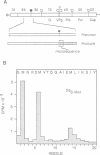
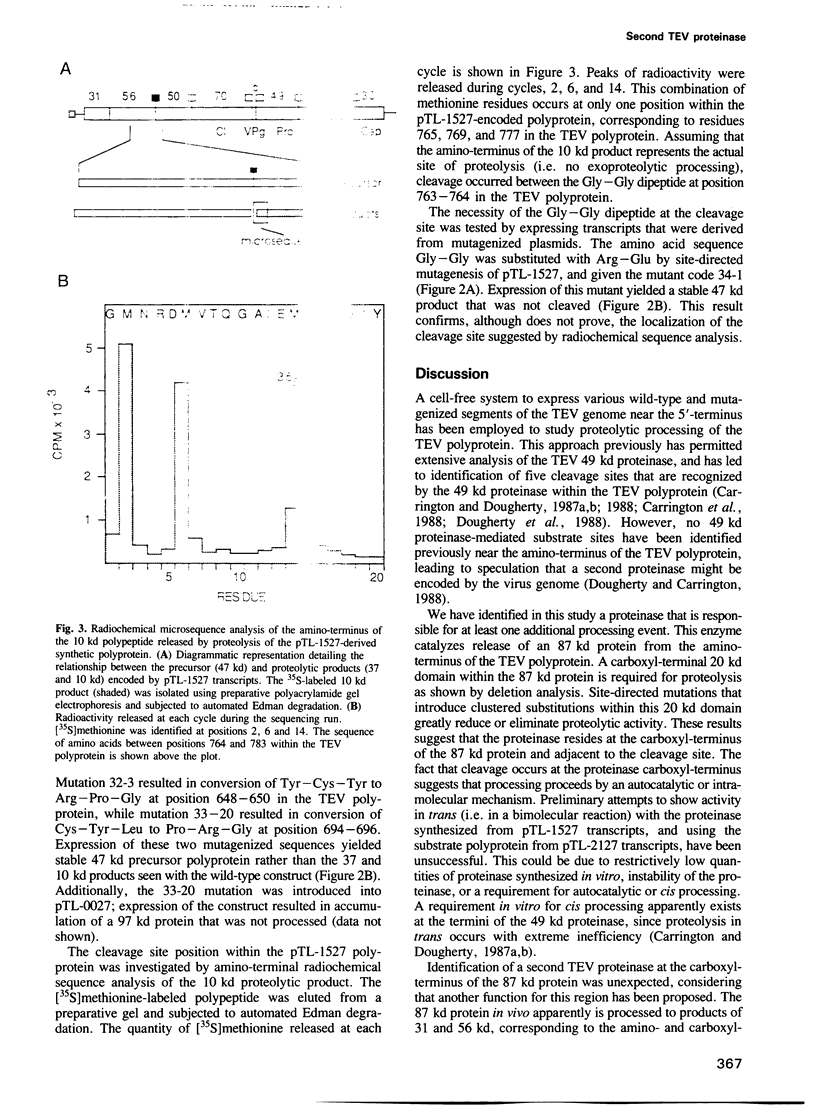
Abstract
The RNA genome of tobacco etch virus (TEV) encodes a large polyprotein precursor that is processed to mature proteins by virus-specific proteinases. Cleavage sites located within the carboxyl-terminal two-thirds of the polyprotein are processed by a TEV-encoded 49 kd proteinase, while the enzyme(s) responsible for cleaving the remaining sites has not been found. In this study, a second TEV-encoded proteinase has been identified based on cell-free expression of defined RNA transcripts. The boundaries of this proteinase have been delineated by deletion analysis and site-directed mutagenesis. The proteolytically active domain has been localized to the carboxyl-terminal half of the 56 kd aphid-transmission helper component. A cleavage site that is recognized by this proteinase has been identified in the polyprotein adjacent to the carboxyl-terminus of the enzyme, and the proteinase appears to cleave by an autocatalytic mechanism. Proteolysis in vitro occurs between a Gly-Gly dipeptide as determined by radiochemical sequencing at the amino-terminus of the proteolytic product.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P., Kamer G., Nicklin M. J., Wimmer E. Similarity in gene organization and homology between proteins of animal picornaviruses and a plant comovirus suggest common ancestry of these virus families. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7251–7267. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold E., Luo M., Vriend G., Rossmann M. G., Palmenberg A. C., Parks G. D., Nicklin M. J., Wimmer E. Implications of the picornavirus capsid structure for polyprotein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J. Viral cysteine proteases are homologous to the trypsin-like family of serine proteases: structural and functional implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7872–7876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Cary S. M., Dougherty W. G. Mutational analysis of tobacco etch virus polyprotein processing: cis and trans proteolytic activities of polyproteins containing the 49-kilodalton proteinase. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2313–2320. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2313-2320.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Dougherty W. G. A viral cleavage site cassette: identification of amino acid sequences required for tobacco etch virus polyprotein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3391–3395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Dougherty W. G. Small nuclear inclusion protein encoded by a plant potyvirus genome is a protease. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2540–2548. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2540-2548.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Parks T. D., Cary S. M., Dougherty W. G. Vectors for cell-free expression and mutagenesis of protein-coding sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):10066–10066. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.10066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty W. G., Carrington J. C., Cary S. M., Parks T. D. Biochemical and mutational analysis of a plant virus polyprotein cleavage site. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1281–1287. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02942.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Toyoda H., Etchison D., Wimmer E. Poliovirus proteinase 2A induces cleavage of eucaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide p220. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2711–2718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2711-2718.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strebel K., Beck E. A second protease of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):893–899. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.893-899.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Nicklin M. J., Murray M. G., Anderson C. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W., Wimmer E. A second virus-encoded proteinase involved in proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):761–770. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90790-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vakharia V. N., Devaney M. A., Moore D. M., Dunn J. J., Grubman M. J. Proteolytic processing of foot-and-mouth disease virus polyproteins expressed in a cell-free system from clone-derived transcripts. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3199–3207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3199-3207.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos P., Verver J., Jaegle M., Wellink J., van Kammen A., Goldbach R. Two viral proteins involved in the proteolytic processing of the cowpea mosaic virus polyproteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):1967–1985. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellink J., van Kammen A. Proteases involved in the processing of viral polyproteins. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1988;98(1-2):1–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01321002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Dewalt P. G., Johnson V. H., Lamb J. G., Semler B. L. Protein 3CD is the major poliovirus proteinase responsible for cleavage of the P1 capsid precursor. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Semler B. L. In vitro molecular genetics as a tool for determining the differential cleavage specificities of the poliovirus 3C proteinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2069–2088. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]