Abstract
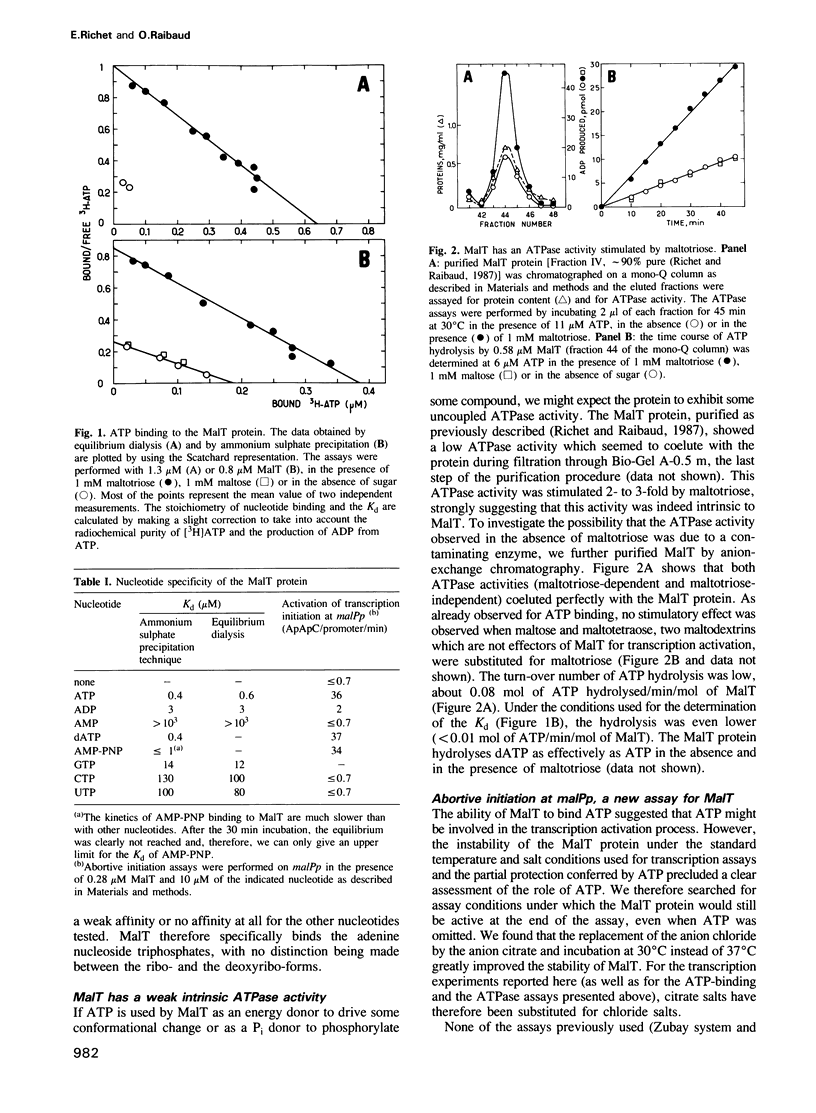
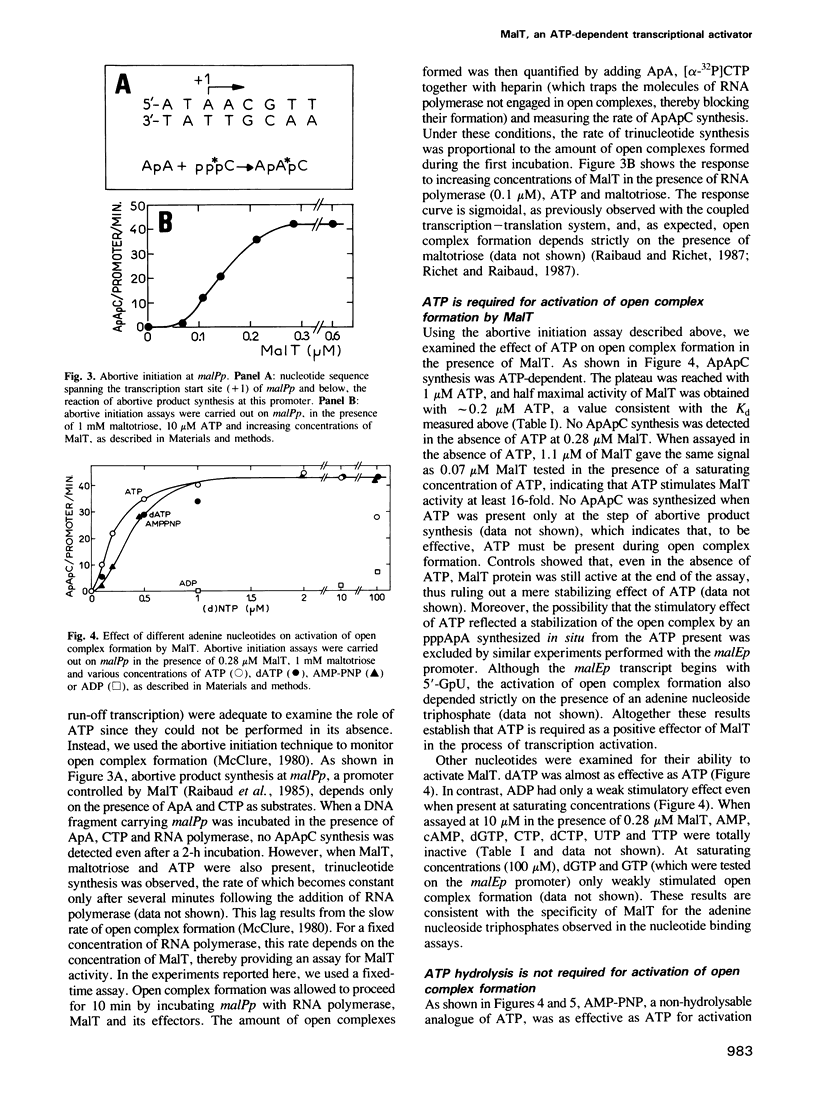
We show that MalT, the transcriptional activator of the Escherichia coli maltose regulon, specifically binds ATP and dATP with a high affinity (Kd = 0.4 microM) and exhibits a weak ATPase activity. Using an abortive initiation assay, we further show that activation of open complex formation by MalT depends on the presence of ATP in addition to that of maltotriose, the inducer of the maltose system. Similar experiments in which ATP was replaced by ADP or AMP-PNP, a non-hydrolysable analogue of ATP, demonstrate that this reaction does not require ATP hydrolysis. As revealed by DNase I footprinting, both ATP and maltotriose are required for the binding of the MalT protein to the mal promoter DNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arakawa T., Timasheff S. N. The mechanism of action of Na glutamate, lysine HCl, and piperazine-N,N'-bis(2-ethanesulfonic acid) in the stabilization of tubulin and microtubule formation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4979–4986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagnara A. S., Finch L. R. Relationships between intracellular contents of nucleotides and 5-phosphoribosyl 1-pyrophosphate in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 16;36(2):422–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramhill D., Kornberg A. Duplex opening by dnaA protein at novel sequences in initiation of replication at the origin of the E. coli chromosome. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):743–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90412-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman A. G., Atkinson D. E. Adenine nucleotide concentrations and turnover rates. Their correlation with biological activity in bacteria and yeast. Adv Microb Physiol. 1977;15:253–306. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60318-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. T., Raibaud O. The nucleotide sequence of the malT gene encoding the positive regulator of the Escherichia coli maltose regulon. Gene. 1986;42(2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90297-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Funnell B. E., Kornberg A. The dnaA protein complex with the E. coli chromosomal replication origin (oriC) and other DNA sites. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):889–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain I., Van Houten B., Thomas D. C., Sancar A. Sequences of Escherichia coli uvrA gene and protein reveal two potential ATP binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4895–4901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobe A., Riggs A. D., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. V. Characterization of super- and pseudo-wild-type repressors. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):181–199. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90328-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Mechanism and control of transcription initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:171–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Rate-limiting steps in RNA chain initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5634–5638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon A. S., Goldberg A. L. Binding of nucleotides to the ATP-dependent protease La from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):14921–14928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Goldberg M. E. The dissociated tryptophanase subunit is inactive. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2820–2824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Gutierrez C., Schwartz M. Essential and nonessential sequences in malPp, a positively controlled promoter in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1201–1208. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1201-1208.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Richet E. Maltotriose is the inducer of the maltose regulon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3059–3061. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3059-3061.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Vidal-Ingigliardi D., Richet E. A complex nucleoprotein structure involved in activation of transcription of two divergent Escherichia coli promoters. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 5;205(3):471–485. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90218-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Raibaud O. Purification and properties of the MalT protein, the transcription activator of the Escherichia coli maltose regulon. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12647–12653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekimizu K., Bramhill D., Kornberg A. ATP activates dnaA protein in initiating replication of plasmids bearing the origin of the E. coli chromosome. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90221-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy T. J., Szmelcman S., Boos W., Schwartz M. On the significance of the retention of ligand by protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2120–2124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt B. L. Escherichia coli transcription termination protein rho has three hydrolytic sites for ATP. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11130–11137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe B., Busby S., Buc H. Cyclic AMP receptor protein: role in transcription activation. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):831–838. doi: 10.1126/science.6372090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




