Summary
Glutamate transport is highly regulated as glutamate directly acts as a neurotransmitter [1-3] and indirectly regulates the synthesis of antioxidants [4-5]. Although glutamate deregulation has been repeatedly linked to serious human diseases such as HIV infection and Alzheimer's [6-8], glutamate's role in the immune system is still poorly understood. We find that a putative glutamate transporter in Drosophila melanogaster, polyphemus (polyph), plays an integral part in the fly's immune response. Flies with a disrupted polyph gene exhibit decreased phagocytosis of microbial-derived bioparticles. When infected with S.aureus, polyph flies show an increase in both susceptibility and bacterial growth. Additionally, the expression of two known glutamate transporters, genderblind and excitatory amino acid transporter 1, in blood cells affects the flies’ ability to phagocytose and survive following an infection. Consistent with previous data showing a regulatory role for glutamate transport in the synthesis of the major antioxidant glutathione, polyph flies produce more reactive oxygen species (ROS) as compared to wildtype when exposed to S.aureus. In conclusion, we demonstrate that a polyph-dependent redox system in blood cells is necessary to maintain the cells’ immune-related functions. Furthermore, our model provides insight into how deregulation of glutamate transport may play a role in disease.
Results and Discussion
The putative amino acid transporter, polyph, is required in blood cells for phagocytosis of microbes
From a genetic screen, we identified a transposon line, Mi[ET1]CG12943MB02238, with a striking defect in phagocytosis. The disrupted gene, CG12943 (Figure 1A) is predicted to contain an amino acid transmembrane transporter domain and be related to Drosophila excitatory amino acid transporter 1(eaat1) with ~20% amino acid similarity. CG12943 was named polyphemus (polyph) after the Cyclops in Greek mythology who failed to guard against Odysseus as polyph flies are similarly unable to defend against an intruding microbe.
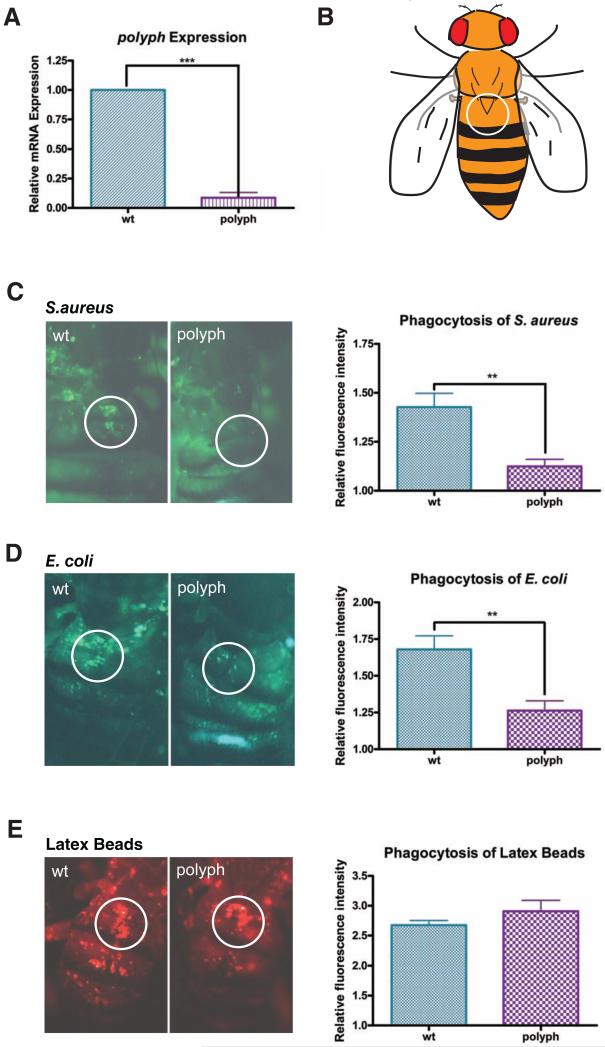
Figure 1. polyph, a putative amino acid transporter, is required for microbial phagocytosis.
(A) Comparison of polyph transcript levels via qPCR in wildtype flies (wt) and flies containing a transposon insertion in the polyph gene (polyph). Relative expression was measured using rp49 as an endogenous control. A pool of ten flies per genotype was used in each experiment. (B) Representation of how the fly is visualized during the in vivo adult phagocytosis assay. The encircled area represents the area of the dorsal vein around which the sessile blood cells congregate. (C, D, E) Representative pictures depicting phagocytosis in wt and polyph flies of (C) fluorescein-labeled S.aureus bioparticles, (D) fluorescein-labeled E.coli bioparticles, and (E) red fluorescently labeled latex beads. Approximately 6 flies per genotype were used in each experiment. Quantification follows. Error bars, ±SE. ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001.
