Abstract
Majority of the patients admitted to a hospital with severe infections are initially started with intravenous medications. Short intravenous course of therapy for 2-3 days followed by oral medications for the remainder of the course is found to be beneficial to many patients. This switch over from intravenous to oral therapy is widely practiced in the case of antibiotics in many developed countries. Even though intravenous to oral therapy conversion is inappropriate for a patient who is critically ill or who has inability to absorb oral medications, every hospital will have a certain number of patients who are eligible for switch over from intravenous to oral therapy. Among the various routes of administration of medications, oral administration is considered to be the most acceptable and economical method of administration. The main obstacle limiting intravenous to oral conversion is the belief that oral medications do not achieve the same bioavailability as that of intravenous medications and that the same agent must be used both intravenously and orally. The advent of newer, more potent or broad spectrum oral agents that achieve higher and more consistent serum and tissue concentration has paved the way for the popularity of intravenous to oral medication conversion. In this review, the advantages of intravenous to oral switch over therapy, the various methods of intravenous to oral conversion, bioavailability of various oral medications for the switch over program, the patient selection criteria for conversion from parenteral to oral route and application of intravenous to oral switch over through case studies are exemplified.
Keywords: Economic impact, intravenous to oral, parenteral medication, switch over
INTRODUCTION
The ideal route of administration of any medication is the one that achieves serum concentrations sufficient to produce the desired effect without producing any untoward effects.[1] Safest and convenient way of medication administration is achieved by oral route. If the given oral medication achieves tissue and blood concentration to the same extent as that of the intravenous (IV) medication, then there is little therapeutic difference between IV and oral medications.[2] The available oral formulations in the market are easier to administer, safe and achieve desired therapeutic concentrations, thus making the per oral (PO) route an ideal choice.[1,3]
World Health Organization (WHO) reports that the irrational use of medicines is a major problem worldwide.[4] The over-use of injections, when oral formulations would be more appropriate, is one of the key factors for the irrational use of medicines. Hence IV to oral switch over within an appropriate time is one of the major aspects to improve the rational use of injections. Moreover, once the culture and sensitivity reports are available, IV to oral switch over enables one to select a cheaper or older antibiotic, which is as effective as the IV antibiotic. This has significance in the light of the WHO world health day theme, 2011: ‘Anti-microbial resistance: No action today, no cure tomorrow’.[5]
Bioavailability of IV medications is always higher than that of their oral counterpart, so that the patient may get relief from symptoms earlier if they receive a complete IV course of therapy, is a concept that is popular among the physicians.[6] But the fact is that for a large number of medications, essentially the same amount of drug is found in the blood when given intravenously or orally. Moreover, they believe that chances of reinfection will be less if they give a complete IV course of antibiotics.[2] As a result, physicians usually tend to opt for the IV medications at the time of admission and continue them till patient discharge.
In the Indian scenario, the concept of early switch over from IV to oral therapy is not common even though it is popular in Western countries.[7,8,9] A study carried out by Palanisamy and colleagues in the general medicine department of a 450 bedded tertiary care hospital in south India for a period of 6 months showed that the average cost of antibiotics and the length of stay of patients could be reduced due to early switch over from parenteral to oral therapy.[10] A new approach to carry out the IV to oral switch over is to establish a computerized intervention. Patient's data along with details of medications received are entered into a computer and on every day at midnight, the computer compiles a list of patients who are matching with selection criteria for switch over. Pharmacist takes the print out of the list and discusses with the physician for switch over according to the clinical status of the patient.[6,11]
