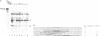Abstract
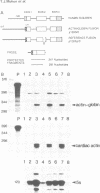
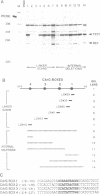
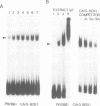
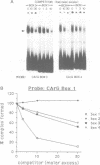
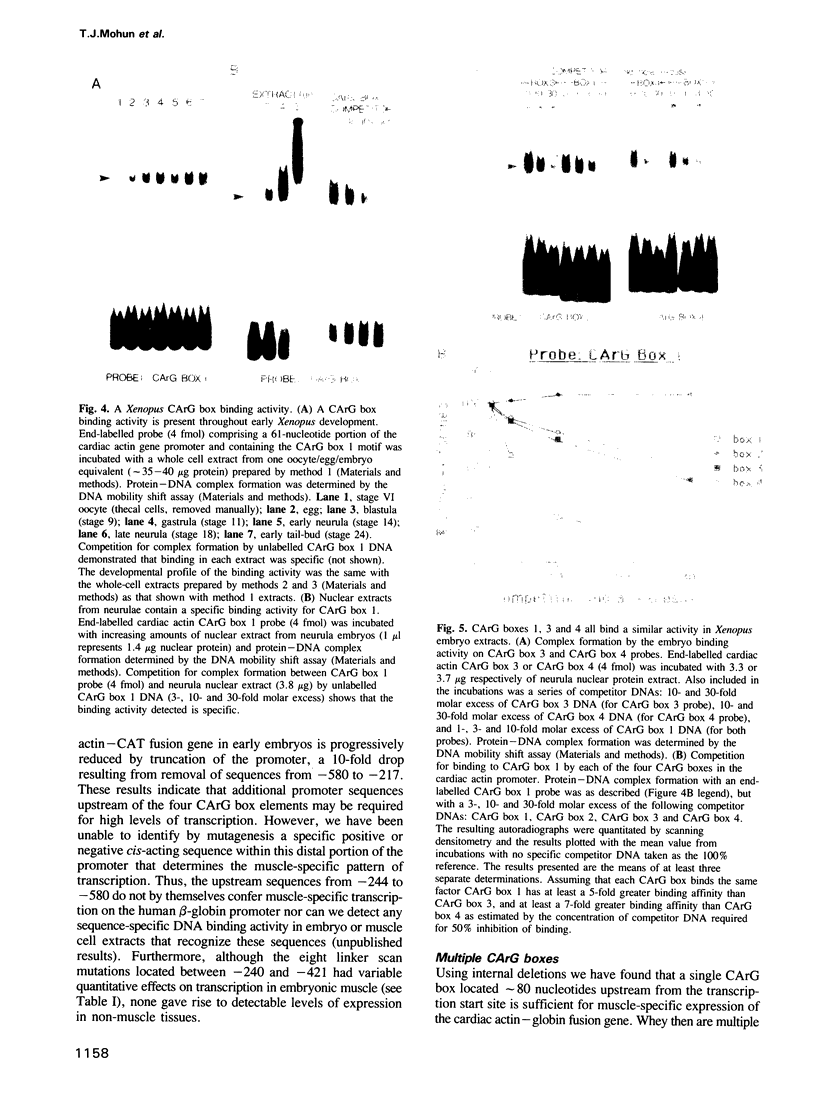
Promoter sequences required for activation of the Xenopus cardiac actin gene in embryonic muscle were analysed by micro-injecting chimeric actin/beta-globin genes into the two-cell Xenopus embryo. Transcription was monitored during subsequent differentiation of embryonic muscle and non-muscle tissues. The effect of a variety of mutations including internal deletions and linker scan mutations between -64 and -396 within the cardiac actin promoter were tested. This region contains four copies of a conserved motif, the CArG box, common to vertebrate striated muscle acting gene promoters. In the Xenopus cardiac actin gene, the most proximal of these motifs (CArG box 1) located at -80, was essential for muscle-specific transcription. Other CArG motifs could functionally substitute for CArG box 1 when placed in this position. CArG boxes 3 and 4 bound the same activity in a neurula embryo nuclear extract as CArG box 1 and the amount of this binding activity was constant through early development.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergsma D. J., Grichnik J. M., Gossett L. M., Schwartz R. J. Delimitation and characterization of cis-acting DNA sequences required for the regulated expression and transcriptional control of the chicken skeletal alpha-actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2462–2475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Martin P. L., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Eukaryotic gene transcription with purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:582–598. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Ptashne M. Cooperative DNA binding of the yeast transcriptional activator GAL4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):382–386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Fairman S., Mohun T. J., Brennan S. Activation of muscle-specific actin genes in Xenopus development by an induction between animal and vegetal cells of a blastula. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):913–922. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B. Methods for nuclear transplantation in amphibia. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;16:125–139. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Wickens M. P. The use of Xenopus oocytes for the expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:370–386. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Miwa T., Boxer L. M., Kedes L. Interaction of nuclear proteins with muscle-specific regulatory sequences of the human cardiac alpha-actin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4110–4119. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Strähle U., Gloss B., Stewart F., Schmid W., Boshart M., Miksicek R., Schütz G. Cooperativity of glucocorticoid response elements located far upstream of the tyrosine aminotransferase gene. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90752-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Blau H., Kedes L. Two-level regulation of cardiac actin gene transcription: muscle-specific modulating factors can accumulate before gene activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2137–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa T., Boxer L. M., Kedes L. CArG boxes in the human cardiac alpha-actin gene are core binding sites for positive trans-acting regulatory factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6702–6706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa T., Kedes L. Duplicated CArG box domains have positive and mutually dependent regulatory roles in expression of the human alpha-cardiac actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2803–2813. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Brennan S., Dathan N., Fairman S., Gurdon J. B. Cell type-specific activation of actin genes in the early amphibian embryo. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):716–721. doi: 10.1038/311716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Garrett N., Gurdon J. B. Upstream sequences required for tissue-specific activation of the cardiac actin gene in Xenopus laevis embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3185–3193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04628.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T., Garrett N., Treisman R. Xenopus cytoskeletal actin and human c-fos gene promoters share a conserved protein-binding site. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):667–673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04806.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscat G. E., Kedes L. Multiple 5'-flanking regions of the human alpha-skeletal actin gene synergistically modulate muscle-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4089–4099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. C., Doering J. L., Brown D. D. Characterization of two xenopus somatic 5S DNAs and one minor oocyte-specific 5S DNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):131–141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phan-Dinh-Tuy F., Tuil D., Schweighoffer F., Pinset C., Kahn A., Minty A. The 'CC.Ar.GG' box. A protein-binding site common to transcription-regulatory regions of the cardiac actin, c-fos and interleukin-2 receptor genes. Eur J Biochem. 1988 May 2;173(3):507–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richler C., Yaffe D. The in vitro cultivation and differentiation capacities of myogenic cell lines. Dev Biol. 1970 Sep;23(1):1–22. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(70)80004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F., Stuart G. W., Palmiter R. D. Building a metal-responsive promoter with synthetic regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1480–1489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topol J., Ruden D. M., Parker C. S. Sequences required for in vitro transcriptional activation of a Drosophila hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Orkin S. H., Maniatis T. Specific transcription and RNA splicing defects in five cloned beta-thalassaemia genes. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):591–596. doi: 10.1038/302591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K., Schimmel P. Two nuclear factors compete for the skeletal muscle actin promoter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9429–9432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Cross G. S., Woodland H. R. Tissue-specific expression of actin genes injected into Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):589–599. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90623-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Activating protein factor binds in vitro to upstream control sequences in heat shock gene chromatin. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):81–84. doi: 10.1038/311081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D., Saxel O. Serial passaging and differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse muscle. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):725–727. doi: 10.1038/270725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]