The phagocytic capacity of polyph flies was measured using an in vivo adult phagocytosis assay [9]. Flies are injected with fluorescently labeled bioparticles. The amount of fluorescence in the dorsal vessel area where sessile phagocytes accumulate is visualized and quantified (Figure 1B). polyph flies were deficient in phagocytosis of S.aureus (Figure 1C), E.coli (Figure 1D), and zymosan (data not shown), while phagocytosis of latex beads was normal (Figure 1E). polyph flies do not have fewer blood cells (Figure S3B), which indicates that polyph flies have adequate numbers of blood cells with functional phagocytic machinery. Hence, the defect in polyph is specific to the inability to phagocytose microbial-derived bioparticles.
Drosophila blood cells can circulate in larvae, while in adult flies they become mainly sessile and difficult to separate from the surrounding tissue [10]. Therefore, blood cell expression of polyph was measured by collecting larval hemolymph which includes circulating blood cells. FlyAtlas does not examine gene expression in the blood cells, but did report an enriched expression of polyph in the testes [11], so the sexes were evaluated separately.
In females, the blood cells have an enriched polyph expression compared to the carcass (Figure S1A). Males also express polyph in their blood cells, with similar levels in their carcass presumably due to testes expression. Adult polyph expression was measured in whole animals. Male expression of the gene was higher than in females but neither sex showed significant upregulation with S.aureus infection. Immunostaining of Flag-tagged Polyph protein confirmed that the putative amino acid transporter localized to the plasma membrane consistent with a role in phagocytosis (Figure S1B).
As blood cells are a major source of polyph mRNA, an RNAi construct against polyph was specifically expressed in blood cells (Figure S2A), which recapitulated the decrease in S.aureus phagocytosis observed in the original mutant (Figure S2B). Furthermore, the phagocytosis defect in the original mutant could be rescued by expressing polyph in blood cells (Figure 2A), confirming that the defect is due to a lack of polyph expression in blood cells.
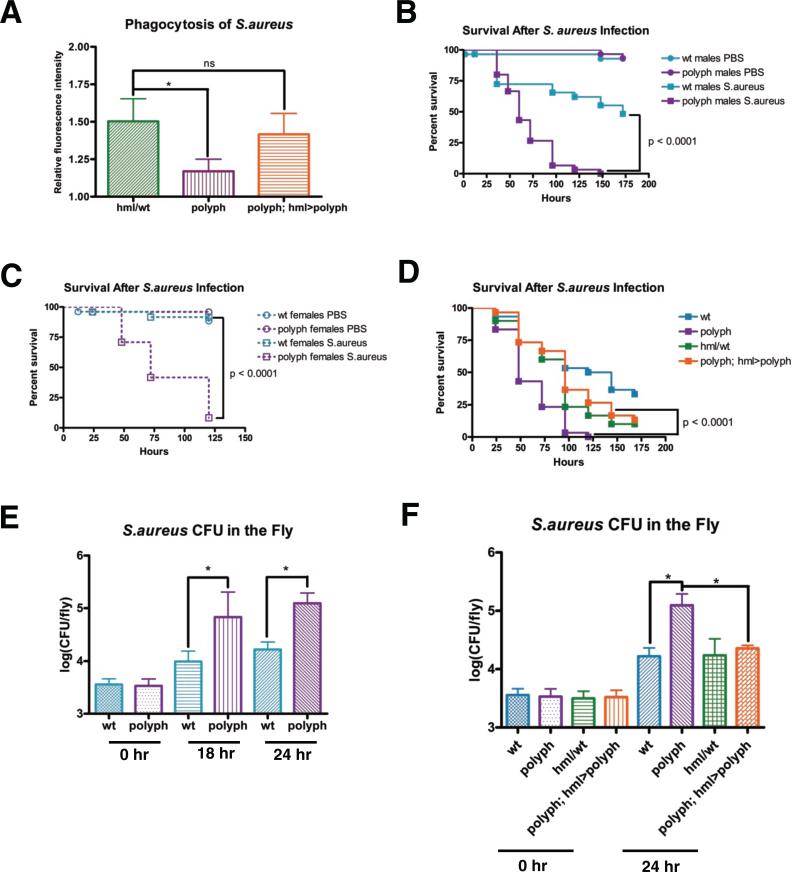
Figure 2. polyph flies have decreased resistance against an S.aureus infection.