Most of the studies related to IV to PO conversions have been restricted to certain antibiotic and certain medical condition like respiratory tract infections.[12,13] Only a few studies have been done to assess physician's knowledge, beliefs and acceptance of the switch over from IV to oral therapy.[2] Antibiotics, gastrointestinal agents (mainly proton pump inhibitors and histamine-2 antagonists), and antifungals are major medication classes that can be utilized in IV to oral switch over.[11] In many of the advanced hospitals in developed countries, flouroquinolones are the predominant drug class which is commonly involved in switch over program.[12,14] The drugs such as metronidazole, azithromycin, and linezolid are also involved in IV to PO conversion program. Less commonly, doxycycline, and trimethoprim/sulphamethoxazole are also involved in switch over. In the case of antifungals, fluconazole and itraconazole are the two major drugs involved in switch over from IV to oral.[11] Various drug classes involved in IV to oral conversion, in the ascending order of preference, are Diuretics < Corticosteroids < Analgesics < Antivirals < Cardiovascular agents < Antifungals < GI agents < Antibacterials.[11]
Advantages of oral over IV route
Early switch over from IV to oral therapy has the following major advantages:
Reduced risk of cannula-related infections: For the administration of IV medications, one is required to insert a cannula, which remains in place for some days and eventually can result in secondary infections caused by bacteria and fungi. This may ultimately lead to the need for additional antibiotics and subsequently financial burden to the patient[1]
Risk of thrombophlebitis: No risk of thrombophlebitis in case of oral administration[1,3,11]
Less expensive than IV therapy: Most of the oral medications available at the market are less expensive as the parenteral medications must be sterile and isotonic, consequently leading to cost savings by the patient[1,15,16]
Reduction in the hidden costs: Hidden costs mainly refer to cost of diluents, equipments for administration, needles, syringes, and nursing time. Needles, syringes, diluents, and other equipments are the unavoidable requisites for the parenteral administration. Above all, an experienced professional must be there to administer the injection. As a result, it may cause a financial burden for the patient and take away valuable nursing time for patient-care[1,15,16]
Earlier discharge: Injections are usually administered in a hospital setting as it requires an experienced professional to administer the medication, especially IV infusions. Hence the patient stay at the hospital is prolonged. Early switch over to oral medications can help to overcome this barrier and may result in early discharge of the patient.[1]
Types of IV to oral conversions
There are mainly three types of IV to PO conversions.[1]
Sequential therapy: It refers to the act of replacing a parenteral version of a medication with its oral counterpart of the same compound. For instance, conversion of inj. pantoprazole 40 mg OD (once daily) to tab. pantoprazole 40 mg OD[16]
Switch therapy: It describes the conversion of an IV medication to a PO equivalent; within the same class and has the same level of potency, but of a different compound. For example, switch over from inj. ceftriaxone 1 g BD (bis in die) to tab. cefixime 200 mg BD,[17] switch over from inj. pantoprazole 40 mg BD to tab. rabeprazole 20 mg BD
Step down therapy: It refers to the conversion from an injectable medication to an oral agent in another class or to a different medication within the same class where the frequency, dose, and the spectrum of activity (in the case of antibiotics) may not be exactly the same. For example, conversion of inj. cefotaxim 1 g to tab. ciprofloxacin 500 mg, switch over from inj. heparin to tab. warfarin.
Practical approaches for conversion of a patient from IV to oral therapy
Establishment of an IV to oral switch over program at a hospital is the stepping stone toward the successful conversion of a patient from IV to oral therapy. It is the sole responsibility of a clinical pharmacist to establish such a guideline with the approval of the Pharmacy and Therapeutics committee of the hospital and ensure that the conversion is done in tune with the guideline.[1,2,18]
First, a clinical pharmacist should identify patients who receive IV medications and also recognize the need for IV medication in those patients and check for the indication
Second, regular follow-up is needed to check whether the patient's clinical status (WBC [white blood cells], vitals, culture report, patient's physical and mental condition, etc.) is improving or not. If the patient is eligible for conversion [Table 3], check whether the conversion was done
Inform the physician about the patients who are eligible for conversion but not converted within the appropriate time
Make suitable recommendations for the selection of an oral medication for conversion
Review the feedback of the physicians
Monitor the patient's clinical progress after the switch over and convert the patient back to parenteral medication, if required
It is always advisable to verify the knowledge and beliefs of physicians regarding the guideline for switch over from IV to oral therapy. A data collection tool like questionnaires can be used for the same.
Table 3.
