Abstract
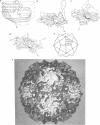
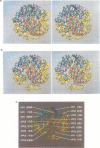
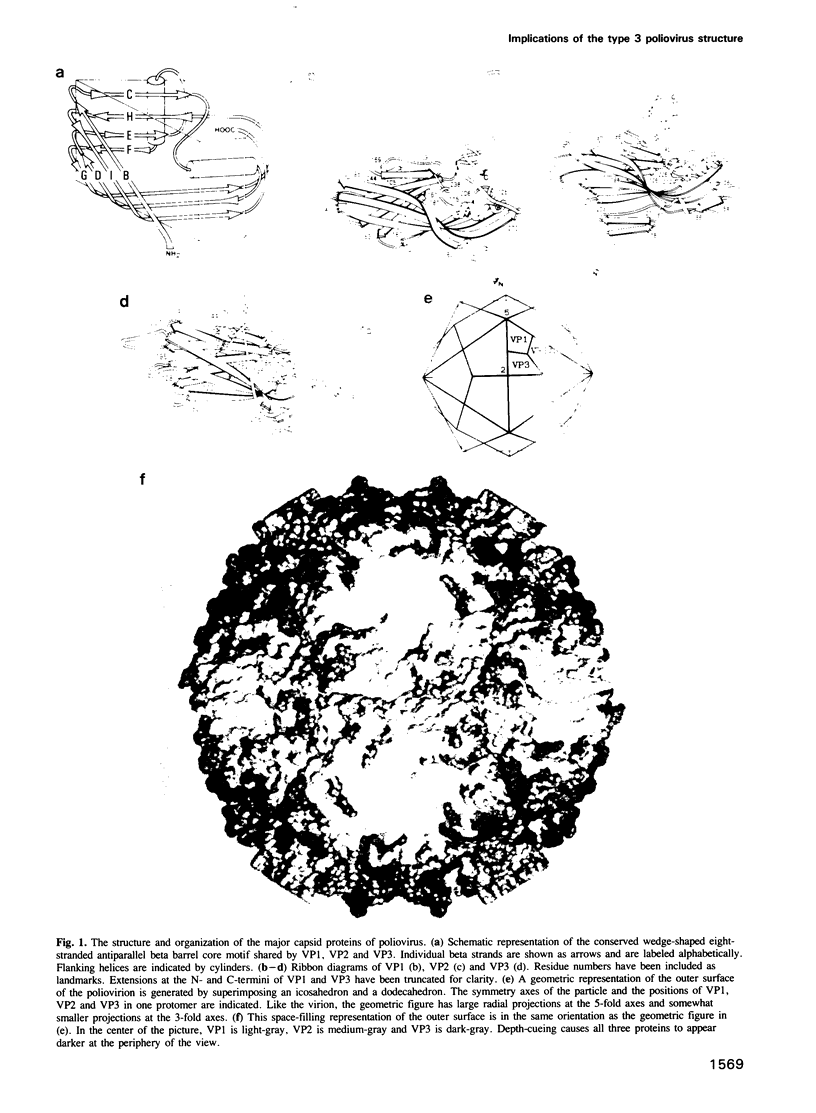
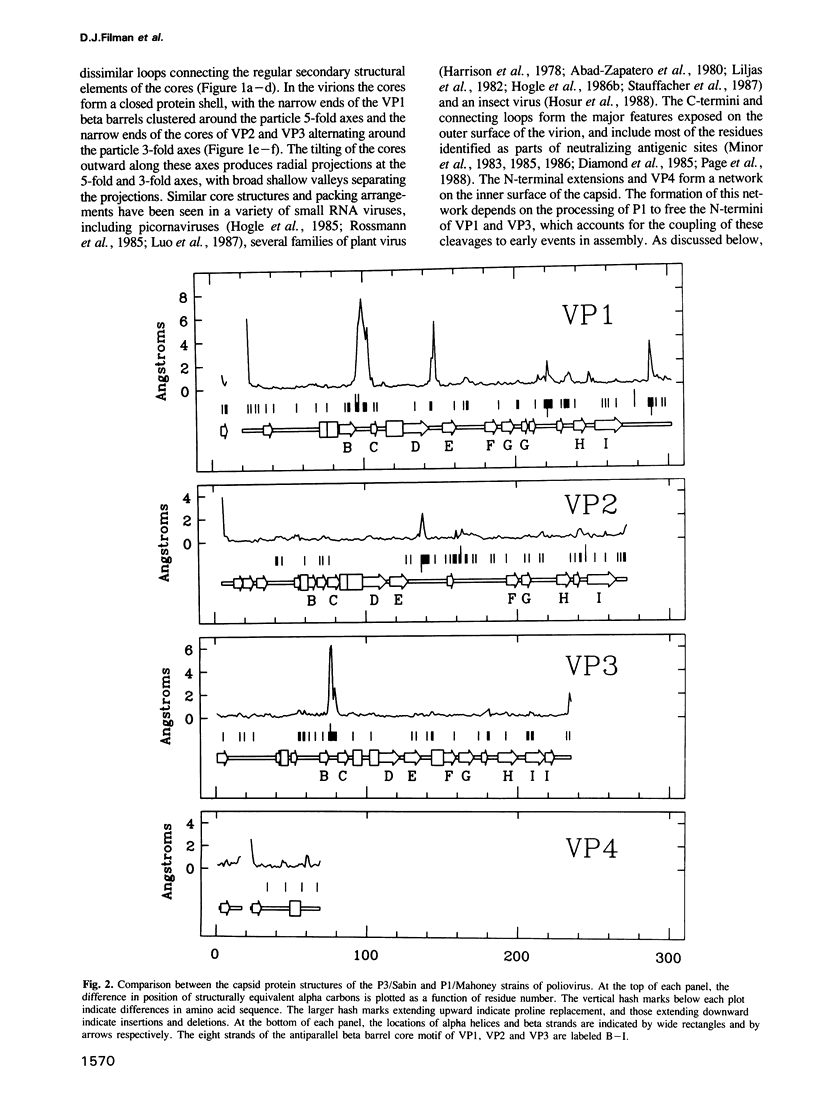
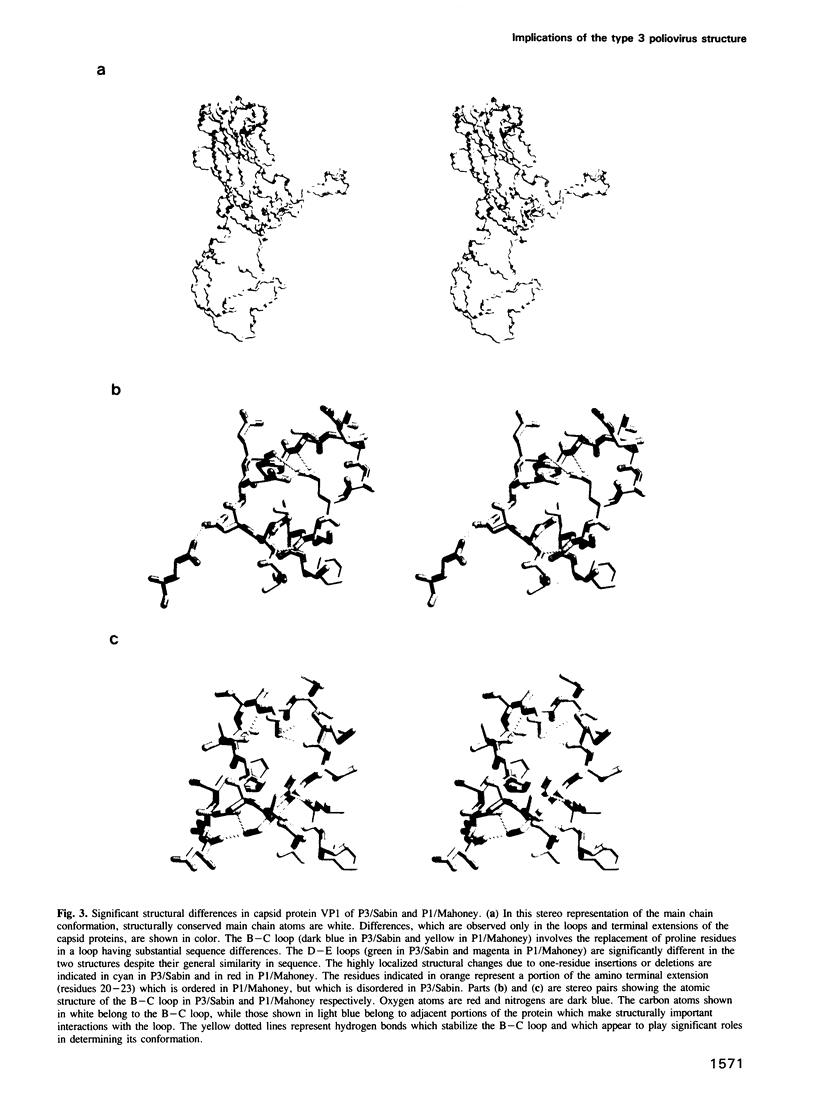
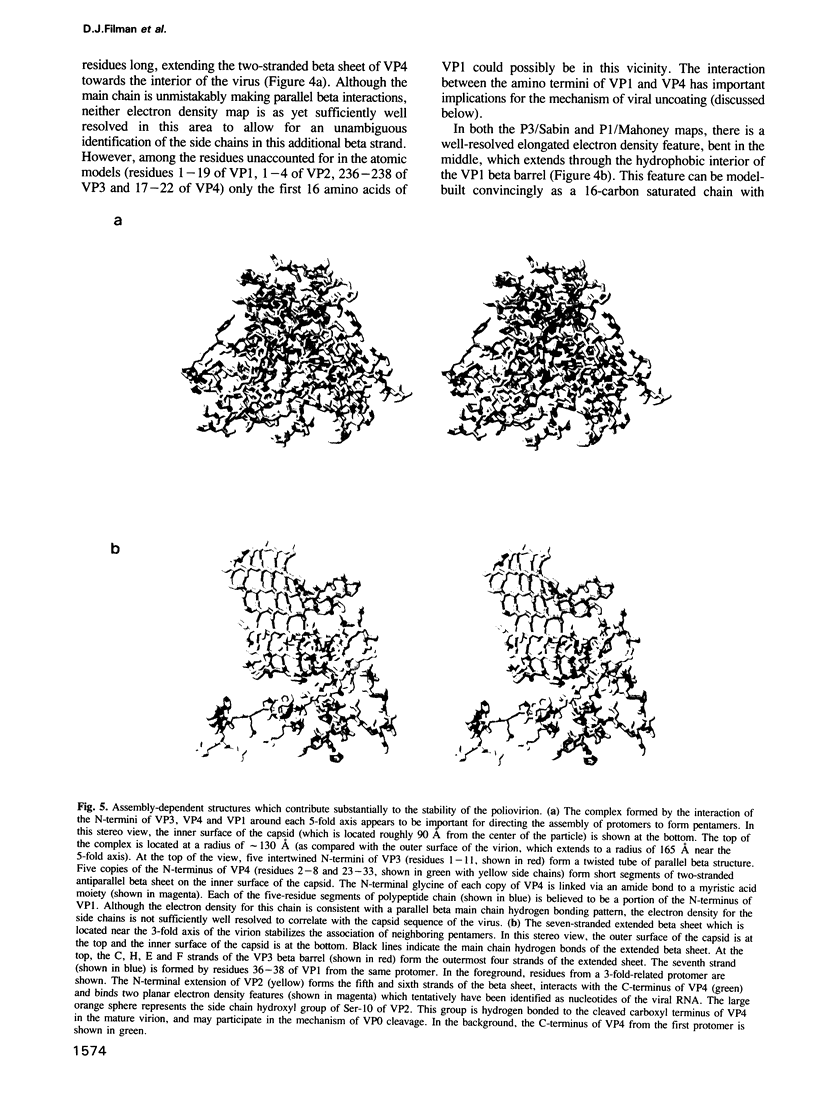
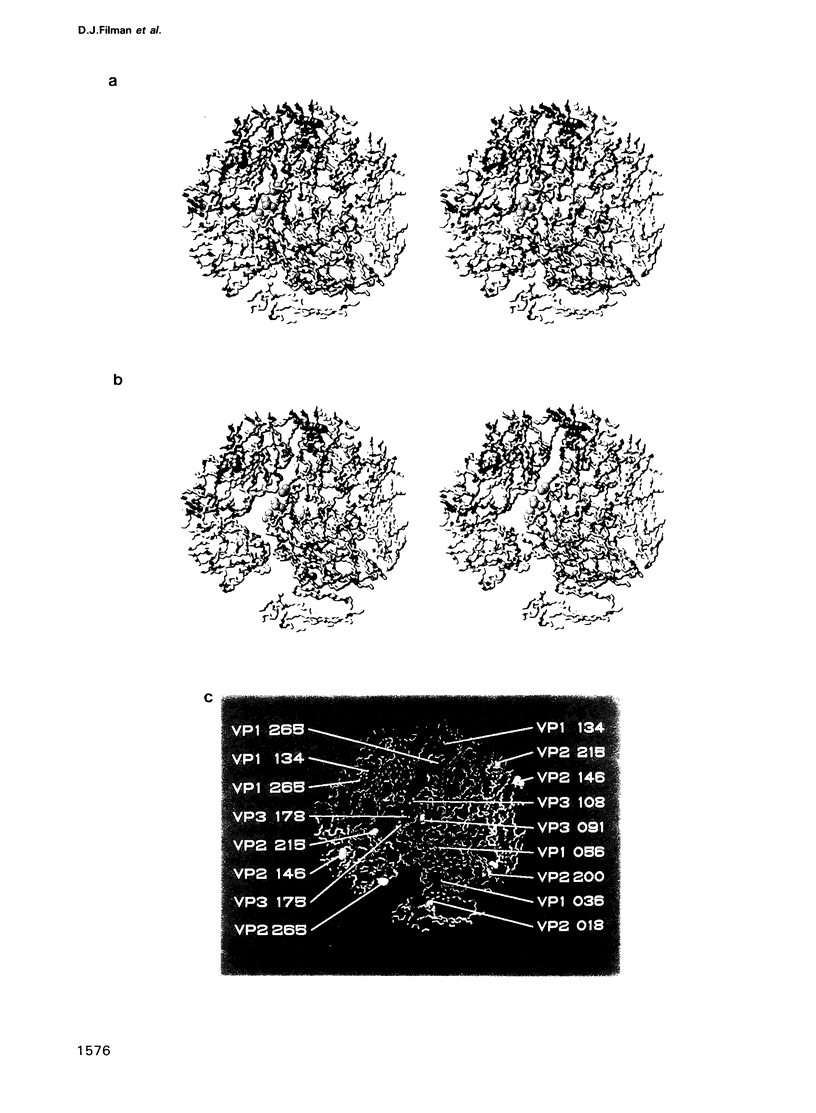
The three-dimensional structure of the Sabin strain of type 3 poliovirus has been determined at 2.4 A resolution. Significant structural differences with the Mahoney strain of type 1 poliovirus are confined to loops and terminal extensions of the capsid proteins, occur in all of the major antigenic sites of the virion and typically involve insertions, deletions or the replacement of prolines. Several newly identified components of the structure participate in assembly-dependent interactions which are relevant to the biologically important processes of viral assembly and uncoating. These include two sites of lipid substitution, two putative nucleotides and a beta sheet formed by the N-termini of capsid proteins VP4 and VP1. The structure provides an explanation for the temperature sensitive phenotype of the P3/Sabin strain. Amino acids that regulate temperature sensitivity in type 3 poliovirus are located in the interfaces between promoters, in the binding site for a lipid substituent and in an assembly-dependent extended beta sheet that stabilizes the association of pentamers. Several lines of evidence indicate that these structural components also control conformational transitions at various stages of the viral life cycle.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold E., Rossmann M. G. The use of molecular-replacement phases for the refinement of the human rhinovirus 14 structure. Acta Crystallogr A. 1988 May 1;44(Pt 3):270–282. doi: 10.1107/s0108767387011875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badger J., Minor I., Kremer M. J., Oliveira M. A., Smith T. J., Griffith J. P., Guerin D. M., Krishnaswamy S., Luo