(A) Quantification of the phagocytosis of fluorescein-labeled S.aureus bioparticles in hml/wt, polyph, and polyph; hml>polyph flies. Approximately 6 flies per genotypewere used in each experiment. Representative survival curves of male (B) and female (C) wt and polyph flies after injection of S.aureus (OD 0.5). n = 24-30 flies. Experiments were performed in triplicate. (D) Representative survival curve of wt, polyph, hml/wt, and polyph; hml>polyph flies after injection of S.aureus (OD 0.5). The wt flies have polyph's genetic background, while hml/wt flies have the same genetic background as the rescue flies in which polyph expression is driven by hmlΔGAL4. n = 28-30 flies. Experiments were performed in triplicate. (E) Comparison of the S.aureus (OD 0.5) recovered in wt and polyph flies 0, 18, and 24 hours postinfection. Bacterial load was measured in 8 individual flies per genotype at each time point in each experiment. Experiment was performed in quadruplicate. (F) Comparison of the S.aureus (OD 0.5) recovered in wt, polyph, hml/wt, and polyph; hml>polyph flies 0 and 24 hours postinfection. Three replicate experiments were performed. Error bars, ±SE. *p<0.05, ns = not significantly different
polyph flies have decreased resistance to an S.aureus infection
polyph flies showed increased susceptibility to S.aureus infection (Figure 2B-C), which could be rescued by expressing polyph in blood cells (Figure 2D). This susceptibility was substantiated by expressing RNAi against the gene specifically in blood cells (Figure S2C). The gene is likely playing a role in resistance rather than tolerance, as there is an increased bacterial load in polyph flies as compared to wildtype (Figure 2E). Blood cell-specific expression of the gene rescues the bacterial growth indicating that polyph is required in the blood cells to control the growth of bacteria during an infection (Figure 2F).
As Polyph is predicted to be an amino acid transporter, the loss of this protein may be affecting fly growth either directly or through a nutrient sensing mechanism. However, there was no difference in weight compared to wildtype (Figure S3C). Additionally, polyph flies are not generally weak as they are not more susceptible to wounding (Figure 2B-C), being kept at 30°C (Figure S3A), or an E.coli infection (data not shown).
polyph does not play a role in the induction of drosomycin or diptericin
When activated by microbes, the Toll and Imd pathways upregulate the production of AMPs, which act to directly kill microbes or limit their growth. S.aureus infection strongly induces drosomycin, while E.coli causes a comparatively weak induction. The opposite is true with diptericin. When infected with either S.aureus or E.coli, polyph flies showed normal induction of both drosomycin and diptericin, which are primarily upregulated by the Toll and Imd pathways respectively [12, 13] (Figure S2D-E). Hence, polyph does not play a major role in either of these pathways, consistent with data showing no effect on another AMP, defensin, when phagocytosis of S.aureus is decreased [14]. It appears that polyph's primary role is modulating the cellular immune response.
polyph flies exhibit increased ROS and decreased bead phagocytosis when exposed to S.aureus
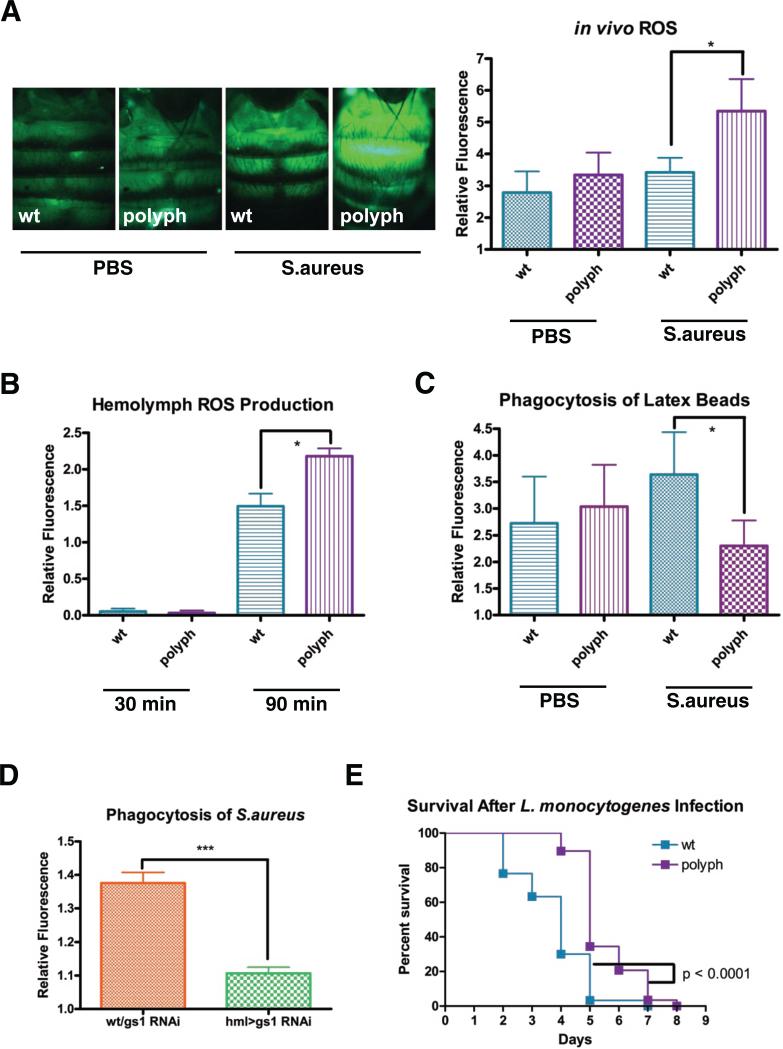