Patient selection criteria for IV to oral switch over therapy
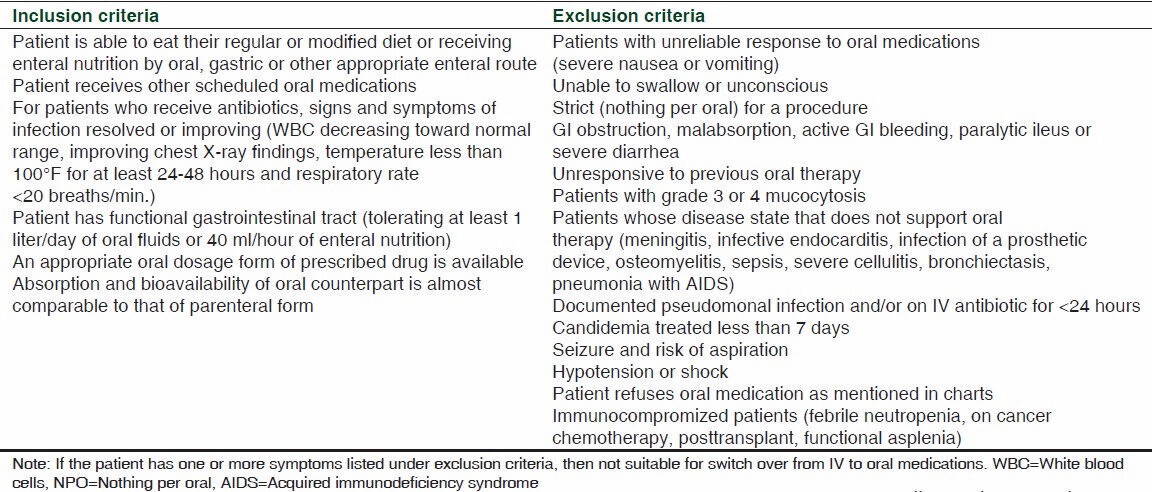
The patient selection criteria for IV to oral switch therapy[1,19,21] is given in Table 3.
Bioavailability of medications included in IV to oral conversion
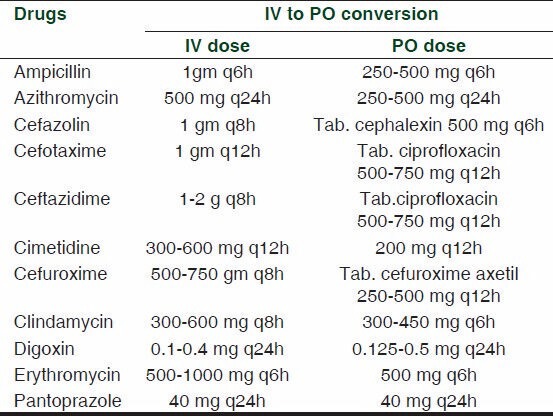
Usually 100% bioavailability is assured only for IV medications and not for other routes like intramuscular or subcutaneous route. When a medication is administered intravenously it can directly reach the blood circulation and thereby assure 100% bioavailability. To be effective, oral antibiotics must achieve serum bactericidal activity almost comparable to that of its IV counterpart.[1,9] Table 1 explains the examples of IV to oral switch over for medications with >90% bioavailablity. Examples of drugs with good bioavailability (60-90%) eligible[19,20] for IV to oral switch over are given in Table 2.
Table 1.
Examples of drugs with excellent bioavailability (>90%) eligible for IV to oral switch over
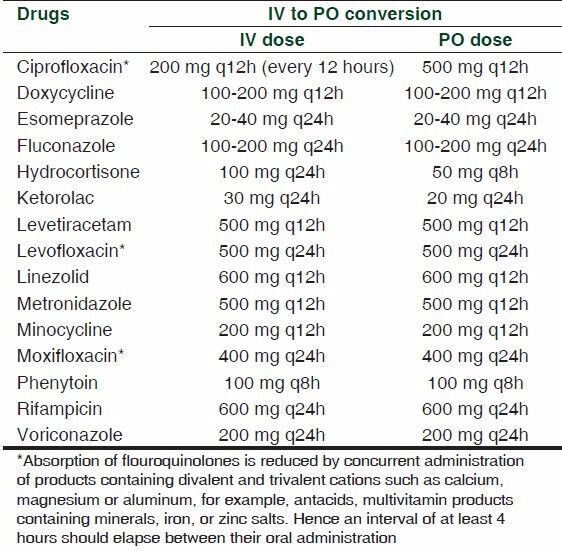
Table 2.
