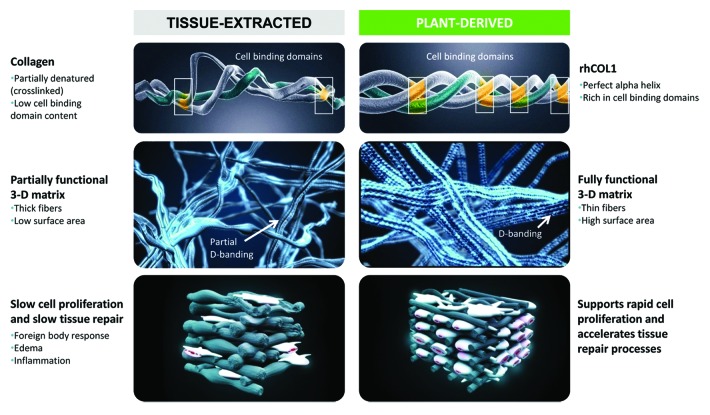
Figure 1. A schematic presentation of the key differences between tissue-extracted vs. plant-derived human collagen. Plant-derived human collagen Type I (rhCOL1) exhibits a natural α-helical structure, with natural cell binding domains, while tissue-extracted collagen is stripped of many of its clinically relevant binding domains, alongside introduction of unwarranted crosslinks, which impact the protein structure and function. Plant-derived human collagen forms functional 3D matrices, surpassing the capacities of their tissue-extracted counterparts. rhCOL1 provides an optimal medium for cell proliferation and accelerated wound healing, with no concerns of antigenicity and immunogenicity.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.