Abstract
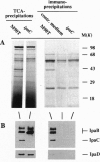
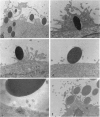
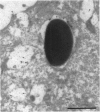
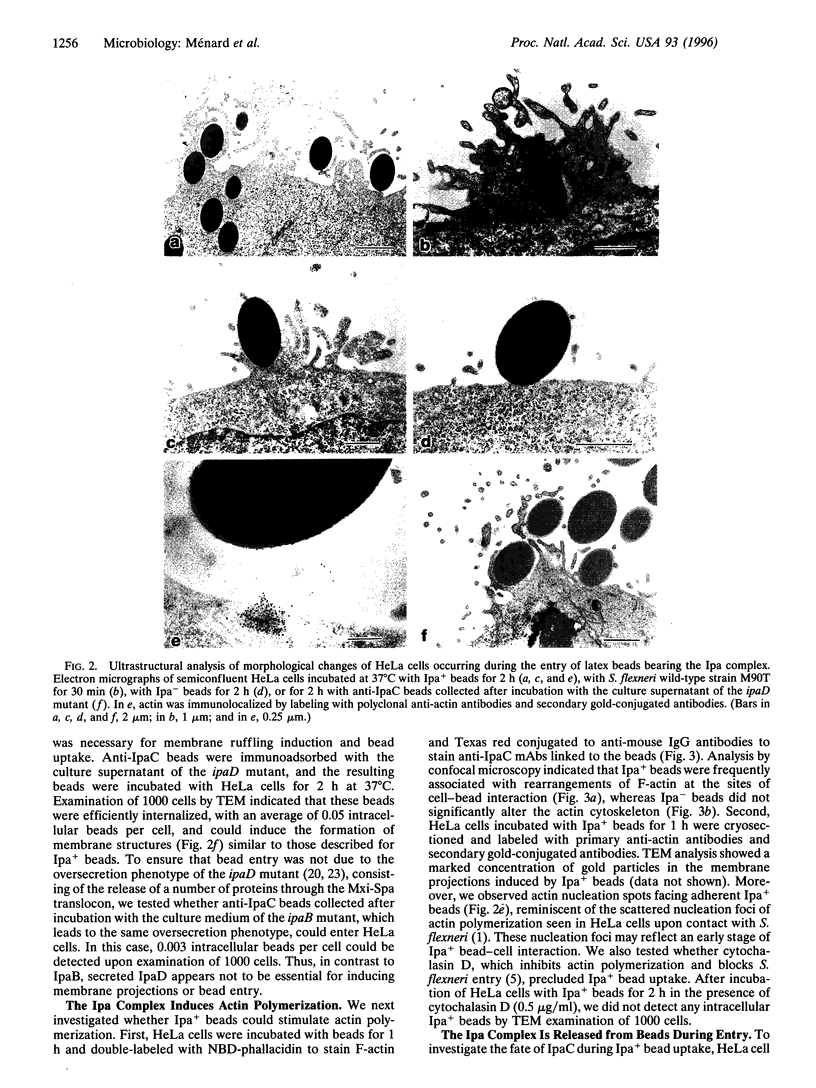
The bacterial pathogen Shigella flexneri causes bacillary dysentery in humans by invading coloncytes. Upon contact with epithelial cells, S. flexneri elicits localized plasma membrane projections sustained by long actin filaments which engulf the microorganism. The products necessary for Shigella entry include three secretory proteins: IpaB, IpaC, and IpaD. Extracellular IpaB and IpaC associate in a soluble complex, the Ipa complex. We have immunopurified this Ipa complex on latex beads and found that they were efficiently internalized into HeLa cells. Like S. flexneri entry, uptake of the beads bearing the Ipa complex was associated with membrane projections and polymerization of actin at the site of cell-bead interaction and was dependent on small Rho GTPases. These results indicate that a secreted factor can promote S. flexneri entry into epithelial cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam T., Arpin M., Prévost M. C., Gounon P., Sansonetti P. J. Cytoskeletal rearrangements and the functional role of T-plastin during entry of Shigella flexneri into HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;129(2):367–381. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.2.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews G. P., Hromockyj A. E., Coker C., Maurelli A. T. Two novel virulence loci, mxiA and mxiB, in Shigella flexneri 2a facilitate excretion of invasion plasmid antigens. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1997–2005. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1997-2005.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barzu S., Nato F., Rouyre S., Mazie J. C., Sansonetti P., Phalipon A. Characterization of B-cell epitopes on IpaB, an invasion-associated antigen of Shigella flexneri: identification of an immunodominant domain recognized during natural infection. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):3825–3831. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.3825-3831.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman T., Erickson K., Galyov E., Persson C., Wolf-Watz H. The lcrB (yscN/U) gene cluster of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis is involved in Yop secretion and shows high homology to the spa gene clusters of Shigella flexneri and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1994 May;176(9):2619–2626. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.9.2619-2626.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Schönherr R., Hobbie S. Enterobacterial hemolysins: activation, secretion and pore formation. Trends Microbiol. 1993 Sep;1(6):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(93)90134-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., McKanna J. A., Cohen S. Rapid induction of morphological changes in human carcinoma cells A-431 by epidermal growth factors. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):260–265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P., Sansonetti P. J. Entry of Shigella flexneri into HeLa cells: evidence for directed phagocytosis involving actin polymerization and myosin accumulation. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2681–2688. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2681-2688.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehio C., Prévost M. C., Sansonetti P. J. Invasion of epithelial cells by Shigella flexneri induces tyrosine phosphorylation of cortactin by a pp60c-src-mediated signalling pathway. EMBO J. 1995 Jun 1;14(11):2471–2482. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07244.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falzano L., Fiorentini C., Donelli G., Michel E., Kocks C., Cossart P., Cabanié L., Oswald E., Boquet P. Induction of phagocytic behaviour in human epithelial cells by Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor type 1. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Sep;9(6):1247–1254. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01254.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Gumbiner B., Falkow S. Penetration of Salmonella through a polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cell monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):221–230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. L., Ryan T. A., Jones B. D., Smith S. J., Falkow S. Ruffles induced by Salmonella and other stimuli direct macropinocytosis of bacteria. Nature. 1993 Aug 12;364(6438):639–642. doi: 10.1038/364639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr, Silverstein S. C. Segmental response of the macrophage plasma membrane to a phagocytic stimulus. J Exp Med. 1974 Feb 1;139(2):323–336. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A., Ochman H. Cognate gene clusters govern invasion of host epithelial cells by Salmonella typhimurium and Shigella flexneri. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3779–3787. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Oaks E. V., Formal S. B. Identification and antigenic characterization of virulence-associated, plasmid-coded proteins of Shigella spp. and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):620–629. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.620-629.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermant D., Ménard R., Arricau N., Parsot C., Popoff M. Y. Functional conservation of the Salmonella and Shigella effectors of entry into epithelial cells. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Aug;17(4):781–789. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.mmi_17040781.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Håkansson S., Bergman T., Vanooteghem J. C., Cornelis G., Wolf-Watz H. YopB and YopD constitute a novel class of Yersinia Yop proteins. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):71–80. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.71-80.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R. Discrimination between intracellular uptake and surface adhesion of bacterial pathogens. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):934–938. doi: 10.1126/science.1674624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Falkow S. A single genetic locus encoded by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis permits invasion of cultured animal cells by Escherichia coli K-12. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):262–264. doi: 10.1038/317262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Just I., Fritz G., Aktories K., Giry M., Popoff M. R., Boquet P., Hegenbarth S., von Eichel-Streiber C. Clostridium difficile toxin B acts on the GTP-binding protein Rho. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10706–10712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Just I., Selzer J., Wilm M., von Eichel-Streiber C., Mann M., Aktories K. Glucosylation of Rho proteins by Clostridium difficile toxin B. Nature. 1995 Jun 8;375(6531):500–503. doi: 10.1038/375500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Baudry B., d'Hauteville H., Hale T. L., Sansonetti P. J. Cloning of plasmid DNA sequences involved in invasion of HeLa cells by Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):164–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.164-171.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels T., Vanooteghem J. C., Lambert de Rouvroit C., China B., Gustin A., Boudry P., Cornelis G. R. Analysis of virC, an operon involved in the secretion of Yop proteins by Yersinia enterocolitica. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):4994–5009. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.4994-5009.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ménard R., Sansonetti P. J., Parsot C. Nonpolar mutagenesis of the ipa genes defines IpaB, IpaC, and IpaD as effectors of Shigella flexneri entry into epithelial cells. J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(18):5899–5906. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.18.5899-5906.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ménard R., Sansonetti P. J. Shigella flexneri: isolation of noninvasive mutants of gram-negative pathogens. Methods Enzymol. 1994;236:493–509. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)36038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ménard R., Sansonetti P., Parsot C. The secretion of the Shigella flexneri Ipa invasins is activated by epithelial cells and controlled by IpaB and IpaD. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 15;13(22):5293–5302. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06863.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ménard R., Sansonetti P., Parsot C., Vasselon T. Extracellular association and cytoplasmic partitioning of the IpaB and IpaC invasins of S. flexneri. Cell. 1994 Nov 4;79(3):515–525. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90260-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama T., Sasaki T., Takaishi K., Kato M., Yaku H., Araki K., Matsuura Y., Takai Y. rac p21 is involved in insulin-induced membrane ruffling and rho p21 is involved in hepatocyte growth factor- and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced membrane ruffling in KB cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2447–2456. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsot C., Ménard R., Gounon P., Sansonetti P. J. Enhanced secretion through the Shigella flexneri Mxi-Spa translocon leads to assembly of extracellular proteins into macromolecular structures. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Apr;16(2):291–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phalipon A., Arondel J., Nato F., Rouyre S., Mazie J. C., Sansonetti P. J. Identification and characterization of B-cell epitopes of IpaC, an invasion-associated protein of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1919–1926. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1919-1926.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa C., Adler B., Tobe T., Okada N., Nagai S., Komatsu K., Yoshikawa M. Functional organization and nucleotide sequence of virulence Region-2 on the large virulence plasmid in Shigella flexneri 2a. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1191–1201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. A., Baer S. C. Phagocytosis by zippers and triggers. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;5(3):89–93. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)88956-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watarai M., Tobe T., Yoshikawa M., Sasakawa C. Contact of Shigella with host cells triggers release of Ipa invasins and is an essential function of invasiveness. EMBO J. 1995 Jun 1;14(11):2461–2470. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07243.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]