According to HomoloGene, polyph is closely related to eaat1, a glutamate transporter in the central nervous system [15-16]. Eaats transport extracellular glutamate into the cell using a sodium/potassium exchange system [17]. The other major branch of glutamate transporters, the X−c transporters, exchange a cystine for a glutamate in a sodium-independent process. The direction of exchange is concentration-dependent [18]. Normally, there is more glutamate inside the cell than outside, with the inverse being true for cystine, thus causing the antiporter to exchange an intracellular glutamate for an extracellular cystine. Once inside the cell, cystine is reduced to cysteine, the limiting reagent in glutathione (GSH) synthesis [4,18]. GSH acts as a major antioxidant in the cell by reducing ROS [19]. Therefore, we measured ROS levels in polyph flies using the substrate CM-H2CDFDA, which becomes fluorescent when oxidized. When flies were first injected with PBS, followed by the substrate, polyph showed no significant difference in ROS levels as compared to wildtype. However, when flies were first exposed to S.aureus and then injected with the substrate, polyph flies made significantly more ROS than wildtype (Figure 3A). To determine if exposure to S.aureus causes an increase of ROS specifically in polyph blood cells, larval hemolymph was bled into PBS and incubated with CM-H2CDFDA and S.aureus ex vivo. These experiments were done with larval-derived hemolymph because of the difficulty collecting adult hemocytes poses. At 30 minutes there was no difference between ROS levels in wildtype and polyph indicating that polyph flies do not have a higher basal level of ROS. However, after 90 minutes, the ROS levels in polyph were significantly higher than that in wildtype (Figure 3B).
Figure 3. polyph has increased ROS in its hemolymph and decreased phagocytosis when exposed to bacteria.
(A) Representative pictures of oxidized CM-H2CDFDA-derived fluorescence in wt and polyph flies after a 30 minute preinjection of either PBS or overnight culture of S.aureus. Approximately 6 flies were used per genotype in each experiment. Quantification follows. (B) Measurement of oxidized CM-H2CDFDA-derived fluorescence in wt and polyph blood cells incubated ex vivo with an overnight S.aureus culture. (C) Quantification of the phagocytosis of red fluorescently labeled latex beads in wt and polyph flies after a 30 minute preinjection of either PBS or overnight culture of S.aureus. Approximately 6 flies per genotype were used in each experiment. (D) Quantification of the phagocytosis of fluorescein-labeled S.aureus bioparticles in wt/gs1 RNAi and hml>gs1 RNAi. Approximately 6 flies per genotypewere used in each experiment. (E) Representative survival curve of wt and polyph flies after injection of L.monocytogenes (OD 0.1). n = 28-30 flies All experiments were done in triplicate. Error bars, ±SE. *p<0.05.
The increase in ROS corresponds with a decrease in polyph flies’ phagocytic capacity upon exposure to S.aureus. When flies are injected with PBS and then latex beads, polyph flies show a phagocytic capacity equal to wildtype. However, when flies were pre-injected with S.aureus, polyph flies take up significantly less latex beads than wildtype (Figure 3C). To examine whether polyph flies have a more limited phagocytic capacity that is overwhelmed by the double injection of bacteria and beads, flies were injected with yellow/green fluorescent beads and then red fluorescent beads. polyph flies were able to uptake the red beads in a manner indistinguishable from wildtype (Figure S3E). Hence, polyph flies do not have a more limited phagocytic capacity but instead become unable to phagocytose upon exposure to S.aureus.
