Abstract
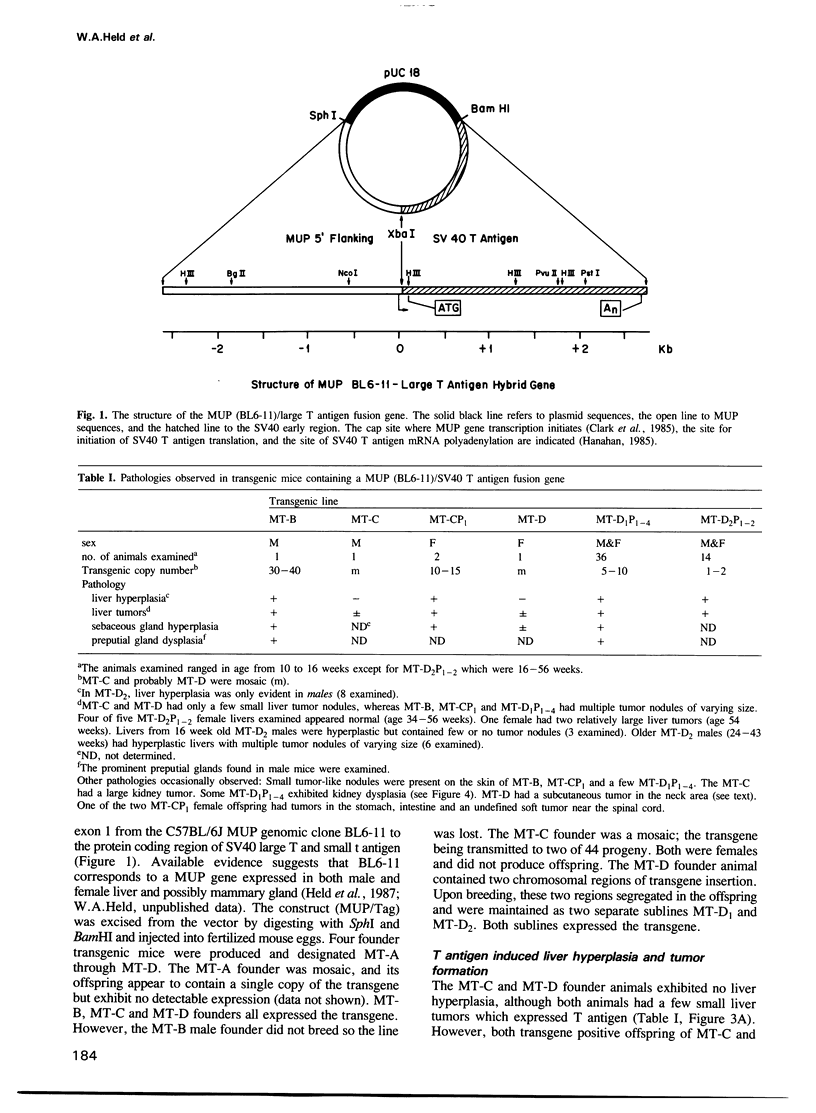
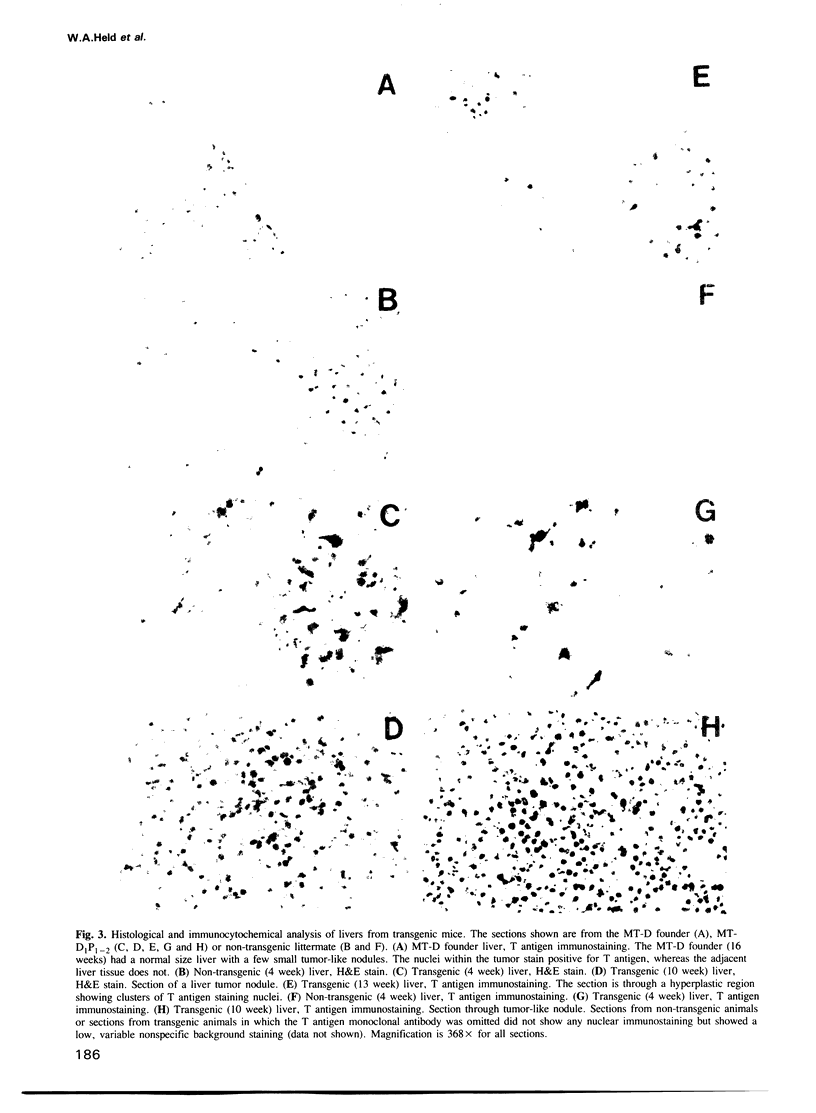
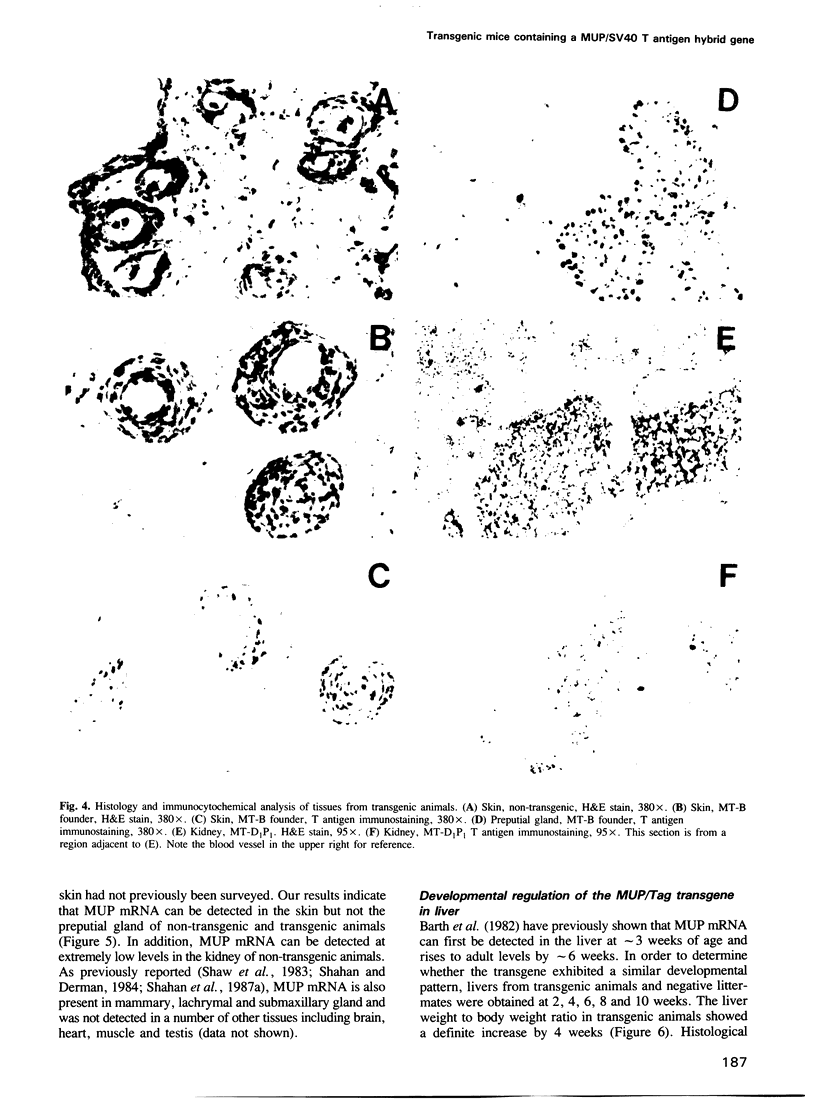
A hybrid mouse major urinary protein (MUP)/SV40 T antigen gene was microinjected into fertilized mouse embryos and the resulting transgenic mice analyzed for the regulated expression of the transgene. Available evidence indicates that the MUP gene used for the hybrid gene construct is expressed in both male and female liver and possibly mammary gland. Three different transgenic lines exhibited a consistent pattern of tissue specific expression of the transgene. As a consequence of transgene expression and T antigen synthesis in the liver, both male and female transgenic animals developed liver hyperplasia and tumors. Transgene expression and liver hyperplasia commenced at approximately 2-4 weeks of age, the same time that MUP gene expression is first detected in the liver. The expression of the transgene resulted in an immediate strong suppression of liver MUP mRNA levels but had relatively little effect on other liver specific mRNAs. From 4 to 8 weeks, the liver increased several fold in size, relative to non-transgenic littermates. Definitive tumor nodules were not apparent until 8-10 weeks. The transgene was also consistently found to be expressed in the skin sebaceous glands and the preputial gland, a modified sebaceous gland. The expression of the transgene in the skin sebaceous glands is consistent with the presence of MUP mRNA in the skin and a putative role for MUPs in the transport and excretion of small molecules. Occasional expression of the transgene in other tissues (kidney and mammary connective tissues) was also noted.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


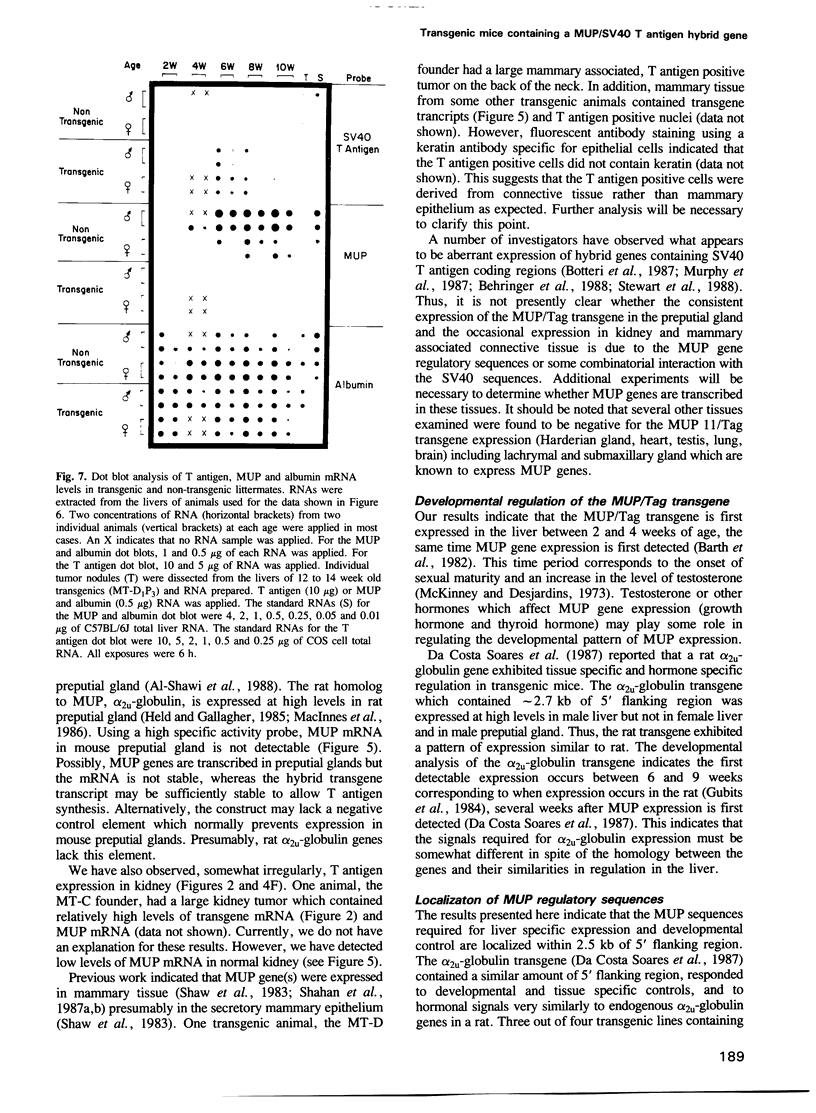


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Shawi R., Burke J., Jones C. T., Simons J. P., Bishop J. O. A Mup promoter-thymidine kinase reporter gene shows relaxed tissue-specific expression and confers male sterility upon transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4821–4828. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth R. K., Gross K. W., Gremke L. C., Hastie N. D. Developmentally regulated mRNAs in mouse liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):500–504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behringer R. R., Peschon J. J., Messing A., Gartside C. L., Hauschka S. D., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Heart and bone tumors in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2648–2652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett K. L., Lalley P. A., Barth R. K., Hastie N. D. Mapping the structural genes coding for the major urinary proteins in the mouse: combined use of recombinant inbred strains and somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1220–1224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Clark A. J., Clissold P. M., Hainey S., Francke U. Two main groups of mouse major urinary protein genes, both largely located on chromosome 4. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):615–620. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01217.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botteri F. M., van der Putten H., Wong D. F., Sauvage C. A., Evans R. M. Unexpected thymic hyperplasia in transgenic mice harboring a neuronal promoter fused with simian virus 40 large T antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3178–3184. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavaggioni A., Sorbi R. T., Keen J. N., Pappin D. J., Findlay J. B. Homology between the pyrazine-binding protein from nasal mucosa and major urinary proteins. FEBS Lett. 1987 Feb 23;212(2):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81349-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. W., Thomas C. A., Jr Recovery of DNA segments from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jan 15;101(2):339–341. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90197-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Clissold P. M., Al Shawi R., Beattie P., Bishop J. Structure of mouse major urinary protein genes: different splicing configurations in the 3'-non-coding region. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1045–1052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01925.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Ghazal P., Bingham R. W., Barrett D., Bishop J. O. Sequence structures of a mouse major urinary protein gene and pseudogene compared. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3159–3165. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04059.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D. T., McLean J. W., Wion K. L., Trent J. M., Drabkin H. A., Lawn R. M. Human apolipoprotein D gene: gene sequence, chromosome localization, and homology to the alpha 2u-globulin superfamily. DNA. 1987 Jun;6(3):199–204. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINLAYSON J. S., POTTER M., RUNNER C. R. ELECTROPHORETIC VARIATION AND SEX DIMORPHISM OF THE MAJOR URINARY PROTEIN COMPLEX IN INBRED MICE: A NEW GENETIC MARKER. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1963 Jul;31:91–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glibetic M. D., Baumann H. Influence of chronic inflammation on the level of mRNA for acute-phase reactants in the mouse liver. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1616–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubits R. M., Lynch K. R., Kulkarni A. B., Dolan K. P., Gresik E. W., Hollander P., Feigelson P. Differential regulation of alpha 2u globulin gene expression in liver, lachrymal gland, and salivary gland. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12803–12809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Heritable formation of pancreatic beta-cell tumours in transgenic mice expressing recombinant insulin/simian virus 40 oncogenes. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):115–122. doi: 10.1038/315115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Held W. A., Toole J. J. Multiple genes coding for the androgen-regulated major urinary proteins of the mouse. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90171-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held W. A., Gallagher J. F., Hohman C. M., Kuhn N. J., Sampsell B. M., Hughes R. G., Jr Identification and characterization of functional genes encoding the mouse major urinary proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3705–3712. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held W. A., Gallagher J. F. Rat alpha 2u-globulin mRNA expression in the preputial gland. Biochem Genet. 1985 Apr;23(3-4):281–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00504325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden H. M., Rypniewski W. R., Law J. H., Rayment I. The molecular structure of insecticyanin from the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta L. at 2.6 A resolution. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1565–1570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf J. L., Gallagher J. F., Held W. A. Differential, multihormonal regulation of the mouse major urinary protein gene family in the liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2232–2240. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauter K., Leinwand L., D'Eustachio P., Ruddle F., Darnell J. E., Jr Structural genes of the mouse major urinary protein are on chromosome 4. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):414–417. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn N. J., Woodworth-Gutai M., Gross K. W., Held W. A. Subfamilies of the mouse major urinary protein (MUP) multi-gene family: sequence analysis of cDNA clones and differential regulation in the liver. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):6073–6090. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.6073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz D. T., Sippel A. E., Ansah-Yiadom R., Feigelson P. Effects of sex hormones on the level of the messenger RNA for the rat hepatic protein alpha 2u globulin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 25;251(12):3594–3598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laperche Y., Lynch K. R., Dolan K. P., Feigelson P. Tissue-specific control of alpha 2u globulin gene expression: constitutive synthesis in the submaxillary gland. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):453–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90465-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder A., Pattengale P. K., Kuo A., Stewart T. A., Leder P. Consequences of widespread deregulation of the c-myc gene in transgenic mice: multiple neoplasms and normal development. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):485–495. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Wells R. G., Reed R. R. Isolation of an olfactory cDNA: similarity to retinol-binding protein suggests a role in olfaction. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1053–1056. doi: 10.1126/science.3493528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacInnes J. I., Nozik E. S., Kurtz D. T. Tissue-specific expression of the rat alpha 2u globulin gene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3563–3567. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney T. D., Desjardins C. Postnatal development of the testis, fighting behavior, and fertility in house mice. Biol Reprod. 1973 Oct;9(3):279–294. doi: 10.1093/biolreprod/9.3.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D., Bishop A., Rindi G., Murphy M. N., Stamp G. W., Hanson J., Polak J. M., Hogan B. Mice transgenic for a vasopressin-SV40 hybrid oncogene develop tumors of the endocrine pancreas and the anterior pituitary. A possible model for human multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. Am J Pathol. 1987 Dec;129(3):552–566. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Hammer R. E., Messing A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Pancreatic neoplasia induced by SV40 T-antigen expression in acinar cells of transgenic mice. Science. 1987 Oct 9;238(4824):188–193. doi: 10.1126/science.2821617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papiz M. Z., Sawyer L., Eliopoulos E. E., North A. C., Findlay J. B., Sivaprasadarao R., Jones T. A., Newcomer M. E., Kraulis P. J. The structure of beta-lactoglobulin and its similarity to plasma retinol-binding protein. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):383–385. doi: 10.1038/324383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. K., Neuhaus O. W. Proof of the hepatic synthesis of a sex-dependent protein in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Sep 26;127(1):82–87. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90478-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer L. Protein structure. One fold among many. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):659–659. doi: 10.1038/327659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
