Abstract
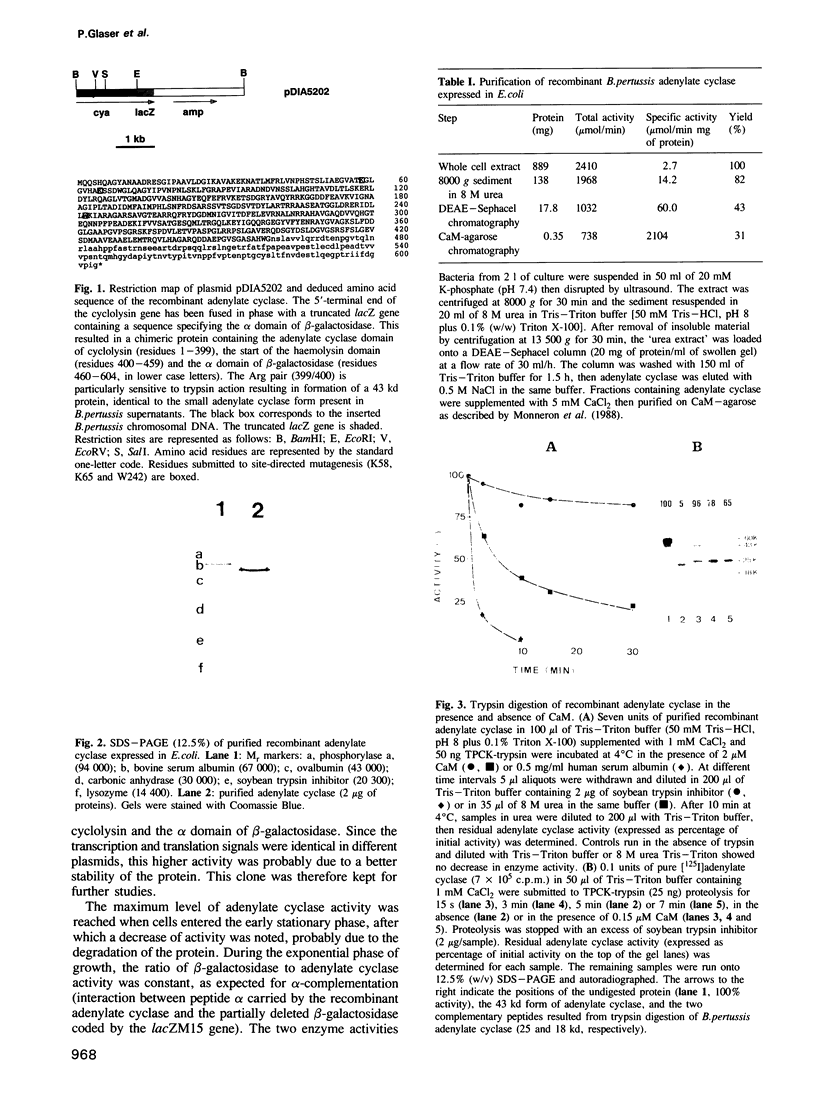
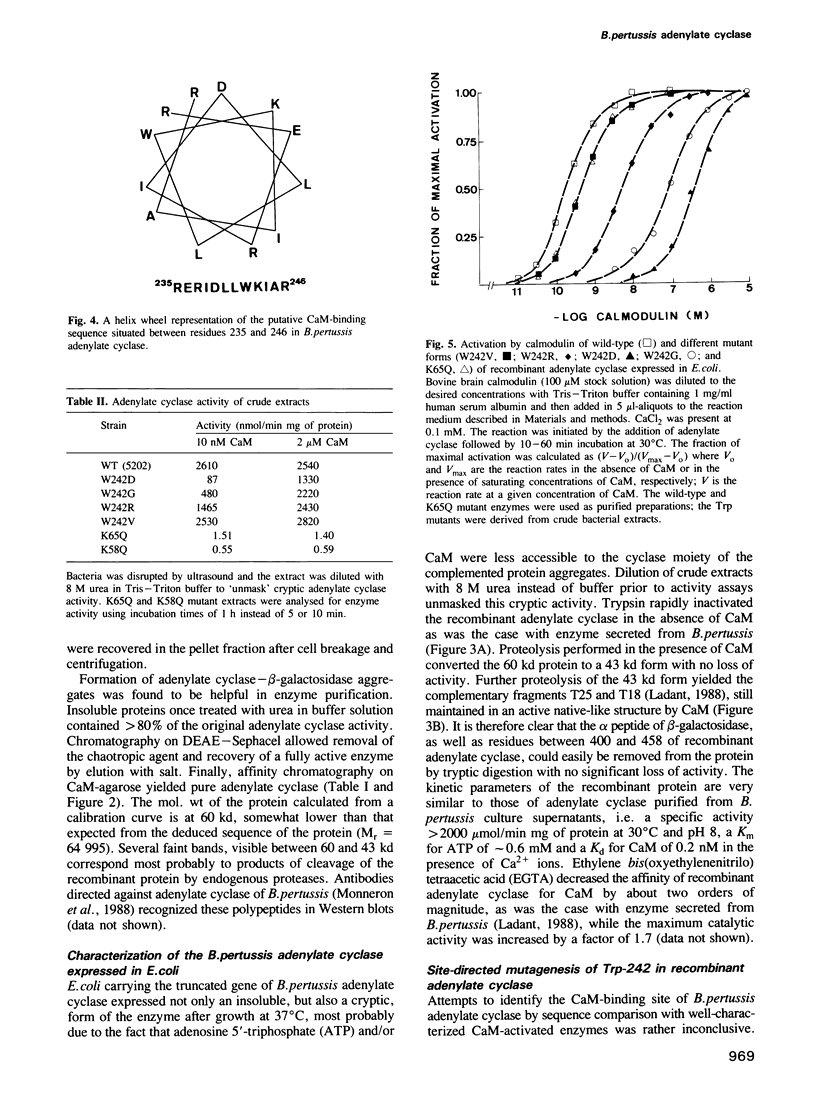
In order to identify molecular features of the calmodulin (CaM) activated adenylate cyclase of Bordetella pertussis, a truncated cya gene was fused after the 459th codon in frame with the alpha-lacZ' gene fragment and expressed in Escherichia coli. The recombinant, 604 residue long protein was purified to homogeneity by ion-exchange and affinity chromatography. The kinetic parameters of the recombinant protein are very similar to that of adenylate cyclase purified from B.pertussis culture supernatants, i.e. a specific activity greater than 2000 mumol/min mg of protein at 30 degrees C and pH 8, a KmATP of 0.6 mM and a Kd for its activator, CaM, of 0.2 nM. Proteolysis with trypsin in the presence of CaM converted the recombinant protein to a 43 kd protein with no loss of activity; the latter corresponds to the secreted form of B.pertussis adenylate cyclase. Site-directed mutagenesis of residue Trp-242 in the recombinant protein yielded mutants expressing full catalytic activity but having altered affinity for CaM. Thus, substitution of an aspartic acid residue for Trp-242 reduced the affinity of adenylate cyclase for CaM greater than 1000-fold. Substitution of a Gln residue for Lys-58 or Lys-65 yielded mutants with a drastically reduced catalytic activity (approximately 0.1% of that of wild-type protein) but with little alteration of CaM-binding. These results substantiated, at the molecular level, our previous genetic and biochemical studies according to which the N-terminal tryptic fragment of secreted B.pertussis adenylate cyclase (residues 1-235/237) harbours the catalytic site, whereas the C-terminal tryptic fragment (residues 235/237-399) corresponds to the main CaM-binding domain of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumenthal D. K., Takio K., Edelman A. M., Charbonneau H., Titani K., Walsh K. A., Krebs E. G. Identification of the calmodulin-binding domain of skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3187–3191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschmeier B., Meyer H. E., Mayr G. W. Characterization of the calmodulin-binding sites of muscle phosphofructokinase and comparison with known calmodulin-binding domains. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9454–9462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer D. L., Eaton J. W. Phagocyte impotence caused by an invasive bacterial adenylate cyclase. Science. 1982 Sep 3;217(4563):948–950. doi: 10.1126/science.6287574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. A., Comte M., Fitton J. E., DeGrado W. F. The interaction of calmodulin with amphiphilic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2527–2534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escuyer V., Duflot E., Sezer O., Danchin A., Mock M. Structural homology between virulence-associated bacterial adenylate cyclases. Gene. 1988 Nov 30;71(2):293–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. C., Kuby S. A., Mildvan A. S. ATP-binding site of adenylate kinase: mechanistic implications of its homology with ras-encoded p21, F1-ATPase, and other nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):907–911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser P., Ladant D., Sezer O., Pichot F., Ullmann A., Danchin A. The calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase of Bordetella pertussis: cloning and expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jan;2(1):19–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser P., Sakamoto H., Bellalou J., Ullmann A., Danchin A. Secretion of cyclolysin, the calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase-haemolysin bifunctional protein of Bordetella pertussis. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3997–4004. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee D. V., Andreasen T. J., Storm D. R. Calcium-independent stimulation of Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase by calmodulin. Biochemistry. 