To confirm that glutamate metabolism and ROS affect phagocytosis, we examined the role of Glutamine synthetase-1 (GS1). GS1 converts glutamate and ammonia into glutamine and regulates ROS production by decreasing glutamate levels [20-21]. Drosophila GS1 also regulates ROS, as flies expressing gs1 RNAi in blood cells have more ROS after infection with S.aureus (Figure S3F). gs1 flies have impaired phagocytosis of S.aureus like polyph (Figure 3D), confirming that glutamate misregulation and increased ROS are associated with decreased phagocytosis.
polyph flies are less susceptible to the intracellular pathogen, Listeria monocytogenes
L.monocytogenes is a facultative intracellular pathogen capable of invading phagocytic cells and subsequently escaping from the phagosome [22]. The bacteria then successfully replicate within the phagocyte and spread to other cells throughout the organism. Interestingly, polyph flies are less susceptible to an L.monocytogenes infection as compared to wildtype flies (Figure 3E). It is possible that the decreased phagocytosis and increased ROS result in reduced bacterial loads, allowing polyph flies to fight off infection more effectively than wildtype flies.
Phagocytosis is affected when amino acid transport is either blocked or modulated in blood cells
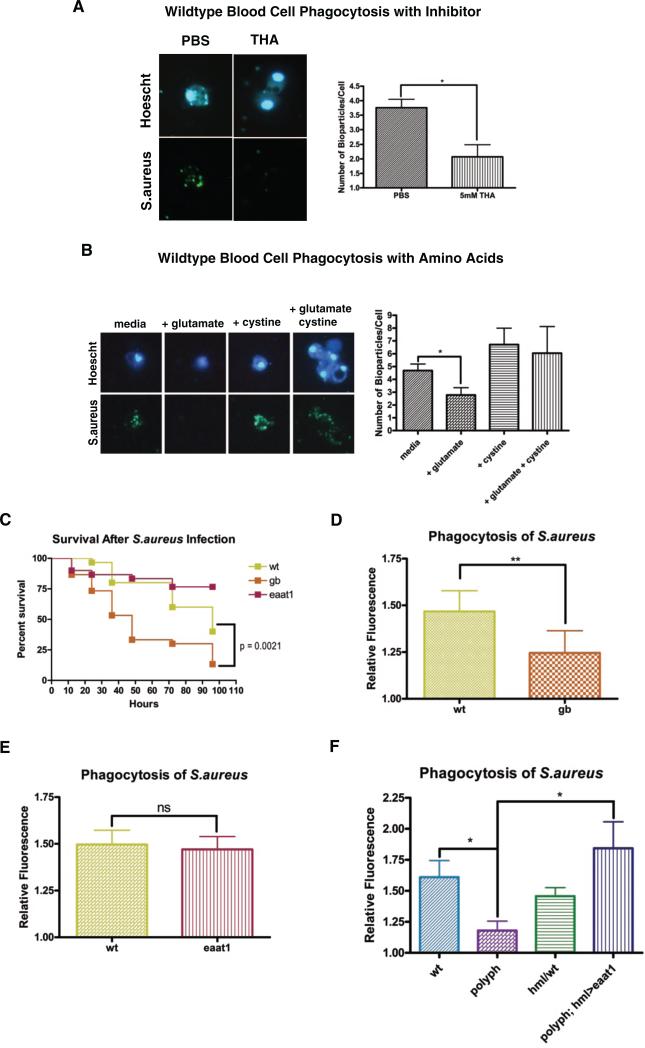
As normal glutamate transport is essential for healthy nerve function, multiple drugs have been developed to modulate glutamate transport. Threo-beta-hydroxyaspartate (THA), an aspartate analog, acts as a general inhibitor of eaat transporters [4]. Hemolymph was collected from wildtype larvae, and following addition of either PBS or THA, the blood cells were assayed for uptake of S.aureus. Blood cells incubated with THA showed significantly less phagocytosis than the blood cells in PBS (Figure 4A), indicating that blocking glutamate transport in wildtype blood cells inhibits phagocytosis. This was supported by measuring the phagocytic capacity of cells in minimal media with glutamate, or cystine, or both added. Cells showed significantly less phagocytosis when incubated with only glutamate and consistently more (albeit not significant p = 0.061) when given cystine (Figure 4B). The base minimal media contained an extremely small amount of cystine (0.099mM) and no glutamate. When excess glutamate was added extracellularly, this mimicked the presumed situation of polyph cells. By artificially forcing a high [glutamate]extracellular and a low [glutamate]intracellular, this drives the glutamate/cystine antiporter to pump glutamate into the cell and cystine out, thereby depleting the cells’ store of cystine and preventing them from making GSH. Without their ability to counteract bacteria-induced ROS, it is possible that the cells become unable to phagocytose efficiently. In contrast, when cells are given high levels of cystine, this drives the antiporter in the canonical direction, allowing the cell to continually make more GSH. These data indicate that glutamate transport into blood cells is a tightly regulated process, which is necessary for blood cells to remain effective against an infection.