Examples of drugs with good bioavailability (60-90%) eligible for IV to oral switch over
Therapeutic application of IV to oral switch over: Special focus on some common disease conditions
Community-acquired pneumonia
About 40-60% of patients admitted with community-acquired pneumonia are eligible for switch over within 2-3 days of treatment.[11] Vital signs and WBC should be monitored before conversion from IV to oral therapy. Flouroquinolones are the first line drugs for the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia. Study which compared IV/PO moxifloxacin with IV/PO amoxicillin-clavulanate with or without clarithromycin proved that moxifloxacin is rated at a higher percentage of clinical cure.[22]
The following case illustrates an IV to PO conversion done at the appropriate time:
A 52-year-old female admitted to the general ward of a hospital with cough and breathing difficulty was treated empirically with inj. Cefoperazone – sulbactam 2 g BD and tab. levofloxacin 500 mg OD. She was also started on inj. pantoprazole 40 mg BD and inj. neurobion forte® (vitamin B1, B6 and B12) OD. Her vitals and WBC counts became normal from the third day of admission. Later her sputum culture showed growth of Candida albicans. She was then started on tab. fluconazole 100 mg BD for 10 days and inj. cefoperazone-sulbactam was stopped, but tab. levofloxacin was continued till discharge. All the other parenteral medications were switched over to the oral form from the third day of admission (inj. pantoprazole to tab. pantoprazole 40 mg OD and inj. neurobion forte® to tab. neurobion forte® OD). The patient's condition improved with the oral medications.
Infectious diarrhea/typhoid (enteric) fever
Acute watery diarrhea is mainly caused by the pathogens Escherichia coli, campylobacter, salmonella or vibrio species. The preferred therapy is a quinolone IV or PO for 5 days. Both IV and oral formulations of quinolones have same bio-availability[1,23,24]
A 28-year-old male admitted for acute gastroenteritis was started on ciprofloxacin 200 mg IV 12 hourly and metronidazole 500 mg IV 8 hourly. He was also started on the same day inj. pantoprazole 40 mg 1-0-1, tab. racecadotril 100 mg 1-1-1 and tab. paracetamol 650 mg prn. From the second day his diarrhea and vomiting subsided and was able to take oral food. His vitals became normal on the third day of admission and WBC count was 9730/μl. It is possible to switch over the IV medications of this patient to the equivalent oral forms at the earliest [Table 1].
CONCLUSION
Large array of medications are suitable for conversion from IV to oral therapy and various types of IV to oral conversions are possible. There are various guidelines available in this regard and each hospital should implement such a guideline at the initiation of a clinical pharmacist in order to accomplish an ideal IV to PO conversion therapy. The clinical pharmacist should thoroughly review the medical records and identify patients who are eligible for parenteral to oral therapy conversion. In the Indian scenario, we have yet to accomplish an ideal IV to PO conversion program in our day-to-day clinical practice.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Kuper KM. Text Book of Competence Assessment Tools for Health-System Pharmacies. 4th ed. ASHP: 2008. Intravenous to oral therapy conversion; pp. 347–60. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lee SL, Azmi S, Wong PS. Clinicians' knowledge, beliefs and acceptance of intravenous-to-oral antibiotic switching, Hospital Pulau Pinang. Med J Malaysia. 2012;67:190–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sevinc F, Prins JM, Koopmans RP, Langendijk PN, Bossuyt PM, Dankert J, et al. Early switch from intravenous to oral antibiotics: Guidelines and implementation in a large teaching hospital. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1999;43:601–6. doi: 10.1093/jac/43.4.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.The pursuit of responsible use of medicines: Sharing and learning from country experiences. [Last accessed on 2013 Jun 29; Last updated on 2013 Jun 22]. Available from: www.who.int/medicines/areas/rationaluse/en/
- 5.World Health Day 2011 . Antibiotic resistance: No action today, no cure tomorrow. [Last accessed on 2013 Jun 29]. Available from: www.euro.who.int .
