Abstract
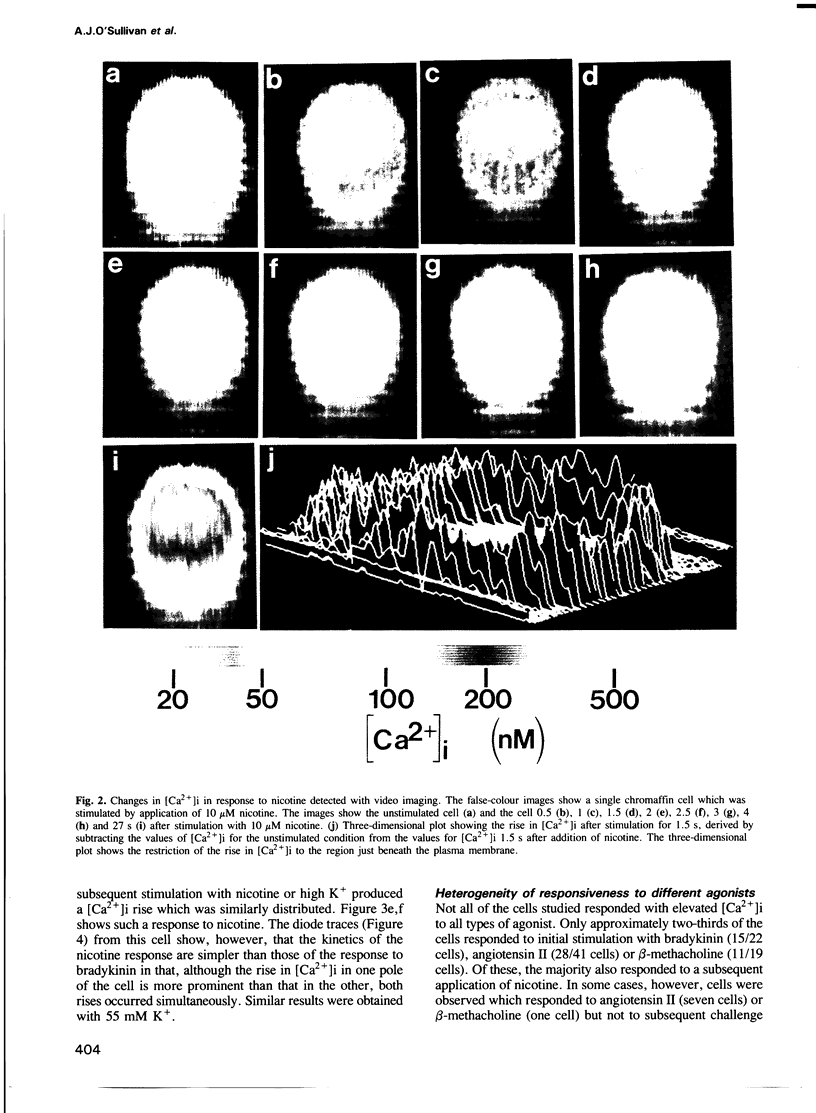
Temporal and spatial changes in the concentration of cytosolic free calcium ([Ca2+]i) in response to a variety of secretagogues have been examined in adrenal chromaffin cells using digital video imaging of fura-2-loaded cells. Depolarization of the cells with high K+ or challenge with nicotine resulted in a rapid and transient elevation of [Ca2+]i beneath the plasma membrane consistent with Ca2+ entry through channels. This was followed by a late phase in which [Ca2+]i rose within the cell interior. Agonists that act through mobilization of inositol phosphates produced an elevation in [Ca2+]i that was most marked in an internal region of the cell presumed to be the site of IP3-sensitive stores. When the same cells were challenged with nicotine or high K+, to trigger Ca2+ entry through voltage-dependent channels, the rise in [Ca2+]i was most prominent in the same localized region of the cells. These results suggest that Ca2+ entry through voltage-dependent channels results in release of Ca2+ from internal stores and that the bulk of the measured rise in [Ca2+]i is not close to the exocytotic sites on the plasma membrane. Analysis of the time courses of changes in [Ca2+]i in response to bradykinin, angiotensin II and muscarinic agonists showed that these agonists produced highly heterogeneous responses in the cell population. This heterogeneity was most marked with muscarinic agonists which in some cells elicited oscillatory changes in [Ca2+]i. Such heterogeneous changes in [Ca2+]i were relatively ineffective in eliciting catecholamine secretion from chromaffin cells. A single large Ca2+ transient, with a component of the rise in [Ca2+]i occurring beneath the plasma membrane, may be the most potent signal for secretion.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alkon D. L., Rasmussen H. A spatial-temporal model of cell activation. Science. 1988 Feb 26;239(4843):998–1005. doi: 10.1126/science.2830669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Neher E. The Ca signal from fura-2 loaded mast cells depends strongly on the method of dye-loading. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo C. R., García A. G., Aunis D. Chromaffin cell calcium channel kinetics measured isotopically through fast calcium, strontium, and barium fluxes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):915–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Knight D. E. Calcium control of exocytosis and endocytosis in bovine adrenal medullary cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Dec 18;296(1080):83–103. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Cobbold P. H., Cuthbertson K. S. Spatial and temporal aspects of cell signalling. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 26;320(1199):325–343. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Cheek T. R. Is the transient nature of the secretory response of chromaffin cells due to inactivation of calcium channels? FEBS Lett. 1985 Mar 11;182(1):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81166-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D. Mechanisms of secretion from adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 25;779(2):201–216. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(84)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D. The relationship between secretion and intracellular free calcium in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biosci Rep. 1984 Jul;4(7):605–611. doi: 10.1007/BF01121918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek T. R., Burgoyne R. D. Effect of activation of muscarinic receptors on intracellular free calcium and secretion in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 30;846(1):167–173. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold P. H., Cheek T. R., Cuthbertson K. S., Burgoyne R. D. Calcium transients in single adrenal chromaffin cells detected with aequorin. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 19;211(1):44–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81271-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold P. H., Rink T. J. Fluorescence and bioluminescence measurement of cytoplasmic free calcium. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 1;248(2):313–328. doi: 10.1042/bj2480313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohan C. S., Connor J. A., Kater S. B. Electrically and chemically mediated increases in intracellular calcium in neuronal growth cones. J Neurosci. 1987 Nov;7(11):3588–3599. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03588.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A. Digital imaging of free calcium changes and of spatial gradients in growing processes in single, mammalian central nervous system cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6179–6183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard D. A., Holz R. W. Cholinergic stimulation of inositol phosphate formation in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: distinct nicotinic and muscarinic mechanisms. J Neurochem. 1987 Nov;49(5):1634–1643. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb01037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Circ Res. 1977 Feb;40(2):119–129. doi: 10.1161/01.res.40.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R. W., Senter R. A., Frye R. A. Relationship between Ca2+ uptake and catecholamine secretion in primary dissociated cultures of adrenal medulla. J Neurochem. 1982 Sep;39(3):635–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao L. S., Schneider A. S. Calcium mobilization and catecholamine secretion in adrenal chromaffin cells. A Quin-2 fluorescence study. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4881–4888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao L. S., Schneider A. S. Muscarinic receptors on bovine chromaffin cells mediate a rise in cytosolic calcium that is independent of extracellular calcium. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2019–2022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. L., Slepetis R. J., Corcoran J. J., Kirshner N. Calcium uptake and catecholamine secretion by cultured bovine adrenal medulla cells. J Neurochem. 1982 Feb;38(2):427–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Baker P. F. Stimulus-secretion coupling in isolated bovine adrenal medullary cells. Q J Exp Physiol. 1983 Jan;68(1):123–143. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1983.sp002691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Kesteven N. T. Evoked transient intracellular free Ca2+ changes and secretion in isolated bovine adrenal medullary cells. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 May 23;218(1211):177–199. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1983.0033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Poenie M., Reuter H., Tsien R. Y., Tsien R. W. Spatial distribution of calcium channels and cytosolic calcium transients in growth cones and cell bodies of sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2398–2402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malgaroli A., Milani D., Meldolesi J., Pozzan T. Fura-2 measurement of cytosolic free Ca2+ in monolayers and suspensions of various types of animal cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2145–2155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard P. J., Gross D., Webb W. W., Fewtrell C. Imaging asynchronous changes in intracellular Ca2+ in individual stimulated tumor mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1854–1858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monck J. R., Reynolds E. E., Thomas A. P., Williamson J. R. Novel kinetics of single cell Ca2+ transients in stimulated hepatocytes and A10 cells measured using fura-2 and fluorescent videomicroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4569–4575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S. N., Thayer S. A., Miller R. J. The effects of excitatory amino acids on intracellular calcium in single mouse striatal neurons in vitro. J Neurosci. 