M., Rossmann M. G. Structural analysis of a series of antiviral agents complexed with human rhinovirus 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3304–3308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Antibodies against the chemically synthesized genome-linked protein of poliovirus react with native virus-specific proteins. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90357-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke K. L., Dunn G., Ferguson M., Minor P. D., Almond J. W. Antigen chimaeras of poliovirus as potential new vaccines. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):81–82. doi: 10.1038/332081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Lesk A. M. Canonical structures for the hypervariable regions of immunoglobulins. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):901–917. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90412-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Lesk A. M., Levitt M., Amit A. G., Mariuzza R. A., Phillips S. E., Poljak R. J. The predicted structure of immunoglobulin D1.3 and its comparison with the crystal structure. Science. 1986 Aug 15;233(4765):755–758. doi: 10.1126/science.3090684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Newman J. F., Filman D., Hogle J. M., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Myristylation of picornavirus capsid protein VP4 and its structural significance. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):482–486. doi: 10.1038/327482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond D. C., Jameson B. A., Bonin J., Kohara M., Abe S., Itoh H., Komatsu T., Arita M., Kuge S., Nomoto A. Antigenic variation and resistance to neutralization in poliovirus type 1. Science. 1985 Sep 13;229(4718):1090–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.2412292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden J. S., Harrison S. C. Proteolytic dissection of turnip crinkle virus subunit in solution. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 3;21(16):3862–3866. doi: 10.1021/bi00259a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Maeda A., Harrison S. C. Structure and assembly of turnip crinkle virus. I. X-ray crystallographic structure analysis at 3.2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 20;191(4):625–638. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90450-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosur M. V., Schmidt T., Tucker R. C., Johnson J. E., Gallagher T. M., Selling B. H., Rueckert R. R. Structure of an insect virus at 3.0 A resolution. Proteins. 1987;2(3):167–176. doi: 10.1002/prot.340020302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icenogle J. P., Minor P. D., Ferguson M., Hogle J. M. Modulation of humoral response to a 12-amino-acid site on the poliovirus virion. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):297–301. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.297-301.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A. Diffraction methods for biological macromolecules. Interactive computer graphics: FRODO. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:157–171. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljas L., Unge T., Jones T. A., Fridborg K., Lövgren S., Skoglund U., Strandberg B. Structure of satellite tobacco necrosis virus at 3.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 25;159(1):93–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo M., Vriend G., Kamer G., Minor I., Arnold E., Rossmann M. G., Boege U., Scraba D. G., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C. The atomic structure of Mengo virus at 3.0 A resolution. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):182–191. doi: 10.1126/science.3026048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A., Wychowski C., Couderc T., Crainic R., Hogle J., Girard M. Engineering a poliovirus type 2 antigenic site on a type 1 capsid results in a chimaeric virus which is neurovirulent for mice. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2839–2847. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J., Caliguiri L. A., Eggers H. J. Inhibition of uncoating of poliovirus by arildone, a new antiviral drug. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90342-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Evans D. M., Ferguson M., Schild G. C., Westrop G., Almond J. W. Principal and subsidiary antigenic sites of VP1 involved in the neutralization of poliovirus type 3. J Gen Virol. 1985 May;66(Pt 5):1159–1165. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-5-1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Ferguson M., Evans D. M., Almond J. W., Icenogle J. P. Antigenic structure of polioviruses of serotypes 1, 2 and 3. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jul;67(Pt 7):1283–1291. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-7-1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Ferguson M., Phillips A., Magrath D. I., Huovilainen A., Hovi T. Conservation in vivo of protease cleavage sites in antigenic sites of poliovirus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jul;68(Pt 7):1857–1865. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-7-1857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Bootman J., Evans D. M., Ferguson M., Reeve P., Spitz M., Stanway G., Cann A. J., Hauptmann R. Location and primary structure of a major antigenic site for poliovirus neutralization. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):674–679. doi: 10.1038/301674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G., Bradley J., Yang X. F., Wimmer E., Moss E. G., Racaniello V. R. Poliovirus host range is determined by a short amino acid sequence in neutralization antigenic site I. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):213–215. doi: 10.1126/science.2838906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G., Kuhn R. J., Arita M., Kawamura N., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. Poliovirus type 1/type 3 antigenic hybrid virus constructed in vitro elicits type 1 and type 3 neutralizing antibodies in rabbits and monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3203–3207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page G. S., Mosser A. G., Hogle J. M., Filman D. J., Rueckert R. R., Chow M. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus serotype 1 neutralizing determinants. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1781–1794. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1781-1794.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Frankenberger E. A., Griffith J. P., Hecht H. J., Johnson J. E., Kamer G., Luo M., Mosser A. G. Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):145–153. doi: 10.1038/317145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. J., Kremer M. J., Luo M., Vriend G., Arnold E., Kamer G., Rossmann M. G., McKinlay M. A., Diana G. D., Otto M. J. The site of attachment in human rhinovirus 14 for antiviral agents that inhibit uncoating. Science. 1986 Sep 19;233(4770):1286–1293. doi: 10.1126/science.3018924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Cann A. J., Hauptmann R., Hughes P., Clarke L. D., Mountford R. C., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Almond J. W. The nucleotide sequence of poliovirus type 3 leon 12 a1b: comparison with poliovirus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5629–5643. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Kohara M., Kataoka Y., Suganuma T., Omata T., Imura N., Nomoto A. Complete nucleotide sequences of all three poliovirus serotype genomes. Implication for genetic relationship, gene function and antigenic determinants. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):561–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]