- 6.Fischer MA, Solomon DH, Teich JM, Avorn J. Conversion from intravenous to oral medications: Assessment of a computerized intervention for hospitalized patients. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163:2585–9. doi: 10.1001/archinte.163.21.2585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cunha BA. Intravenous-to oral antibiotic switch therapy. A cost-effective approach. Postgrad Med. 1997;101:111–2. doi: 10.3810/pgm.1997.04.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.McLaughlin CM, Bodasing N, Boyter AC, Fenelon C, Fox JG, Seaton RA. Pharmacy-implemented guidelines on switching from intravenous to oral antibiotics: An intervention study. QJM. 2005;98:745–52. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hci114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gyawali S, Shankar PR, Saha A, Mohan L. Study of prescription of injectable drugs and intravenous fluids to inpatients in a teaching hospital in Western Nepal. Mcgill J Med. 2009;12:13–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Palanisamy A, Narmatha MP, Rajendran NN, Rajalingam B, Sriram S. Conversion of intravenous-to-oral antimicrobial therapy in South Indian population. IJRPBS. 2011;2:1258–60. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Banko H, Goldwater SH, Adams E. Smoothing the path for intravenous (IV) to oral (PO) conversion: Where have we come in 11 years? Hosp Pharm. 2009;44:959–67. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cunha BA. Oral versus IV treatment for catheter-related bloodstream infections. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1800–1. doi: 10.3201/eid1311.070729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.File TM, Jr, Segreti J, Dunbar L, Player R, Kohler R, Williams RR, et al. A multicenter, randomized study comparing the efficacy and safety of intravenous and/or oral levofloxacin versus ceftriaxone and/or cefuroxime axetil in treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1997;41:1965–72. doi: 10.1128/aac.41.9.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Castro-Guardiola A, Viejo-Rodríguez AL, Soler-Simon S, Armengou-Arxé A, Bisbe-Company V, Peñarroja-Matutano G, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral and early-switch therapy for community-acquired pneumonia: A randomized controlled trial. Am J Med. 2001;111:367–74. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(01)00868-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jensen KM, Paladino JA. Cost-Effectiveness of abbreviating the duration of intravenous antibacterial therapy with oral fluoroquinolones. Pharmacoeconomics. 1997;11:64–74. doi: 10.2165/00019053-199711010-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Galanter W, Liu XF, Lambert BL. Analysis of computer alerts suggesting oral medication use during computerized order entry of iv. medications. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2010;67:1101–5. doi: 10.2146/ajhp090357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hamilton-Miller JM. Switch therapy: The theory and practice of early change from parenteral to non-parenteral antibiotic administration. Clin Microbiol Infect. 1996;2:12–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.1996.tb00194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.NHS Grampian medicines management. [Last accessed on 2013 Jun 29; Last updated on 2012 Jun]. Available from: http//www.nhsgrampian.com/grampianfoi/files/NHSIVOST.pdf .
- 19.Wetzstein GA. Intravenous to oral (iv: po) anti-infective conversion therapy. Cancer Control. 2000;7:170–6. doi: 10.1177/107327480000700211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.IV to oral conversion program. [Last accessed on 2013 Jun 29; Last updated on 2013 Jun 20]. Available from: http://legacy.uspharmacist.com/oldformat.asp?url = newlook/files/Feat/ACF3023.cfm .
- 21.Zamin MT, Pitre MM, Conly JM. Development of an intravenous-to-oral route conversion program for antimicrobial therapy at a Canadian tertiary care health facility. Ann Pharmacother. 1997;31:564–70. doi: 10.1177/106002809703100507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lee RW, Lindstrom ST. Early switch to oral antibiotics and early discharge guidelines in the management of community-acquired pneumonia. Respirology. 2007;12:111–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2006.00931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Janknegt R, van der Meer JW. Sequential therapy with intravenous and oral cephalosporins. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1994;33:169–77. doi: 10.1093/jac/33.1.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cunha BA. Text book of essentials of antibiotic prescribing. 10th ed. USA: Jones and Barlett Publishers; 2011. pp. 10–25. [Google Scholar]