Abstract
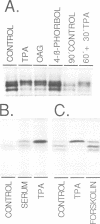
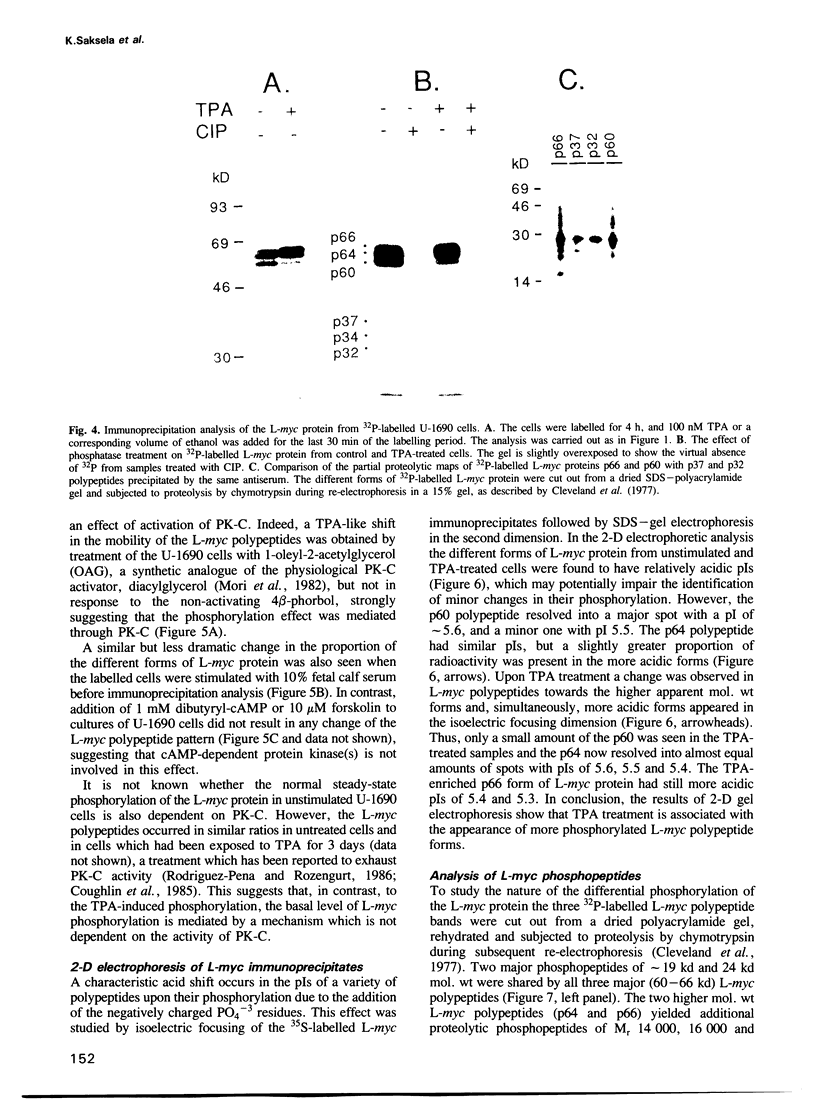
We have examined post-translational modification of the L-myc protein using polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies against a peptide well conserved in the predicted amino acid sequences of the c-myc, N-myc and L-myc genes. These antibodies precipitate three polypeptides of Mr 60-66,000 from [35S]methionine or [32P]orthophosphate-labelled human small cell lung cancer cell lines expressing amplified L-myc genes, but not the other myc genes. Treatment of the L-myc immunoprecipitates with alkaline phosphatase prior to electrophoresis converts the three methionine-labelled polypeptides into a single band migrating at Mr 59,000, and efficiently removes radioactivity from the 32P-labelled L-myc protein, suggesting that, in contrast to the c-myc and N-myc proteins, the L-myc polypeptide heterogeneity is due to differential phosphorylation of a common precursor. When the phorbol ester 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate (TPA) or serum is added to cultures of U-1690 cells the Mr 66,000 polypeptide is rapidly enriched while the Mr 60,000 form is decreased in the L-myc immunoprecipitates. This effect is correlated with the ability of phorbol ester and diacylglycerol analogues to activate protein kinase C. The TPA-induced phosphorylation of the L-myc protein occurs in a protein synthesis-independent manner as it is not inhibited by cycloheximide or anisomycin. These data indicate that the phosphorylation of the L-myc nuclear oncoprotein is modulated in response to TPA via a rapid signal transduction system involving protein kinase C. This mechanism could play an important role in the response of lung cells to e.g. bombesin-related growth factors.