Figure 4. Survival and phagocytosis are affected when blood cell amino acid transport is modulated.
Wildtype blood cells in hemolymph were incubated ex vivo with fluorescein S.aureus bioparticles in PBS or 5mM THA (A), or media plus nothing, glutamate, cystine, or glutamate and cystine (B). After 30 minutes the number of bioparticles/cell was counted in approximately 20 cells per group in each experiment. (C) Representative survival curves of wt, gb and eaat1 flies after injection of S.aureus (OD 0.05). n = 30 flies. Quantification of the phagocytosis of fluorescein-labeled S.aureus bioparticles in wt and gb flies (D), wt and eaat1 flies (E), and wt,polyph, hml/wt and polyph; hml>eaat1 flies (F). Approximately 6 flies per genotype were used in each experiment. All experiments were performed at least in triplicate. Error bars, ±SE. *p<0.05, ** p<0.01, ns = not significantly different.
Other amino acid transporters, when expressed in blood cells, play a similar role in the immune response as polyph
Glutamate, an important neurotransmitter, plays a complicated role in glutamate toxicity, a phenomenon where neurons become sick from increased intracellular ROS due to excess extracellular glutamate [23-24]. The glutamate/cystine antiporter is concentration-dependent, so if eaat1 is functioning properly, there is more intracellular glutamate than extracellular, driving glutamate out and cystine in [18]. However, if eaat1 or the glutamate/cystine antiporter, genderblind (gb) is mutated, then cystine is no longer transported in, GSH is limited, and ROS rises. The role of gb in glutamate transport and GSH synthesis is well established [25]. gb larvae had significantly less glutamate in their hemolymph compared to wildtype [26]. However, the role of gb in an immunological response was unknown. We examined if eaat1 or gb were expressed on blood cells and if mutants showed phenotypes similar to polyph.
gb (Figure S1C) but not eaat1 (Figure S1D) was expressed in blood cells. Consistent with this,gb mutants showed both increased susceptibility to S.aureus infection and decreased phagocytosis of S.aureus, whereas eaat1 mutants did not (Figure 4C,D,E). Conversely, to determine whether polyph plays a role in the CNS, we performed a climbing assay. When knocked down, flies will instinctively climb upward. eaat1 mutants have a motor defect due to inefficient glutamate transport in their CNS, and climb more slowly than wildtype [15]. This motor defect was observed in eaat1 flies but not in polyph (Figure S3D), indicating that polyph does not play a major role in the nervous system.
If Polyph is functioning in a similar manner to Eaat1 but in a different tissue, then blood cell-specific expression of eaat1 in a polyph mutant background should rescue the phenotypes seen in polyph flies. There is indeed strong rescue of the phagocytosis phenotype in polyph; hml>eaat1 flies (Figure 4F). These data indicate that Polyph is an important glutamate transporter expressed on blood cells. It works with the cystine/glutamate antiporter Gb to control internal ROS in order to maintain macrophage function. Our model (Movie S1) indicates that polyph flies have increased extracellular glutamate in their hemolymph due to an inability to effectively transport it into the cell. This leads to a decrease in GSH and an increase in internal ROS. Without tight regulation of glutamate transport across the blood cell membrane, the fly loses its resistance to a pathogenic infection due to a decrease in phagocytic capacity.
With an unbalanced GSH redox system, there is potential for human disease. People with a glutathione reductase deficiency have impaired neutrophil function. When the antioxidant GSH reduces ROS, it is converted into its oxidized state, GSSG. Glutathione reductase facilitates conversion of GSSG back to its reduced state GSH. Without the enzyme, the redox system skews towards the oxidized state and is less able to reduce free reactive species. Neutrophils from individuals with the genetic disorder could maintain normal levels of ROS for a short period of time, but not after an extended incubation with bacteria [27]. These findings support our model, and show that understanding the delicate balance of this system has relevance to human disease. Additionally, increased glutamate levels in the plasma have been associated with other diseases including ALS [28], epilepsy [29], stroke-associated headache [30], HIV-associated dementia (HAD) [31], Parkinson's disease [32], breast cancer, colorectal carcinoma, and AIDS [33]. Our results demonstrate that a tightly regulated redox system in the blood cells is necessary to maintain immune cell function and therefore the health of the whole organism.
Experimental Methods
Please see the Supplemental Information.
Supplementary Material
Movie S1: Model
In wildtype cells, Polyph transports glutamate from the extracellular space to the intracellular space using the sodium/potassium gradient as power. Genderblind then uses the glutamate gradient across the cell to exchange an intracellular glutamate for a molecule of cystine. Once cystine enters the cell, it becomes reduced to cysteine, which is the limiting reagent for the production of the tripeptide glutathione. Glutathione is then able to reduce intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS).