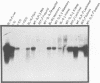
- Shahan K., Denaro M., Gilmartin M., Shi Y., Derman E. Expression of six mouse major urinary protein genes in the mammary, parotid, sublingual, submaxillary, and lachrymal glands and in the liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1947–1954. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahan K., Derman E. Tissue-specific expression of major urinary protein (MUP) genes in mice: characterization of MUP mRNAs by restriction mapping of cDNA and by in vitro translation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2259–2265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahan K., Gilmartin M., Derman E. Nucleotide sequences of liver, lachrymal, and submaxillary gland mouse major urinary protein mRNAs: mosaic structure and construction of panels of gene-specific synthetic oligonucleotide probes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1938–1946. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. H., Held W. A., Hastie N. D. The gene family for major urinary proteins: expression in several secretory tissues of the mouse. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):755–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares V. da C., Gubits R. M., Feigelson P., Costantini F. Tissue-specific and hormonally regulated expression of a rat alpha 2u globulin gene in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3749–3758. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart T. A., Hecht N. B., Hollingshead P. G., Johnson P. A., Leong J. A., Pitts S. L. Haploid-specific transcription of protamine-myc and protamine-T-antigen fusion genes in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1748–1755. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain J. L., Stewart T. A., Leder P. Parental legacy determines methylation and expression of an autosomal transgene: a molecular mechanism for parental imprinting. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):719–727. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90330-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unterman R. D., Lynch K. R., Nakhasi H. L., Dolan K. P., Hamilton J. W., Cohn D. V., Feigelson P. Cloning and sequence of several alpha 2u-globulin cDNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3478–3482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]