Abstract
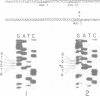
An unusual splicing mutation has been characterized in the pro alpha 1(I) collagen gene of a sporadic case of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Type VII. Cloning of primer extended cDNA in conjunction with R-looping experiments established that nearly half of the pro alpha 1(I) collagen gene transcripts are abnormally spliced, for they lack exon 6 sequences. Analysis of cloned genomic fragments revealed that one of the proband's alleles displays the substitution of an A for a G in the last nucleotide of exon 6. The change converts the normal Met (ATG) codon to Ile (ATA) and, in addition, obliterates a NcoI restriction site. The latter event was exploited to demonstrate the de novo nature of the mutation since DNA from the unaffected parents was fully digested with the enzyme, after in vitro amplification by the polymerase chain reaction. Further confirmation of the missplicing was obtained by transient expression into animal cells of allelic minigene constructs. Finally, Western blot analysis of cyanogen bromide cleaved collagen and nucleotide sequencing of appropriately selected cDNA clones demonstrated the production of relatively low amounts of correctly spliced molecules harboring the Ile substitution, as well.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Hornig H., Padgett R. A., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Sequence requirements for splicing of higher eukaryotic nuclear pre-mRNA. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90620-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arpaia E., Dumbrille-Ross A., Maler T., Neote K., Tropak M., Troxel C., Stirling J. L., Pitts J. S., Bapat B., Lamhonwah A. M. Identification of an altered splice site in Ashkenazi Tay-Sachs disease. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):85–86. doi: 10.1038/333085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Gargiulo V., Williams C. J., Ramirez F. Multiexon deletion in an osteogenesis imperfecta variant with increased type III collagen mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):691–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., de Wet W., Bernard M., Ding J. F., Morabito M., Myers J., Williams C., Ramirez F. Human pro alpha 1(I) collagen gene structure reveals evolutionary conservation of a pattern of introns and exons. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):337–340. doi: 10.1038/310337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole W. G., Chan D., Chambers G. W., Walker I. D., Bateman J. F. Deletion of 24 amino acids from the pro-alpha 1(I) chain of type I procollagen in a patient with the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5496–5503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alessio M., Bernard M., Pretorius P. J., de Wet W., Ramirez F., Pretorious P. J. Complete nucleotide sequence of the region encompassing the first twenty-five exons of the human pro alpha 1(I) collagen gene (COL1A1) Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Paz M. A., Gallop P. M. Cross-linking in collagen and elastin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:717–748. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Shapiro F. D., Aldridge J. F. A heterozygous collagen defect in a variant of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII. Evidence for a deleted amino-telopeptide domain in the pro-alpha 2(I) chain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11322–11329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka Y., Palella T. D., O'Toole T. E., Tarlé S. A., Kelley W. N. Human adenine phosphoribosyltransferase. Identification of allelic mutations at the nucleotide level as a cause of complete deficiency of the enzyme. J Clin Invest. 1987 Nov;80(5):1409–1415. doi: 10.1172/JCI113219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvit J., DiLella A. G., Brayton K., Ledley F. D., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. GT to AT transition at a splice donor site causes skipping of the preceding exon in phenylketonuria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5613–5628. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Gay S. The collagens: an overview and update. Methods Enzymol. 1987;144:3–41. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)44170-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Urlaub G., Chasin L. Spontaneous splicing mutations at the dihydrofolate reductase locus in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1926–1935. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. A role for exon sequences and splice-site proximity in splice-site selection. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Wall R. A mechanism for RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1877–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffner D. E., Dugaiczyk A. Splicing mutation in human hereditary analbuminemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2125–2129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. D., Byers P. H., Martin G. R. Production of procollagen by human fibroblasts in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3260–3262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L. M., Danna K. J. Efficient infection of monkey cells with DNA of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7575–7578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmann B., Tuderman L., Peltonen L., Martin G. R., McKusick V. A., Prockop D. J. Evidence for a structural mutation of procollagen type I in a patient with the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8887–8893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton D., Eckhart W. N-terminal amino acid sequences of the polyoma middle-size T antigen are important for protein kinase activity and cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):817–821. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tromp G., Prockop D. J. Single base mutation in the pro alpha 2(I) collagen gene that causes efficient splicing of RNA from exon 27 to exon 29 and synthesis of a shortened but in-frame pro alpha 2(I) chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5254–5258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsipouras P., Ramirez F. Genetic disorders of collagen. J Med Genet. 1987 Jan;24(1):2–8. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.1.2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil D., Bernard M., Combates N., Wirtz M. K., Hollister D. W., Steinmann B., Ramirez F. Identification of a mutation that causes exon skipping during collagen pre-mRNA splicing in an Ehlers-Danlos syndrome variant. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8561–8564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz M. K., Glanville R. W., Steinmann B., Rao V. H., Hollister D. W. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VIIB. Deletion of 18 amino acids comprising the N-telopeptide region of a pro-alpha 2(I) chain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16376–16385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet W., Bernard M., Benson-Chanda V., Chu M. L., Dickson L., Weil D., Ramirez F. Organization of the human pro-alpha 2(I) collagen gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16032–16036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wett W., Sippola M., Tromp G., Prockop D., Chu M. L., Ramirez F. Use of R-loop mapping for the assessment of human collagen mutations. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3857–3862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]