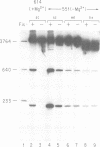
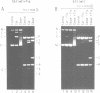
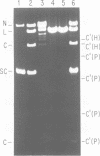
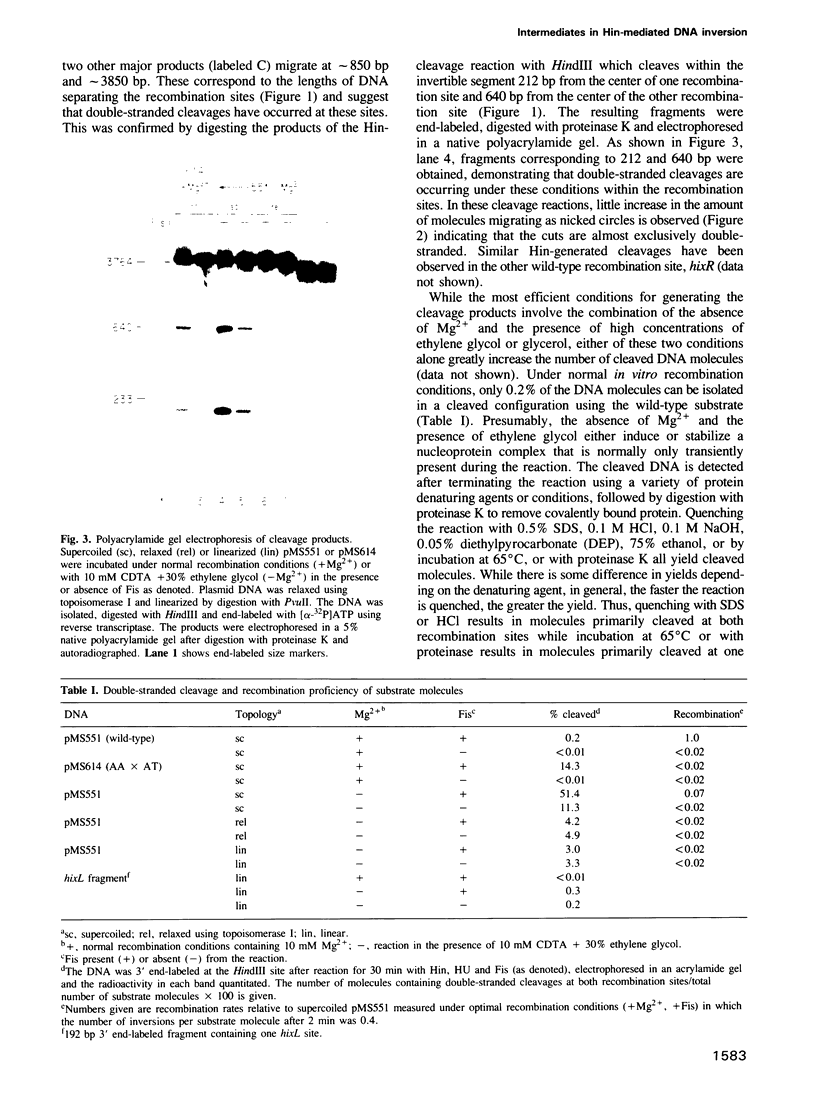
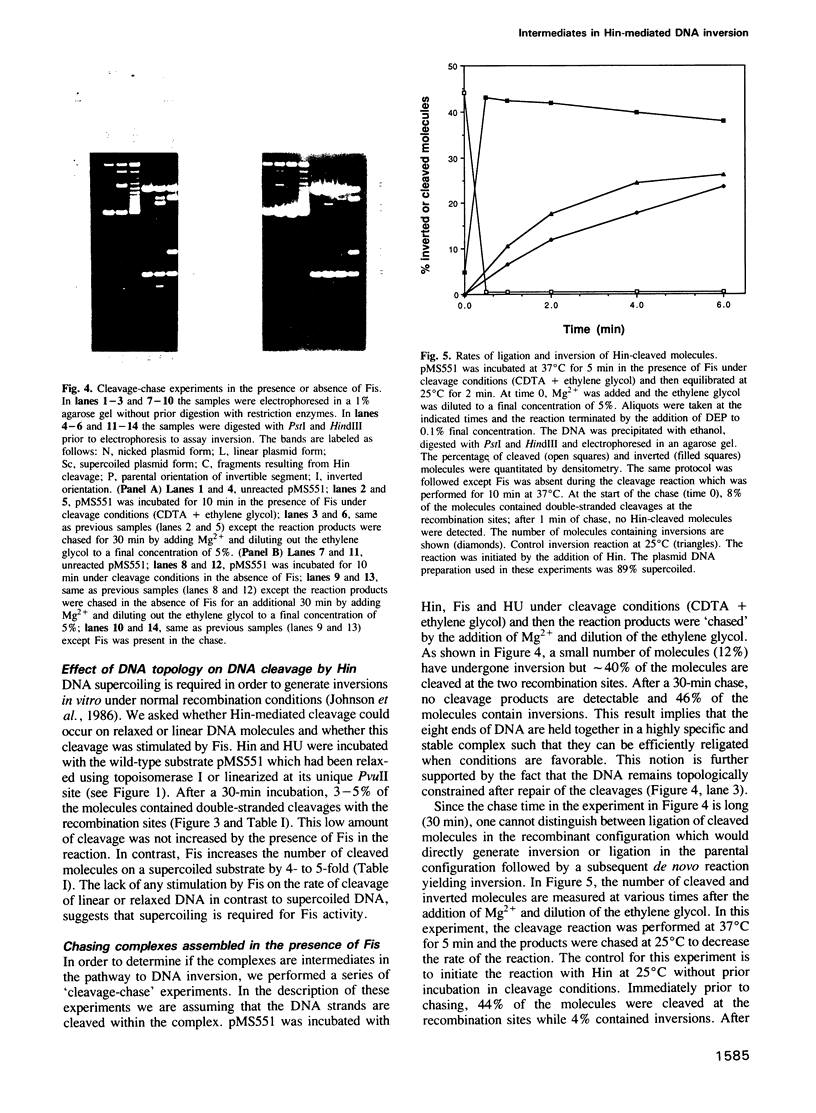
Abstract
The site-specific inversion reaction controlling flagellin synthesis in Salmonella involves the function of three proteins: Hin, Fis and HU. The DNA substrate must be supercoiled and contain a recombinational enhancer sequence in addition to the two recombination sites. Using mutant substrates or modified reaction conditions, large amounts of complexes can be generated which are recognized by double-stranded breaks within both recombination sites upon quenching. The cleaved molecules contain 2-bp staggered cuts within the central dinucleotide of the recombination site. Hin is covalently associated with the 5' end while the protruding 3' end contains a free hydoxyl. We demonstrate that complexes generated in the presence of an active enhancer are intermediates that have advanced past the major rate limiting step(s) of the reaction. In the absence of a functional enhancer, Hin is also able to assemble and catalyze site-specific cleavages within the two recombination sites. However, these complexes are kinetically distinct from the complexes assembled with a functional enhancer and cannot generate inversion without an active enhancer. The results suggest that strand exchange leading to inversion is mediated by double-stranded cleavage of DNA at both recombination sites followed by the rotation of strands to position the DNA into the recombinant configuration. The role of the enhancer and DNA supercoiling in these reactions is discussed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Been M. D., Champoux J. J. DNA breakage and closure by rat liver type 1 topoisomerase: separation of the half-reactions by using a single-stranded DNA substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2883–2887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruist M. F., Glasgow A. C., Johnson R. C., Simon M. I. Fis binding to the recombinational enhancer of the Hin DNA inversion system. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):762–772. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L. The mechanism of conservative site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:77–105. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.000453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Reed R. R. Transpositional recombination in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:863–896. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halligan B. D., Davis J. L., Edwards K. A., Liu L. F. Intra- and intermolecular strand transfer by HeLa DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3995–4000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfull G. F., Grindley N. D. Analysis of gamma delta resolvase mutants in vitro: evidence for an interaction between serine-10 of resolvase and site I of res. