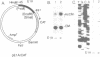Abstract
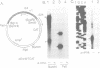
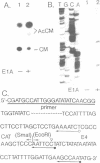
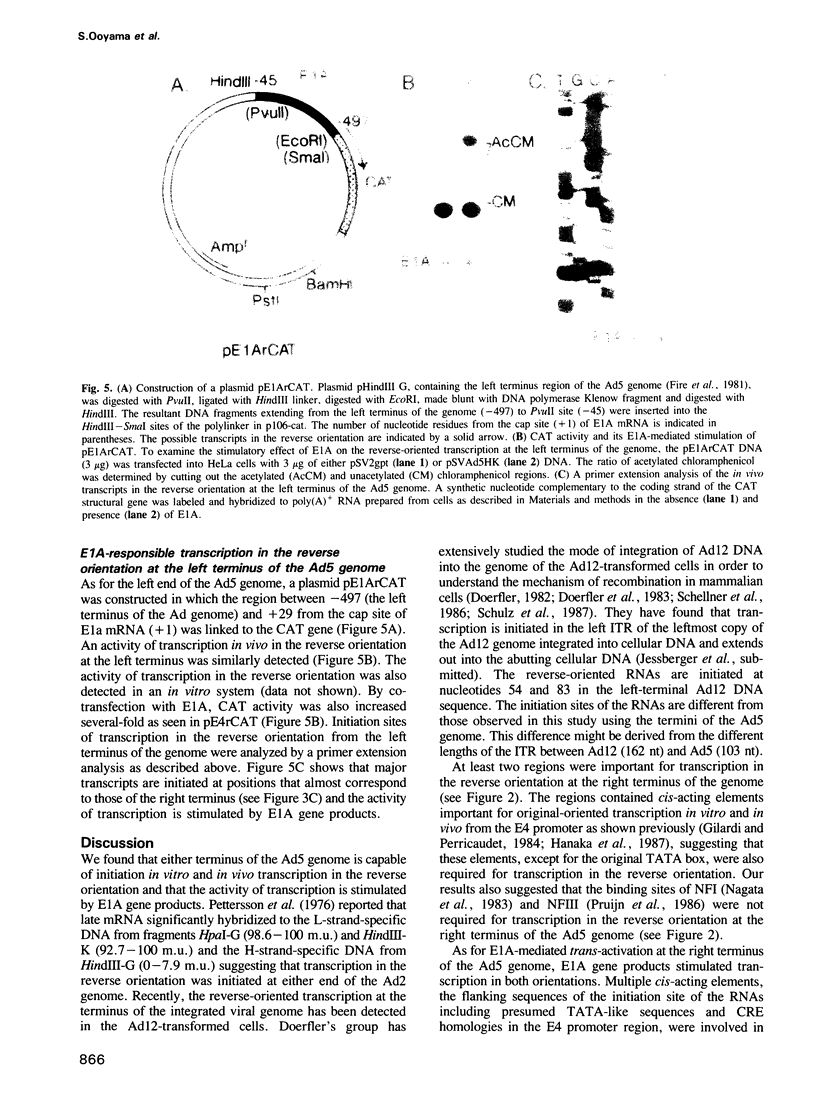
The right terminus of the adenovirus type 5 (Ad5) genome, which contained the early-region 4 (E4) promoter, was capable of initiating transcription in the reverse orientation in in vitro and in vivo assays. Multiple cis-acting elements, required for original-oriented transcription, were also important for reverse-oriented transcription except for the original TATA box. We constructed a plasmid in which the E4 promoter region was linked to the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in the original orientation and linked to the lacZ gene in the reverse orientation and tested the ability of a co-transfected E1A gene to stimulate transcription in both orientations. Activities of transcription in both orientations were stimulated 6- to 10-fold in this assay. More than one cis-acting element was necessary for the stimulation. The region between -39 and -177 was necessary for the E1A-mediated trans-activation of transcription in both orientations, indicating that the region functioned in a bidirectional manner. The activity of transcription in the reverse orientation was similarly detected at the left terminus of the Ad genome and the activity was stimulated several-fold by E1A gene products.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes P., Buckbinder L., Leza M. A., Rak N., Hearing P., Merino A., Reinberg D. EivF, a factor required for transcription of the adenovirus EIV promoter, binds to an element involved in EIa-dependent activation and cAMP induction. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):975–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W., Gahlmann R., Stabel S., Deuring R., Lichtenberg U., Schulz M., Eick D., Leisten R. On the mechanism of recombination between adenoviral and cellular DNAs: the structure of junction sites. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;109:193–228. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69460-8_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. Uptake, fixation, and expression of foreign DNA in mammalian cells: the organization of integrated adenovirus DNA sequences. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;101:127–194. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68654-2_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fire A., Baker C. C., Manley J. L., Ziff E. B., Sharp P. A. In vitro transcription of adenovirus. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):703–719. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.703-719.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi P., Perricaudet M. The E4 promoter of adenovirus type 2 contains an E1A dependent cis-acting element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9035–9049. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi P., Perricaudet M. The E4 transcriptional unit of Ad2: far upstream sequences are required for its transactivation by E1A. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7877–7888. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanaka S., Nishigaki T., Sharp P. A., Handa H. Regulation of in vitro and in vivo transcription of early-region IV of adenovirus type 5 by multiple cis-acting elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2578–2587. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa H., Sharp P. A. Requirement for distal upstream sequences for maximal transcription in vitro of early region IV of adenovirus. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):791–798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S., Shenk T. Adenoviral control regions activated by E1A and the cAMP response element bind to the same factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4171–4175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Green M. R. A cellular transcription factor E4F1 interacts with an E1a-inducible enhancer and mediates constitutive enhancer function in vitro. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1345–1353. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Hai T. Y., SivaRaman L., Thimmappaya B., Hurst H. C., Jones N. C., Green M. R. A cellular protein, activating transcription factor, activates transcription of multiple E1A-inducible adenovirus early promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8355–8359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Expression of a bacterial gene in mammalian cells. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1422–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.6251549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Specific binding of a cellular DNA replication protein to the origin of replication of adenovirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6177–6181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishigaki T., Hanaka S., Kingston R. E., Handa H. A specific domain of the adenovirus EIV promoter is necessary to maintain susceptibility of the integrated promoter to EIA transactivation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):353–360. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson U., Tibbetts C., Philipson L. Hybridization maps of early and late messenger RNA sequences on the adenovirus type 2 genome. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 15;101(4):479–501. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., van Driel W., van der Vliet P. C. Nuclear factor III, a novel sequence-specific DNA-binding protein from HeLa cells stimulating adenovirus DNA replication. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):656–659. doi: 10.1038/322656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz M., Freisem-Rabien U., Jessberger R., Doerfler W. Transcriptional activities of mammalian genomes at sites of recombination with foreign DNA. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):344–353. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.344-353.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Imai T., Sharp P. A., Handa H. Identification of two transcription factors that bind to specific elements in the promoter of the adenovirus early-region 4. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1290–1300. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]