Full text
PDF



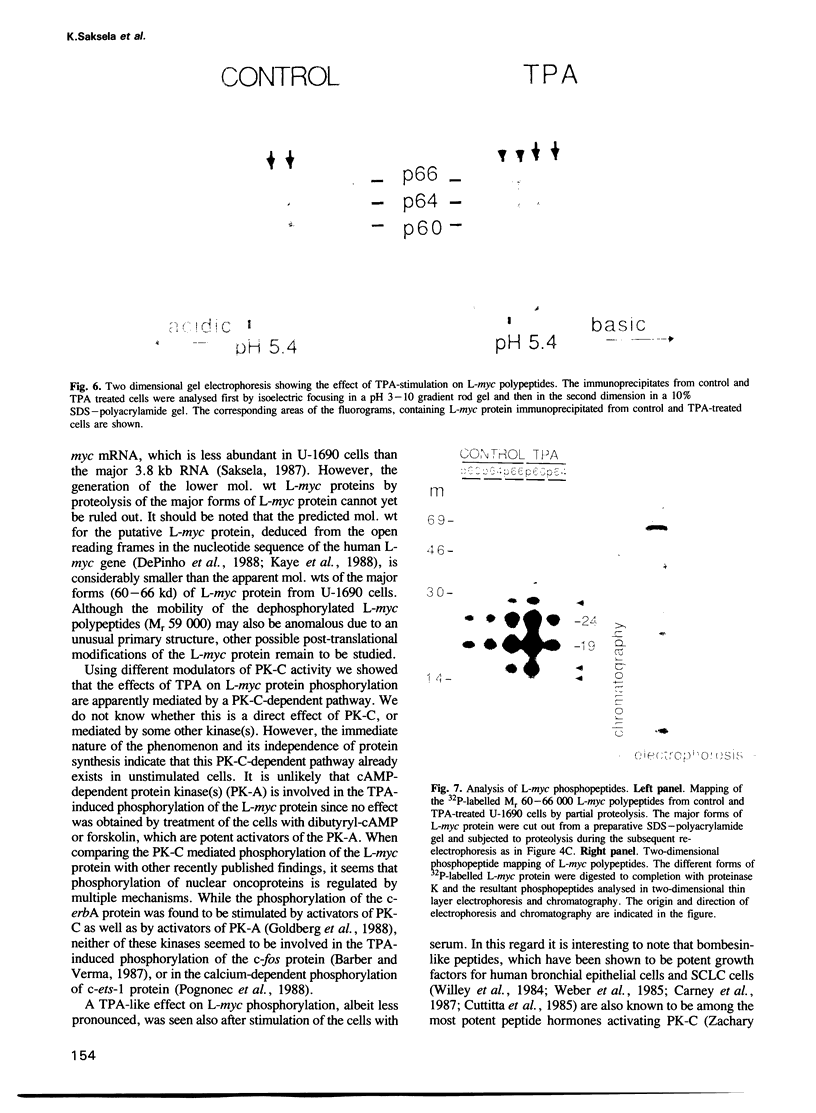



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Schwab M., Lin C. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Homogeneously staining chromosomal regions contain amplified copies of an abundantly expressed cellular oncogene (c-myc) in malignant neuroendocrine cells from a human colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1707–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., DePinho R., Zimmerman K., Legouy E., Hatton K., Ferrier P., Tesfaye A., Yancopoulos G., Nisen P. The human myc gene family. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 2):931–941. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baillie-Johnson H., Twentyman P. R., Fox N. E., Walls G. A., Workman P., Watson J. V., Johnson N., Reeve J. G., Bleehen N. M. Establishment and characterisation of cell lines from patients with lung cancer (predominantly small cell carcinoma). Br J Cancer. 1985 Oct;52(4):495–504. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber J. R., Verma I. M. Modification of fos proteins: phosphorylation of c-fos, but not v-fos, is stimulated by 12-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate and serum. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2201–2211. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beimling P., Benter T., Sander T., Moelling K. Isolation and characterization of the human cellular myc gene product. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 5;24(23):6349–6355. doi: 10.1021/bi00344a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergh J., Nilsson K., Dahl D., Andersson L., Virtanen I., Lehto V. P. Expression of intermediate filaments in established human lung cancer cell lines. An indicator of differentiation and derivation. Lab Invest. 1984 Sep;51(3):307–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T., Müller R. Stimulation and inhibition of growth by EGF in different A431 cell clones is accompanied by the rapid induction of c-fos and c-myc proto-oncogenes. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1193–1197. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03759.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler A. P., Byus C. V., Slaga T. J. Phosphorylation of histones is stimulated by phorbol esters in quiescent Reuber H35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9421–9425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. N., Cuttitta F., Moody T. W., Minna J. D. Selective stimulation of small cell lung cancer clonal growth by bombesin and gastrin-releasing peptide. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 1;47(3):821–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Boyle W. J., Meek J., Smeal T., Hunter T., Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Classon M., Henriksson M., Sümegi J., Klein G., Hammarskjöld M. L., Hammaskjöld M. L. Elevated c-myc expression facilitates the replication of SV40 DNA in human lymphoma cells. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):272–274. doi: 10.1038/330272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Gould K. L., Cartwright C. A., Hunter T. Tyr527 is phosphorylated in pp60c-src: implications for regulation. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1431–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2420005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Lee W. M., Williams P. W., Giels G. M., Williams L. T. c-myc gene expression is stimulated by agents that activate protein kinase C and does not account for the mitogenic effect of PDGF. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuttitta F., Carney D. N., Mulshine J., Moody T. W., Fedorko J., Fischler A., Minna J. D. Bombesin-like peptides can function as autocrine growth factors in human small-cell lung cancer. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):823–826. doi: 10.1038/316823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I. Two dimensional gel electrophoresis and computer analysis of proteins synthesized by clonal cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7961–7977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg Y., Glineur C., Gesquière J. C., Ricouart A., Sap J., Vennström B., Ghysdael J. Activation of protein kinase C or cAMP-dependent protein kinase increases phosphorylation of the c-erbA-encoded thyroid hormone receptor and of the v-erbA-encoded protein. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2425–2433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurley L. R., D'Anna J. A., Barham S. S., Deaven L. L., Tobey R. A. Histone phosphorylation and chromatin structure during mitosis in Chinese hamster cells. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar;84(1):1–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by the human c-myc oncogene: differential expression in neoplastic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2486–2497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., King M. W., Bentley D. L., Anderson C. W., Eisenman R. N. A non-AUG translational initiation in c-myc exon 1 generates an N-terminally distinct protein whose synthesis is disrupted in Burkitt's lymphomas. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila R., Schwab G., Wickstrom E., Loke S. L., Pluznik D. H., Watt R., Neckers L. M. A c-myc antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits entry into S phase but not progress from G0 to G1. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):445–449. doi: 10.1038/328445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A tail of two src's: mutatis mutandis. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90745-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Itani T., Kiji Y., Ariga H. Possible function of the c-myc product: promotion of cellular DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2365–2371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Okazaki T., Itani T., Ogata M., Sato Y., Ariga H. An initiation site of DNA replication with transcriptional enhancer activity present upstream of the c-myc gene. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3135–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03180.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacke C. M., Meisenhelder J., Brown K. D., Gould K. L., Gould S. J., Hunter T. Early phosphorylation events following the treatment of Swiss 3T3 cells with bombesin and the mammalian bombesin-related peptide, gastrin-releasing peptide. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2889–2898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04584.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaddurah-Daouk R., Greene J. M., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Kingston R. E. Activation and repression of mammalian gene expression by the c-myc protein. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):347–357. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye F., Battey J., Nau M., Brooks B., Seifter E., De Greve J., Birrer M., Sausville E., Minna J. Structure and expression of the human L-myc gene reveal a complex pattern of alternative mRNA processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):186–195. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamph W. W., Wamsley P., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. Induction of proto-oncogene JUN/AP-1 by serum and TPA. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):629–631. doi: 10.1038/334629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori T., Takai Y., Yu B., Takahashi J., Nishizuka Y., Fujikura T. Specificity of the fatty acyl moieties of diacylglycerol for the activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biochem. 1982 Feb;91(2):427–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Müller D., Kurz C., Renz M. Different types of modification in c-fos and its associated protein p39: modulation of DNA binding by phosphorylation. Oncogene Res. 1987;2(1):19–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nau M. M., Brooks B. J., Battey J., Sausville E., Gazdar A. F., Kirsch I. R., McBride O. W., Bertness V., Hollis G. F., Minna J. D. L-myc, a new myc-related gene amplified and expressed in human small cell lung cancer. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):69–73. doi: 10.1038/318069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patskan G. J., Baxter C. S. Specific stimulation of histone H2B and H4 phosphorylation in mouse lymphocytes by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):12899–12903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Leder P. Nuclear localization and DNA binding properties of a protein expressed by human c-myc oncogene. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):718–721. doi: 10.1126/science.6463648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pognonec P., Boulukos K. E., Gesquière J. C., Stéhelin D., Ghysdael J. Mitogenic stimulation of thymocytes results in the calcium-dependent phosphorylation of c-ets-1 proteins. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):977–983. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02904.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn L. A., Moore G. E., Morgan R. T., Woods L. K. Cell lines from human colon carcinoma with unusual cell products, double minutes, and homogeneously staining regions. Cancer Res. 1979 Dec;39(12):4914–4924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Evan G. I., Bishop J. M. The protein encoded by the human proto-oncogene c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7742–7746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Hayman M. J., Bister K. Phosphorylation of specific sites in the gag-myc polyproteins encoded by MC29-type viruses correlates with their transforming ability. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1111–1116. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Stanton L., Schwab M., Bishop J. M. Human proto-oncogene N-myc encodes nuclear proteins that bind DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4450–4457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Phosphorylation of an acidic mol. wt. 80 000 cellular protein in a cell-free system and intact Swiss 3T3 cells: a specific marker of protein kinase C activity. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):77–83. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04180.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Pritzl P., Bornstein P. A new mapping technique for collagen chains. Coll Relat Res. 1981;1(1):3–15. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(80)80003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela K., Bergh J., Lehto V. P., Nilsson K., Alitalo K. Amplification of the c-myc oncogene in a subpopulation of human small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1985 Apr;45(4):1823–1827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela K. Expression of the L-myc gene is under positive control by short-lived proteins. Oncogene. 1987;1(3):291–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Damm K., Goldberg Y., Ghysdael J., Leutz A., Beug H., Vennström B. The c-erb-A protein is a high-affinity receptor for thyroid hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):635–640. doi: 10.1038/324635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Echle B., Walter G. Simian virus 40 large T antigen is phosphorylated at multiple sites clustered in two separate regions. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):116–133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.116-133.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Klempnauer K. H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Gilbert F., Brodeur G., Goldstein M., Trent J. Amplified DNA with limited homology to myc cellular oncogene is shared by human neuroblastoma cell lines and a neuroblastoma tumour. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):245–248. doi: 10.1038/305245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Human N-myc gene contributes to neoplastic transformation of mammalian cells in culture. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):160–162. doi: 10.1038/316160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Chou W., Rodgers K. Phosphorylation downregulates the DNA-binding activity of simian virus 40 T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):888–894. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.888-894.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L., Watt R. A., Sullivan N. F. The v- and c-myc oncogene proteins colocalize in situ with small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Oncogene. 1987 Mar;1(1):5–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K., Bos T. J., Doolittle R. F. Homology between the DNA-binding domain of the GCN4 regulatory protein of yeast and the carboxyl-terminal region of a protein coded for by the oncogene jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3316–3319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber S., Zuckerman J. E., Bostwick D. G., Bensch K. G., Sikic B. I., Raffin T. A. Gastrin releasing peptide is a selective mitogen for small cell lung carcinoma in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):306–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI111690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey J. C., Lechner J. F., Harris C. C. Bombesin and the C-terminal tetradecapeptide of gastrin-releasing peptide are growth factors for normal human bronchial epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jul;153(1):245–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90466-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winqvist R., Saksela K., Alitalo K. The myc proteins are not associated with chromatin in mitotic cells. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2947–2950. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02237.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Sinnett-Smith J. W., Rozengurt E. Early events elicited by bombesin and structurally related peptides in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. I. Activation of protein kinase C and inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2211–2222. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman K. A., Yancopoulos G. D., Collum R. G., Smith R. K., Kohl N. E., Denis K. A., Nau M. M., Witte O. N., Toran-Allerand D., Gee C. E. Differential expression of myc family genes during murine development. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):780–783. doi: 10.1038/319780a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]