1982 May 25;21(11):2759–2764. doi: 10.1021/bi00540a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn B. Overproduction of phage lambda repressor under control of the lac promotor of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Nov 17;148(3):243–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00332898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley R. M., Means A. R., Kemp B. E., Shenolikar S. Mapping of calmodulin-binding domain of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II from rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):122–128. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80688-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski E., Farfel Z. Bordetella pertussis invasive adenylate cyclase. Partial resolution and properties of its cellular penetration. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5526–5532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P., Maeda M., Fischer R., Verma A. K., Krebs J., Penniston J. T., Carafoli E. Identification and primary structure of a calmodulin binding domain of the Ca2+ pump of human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2905–2910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennelly P. J., Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Rabbit skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase. The calmodulin binding domain as a potential active site-directed inhibitory domain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):11958–11963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladant D., Brezin C., Alonso J. M., Crenon I., Guiso N. Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase. Purification, characterization, and radioimmunoassay. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):16264–16269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladant D. Interaction of Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase with calmodulin. Identification of two separated calmodulin-binding domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2612–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mock M., Labruyère E., Glaser P., Danchin A., Ullmann A. Cloning and expression of the calmodulin-sensitive Bacillus anthracis adenylate cyclase in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988 Apr 29;64(2):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90342-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monneron A., Ladant D., d'Alayer J., Bellalou J., Bârzu O., Ullmann A. Immunological relatedness between Bordetella pertussis and rat brain adenylyl cyclases. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):536–539. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller W., Amons R. Phosphate-binding sequences in nucleotide-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 1;186(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamaye K. L., Eckstein F. Inhibition of restriction endonuclease Nci I cleavage by phosphorothioate groups and its application to oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9679–9698. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil K. T., Wolfe H. R., Jr, Erickson-Viitanen S., DeGrado W. F. Fluorescence properties of calmodulin-binding peptides reflect alpha-helical periodicity. Science. 1987 Jun 12;236(4807):1454–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.3589665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattuck R. L., Oldenburg D. J., Storm D. R. Purification and characterization of a calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase from Bordetella pertussis. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 5;24(23):6356–6362. doi: 10.1021/bi00344a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L. Virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:661–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Cook G. H., Goldhammer A. R., Berkowitz S. A. Calmodulin activates prokaryotic adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3841–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





