Abstract
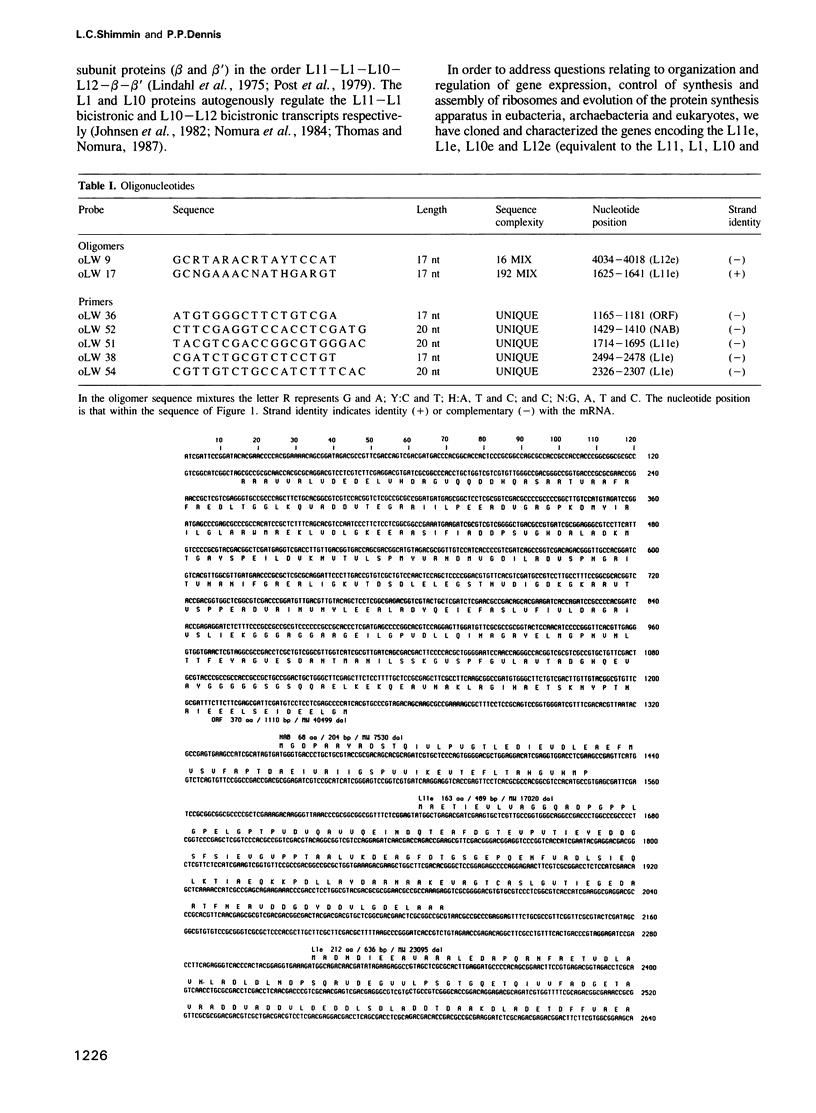
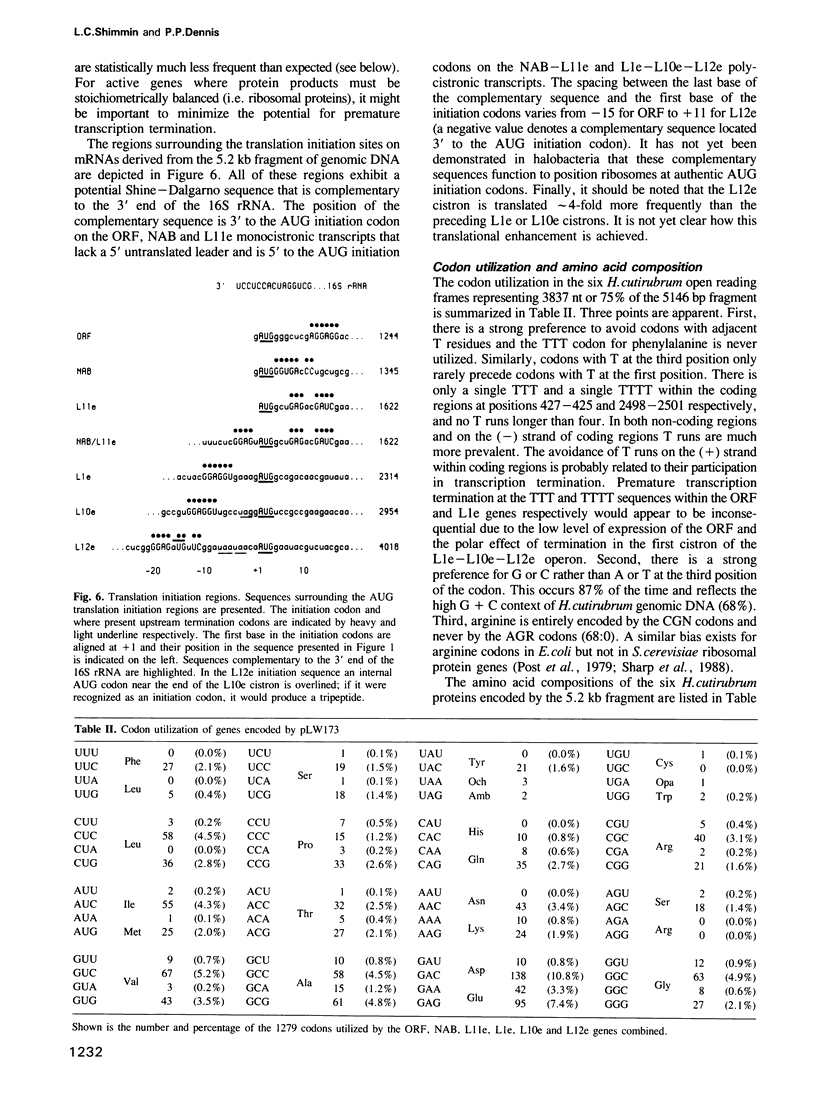
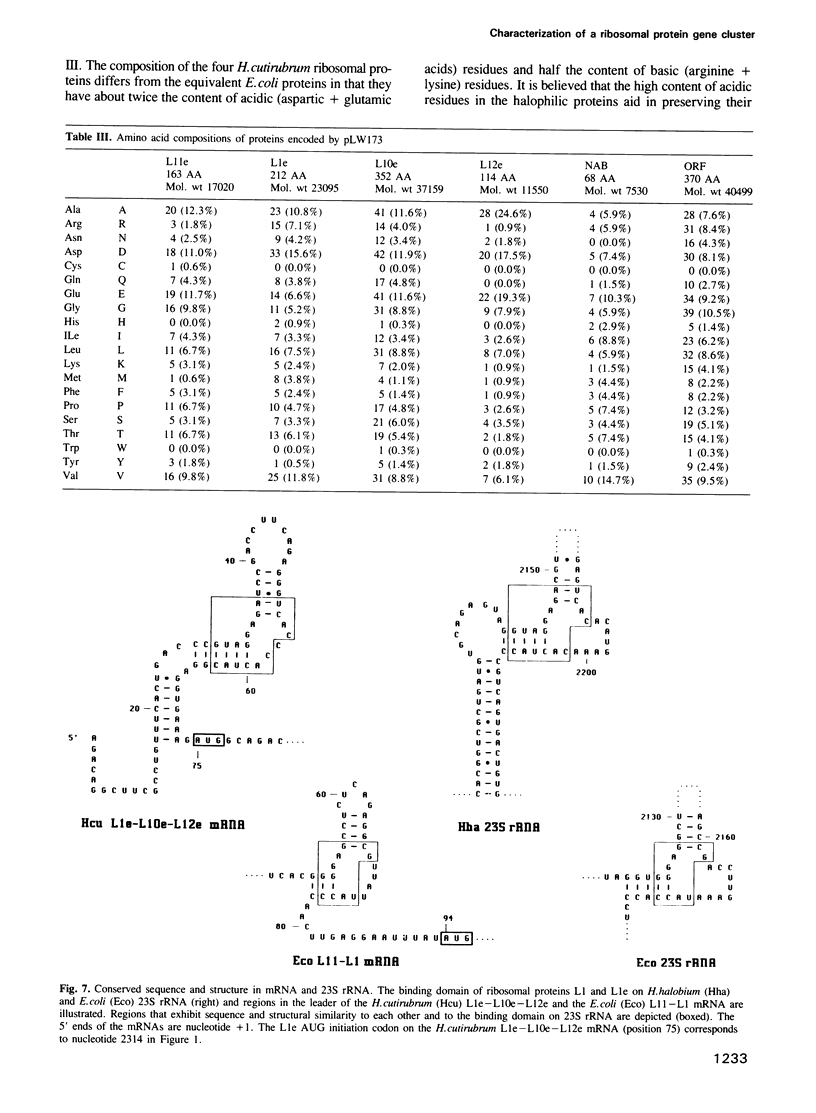
We have cloned and characterized a 5.2 kb fragment of genomic Halobacterium cutirubrum DNA encoding two potential proteins of unknown function (ORF and NAB) and four proteins which are equivalent to the L11, L1, L10 and L12 ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli (L11e, L1e, L10e and L12e). The ribosomal protein genes are clustered in the same order as that in E. coli although the transcription pattern differs. Transcripts characterized include (i) abundant monocistronic L11e and tricistronic L1e-L10e-L12e transcripts; (ii) less abundant bicistronic NAB-L11e and monocistronic NAB transcripts and (iii) a very rare ORF monocistronic transcript. The consensus sequence in the promoter region is TTCGA ... 4-10 nucleotides ... TTAA ... 25-26 nucleotides ... initiation site; termination generally occurs on poly(T) tracts following GC-rich regions. Poly(T) tracts in the sense strands within coding regions are notably absent; this is probably related to their participation in transcription termination and to the fact that these ribosomal protein genes are highly expressed and stoichiometrically balanced. In the third position of the codons G or C is utilized 87% of the time. The 74 nt long untranslated leader of the L1e-L10e-L12e transcript contains a region that has a sequence and structure almost identical to a region within the binding domain for the L1e protein in 23S rRNA and highly similar to the E. coli L11-L1 mRNA leader sequence that has been implicated in autogenous translational regulation. Other transcripts are initiated at or adjacent to the ATG translation initiation codon.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayley S. T., Morton R. A. Recent developments in the molecular biology of extremely halophilic bacteria. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1978;6(2):151–205. doi: 10.3109/10408417809090622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauclerk A. A., Cundliffe E., Dijk J. The binding site for ribosomal protein complex L8 within 23 s ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6559–6563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauclerk A. A., Hummel H., Holmes D. J., Böck A., Cundliffe E. Studies of the GTPase domain of archaebacterial ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):245–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boissy R., Astell C. R. An Escherichia coli recBCsbcBrecF host permits the deletion-resistant propagation of plasmid clones containing the 5'-terminal palindrome of minute virus of mice. Gene. 1985;35(1-2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Thomm M., Beckler G. S., Frey G., Stetter K. O., Reeve J. N. An archaebacterial RNA polymerase binding site and transcription initiation of the hisA gene in Methanococcus vannielii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):135–150. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chant J., Dennis P. Archaebacteria: transcription and processing of ribosomal RNA sequences in Halobacterium cutirubrum. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1091–1097. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04327.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis P. P. Multiple promoters for the transcription of the ribosomal RNA gene cluster in Halobacterium cutirubrum. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):457–461. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijk J., Garrett R. A., Müller R. Studies on the binding of the ribosomal protein complex L7/12-L10 and protein L11 to the 5'-one third of 23S RNA: a functional centre of the 50S subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 25;6(8):2717–2729. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.8.2717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing W. L., Dennis P. P. Transcription products from the rplKAJL-rpoBC gene cluster. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 20;194(4):609–620. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90238-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg H., Wachtel E. J. Structural studies of halophilic proteins, ribosomes, and organelles of bacteria adapted to extreme salt concentrations. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1987;16:69–92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.16.060187.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harauz G., Stoeffler-Meilicke M., van Heel M. Characteristic views of prokaryotic 50S ribosomal subunits. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(4):347–357. doi: 10.1007/BF02101154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui I., Dennis P. P. Characterization of the ribosomal RNA gene clusters in Halobacterium cutirubrum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):899–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsen M., Christensen T., Dennis P. P., Fiil N. P. Autogenous control: ribosomal protein L10-L12 complex binds to the leader sequence of its mRNA. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):999–1004. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01284.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjems J., Garrett R. A. Novel expression of the ribosomal RNA genes in the extreme thermophile and archaebacterium Desulfurococcus mobilis. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3521–3530. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjems J., Leffers H., Garrett R. A., Wich G., Leinfelder W., Böck A. Gene organization, transcription signals and processing of the single ribosomal RNA operon of the archaebacterium Thermoproteus tenax. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4821–4835. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. A. Ribosome evolution: the structural bases of protein synthesis in archaebacteria, eubacteria, and eukaryotes. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;30:163–194. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60686-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. A., Strycharz W. A. Ribosomal proteins L1, L17 and L27 from Escherichia coli localized at single sites on the large subunit by immune electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 25;153(4):979–992. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90462-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljas A. Structural studies of ribosomes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1982;40(3):161–228. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(82)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl L., Jaskunas S. R., Dennis P. P., Nomura M. Cluster of genes in Escherichia coli for ribosomal proteins, ribosomal RNA, and RNA polymerase subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2743–2747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl L., Zengel J. M. Ribosomal genes in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:297–326. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheson A. T., Yaguchi M., Christensen P., Rollin C. F., Hasnain S. Purification, properties, and N-terminal amino acid sequence of certain 50S ribosomal subunit proteins from the archaebacterium Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;62(6):426–433. doi: 10.1139/o84-058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Kramer F. R. Structure-independent nucleotide sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2232–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Nishimura S., Seela F. Improvement of the dideoxy chain termination method of DNA sequencing by use of deoxy-7-deazaguanosine triphosphate in place of dGTP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1319–1324. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. Specific accessory sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae introns control assembly of pre-mRNAs into spliceosomes. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3833–3839. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02720.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:119–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson I., Liljas A. The stoichiometry and reconstitution of a stable protein complex from Escherichia coli ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 1;98(1):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson I. Studies on the RNA and protein binding sites of the E. coli ribosomal protein L10. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2637–2646. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Strycharz G. D., Nomura M., Lewis H., Dennis P. P. Nucleotide sequence of the ribosomal protein gene cluster adjacent to the gene for RNA polymerase subunit beta in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1697–1701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez C., Shimmin L. C., Newton C. H., Matheson A. T., Dennis P. P. Structure and evolution of the L11, L1, L10, and L12 equivalent ribosomal proteins in eubacteria, archaebacteria, and eucaryotes. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):234–244. doi: 10.1139/m89-036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Zillig W. Analysis of transcription in the archaebacterium Sulfolobus indicates that archaebacterial promoters are homologous to eukaryotic pol II promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):1–19. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEHGAL S. N., GIBBONS N. E. Effect of some metal ions on the growth of Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Apr;6:165–169. doi: 10.1139/m60-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander G. Ribosomal protein L1 from Escherichia coli. Its role in the binding of tRNA to the ribosome and in elongation factor g-dependent gtp hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10098–10103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimmin L. C., Newton C. H., Ramirez C., Yee J., Downing W. L., Louie A., Matheson A. T., Dennis P. P. Organization of genes encoding the L11, L1, L10, and L12 equivalent ribosomal proteins in eubacteria, archaebacteria, and eucaryotes. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):164–170. doi: 10.1139/m89-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strycharz W. A., Nomura M., Lake J. A. Ribosomal proteins L7/L12 localized at a single region of the large subunit by immune electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 5;126(2):123–140. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90355-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R., Dabbs E. R. Functional studies on ribosomes lacking protein L1 from mutant Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Nov;112(2):425–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb07222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. S., Nomura M. Translational regulation of the L11 ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli: mutations that define the target site for repression by L1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):3085–3096. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomm M., Wich G. An archaebacterial promoter element for stable RNA genes with homology to the TATA box of higher eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):151–163. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wich G., Hummel H., Jarsch M., Bär U., Böck A. Transcription signals for stable RNA genes in Methanococcus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2459–2479. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Fox G. E. Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: the primary kingdoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5088–5090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zillig W., Klenk H. P., Palm P., Pühler G., Gropp F., Garrett R. A., Leffers H. The phylogenetic relations of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases of archaebacteria, eukaryotes, and eubacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):73–80. doi: 10.1139/m89-011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



