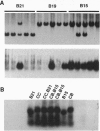
Abstract
beta 2-Microglobulin is an essential subunit of major histocompatibility complex (Mhc) class I molecules, which present antigenic peptides to T lymphocytes. We sequenced a number of cDNAs and two genomic clones corresponding to chicken beta 2-microglobulin. The chicken beta 2-microglobulin gene has a similar genomic organization but smaller introns and higher G+C content than mammalian beta 2-microglobulin genes. The promoter region is particularly G+C-rich and contains, in addition to interferon regulatory elements, potential S/W, X, and Y boxes that were originally described for mammalian class II but not class I alpha or beta 2-microglobulin genes. There is a single chicken beta 2-microglobulin gene that has little polymorphism in the coding region. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms from Mhc homozygous lines, Mhc congenic lines, and backcross families, as well as in situ hybridization, show that the beta 2-microglobulin gene is located on a microchromosome different from the one that contains the chicken Mhc. We propose that the structural similarities between the beta 2-microglobulin and Mhc genes in the chicken are due to their presence on microchromosomes and suggest that these features and the microchromosomes appeared by deletion of DNA in the lineage leading to the birds.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auer H., Mayr B., Lambrou M., Schleger W. An extended chicken karyotype, including the NOR chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;45(3-4):218–221. doi: 10.1159/000132457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Mathis D. Regulation of major histocompatibility complex class-II genes: X, Y and other letters of the alphabet. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:681–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickmore W. A., Sumner A. T. Mammalian chromosome banding--an expression of genome organization. Trends Genet. 1989 May;5(5):144–148. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. E., Bacon L. D. Linkage of the major histocompatibility (B) complex and the nucleolar organizer in the chicken. Assignment to a microchromosome. J Hered. 1985 May-Jun;76(3):146–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinckerhoff C. E., Mitchell T. I., Karmilowicz M. J., Kluve-Beckerman B., Benson M. D. Autocrine induction of collagenase by serum amyloid A-like and beta 2-microglobulin-like proteins. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):655–657. doi: 10.1126/science.2536953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bumstead N., Palyga J. A preliminary linkage map of the chicken genome. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):690–697. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90143-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dargemont C., Dunon D., Deugnier M. A., Denoyelle M., Girault J. M., Lederer F., Lê K. H., Godeau F., Thiery J. P., Imhof B. A. Thymotaxin, a chemotactic protein, is identical to beta 2-microglobulin. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):803–806. doi: 10.1126/science.2683083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez-Steglich M., Carrier A., Auffray C., Schmid M. Assignment of the chicken tyrosine hydroxylase gene to chromosome 6 by FISH. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1992;60(2):138–139. doi: 10.1159/000133324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez-Steglich M., Lichter P., Carrier A., Auffray C., Schmid M. Mapping the beta NGF gene in situ to a microchromosome in chicken. Genomics. 1992 Apr;12(4):829–832. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90318-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunon D., Kaufman J., Salomonsen J., Skjoedt K., Vainio O., Thiery J. P., Imhof B. A. T cell precursor migration towards beta 2-microglobulin is involved in thymus colonization of chicken embryos. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3315–3322. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07531.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh D. TFD: the transcription factors database. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2091–2093. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glimcher L. H., Kara C. J. Sequences and factors: a guide to MHC class-II transcription. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:13–49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemot F., Billault A., Pourquié O., Béhar G., Chaussé A. M., Zoorob R., Kreibich G., Auffray C. A molecular map of the chicken major histocompatibility complex: the class II beta genes are closely linked to the class I genes and the nucleolar organizer. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2775–2785. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güssow D., Rein R., Ginjaar I., Hochstenbach F., Seemann G., Kottman A., Ploegh H. L. The human beta 2-microglobulin gene. Primary structure and definition of the transcriptional unit. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3132–3138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist G. P. Evolution of chromosome bands: molecular ecology of noncoding DNA. J Mol Evol. 1989 Jun;28(6):469–486. doi: 10.1007/BF02602928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Stubblefield E., Payvar F., Engel J. D., Dodgson J. B., Spector D., Cordell B., Schimke R. T., Varmus H. E. Gene localization by chromosome fractionation: globin genes are on at least two chromosomes and three estrogen-inducible genes are on three chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1348–1352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J., Andersen R., Avila D., Engberg J., Lambris J., Salomonsen J., Welinder K., Skjødt K. Different features of the MHC class I heterodimer have evolved at different rates. Chicken B-F and beta 2-microglobulin sequences reveal invariant surface residues. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 1;148(5):1532–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J., Salomonsen J., Skjødt K. B-G cDNA clones have multiple small repeats and hybridize to both chicken MHC regions. Immunogenetics. 1989;30(6):440–451. doi: 10.1007/BF02421176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J., Salomonsen J. What in the dickens is with these chickens? An only slightly silly response to the first draft of Langman and Cohn. Res Immunol. 1993 Jul-Sep;144(6-7):495–519. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(93)80154-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J., Völk H., Wallny H. J. A "minimal essential Mhc" and an "unrecognized Mhc": two extremes in selection for polymorphism. Immunol Rev. 1995 Feb;143:63–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1995.tb00670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Israël A., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. Detailed analysis of the mouse H-2Kb promoter: enhancer-like sequences and their role in the regulation of class I gene expression. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90760-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Orr H. T. Cloning and complete sequence of an HLA-A2 gene: analysis of two HLA-A alleles at the nucleotide level. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2727–2733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroemer G., Zoorob R., Auffray C. Structure and expression of a chicken MHC class I gene. Immunogenetics. 1990;31(5-6):405–409. doi: 10.1007/BF02115020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonergan M., Dey A., Becker K. G., Drew P. D., Ozato K. A regulatory element in the beta 2-microglobulin promoter identified by in vivo footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6629–6639. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono H., Figueroa F., O'hUigin C., Klein J. Cloning of the beta 2-microglobulin gene in the zebrafish. Immunogenetics. 1993;38(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00216384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Seidman J. G. Structure of wild-type and mutant mouse beta 2-microglobulin genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):661–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer D. S., Maguire J. E. Regulation of the expression of class I MHC genes. Crit Rev Immunol. 1990;10(3):235–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegelström H., Ebenhard T., Ryttman H. Rate of karyotype evolution and speciation in birds. Hereditas. 1983;98(2):235–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1983.tb00600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tregaskes C. A., Kong F. K., Paramithiotis E., Chen C. L., Ratcliffe M. J., Davison T. F., Young J. R. Identification and analysis of the expression of CD8 alpha beta and CD8 alpha alpha isoforms in chickens reveals a major TCR-gamma delta CD8 alpha beta subset of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1995 May 1;154(9):4485–4494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welinder K. G., Jespersen H. M., Walther-Rasmussen J., Skjødt K. Amino acid sequences and structures of chicken and turkey beta 2-microglobulin. Mol Immunol. 1991 Jan-Feb;28(1-2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90102-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoorob R., Béhar G., Kroemer G., Auffray C. Organization of a functional chicken class II B gene. Immunogenetics. 1990;31(3):179–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00211553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]