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5429–5433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H. E., Iida S., Arber W., Bickle T. A. Site-specific DNA inversion is enhanced by a DNA sequence element in cis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3776–3780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Hiestand-Nauer R. Localized conversion at the crossover sequences in the site-specific DNA inversion system of bacteriophage P1. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90539-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Meyer J., Kennedy K. E., Arber W. A site-specific, conservative recombination system carried by bacteriophage P1. Mapping the recombinase gene cin and the cross-over sites cix for the inversion of the C segment. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1445–1453. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01336.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Ball C. A., Pfeffer D., Simon M. I. Isolation of the gene encoding the Hin recombinational enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3484–3488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Bruist M. F., Simon M. I. Host protein requirements for in vitro site-specific DNA inversion. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):531–539. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90878-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Glasgow A. C., Simon M. I. Spatial relationship of the Fis binding sites for Hin recombinational enhancer activity. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):462–465. doi: 10.1038/329462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Simon M. I. Hin-mediated site-specific recombination requires two 26 bp recombination sites and a 60 bp recombinational enhancer. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):781–791. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahmann R., Rudt F., Koch C., Mertens G. G inversion in bacteriophage Mu DNA is stimulated by a site within the invertase gene and a host factor. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):771–780. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamp D., Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Kwoh D., Zipser D., Kahmann R. Site-specific recombination in phage mu. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1159–1167. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaar R., van de Putte P., Cozzarelli N. R. Gin-mediated DNA inversion: product structure and the mechanism of strand exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):752–756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaar R., van de Putte P. Topological aspects of site-specific DNA-inversion. Bioessays. 1987 Nov;7(5):195–200. doi: 10.1002/bies.950070502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P., Richet E., Nash H. A. Lambda integrative recombination: supercoiling, synapsis, and strand exchange. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:735–744. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klippel A., Mertens G., Patschinsky T., Kahmann R. The DNA invertase Gin of phage Mu: formation of a covalent complex with DNA via a phosphoserine at amino acid position 9. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1229–1237. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02935.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C., Vandekerckhove J., Kahmann R. Escherichia coli host factor for site-specific DNA inversion: cloning and characterization of the fis gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4237–4241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Interaction between DNA and Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I. Formation of complexes between the protein and superhelical and nonsuperhelical duplex DNAs. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11082–11088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Van de Putte P. Genetic switches by DNA inversions in prokaryotes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 16;782(2):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray W. J., Jr, Long J. W. The construction and testing of a simple, slow delivery-rapid quench apparatus. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 7;15(18):3990–3993. doi: 10.1021/bi00663a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R., Grindley N. D. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination in vitro: DNA cleavage and protein-DNA linkage at the recombination site. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):721–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R., Moser C. D. Resolvase-mediated recombination intermediates contain a serine residue covalently linked to DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:245–249. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Abcarian P., Nash H. A. The interaction of recombination proteins with supercoiled DNA: defining the role of supercoiling in lambda integrative recombination. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1011–1021. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90700-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Schmid C. W. Pyrimidine-specific chemical reactions useful for DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 24;8(20):4613–4619. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.20.4613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski P. Site-specific recombinases: changing partners and doing the twist. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.341-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Phase variation: genetic analysis of switching mutants. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):845–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinkler C., Rosen G., Boyer P. D. Light-driven ATP formation from 32Pi by chloroplast thylakoids without detectable labeling of ADP, as measured by rapid mixing and acid quench techniques. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2507–2510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieg J., Simon M. Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of an invertible controlling element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4196–4200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]