Abstract
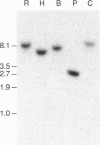
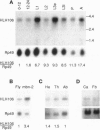
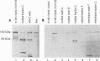
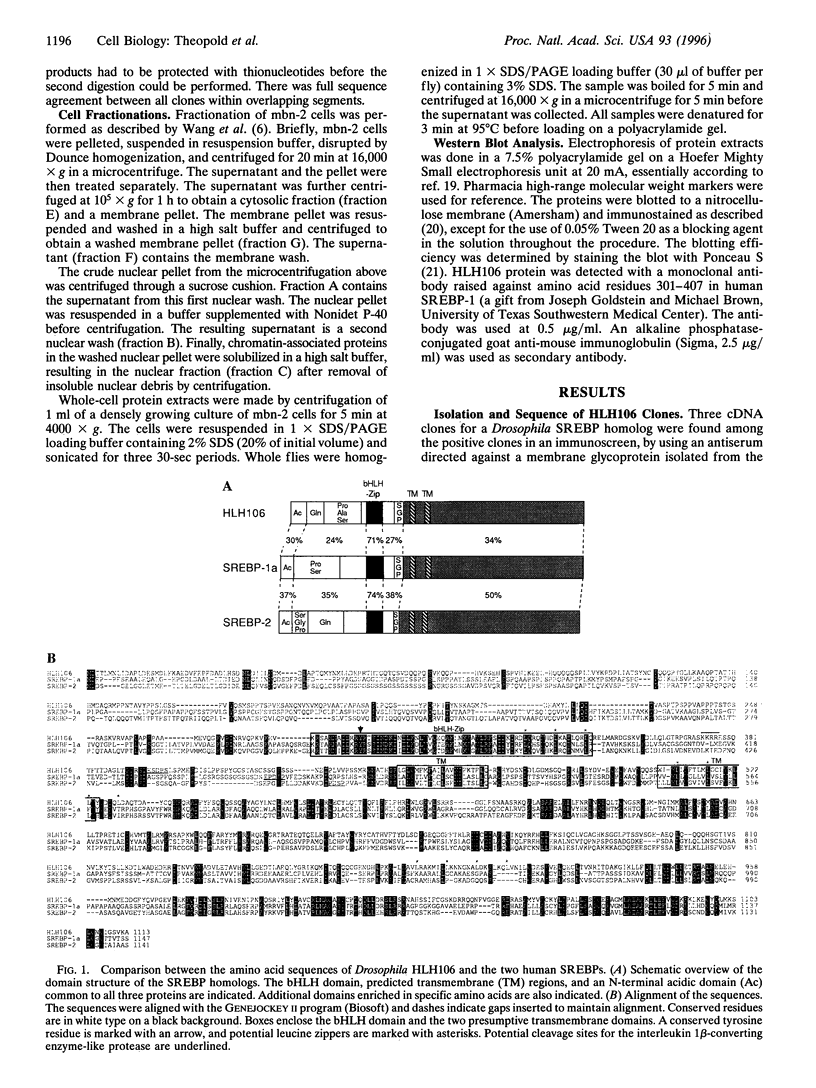
We cloned a Drosophila homolog to the sterol responsive element binding proteins (SREBPs). In vertebrates, the SREBPs are regulated by a mechanism that involves cleavage of the protein that normally residues in the cellular membranes and translocation of the released transcription factor into the nucleus. Regulation of the Drosophila factor HLH106 apparently follows the same mechanism, and we find the full-length gene product in the membrane fraction and a shorter cross-reacting form in the nuclear fraction. This nuclear form, which may correspond to proteolytically activated HLH106, is abundant in the blood cell line mbn-2. The general domain structure of HLH106 is very similar to that in SREBP. HLH106 is expressed throughout development, and it is present at high levels in Drosophila cell lines. In contrast to the rat homolog, HLH106 transcripts are not more abundant in adipose tissue than in other tissues.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Echalier G., Ohanessian A. Isolement, en cultures in vitro, de lignées cellulaires diploïdes de Drosophila melanogaster. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1969 Mar 31;268(13):1771–1773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasic G. P. Basic-helix-loop-helix transcription factor and sterol sensor in a single membrane-bound molecule. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):17–19. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gateff E. Malignant neoplasms of genetic origin in Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1978 Jun 30;200(4349):1448–1459. doi: 10.1126/science.96525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua X., Yokoyama C., Wu J., Briggs M. R., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Wang X. SREBP-2, a second basic-helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper protein that stimulates transcription by binding to a sterol regulatory element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11603–11607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. B., Spotts G. D., Halvorsen Y. D., Shih H. M., Ellenberger T., Towle H. C., Spiegelman B. M. Dual DNA binding specificity of ADD1/SREBP1 controlled by a single amino acid in the basic helix-loop-helix domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2582–2588. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kylsten P., Samakovlis C., Hultmark D. The cecropin locus in Drosophila; a compact gene cluster involved in the response to infection. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):217–224. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08098.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law J. H., Ribeiro J. M., Wells M. A. Biochemical insights derived from insect diversity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:87–111. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law J. H., Wells M. A. Insects as biochemical models. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16335–16338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P. O., Rosbash M. Sequence, structure, and codon preference of the Drosophila ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5495–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samakovlis C., Asling B., Boman H. G., Gateff E., Hultmark D. In vitro induction of cecropin genes--an immune response in a Drosophila blood cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 16;188(3):1169–1175. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91354-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato R., Yang J., Wang X., Evans M. J., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Assignment of the membrane attachment, DNA binding, and transcriptional activation domains of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 (SREBP-1). J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 24;269(25):17267–17273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider I. Cell lines derived from late embryonic stages of Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1972 Apr;27(2):353–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonbaum C. P., Lee S., Mahowald A. P. The Drosophila yolkless gene encodes a vitellogenin receptor belonging to the low density lipoprotein receptor superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1485–1489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipos L., von Heijne G. Predicting the topology of eukaryotic membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1993 May 1;213(3):1333–1340. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. R., Osborne T. F., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Identification of nucleotides responsible for enhancer activity of sterol regulatory element in low density lipoprotein receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2306–2310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soulages J. L., Wells M. A. Lipophorin: the structure of an insect lipoprotein and its role in lipid transport in insects. Adv Protein Chem. 1994;45:371–415. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60644-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempst P., Link A. J., Riviere L. R., Fleming M., Elicone C. Internal sequence analysis of proteins separated on polyacrylamide gels at the submicrogram level: improved methods, applications and gene cloning strategies. Electrophoresis. 1990 Jul;11(7):537–553. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theopold U., Pintér M., Daffre S., Tryselius Y., Friedrich P., Nässel D. R., Hultmark D. CalpA, a Drosophila calpain homolog specifically expressed in a small set of nerve, midgut, and blood cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;15(2):824–834. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.2.824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tontonoz P., Kim J. B., Graves R. A., Spiegelman B. M. ADD1: a novel helix-loop-helix transcription factor associated with adipocyte determination and differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4753–4759. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida K., Wells M. A. Isolation and characterization of a lipoprotein receptor from the fat body of an insect, Manduca sexta. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5761–5767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Pai J. T., Wiedenfeld E. A., Medina J. C., Slaughter C. A., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Purification of an interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme-related cysteine protease that cleaves sterol regulatory element-binding proteins between the leucine zipper and transmembrane domains. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 28;270(30):18044–18050. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.30.18044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Sato R., Brown M. S., Hua X., Goldstein J. L. SREBP-1, a membrane-bound transcription factor released by sterol-regulated proteolysis. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Sato R., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Sterol-resistant transcription in CHO cells caused by gene rearrangement that truncates SREBP-2. Genes Dev. 1994 Aug 15;8(16):1910–1919. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.16.1910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama C., Wang X., Briggs M. R., Admon A., Wu J., Hua X., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. SREBP-1, a basic-helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper protein that controls transcription of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):187–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]