Abstract
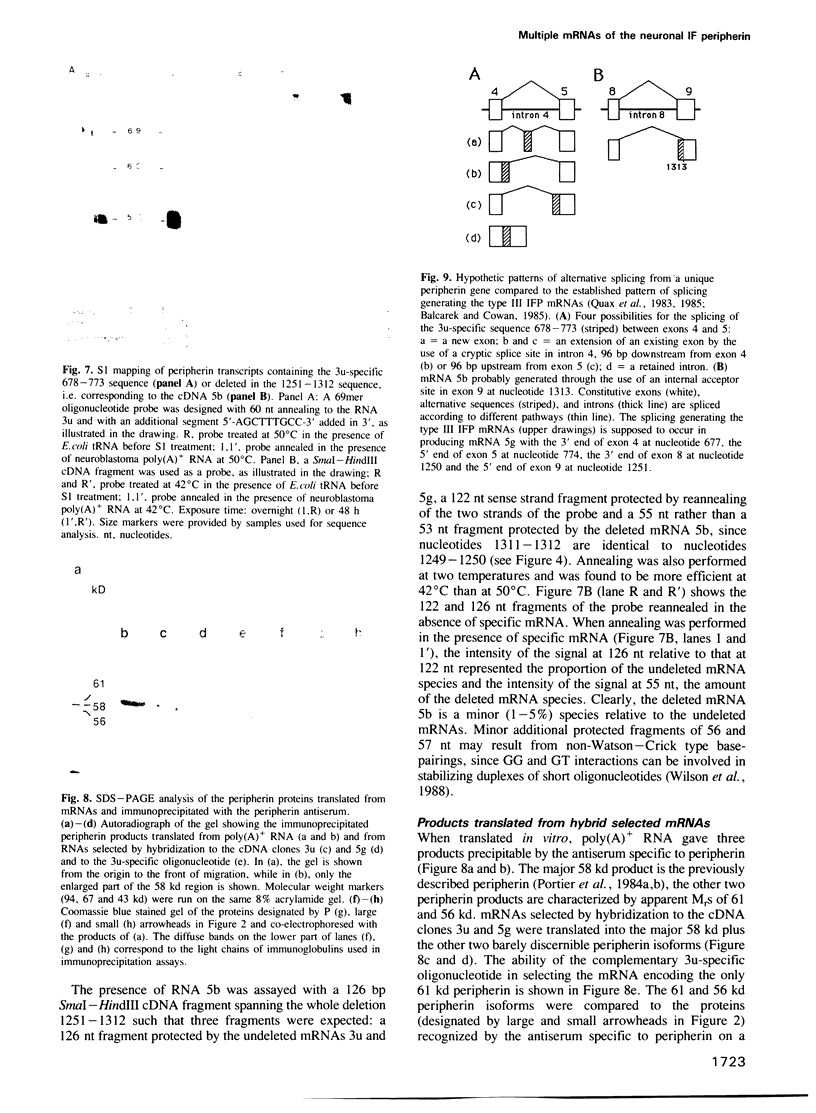
Three cDNA clones of 1.6 (3u), 1.2 (5g) and 0.6 (5b) kbp, specific for peripherin, a neuronal intermediate filament protein (IFP), have been isolated from a murine neuroblastoma cell lambda gt11 library by immunoscreening using peripherin antiserum. Antibodies eluted from the fusion proteins produced by clones 3u and 5g recognize the peripherin spots on immunoblots. Where they overlap the three cDNAs have identical sequences. cDNA 5g exhibits the closest homology to type III IFP cDNAs. cDNA 3u is identical to the corresponding region of cDNA 5g, except for the insertion of a 96 bp fragment at a position corresponding to the junction of exons 4 and 5 in type III IFP cDNAs. cDNA 5b is also identical to the corresponding region of cDNA 5g, except for the deletion of a 62 bp fragment at the junction of exons 8 and 9 in type III IFP cDNAs. S1 mapping experiments performed with probes covering the 3' end of the two unexpected regions show that three distinct mRNAs correspond to the three cDNAs. Moreover, three peripherin products, two minor 61 and 56 kd products in addition to the major 58 kd peripherin, are observed when poly(A)+ RNA is in vitro translated, the 61 kd peripherin being translated from the 3u-selected RNA. The three RNAs originate from alternative splicing of a unique peripherin gene, thus generating polymorphism of peripherin.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aletta J. M., Angeletti R., Liem R. K., Purcell C., Shelanski M. L., Greene L. A. Relationship between the nerve growth factor-regulated clone 73 gene product and the 58-kilodalton neuronal intermediate filament protein (peripherin). J Neurochem. 1988 Oct;51(4):1317–1320. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Andreadis A., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:467–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croizat B., Berthelot F., Ferrandes B., Eymard P., Sahuquillo C. Différenciation morphologique du neuroblastome par l'acide 1 méthyl cyclohexane carboxylique (CCA) et certains dérivés en C1. C R Seances Acad Sci D. 1979 Dec 17;289(16):1283–1286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escurat M., Gumpel M., Lachapelle F., Gros F., Portier M. M. Expression comparée de deux protéines de filaments intermédiaires, la périphérine et la protéine de neurofilament 68 kDa, au cours du développement embryonnaire du rat. C R Acad Sci III. 1988;306(14):447–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. Z., Chaudhary N., Blobel G. cDNA sequencing of nuclear lamins A and C reveals primary and secondary structural homology to intermediate filament proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6450–6454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Grund C., Achtstätter T. Co-expression of cytokeratins and neurofilament proteins in a permanent cell line: cultured rat PC12 cells combine neuronal and epithelial features. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1933–1943. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of chicken muscle desmin provides a common structural model for intermediate filament proteins. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1649–1656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagus R. Characterization of in vitro translation products. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:296–304. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J. P., Ramachandran K., Grosveld F. Cloning of a cDNA encoding the smallest neurofilament protein from the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 21;825(4):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard D. G., Gorham J. D., Cole P., Greene L. A., Ziff E. B. A nerve growth factor-regulated messenger RNA encodes a new intermediate filament protein. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):181–193. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard D. G., Ziff E. B., Greene L. A. Identification and characterization of mRNAs regulated by nerve growth factor in PC12 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3156–3167. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Cowan N. J. Genetics, evolution, and expression of the 68,000-mol-wt neurofilament protein: isolation of a cloned cDNA probe. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):843–850. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D., McCrohon S., Fuchs E. Remarkable conservation of structure among intermediate filament genes. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):491–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90456-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon F. D., Kirschner M. W., Caput D. Homologies in both primary and secondary structure between nuclear envelope and intermediate filament proteins. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):463–468. doi: 10.1038/319463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parysek L. M., Chisholm R. L., Ley C. A., Goldman R. D. A type III intermediate filament gene is expressed in mature neurons. Neuron. 1988 Jul;1(5):395–401. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90189-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parysek L. M., Goldman R. D. Characterization of intermediate filaments in PC12 cells. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):781–791. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00781.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perreau J., Lilienbaum A., Vasseur M., Paulin D. Nucleotide sequence of the human vimentin gene and regulation of its transcription in tissues and cultured cells. Gene. 1988;62(1):7–16. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90575-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portier M. M., Brachet P., Croizat B., Gros F. Regulation of peripherin in mouse neuroblastoma and rat PC 12 pheochromocytoma cell lines. Dev Neurosci. 1983;6(4-5):215–226. doi: 10.1159/000112348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portier M. M., de Néchaud B., Gros F. Peripherin, a new member of the intermediate filament protein family. Dev Neurosci. 1983;6(6):335–344. doi: 10.1159/000112360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M., Mirsky R., Raff M. C., Thorpe R., Dowding A. J., Anderton B. H. All classes of intermediate filaments share a common antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., Egberts W. V., Hendriks W., Quax-Jeuken Y., Bloemendal H. The structure of the vimentin gene. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., van den Broek L., Egberts W. V., Ramaekers F., Bloemendal H. Characterization of the hamster desmin gene: expression and formation of desmin filaments in nonmuscle cells after gene transfer. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):327–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Rice R. H., Roop D. R., Trus B. L., Steven A. C. Complete amino acid sequence of a mouse epidermal keratin subunit and implications for the structure of intermediate filaments. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):794–800. doi: 10.1038/302794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Roop D. R. Molecular and cellular biology of intermediate filaments. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:593–625. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. A., Ziff E. B. Structure of the gene encoding peripherin, an NGF-regulated neuronal-specific type III intermediate filament protein. Neuron. 1989 Jan;2(1):1043–1053. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90228-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan R. S., Fitzpatrick D. F. Alkaline phosphatase conjugated protein A as a sensitive reagent to immunoscreen an expression cDNA plasmid library: isolation of cDNA to the calcium-binding protein of the chick embryonic chorioallantoic membrane. Anal Biochem. 1986 Dec;159(2):329–335. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Hollenberg S. M., Ong E. S., Harmon J. M., Brower S. T., Cidlowski J., Thompson E. B., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Identification of human glucocorticoid receptor complementary DNA clones by epitope selection. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):740–742. doi: 10.1126/science.2581314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. D., Dotrong M. H., Zuo E. T., Zon G. Unusual duplex formation in purine rich oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):5137–5151. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.5137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehner Z. E., Li Y., Roe B. A., Paterson B. M., Sax C. M. The chicken vimentin gene. Nucleotide sequence, regulatory elements, and comparison to the hamster gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8112–8120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff E. B. Transcription and RNA processing by the DNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):491–499. doi: 10.1038/287491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]