In polyph mutant cells, Polyph is no longer able to transport glutamate into the cell which prevents the glutamate gradient from driving the transport of cystine into the cell through Genderblind. Without cysteine, the cell is unable to manufacture glutathione and ROS builds within the cell.
Highlights.
A putative glutamate transporter, polyph, is expressed in Drosophila blood cells
polyph flies have decreased phagocytosis of microbial-derived particles
polyph flies have decreased resistance to a S.aureus infection
polyph plays an important role regulating amino acid transport and ROS production
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Becky Brisson for identifying the mutant that led to the beginning of this project, Mimi Shirasu-Hiza for L.monocytogenes, Stephen Mount for advice, and Javier Robalino for reviewing the manuscript. Also, we thank the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center and the Vienna Drosophila RNAi Center for providing flies.
Abbreviations
- AMP
antimicrobial peptide
- CNS
central nervous system
- EAAT
excitatory amino acid transporter
- GSH
glutathione
- GSSG
glutathione disulfide
- HAD
HIV-associated dementia
- PAMP
pathogen-associated molecular pattern
- ROS
reactive oxygen species
- THA
threo-beta-hydroxyaspartate
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Fonnum F. Glutamate: a neurotransmitter in mammalian brain. J. Neurochem. 1984;42:1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Niciu MJ, Kelmendi B, Sanacora G. Overview of glutamatergic neurotransmission in the nervous system. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012;100:656–664. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2011.08.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Omote H, Miyaji T, Juge N, Moriyama Y. Vesicular neurotransmitter transporter: bioenergetics and regulation of glutamate transport. Biochemistry. 2011;50:5558–5565. doi: 10.1021/bi200567k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rimaniol AC, Mialocq P, Clayette P, Dormont D, Gras G. Role of glutamate transporters in the regulation of glutathione levels in human macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2001;281:C1964–1970. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.2001.281.6.C1964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Watanabe H, Bannai S. Induction of cystine transport activity in mouse peritoneal macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 1987;165:628–640. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Graves MC, Fiala M, Dinglasan LA, Liu NQ, Sayre J, Chiappelli F, van Kooten C, Vinters HV. Inflammation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spinal cord and brain is mediated by activated macrophages, mast cells and T cells. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Other Motor Neuron Disord. 2004;5:213–219. doi: 10.1080/14660820410020286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Piani D, Frei K, Pfister HW, Fontana A. Glutamate uptake by astrocytes is inhibited by reactive oxygen intermediates but not by other macrophage-derived molecules including cytokines, leukotrienes or platelet-activating factor. J. Neuroimmunol. 1993;48:99–104. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tian C, Erdmann N, Zhao J, Cao Z, Peng H, Zheng J. HIV-infected macrophages mediate neuronal apoptosis through mitochondrial glutaminase. J. Neurochem. 2008;105:994–1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05197.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Elrod-Erickson M, Mishra S, Schneider D. Interactions between the cellular and humoral immune responses in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2000;10:781–784. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00569-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lanot R, Zachary D, Holder F, Meister M. Postembryonic hematopoiesis in Drosophila. Dev. Biol. 2001;230:243–257. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2000.0123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chintapalli VR, Wang J, Dow JA. Using FlyAtlas to identify better Drosophila melanogaster models of human disease. Nat. Genet. 2007;39:715–720. doi: 10.1038/ng2049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lemaitre B, Nicolas E, Michaut L, Reichhart JM, Hoffmann JA. The dorsoventral regulatory gene cassette spatzle/Toll/cactus controls the potent antifungal response in Drosophila adults. Cell. 1996;86:973–983. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80172-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lemaitre B, Kromer-Metzger E, Michaut L, Nicolas E, Meister M, Georgel P, Reichhart JM, Hoffmann JA. A recessive mutation, immune deficiency (imd), defines two distinct control pathways in the Drosophila host defense. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 1995;92:9465–9469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.21.9465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nehme NT, Quintin J, Cho JH, Lee J, Lafarge MC, Kocks C, Ferrandon D. Relative roles of the cellular and humoral responses in the Drosophila host defense against three gram-positive bacterial infections. PLoS One. 2011;6:e14743. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Stacey SM, Muraro NI, Peco E, Labbé A, Thomas GB, Baines RA, van Meyel DJ. Drosophila glial glutamate transporter Eaat1 is regulated by fringe-mediated notch signaling and is essential for larval locomotion. J. Neurosci. 2010;30:14446–14457. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1021-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Takayasu Y, Iino M, Takatsuru Y, Tanaka K, Ozawa S. Functions of glutamate transporters in cerebellar Purkinje cell synapses. Acta. Physiol. 2009;197:1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2009.02019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Barbour B, Brew H, Attwell D. Electrogenic glutamate uptake in glial cells is activated by intracellular potassium. Nature. 1988;335:433–435. doi: 10.1038/335433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bannai S. Exchange of cystine and glutamate across plasma membrane of human fibroblasts. J. Biol.Chem. 1986;261:2256–2263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Deneke SM, Fanburg BL. Regulation of cellular glutathione. Am. J. Physiol. 1989;257:L163–173. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.4.L163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Castegna A, Palmieri L, Spera I, Porcelli V, Fabis-Pedrini MJ, Kean RB, Barkhouse DA, Curtis MT, Hooper DC. Oxidative stress and reducted glutamine synthetase activity in the absence of inflammation in the cortex of mice with experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Neuroscience. 2011;185:97–105. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.04.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gras G, Porcheray F, Samah B, Leone C. The glutamate-glutamine cycle as an inducible, protective face of macrophage activation. J.Leuk.Biol. 2006;80:1067–1075. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0306153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cossart P, Vicente MF, Mengaud J, Baquero F, Perez-Diaz JC, Berche P. Listeriolysin O is essential for virulence of Listeria monocytogenes: direct evidence obtained by gene complementation. Infect. Immun. 1989;57:3629–3636. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3629-3636.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Miyamoto M, Murphy TH, Schnaar RL, Coyle JT. Antioxidants protect against glutamate-induced cytotoxicity in a neuronal cell line. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1989;250:1132–1140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Murphy TH, Miyamoto M, Sastre A, Schnaar RL, Coyle JT. Glutamate toxicity in a neuronal cell line involves inhibition of cystine transport leading to oxidative stress. Neuron. 1989;2:1547–1558. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Augustin H, Grosjean Y, Chen K, Sheng Q, Featherstone DE. Nonvesicular release of glutamate by glial xCT transporters suppresses glutamate receptor clustering in vivo. J. Neurosci. 2007;27:111–123. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4770-06.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Piyankarage SC, Augustin H, Grosjean Y, Featherstone DE, Shippy SA. Hemolymph amino acid analysis of individual Drosophila larvae. Anal. Chem. 2008;80:1201–1207. doi: 10.1021/ac701785z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Roos D, Weening RS, Voetman AA, van Schaik ML, Bot AA, Meerhof LJ, Loos JA. Protection of phagocytic leukocytes by endogenous glutathione: studies in a family with glutathione reductase deficiency. Blood. 1979;53:851–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Iwasaki Y, Ikeda K, Kinoshita M. Plasma amino acid levels in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 1992;107:219–222. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(92)90292-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Janjua NA, Kabuto H, Mori A. Increased plasma glutamic acid in a genetic model of epilepsy. Neurochem. Res. 1992;17:293–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00966673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Castillo J, Martínez F, Corredera E, Aldrey JM, Noya M. Amino acid transmitters in patients with headache during the acute phase of cerebrovascular ischemic disease. Stroke. 1995;26:2035–2039. doi: 10.1161/01.str.26.11.2035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ferrarese C, Aliprandi A, Tremolizzo L, Stanzani L, De Micheli A, Dolara A, Frattola L. Increased glutamate in CSF and plasma of patients with HIV dementia. Neurology. 2001;57:671–675. doi: 10.1212/wnl.57.4.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Iwasaki Y, Ikeda K, Shiojima T, Kinoshita M. Increased plasma concentrations of aspartate, glutamate and glycine in Parkinson's disease. Neurosci. Lett. 1992;145:175–177. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90015-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ollenschläger G, Karner J, Karner-Hanusch J, Jansen S, Schindler J, Roth E. Plasma glutamate--a prognostic marker of cancer and of other immunodeficiency syndromes? Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 1989;49:773–777. doi: 10.3109/00365518909091556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Movie S1: Model
In wildtype cells, Polyph transports glutamate from the extracellular space to the intracellular space using the sodium/potassium gradient as power. Genderblind then uses the glutamate gradient across the cell to exchange an intracellular glutamate for a molecule of cystine. Once cystine enters the cell, it becomes reduced to cysteine, which is the limiting reagent for the production of the tripeptide glutathione. Glutathione is then able to reduce intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS).
In polyph mutant cells, Polyph is no longer able to transport glutamate into the cell which prevents the glutamate gradient from driving the transport of cystine into the cell through Genderblind. Without cysteine, the cell is unable to manufacture glutathione and ROS builds within the cell.