Abstract
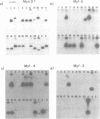
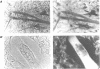
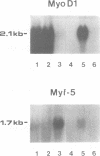
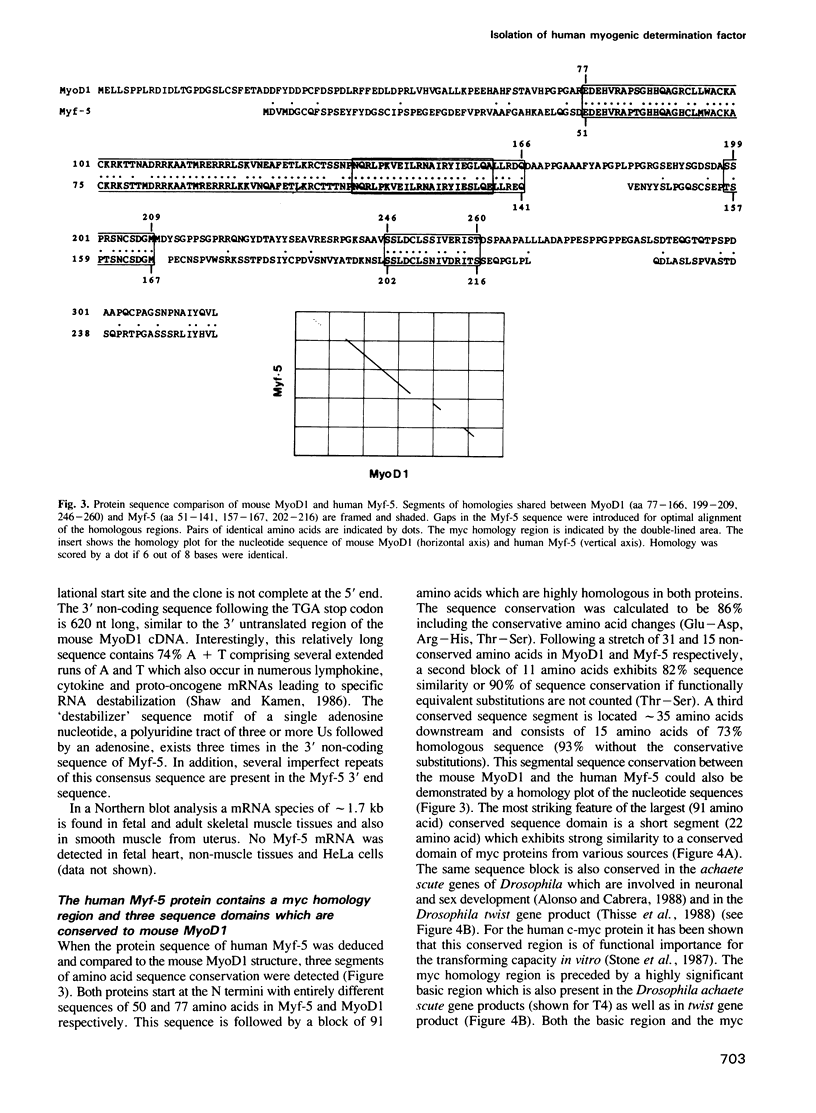
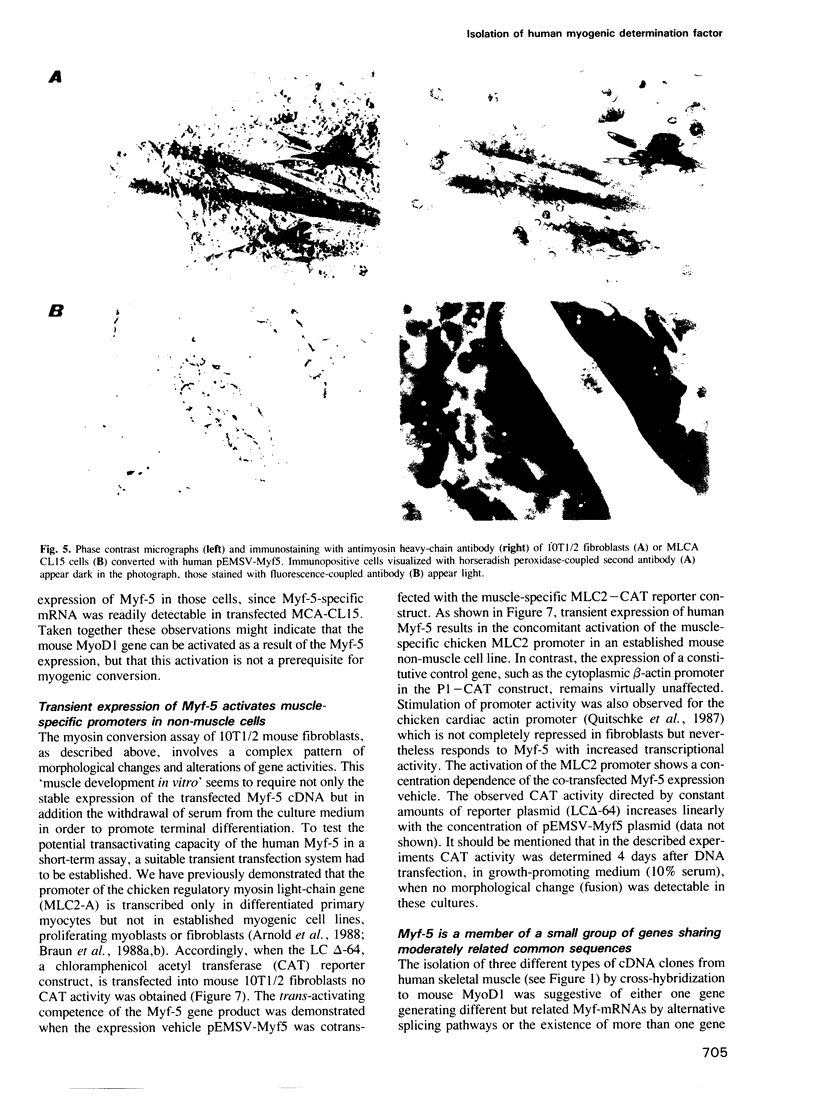
We have isolated the cDNA encoding a novel human myogenic factor, Myf-5, by weak cross-hydridization to the mouse MyoD1 probe. Nucleotide sequence analysis and the identification of the corresponding gene indicate that human Myf-5 is a member of a small gene family which also contains the human homologue to MyoD1. Although structurally related to the mouse factor, the human Myf-5 constitutes a different protein which nevertheless is capable of inducing the myogenic phenotype in embryonic C3H mouse 10T1/2 'fibroblasts'. The existence of more than one MyoD1-like protein in human skeletal muscle is further suggested by the detection of several similar but distinct cDNA clones. The phenotypic conversion of 10T1/2 cells by the human factor is recognized by the capacity of the cells to form multinucleated syncytia and synthesize sarcomeric myosin heavy chains. Moreover, transient expression of Myf-5 in 10T1/2 cells leads to the activation of a co-transfected muscle-specific CAT reporter gene which by itself is transcriptionally silent in the non-muscle cell background. The deduced amino acid sequence of clone Myf-5 reveals a region which is highly similar to myc proteins and the developmental factors from Drosophila encoded by the achaete scute locus and the twist gene. The myc homology region and a preceding cluster of basic amino acids are located in a larger sequence domain with strong similarity to the mouse myogenic factor MyoD1. Two additional short segments with high serine and threonine content are conserved between the two proteins.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso M. C., Cabrera C. V. The achaete-scute gene complex of Drosophila melanogaster comprises four homologous genes. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2585–2591. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold H. H., Tannich E., Paterson B. M. The promoter of the chicken cardiac myosin light chain 2 gene shows cell-specific expression in transfected primary cultures of chicken muscle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2411–2429. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Buschhausen-Denker G., Tannich E., Arnold H. H. The interaction of nuclear proteins with essential promoter element of the chicken cardiac myosin light chain 2 gene is involved in muscle-specific transcription. FEBS Lett. 1988 Nov 7;239(2):309–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80941-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera C. V., Martinez-Arias A., Bate M. The expression of three members of the achaete-scute gene complex correlates with neuroblast segregation in Drosophila. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):425–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90496-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R. Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking translational start sites in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1353–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaddurah-Daouk R., Greene J. M., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Kingston R. E. Activation and repression of mammalian gene expression by the c-myc protein. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):347–357. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Regulation of heat shock protein 70 gene expression by c-myc. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):280–282. doi: 10.1038/312280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny S. F., Emerson C. P., Jr 5-Azacytidine induction of stable mesodermal stem cell lineages from 10T1/2 cells: evidence for regulatory genes controlling determination. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):791–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Paterson B. M., Weintraub H. Transfection of a DNA locus that mediates the conversion of 10T1/2 fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):649–656. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90507-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lech K., Anderson K., Brent R. DNA-bound Fos proteins activate transcription in yeast. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90506-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse P., Arnold H. H. The down-regulation of the chicken cytoplasmic beta actin during myogenic differentiation does not require the gene promoter but involves the 3' end of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):2787–2803. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinney D. F., Pearson-White S. H., Konieczny S. F., Latham K. E., Emerson C. P., Jr Myogenic lineage determination and differentiation: evidence for a regulatory gene pathway. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):781–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90095-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff C. A., Brankow D. W., Heidelberger C. Establishment and characterization of a cloned line of C3H mouse embryo cells sensitive to postconfluence inhibition of division. Cancer Res. 1973 Dec;33(12):3231–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel U., Bober E., Winter B., Lenz S., Lohse P., Goedde H. W., Grzeschik K. H., Arnold H. H. Alkali myosin light chains in man are encoded by a multigene family that includes the adult skeletal muscle, the embryonic or atrial, and nonsarcomeric isoforms. Gene. 1988 Jun 15;66(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90231-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuin T., Billings P. C., Lillehaug J. R., Patierno S. R., Roy-Burman P., Landolph J. R. Enhanced expression of c-myc and decreased expression of c-fos protooncogenes in chemically and radiation-transformed C3H/10T1/2 Cl 8 mouse embryo cell lines. Cancer Res. 1986 Oct;46(10):5302–5311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J., de Lange T., Ramsay G., Jakobovits E., Bishop J. M., Varmus H., Lee W. Definition of regions in human c-myc that are involved in transformation and nuclear localization. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1697–1709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. M., Jones P. A. Multiple new phenotypes induced in 10T1/2 and 3T3 cells treated with 5-azacytidine. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):771–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90317-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thisse B., Stoetzel C., Gorostiza-Thisse C., Perrin-Schmitt F. Sequence of the twist gene and nuclear localization of its protein in endomesodermal cells of early Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2175–2183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villares R., Cabrera C. V. The achaete-scute gene complex of D. melanogaster: conserved domains in a subset of genes required for neurogenesis and their homology to myc. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):415–424. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90495-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]