1987 Dec;7(12):4145–4158. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-12-04145.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Sasakawa N., Yamamoto S., Kato R. Functional shift from muscarinic to nicotinic cholinergic receptors involved in inositol trisphosphate and cyclic GMP accumulation during the primary culture of adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 15;251(2):397–403. doi: 10.1042/bj2510397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan A. J., Burgoyne R. D. The role of cytoplasmic pH in the inhibitory action of high osmolarity on secretion from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 13;969(3):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M., Alderton J., Steinhardt R., Tsien R. Calcium rises abruptly and briefly throughout the cell at the onset of anaphase. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):886–889. doi: 10.1126/science.3755550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M., Alderton J., Tsien R. Y., Steinhardt R. A. Changes of free calcium levels with stages of the cell division cycle. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):147–149. doi: 10.1038/315147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Biden T. J., Janjic D., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Wollheim C. B. Rapid mobilization of Ca2+ from rat insulinoma microsomes by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1984 Jun 7;309(5968):562–564. doi: 10.1038/309562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel W., Winiger B. P., Mollard P., Vacher P., Wuarin F., Zahnd G. R., Wollheim C. B., Dufy B. Oscillations of cytosolic Ca2+ in pituitary cells due to action potentials. Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329(6141):719–721. doi: 10.1038/329719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoehr S. J., Smolen J. E., Holz R. W., Agranoff B. W. Inositol trisphosphate mobilizes intracellular calcium in permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1986 Feb;46(2):637–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb13014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Bayerdörffer E., Haase W., Irvine R. F., Schulz I. Effect of inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate on isolated subcellular fractions of rat pancreas. J Membr Biol. 1984;81(3):241–253. doi: 10.1007/BF01868717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Rink T. J., Poenie M. Measurement of cytosolic free Ca2+ in individual small cells using fluorescence microscopy with dual excitation wavelengths. Cell Calcium. 1985 Apr;6(1-2):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(85)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe P., Krause K. H., Hashimoto S., Zorzato F., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J., Lew D. P. "Calciosome," a cytoplasmic organelle: the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ store of nonmuscle cells? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1091–1095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wier W. G., Cannell M. B., Berlin J. R., Marban E., Lederer W. J. Cellular and subcellular heterogeneity of [Ca2+]i in single heart cells revealed by fura-2. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):325–328. doi: 10.1126/science.3798114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Repetitive transient rises in cytoplasmic free calcium in hormone-stimulated hepatocytes. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):600–602. doi: 10.1038/319600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimlichman R., Goldstein D. S., Zimlichman S., Stull R., Keiser H. R. Angiotensin II increases cytosolic calcium and stimulates catecholamine release in cultured bovine adrenomedullary cells. Cell Calcium. 1987 Aug;8(4):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(87)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






