptional activation of NF-κB reporters after transient transfection of 293T cells (Fig. 8D). Under these conditions, TRAF dominant negative proteins also inhibited PKR-mediated NF-κB activation. Expression of the CYLD tumor suppressor, which deubiquitinates TRAFs, thus inhibiting TRAF-mediated NF-κB activation (6, 59), also interfered with PKR-mediated NF-κB activation (Fig. 8D). To further prove a functional involvement of TRAF proteins in NF-κB activation by PKR, we used 3T3 cells derived from double-knockout (DKO) animals deficient in both TRAF2 and TRAF5 expression (DKO 3T3) (57). PKR was expressed in WT or DKO 3T3 cells, and NF-κB activation was measured in nuclear cell extracts (Fig. 9). PKR expression resulted in a more-than-fourfold induction of NF-κB activity in WT 3T3 cells, while no apparent NF-κB activation could be observed in cells devoid of TRAF2 and TRAF5 (Fig. 9A). Since we have previously shown that NF-κB activation by PKR is involved in induction of apoptosis (18), we analyzed cell death induced by PKR in DKO 3T3 cells. In agreement with our previous observation, absence of TRAF2 and TRAF5 resulted in diminished levels of PKR-triggered cell death (Fig. 9C). Finally, we analyzed the effect of pIC treatment on NF-κB activation in DKO 3T3 cells. NF-κB activation after pIC treatment was impaired in cells lacking TRAF2 and TRAF5, as assessed by IκBα degradation and NF-κB gel shift analysis (Fig. 9 D and E and data not shown). Altogether, the results presented in Fig. 8 and 9 are consistent with a role for TRAFs as downstream PKR effectors mediating NF-κB activation.
FIG. 9.
Absence of PKR-dependent NF-κB activation in 3T3 cells deficient in TRAF2 and TRAF5. (A) 3T3 cells grown in 10-cm-diameter plates, obtained from WT mice (WT 3T3) or mice deficient in both TRAF2 and TRAF5 (DKO 3T3), were mock infected (M) or infected with 5 PFU of VV per cell (VV) or 5 PFU of VV PKR per cell (PKR). Nuclear extracts were prepared at 20 hpi and analyzed by gel shift assay with a probe specific for NF-κB. (B) Extracts (50 μg) from the same cells were analyzed for PKR expression by Western blotting (WB). (C) Cells infected as described for panel A were analyzed for induction of apoptosis as indicated in Materials and Methods. The lane numbers in panels B and C are the same as those in panel A. O.D., optical density. DKO (D) or WT (E) 3T3 cells were treated with 10 μg of pIC per ml for the times indicated, and levels of IκBα and β-actin were analyzed by Western blotting. The arrows indicate specific proteins.
DISCUSSION
PKR activates NF-κB through the IKK signalosome in response to dsRNA and viruses (5, 8, 19, 68). Although some models have been proposed, the precise molecular mechanism by which PKR activates IKK remains to be elucidated. TRAFs are adapter proteins mediating NF-κB activation in response to certain membrane receptors. We identified two possible TRAF-interacting motifs in PKR by sequence analysis; one is present in the dsRBD2 subdomain, and the other is found in its kinase domain. Molecular modeling confirmed that the PKR-TRAF interaction is structurally feasible, suggesting alternative docking positions for the two structural motifs. One of these arrangements implicates dsRBD2 in the same surface patch as used for dsRNA binding, suggesting a common recognition mechanism for PKR. The other situates the kinase domain in close contact with the TRAF trimer, allowing a more stable interaction and maintaining the possibility that the dsRBD domains are free to bind other molecules or protein domains. Therefore, we decided to further analyze a role for TRAFs in mediating PKR activation.
In this investigation, we found that PKR interacts and colocalizes with different TRAF family members (at least TRAF2, -5, and -6), as demonstrated by immunoprecipitation and immunofluorescence studies. Binding studies with truncated mutant forms of TRAF served to map the interaction domain with PKR to the TRAF protein C terminus. In addition, mutant forms of PKR revealed that the PKR kinase domain is involved in the interaction with TRAF family proteins. These data are compatible with our previous report showing the requirement of PKR domains for recruitment of the IKK complex (20). These observations are also consistent with the predicted presence of a TRAF-interacting motif in the PKR kinase domain and fit with the model presented in Fig. 1D. TRAFs are modular proteins in which the TRAF domain interacts with upstream recruiter molecules, and their N-terminal domain is involved in interaction with and activation of downstream molecules. Thus, our data locate TRAFs downstream of PKR.
