Abstract
Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0 suppresses black root rot of tobacco, a disease caused by the fungus Thielaviopsis basicola. Strain CHA0 excretes several metabolites with antifungal properties. The importance of one such metabolite, hydrogen cyanide, was tested in a gnotobiotic system containing an artificial, iron-rich soil. A cyanidenegative (hcn) mutant, CHA5, constructed by a gene replacement technique, protected the tobacco plant less effectively than did the wild-type CHA0. Complementation of strain CHA5 by the cloned wild-type hcn+ genes restored the strain's ability to suppress disease. An artificial transposon carrying the hcn+ genes of strain CHA0 (Tnhcn) was constructed and inserted into the genome of another P.fluorescens strain, P3, which naturally does not produce cyanide and gives poor plant protection. The P3::Tnhcn derivative synthesized cyanide and exhibited an improved ability to suppress disease. All bacterial strains colonized the roots similarly and did not influence significantly the survival of T.basicola in soil. We conclude that bacterial cyanide is an important but not the only factor involved in suppression of black root rot.
Keywords: black root rot, cyanide, disease suppression, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Thielaviopsis basicola
Full text
PDF



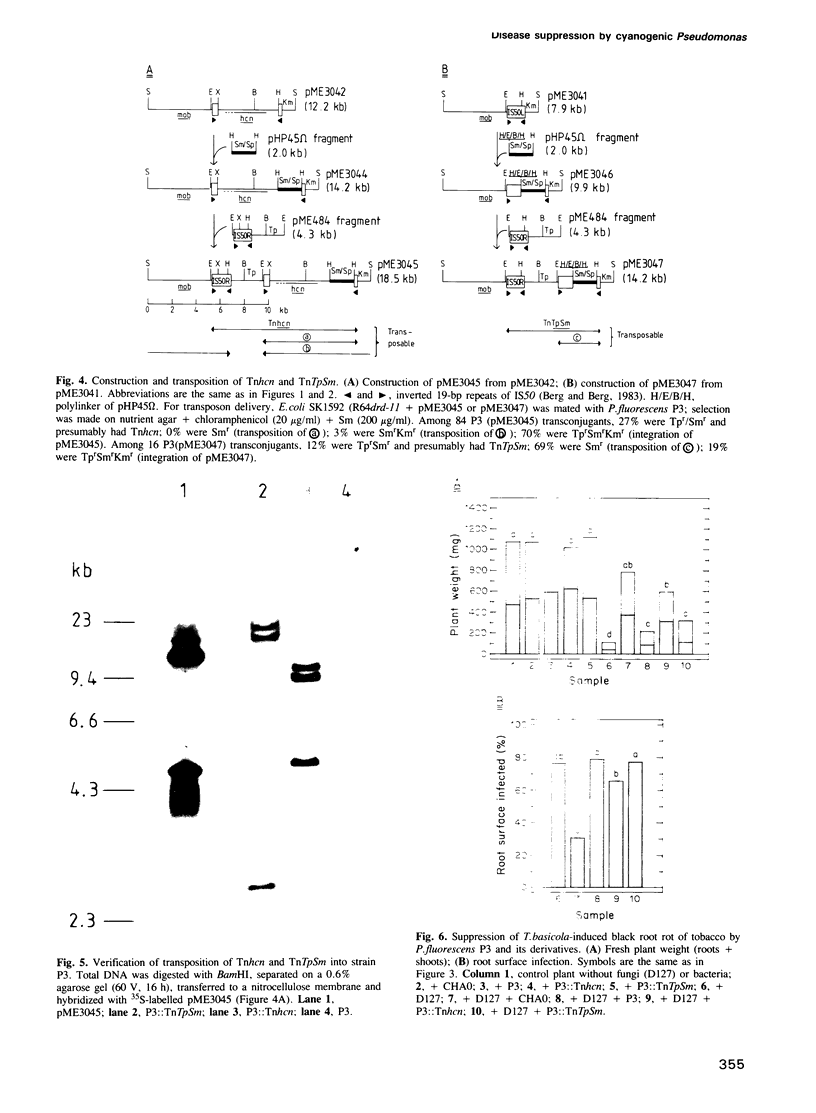



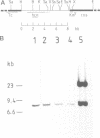
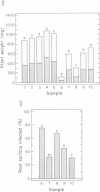
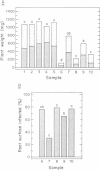
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Askeland R. A., Morrison S. M. Cyanide production by Pseudomonas fluorescens and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jun;45(6):1802–1807. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.6.1802-1807.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulnois G. J., Varley J. M., Sharpe G. S., Franklin F. C. Transposon donor plasmids, based on ColIb-P9, for use in Pseudomonas putida and a variety of other gram negative bacteria. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(1):65–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00383313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castric K. F., Castric P. A. Method for rapid detection of cyanogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):701–702. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.701-702.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castric P. A. Glycine metabolism by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: hydrogen cyanide biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):826–831. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.826-831.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castric P. A. Hydrogen cyanide production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa at reduced oxygen levels. Can J Microbiol. 1983 Oct;29(10):1344–1349. doi: 10.1139/m83-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney R. H., Scott J. R., Vapnek D. Integration of the plasmid prophages P1 and P7 into the chromosome of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1979 May 15;130(2):161–173. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90424-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellay R., Frey J., Krisch H. Interposon mutagenesis of soil and water bacteria: a family of DNA fragments designed for in vitro insertional mutagenesis of gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergen J. P., Stern R. H., Wensink P. C. Filter replicas and permanent collections of recombinant DNA plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2115–2136. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Y., Watson J. M., Haas D., Leisinger T. Genetic and molecular characterization of the Pseudomonas plasmid pVS1. Plasmid. 1984 May;11(3):206–220. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. A., Rothstein S. J., Reznikoff W. S. A restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn5 and location of a region encoding neomycin resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00267254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., WARD M. K., RANEY D. E. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Aug;44(2):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauf V. C., Nester E. W. Wide host range cloning vectors: a cosmid clone bank of an Agrobacterium Ti plasmid. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meynell E., Datta N. Mutant drug resistant factors of high transmissibility. Nature. 1967 May 27;214(5091):885–887. doi: 10.1038/214885a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Brammar W. J., Murray K. Lambdoid phages that simplify the recovery of in vitro recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02425325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rella M., Mercenier A., Haas D. Transposon insertion mutagenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with a Tn5 derivative: application to physical mapping of the arc gene cluster. Gene. 1985;33(3):293–303. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroth M. N., Hancock J. G. Disease-suppressive soil and root-colonizing bacteria. Science. 1982 Jun 25;216(4553):1376–1381. doi: 10.1126/science.216.4553.1376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisich V. A., Holloway B. W. A mutant sex factor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1972 Feb;19(1):91–108. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300014294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trutko S. M., Golovchenko N. P., Akimenko V. K. Izuchenie tsianidrezistentnogo dykhaniia bakterii Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biokhimiia. 1979 Apr;44(4):720–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. J., Saul M. W., Sherratt D. J. ColE1 plasmid mobility: essential and conditional functions. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Feb 16;170(1):103–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00268585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]