Abstract
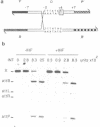
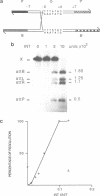
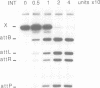
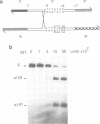
Integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda occurs by two sequential, reciprocal strand exchanges at specific positions within the attachment sites. Both exchanges are promoted by the lambda Int protein; the first forms a Holliday structure, and the second resolves it to recombinant products. Recombination requires sequence homology within the 7 bp 'overlap' region that separates the two points of strand exchange. To see if homology promotes the second strand exchange, we constructed attachment site Holliday structures by annealing DNA strands and then assayed Int-promoted resolution. Holliday structures corresponding to strand exchange between sites with homologous overlap regions were efficiently resolved to give mixtures of recombinants and parents. Holliday structures corresponding to exchanges between heterologous sites fell into two classes. Members of the first class, in which heterology limited but did not completely prevent migration of the branchpoint within the overlap region, were resolved efficiently and preferentially to parental molecules. We propose that resolution to recombinants occurs only if homology allows branch migration from the first to the second exchange site. Members of the second class, in which heterology constrained the branchpoint within an Int binding site, were resolved poorly. We suggest that Holliday structures that have a branchpoint within an Int binding site are poor substrates for Int.
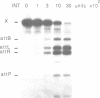
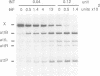
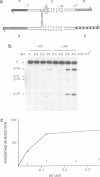
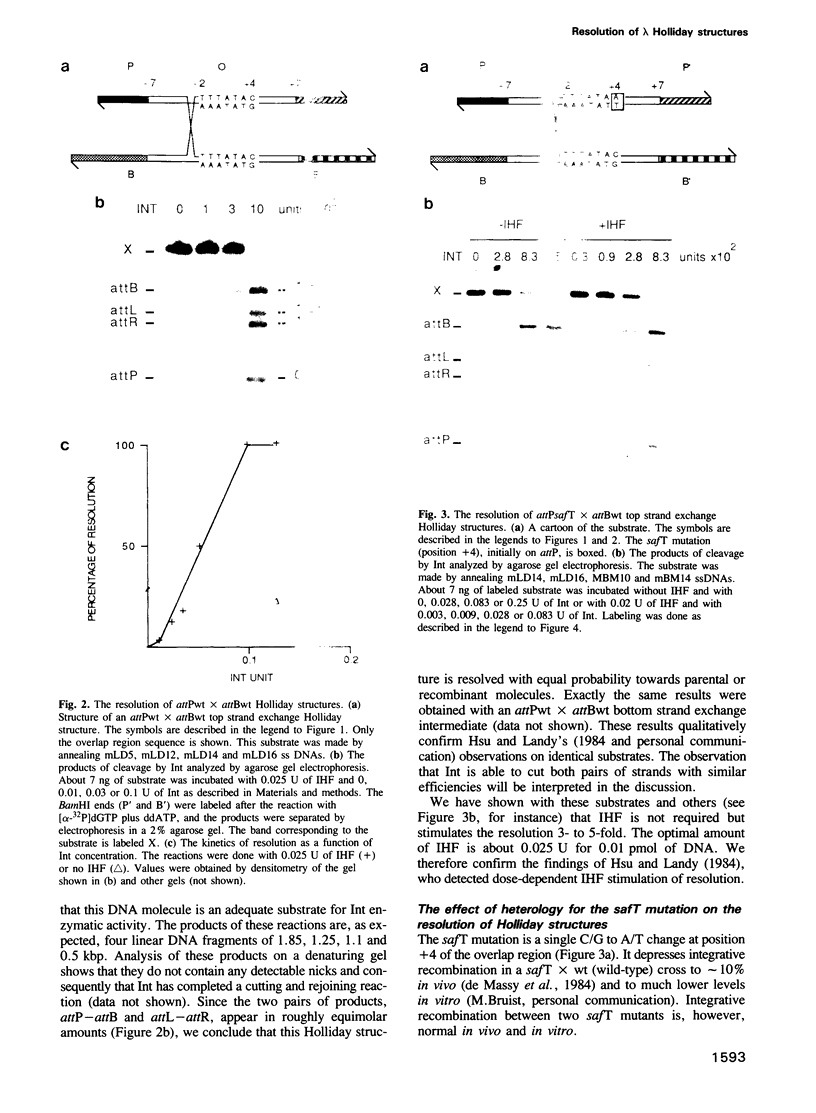
Full text
PDF



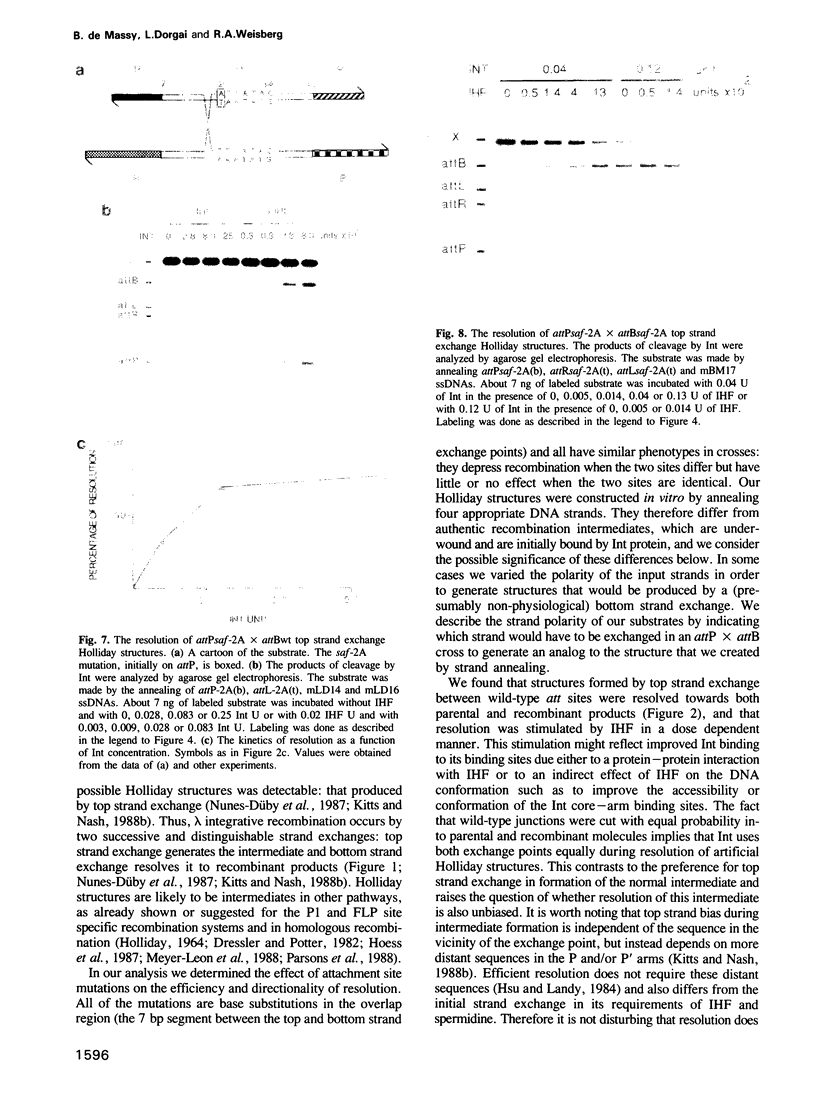



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews B. J., McLeod M., Broach J., Sadowski P. D. Interaction of the FLP recombinase of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae 2 micron plasmid with mutated target sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2482–2489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argos P., Landy A., Abremski K., Egan J. B., Haggard-Ljungquist E., Hoess R. H., Kahn M. L., Kalionis B., Narayana S. V., Pierson L. S., 3rd The integrase family of site-specific recombinases: regional similarities and global diversity. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):433–440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer C. E., Gardner J. F., Gumport R. I. Extent of sequence homology required for bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 20;181(2):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Better M., Lu C., Williams R. C., Echols H. Site-specific DNA condensation and pairing mediated by the int protein of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5837–5841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. H., Churchill M. E., Tullius T. D., Kallenbach N. R., Seeman N. C. Construction and analysis of monomobile DNA junctions. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):6032–6038. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill M. E., Tullius T. D., Kallenbach N. R., Seeman N. C. A Holliday recombination intermediate is twofold symmetric. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4653–4656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Nash H. A. The mechanism of phage lambda site-specific recombination: site-specific breakage of DNA by Int topoisomerase. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):795–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickie P., McFadden G., Morgan A. R. The site-specific cleavage of synthetic Holliday junction analogs and related branched DNA structures by bacteriophage T7 endonuclease I. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14826–14836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler D., Potter H. Molecular mechanisms in genetic recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:727–761. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H., Green L. Some properties of site-specific and general recombination inferred from int-initiated exchanges by bacteriophage lambda. Genetics. 1979 Oct;93(2):297–307. doi: 10.1093/genetics/93.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Nash H., Weisberg R. A. Strand exchange in site-specific recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1363–1367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. H., Kolodner R. Effect of DNA structure and nucleotide sequence on Holliday junction resolution by a Saccharomyces cerevisiae endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):69–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90439-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoess R. H., Wierzbicki A., Abremski K. The role of the loxP spacer region in P1 site-specific recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2287–2300. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoess R., Wierzbicki A., Abremski K. Isolation and characterization of intermediates in site-specific recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6840–6844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Landy A. Resolution of synthetic att-site Holliday structures by the integrase protein of bacteriophage lambda. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):721–726. doi: 10.1038/311721a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Simon M. I. Hin-mediated site-specific recombination requires two 26 bp recombination sites and a 60 bp recombinational enhancer. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):781–791. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Nash H. A. Nicking-closing activity associated with bacteriophage lambda int gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3760–3764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Nash H. A. An intermediate in the phage lambda site-specific recombination reaction is revealed by phosphorothioate substitution in DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):6839–6856. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Nash H. A. Bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination proceeds with a defined order of strand exchanges. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):95–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90602-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Nash H. A. Homology-dependent interactions in phage lambda site-specific recombination. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):346–348. doi: 10.1038/329346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Leon L., Huang L. C., Umlauf S. W., Cox M. M., Inman R. B. Holliday intermediates and reaction by-products in FLP protein-promoted site-specific recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3784–3796. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Weisberg R., Enquist L., Mizuuchi M., Buraczynska M., Foeller C., Hsu P. L., Ross W., Landy A. Structure and function of the phage lambda att site: size, int-binding sites, and location of the crossover point. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):429–437. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes-Düby S. E., Matsumoto L., Landy A. Site-specific recombination intermediates trapped with suicide substrates. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):779–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. L., Prasad P. V., Harshey R. M., Jayaram M. Step-arrest mutants of FLP recombinase: implications for the catalytic mechanism of DNA recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3303–3310. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet E., Abcarian P., Nash H. A. The interaction of recombination proteins with supercoiled DNA: defining the role of supercoiling in lambda integrative recombination. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1011–1021. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90700-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A. Bacteriophage lambda int protein recognizes two classes of sequence in the phage att site: characterization of arm-type sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7724–7728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Landy A. Patterns of lambda Int recognition in the regions of strand exchange. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90355-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski P. Site-specific recombinases: changing partners and doing the twist. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.341-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senecoff J. F., Bruckner R. C., Cox M. M. The FLP recombinase of the yeast 2-micron plasmid: characterization of its recombination site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7270–7274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senecoff J. F., Cox M. M. Directionality in FLP protein-promoted site-specific recombination is mediated by DNA-DNA pairing. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7380–7386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umlauf S. W., Cox M. M. The functional significance of DNA sequence structure in a site-specific genetic recombination reaction. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1845–1852. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03017.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisberg R. A., Enquist L. W., Foeller C., Landy A. Role for DNA homology in site-specific recombination. The isolation and characterization of a site affinity mutant of coliphage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 25;170(2):319–342. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin S., Bushman W., Landy A. Interaction of the lambda site-specific recombination protein Xis with attachment site DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1040–1044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Massy B., Studier F. W., Dorgai L., Appelbaum E., Weisberg R. A. Enzymes and sites of genetic recombination: studies with gene-3 endonuclease of phage T7 and with site-affinity mutants of phage lambda. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:715–726. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Massy B., Weisberg R. A., Studier F. W. Gene 3 endonuclease of bacteriophage T7 resolves conformationally branched structures in double-stranded DNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 20;193(2):359–376. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90224-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]