Initially, we used truncated TRAF proteins that act as dominant negative mutant proteins (52) to address the effect of TRAFs on PKR signaling. Thus, we showed that expression of dominant negative mutant TRAFs inhibited NF-κB activation triggered by PKR without affecting eIF2α phosphorylation, further suggesting a role for TRAF as a mediator of NF-κB activation located downstream of PKR. These observations were confirmed through the use of transient-expression systems and cells devoid of TRAF2 and TRAF5 expression.
It is also interesting that we observed the PKR-TRAF interaction upon IFN treatment. While the simplest explanation is that this is a result of increased PKR levels, it is tempting to suggest that an IFN-induced event contributes to the recruitment and binding of TRAFs to PKR. Further studies showed us that the recruitment of TRAFs to PKR is induced by pIC, or more generally by PKR dimerization (Fig. 5). Biochemical and structural analyses of TRAFs indicate their ability to self-associate. Therefore, TRAFs are particularly well suited to interact with and transduce signals from targets such as TNF receptors, which oligomerize in response to ligand binding (45). In addition to mediating signaling in response to extracellular receptors, TRAF proteins have also been linked to JNK activation induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress via IRE1 dimerization (61). It is noteworthy that it has also been shown that just clustering the N-terminal domain of TRAF family proteins is enough to begin downstream signaling events (25). This clustering is thought to promote activation of proximal components of IKK signaling that are bound to the N-terminal domain of TRAF family proteins. dsRNA is the main physiological activator of PKR; upon its binding, it induces first PKR dimerization and later a conformational change that renders the kinase susceptible to autophosphorylation and its full activation. Hence, activation of PKR can be seen as a consequence of elevated dsRNA levels, and PKR itself can act as a dsRNA receptor. dsRNA-induced dimerization and activation of PKR could thus lead to multimerization of TRAF family proteins. In this sense, activation of NF-κB by dsRNA can proceed by a pathway similar to that used by cells to respond to extracellular signals like TNF-α. In addition to triggering PKR-mediated NF-κB activation, dsRNA also induces NF-κB through extracellular binding to TLR-3 (2, 30). Interestingly, PKR functions downstream of another TLR, TLR-4, and TIRAP is the adapter protein involved in this pathway (27). A complex containing TRAF6 has been located downstream of PKR in both the TLR-3 and TLR-4 pathways (27, 30), thus further suggesting the relevance of the interaction between PKR and TRAFs.
In conclusion, our data provide evidence of the physical and functional interaction between PKR and TRAFs. In view of the data presented here and in previous reports, we can propose a model in which, upon dimerization, PKR would bind via its kinase domain to the TRAF protein C-terminal domain. This binding would be a requisite step for the recruitment and activation of the IKK complex by TRAFs, probably with the help of additional factors. This is the first report suggesting that TRAFs mediate NF-κB signaling as a result of an intracellular stimulus, dsRNA accumulation.
Acknowledgments
We thank Charles Weissmann, Jorge Moscat, Tom Dever, Rene Bernards, George Mosialos, and Elaine Meurs for providing reagents and Lola Martínez and Victoria Jimenez for skilled technical assistance. Review of the manuscript by Preeti Kerai is also appreciated.
This investigation was supported by research grants BMC2002-03246 and BIO2000-0340-P4 from Spain and QLK2-CT2002-00954 from the European Union to M.E., by grants SAF2000-0028 and FIPSE to J.A., and by the Fundación Ramón Areces (P.G.-P.). H.N. is supported by a grant from the Human Frontier Science Program. M.A.G. and J.G. were supported by fellowships from the Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología, Madrid, Spain.
REFERENCES
- 1.Akiba, H., H. Nakano, S. Nishinaka, M. Shindo, T. Kobata, M. Atsuta, C. Morimoto, C. F. Ware, N. L. Malinin, D. Wallach, H. Yagita, and K. Okumura. 1998. CD27, a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, activates NF-κB and stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase via TRAF2, TRAF5 and NF-κB-inducing kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 273:13353-13358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Alexopoulou, L., A. C. Holt, R. Medzhitov, and R. A. Flavell. 2001. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-κB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 413:732-738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Arch, R. H., R. W. Gedrich, and C. B. Thompson. 1998. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs)—a family of adapter proteins that regulates life and death. Genes Dev. 12:2821-2830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Arenzana-Seisdedos, F., J. Thompson, M. S. Rodriguez, F. Bachelerie, D. Thomas, and R. T. Hay. 1995. Inducible nuclear expression of newly synthesized IκBα negatively regulates DNA-binding and transcriptional activities of NF-κB. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15:2689-2696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bonnet, M. C., R. Weil, E. Dam, A. G. Hovanessian, and E. F. Meurs. 2000. PKR stimulates NF-κB irrespective of its kinase function by interacting with the IκB kinase complex. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:4532-4542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brummelkamp, T. R., S. M. Nijman, A. M. Dirac, and R. Bernards. 2003. Loss of the cylindromatosis tumour suppressor inhibits apoptosis by activating NF-κB. Nature 424:797-801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cao, Z., J. Xiong, M. Takeuchy, T. Kurama, and D. V. Goeddel. 1996. TRAF6 is a signal transducer for interleukin 1. Nature 383:443-446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chu, W. M., D. Ostertag, Z. W. Li, L. Chang, Y. Chen, Y. Hu, B. Williams, J. Perrault, and M. Karin. 1999. JNK2 and IKKβ are required for activating the innate response to viral infection. Immunity 11:721-731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chung, J. Y., Y. C. Park, H. Ye, and H. Wu. 2002. All TRAFs are not created equal: common and distinct molecular mechanisms of TRAF-mediated signal transduction. J. Cell Sci. 115:679-688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Clemens, M. J., and A. Elia. 1997. The double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR: structure and function. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 17:503-524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cuddihy, A. R., S. Li, N. W. N. Tam, A. H. Wong, Y. Taya, N. Abraham, J. C. Bell, and A. E. Koromilas. 1999. Double-stranded-RNA-activated protein kinase PKR enhances transcriptional activation by tumor suppressor p53. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19:2475-2484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Der, S. D., Y. Yang, C. Weissmann, and B. R. G. Williams. 1997. A double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway mediating stress-induced apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:3279-3283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Devergne, O., E. Hatzivassiliou, K. M. Izumi, K. M. Kaye, M. F. Kleijnen, E. Kieff, and G. Mosialos. 1996. Association of TRAF1, TRAF2, and TRAF3 with an Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 domain important for B-lymphocyte transformation: role in NF-κB activation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16:7098-7108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Devin, A., A. Cook, Y. Lin, Y. Rodriguez, M. Kelliher, and Z. Liu. 2000. The distinct roles of TRAF2 and RIP in IKK activation by TNF-R1: TRAF2 recruits IKK to TNF-R1 while RIP mediates IKK activation. Immunity 12:419-429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fuerst, T. R., P. L. Earl, and B. Moss. 1987. Use of a hybrid vaccinia virus-T7 RNA polymerase system for expression of target genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7:2538-2544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ghosh, S., and M. Karin. 2002. Missing pieces in the NF-κB puzzle. Cell 109:S81-S96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ghosh, S., J. M. Michael, and E. B. Kopp. 1998. NF-κB and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 16:225-260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gil, J., J. Alcami, and M. Esteban. 1999. Induction of apoptosis by double-stranded-RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) involves the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 and NF-κB. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19:4653-4663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gil, J., J. Alcami, and M. Esteban. 2000. Activation of NF-κB by the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase PKR involves the IκB kinase complex. Oncogene 19:1369-1378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gil, J., J. Rullas, M. A. Garcia, J. Alcami, and M. Esteban. 2001. The catalytic activity of dsRNA-dependent protein kinase, PKR, is required for NF-κB activation. Oncogene 20:385-394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Goh, K. C., M. J. deVeer, and B. R. Williams. 2000. The protein kinase PKR is required for p38 MAPK activation and the innate immune response to bacterial endotoxin. EMBO J. 19:4292-4297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Guex, N., A. Diemand, and M. C. Peitsch. 1999. Protein modelling for all. Trends Biochem. Sci. 24:364-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Guex, N., and M. C. Peitsch. 1997. SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: an environment for comparative protein modelling. Electrophoresis 18:2714-2723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hanks, S., and A. M. Quinn. 1991. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members. Methods Enzymol. 200:38-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hibi, M., A. Lin, T. Smeal, A. Minden, and M. Karin. 1993. Identification of an oncoprotein- and UV-responsive protein kinase that binds and potentiates the c-Jun activation domain. Genes Dev. 7:2135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hooft, R. W. W., G. Vriend, C. Sander, and E. E. Abola. 1996. Errors in protein structures. Nature 381:272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Horng, T., G. M. Barton, and R. Medzhitov. 2001. TIRAP: and adapter molecule in the Toll signalling pathway. Nature 412:835-841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hsu, H., J. Xiong, and D. V. Goeddel. 1995. The TNF receptor 1-associated protein TRADD signals cell death and NF-κB activation. Cell 81:495-504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jacobs, B. L., and J. O. Langland. 1996. When two strands are better than one: the mediators and modulators of the cellular responses to double-stranded RNA. Virology 219:339-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jiang, Z., M. Zamanian-Daryoush, H., Nie, A. M. Silva, B. R. Williams, and X. Li. 2003. Poly I:C-induced TLR3-mediated activation of NFκB and MAP kinases is through an IRAK-independent pathway employing signaling components TLR3-TRAF6-TAK1-TAB2-PKR. J. Biol. Chem. 278:16713-16719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kumar, A., Y. Yang, V. Flati, S. Der, S. Kadereit, A. Deb, J. Haque, L. Reis, C. Weissmann, and B. R. G. Williams. 1997. Deficient cytokine signaling in mouse embryo fibroblasts with a targeted deletion in the PKR gene: role of IRF-1 and NF-κB. EMBO J. 16:406-416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lee, F. S., J. Hagler, Z. J. Chen, and T. Maniatis. 1997. Activation of the IκBα kinase complex by MEKK1, a kinase of the JNK pathway. Cell 88:213-222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lee, S. B., and M. Esteban. 1994. The interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induces apoptosis. Virology 199:491-496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lee, S. B., D. Rodriguez, J. R. Rodriguez, and M. Esteban. 1997. The apoptosis pathway triggered by the IFN-induced dsRNA activated protein kinase PKR requires the third basic domain, initiates up-stream of Bcl-2 and involves ICE-like proteases. Virology 231:81-88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lee, S. B., R. Bablanian, and M. Esteban. 1996. Regulated expression of the interferon-induced protein kinase p68 (PKR) by vaccinia virus recombinants inhibits the replication of vesicular stomatitis virus but not that of poliovirus. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 16:1073-1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lee, S. B., Z. Melkova, W. Yan, B. R. Williams, A. G. Hovanessian, and M. Esteban. 1993. The interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated human p68 protein kinase potently inhibits protein synthesis in cultured cells. Virology 192:380-385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Levin, D., and I. M. London. 1978. Regulation of protein synthesis: activation by double-stranded RNA of a protein kinase that phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75:1121-1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mackett, M., G. L. Smith, and B. Moss. 1984. Vaccinia virus: a selectable eukaryotic cloning and expression vector. J. Virol. 49:857-864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Meurs, E. F., K. Chong, J. Galabru, N. S. Thomas, I. M. Kerr, B. R. Williams, and A. G. Hovanessian. 1990. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induced by interferon. Cell 67:379-390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nakano, H., H. Oshima, L. Chung, L. Abbott, C. F. Ware, H. Yagita, and K. Okumura. 1996. TRAF5, an activator of NF-κB and putative signal transducer for the lymphotoxin-B receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 271:14661-14664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Nanduri, S., B. K. Carpick, Y. Yang, B. R. Williams, and J. Qin. 1998. Structure of the double stranded RNA-binding domain of the protein kinase PKR reveals the molecular basis of its dsRNA-mediated activation. EMBO J. 17:5458-5465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nanduri, S., F. Rahman, B. R. Williams, and J. Qin. 2000. A dynamically tuned double-stranded RNA binding mechanism for the activation of antiviral kinase PKR. EMBO J. 19:5567-5574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Narayana, N., S. Cox, S. Shaltiel, S. S. Taylor, and N. Xuong. 1997. Crystal structure of a polyhistidine-tagged recombinant catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase complexed with the peptide inhibitor PKI(5-24) and adenosine. Biochemistry 15:4438-4448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nemoto, S., J. A. DiDonato, and A. Lin. 1998. Coordinate regulation of IκB kinases by mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1 and NF-κB-inducing kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18:7336-7343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Park, Y. C., V. Burkitt, A. R. Villa, L. Tong, and H. Wu. 1999. Structural basis for self-association and receptor recognition of human TRAF2. Nature 398:533-538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Peitsch, M. C. 1995. Protein modeling by E-mail. Bio/Technology 13:658-660. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Peitsch, M. C. 1996. ProMod and Swiss-Model: Internet-based tools for automated comparative protein modelling. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 24:274-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Pomerantz, J. L., and D. Baltimore. 2002. Two pathways to NF-κB. Mol. Cell 10:693-695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Renard, P., I. Ernest, A. Houbion, M. Art, H. Le Calvez, M. Raes, and J. Remacle. 2001. Development of a sensitive multi-well colorimetric assay for active NFκB.Nucleic Acids Res. 29:E21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ritchie, D. W., and G. J. Kemp. 2000. Protein docking using spherical polar Fourier correlations. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 39:178-194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Roff, M., J. Thompson, M. S. Rodriguez, J. M. Jaque, F. Baleux, F. Arenzana-Seisdedos, and R. T. Hay. 1996. Role of IκBα ubiquitination in signal-induced activation of NFκB in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 271:7844-7850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Rothe, M., S. C. Wong, W. J. Henzel, and D. V. Goeddel. 1994. A novel family of putative signal transducers associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the 75 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell 78:681-692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Rothe, M., V. Sarma, V. M. Dixit, and D. V. Goeddel. 1995. TRAF2-mediated activation of NF-κB by TNF receptor 2 and CD40. Science 269:1424-1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sanz, L., P. Sanchez, M. J. Lallena, M. T. Diaz-Meco, and J. Moscat. 1999. The interaction of p62 with RIP links the atypical PKCs to NF-κB activation. EMBO J. 18:3044-3053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sayle, R. A., and E. J. Milner-White. 1995. RasMol: biomolecular graphics for all. Trends Biochem. Sci. 20:374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Srivastava, S. P., K. U. Kumar, and R. J. Kaufman. 1998. Phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 mediates apoptosis in response to activation of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 273:2416-2423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Tada, K., T. Okazaki, S. Sakon, T. Kobarai, K. Kurosawa, S. Yamaoka, H. Hashimoto, T. W. Mak, H. Yagita, K. Okumura, W. C. Yeh, and H. Nakano. 2001. Critical roles of TRAF2 and TRAF5 in tumor necrosis factor-induced NF-κB activation and protection from cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 276:36530-36534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Takeuchi, M., M. Rothe, D. V. and Goeddel. 1996. Anatomy of TRAF2. Distinct domains for nuclear factor-κB activation and association with tumor necrosis factor signaling proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 271:19935-19942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Trompouki, E., E. Hatzivassiliou, T. Tsichritzis, H. Farmer, A. Ashworth, and G. Mosialos. 2003. CYLD is a deubiquitinating enzyme that negatively regulates NF-κB activation by TNFR family members. Nature 424:793-796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ung, T. L., C. Cao, J. Lu, K. Ozato, and T. E. Dever. 2001. Heterologous dimerization domains functionally substitute for the double-stranded RNA binding domains of the kinase PKR. EMBO J. 20:3728-3737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Urano, F., X. Wang, A. Bertolotti, Y. Zhang, P. Chung, H. P. Harding, and D. Ron. 2000. Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1. Science 287:664-666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Vakser, I. A. 1995. Protein docking for low-resolution structures. Protein Eng. 8:371-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Verma, I. M., J. K. Stevenson, E. M. Schwarz, D. Van Antwerp, and S. Miyamoto. 1995. Rel/NF-κB/IκB family: intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev. 9:2723-2735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Visvanathan, K. V., and S. Goodbourn. 1989. Double-stranded RNA activates binding of NF-κB to an inducible element in the human beta-interferon promoter. EMBO J. 8:1129-1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Vriend, G. 1990. WHAT IF: a molecular modelling and drug design program. J. Mol. Graph. 8:52-56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Wesche, H., W. J. Henzel, W. Shillinglaw, S. Li, and Z. Cao. 1997. MyD88: an adapter that recruits IRAK to the IL-1 receptor complex. Immunity 7:837-847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ye, H., Y. C. Park, M. Kreishman, E. Kieff, and H. Wu. 1999. The molecular basis for the recognition of diverse receptor sequences by TRAF2. Mol. Cell 4:321-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Zamanian, D. M., T. H. Mogensen, J. A. DiDonato, and B. R. Williams. 2000. NF-κB activation by double-stranded-RNA-activated protein kinase (PKR) is mediated through NF-κB-inducing kinase and IκB kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:1278-1290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]