Abstract
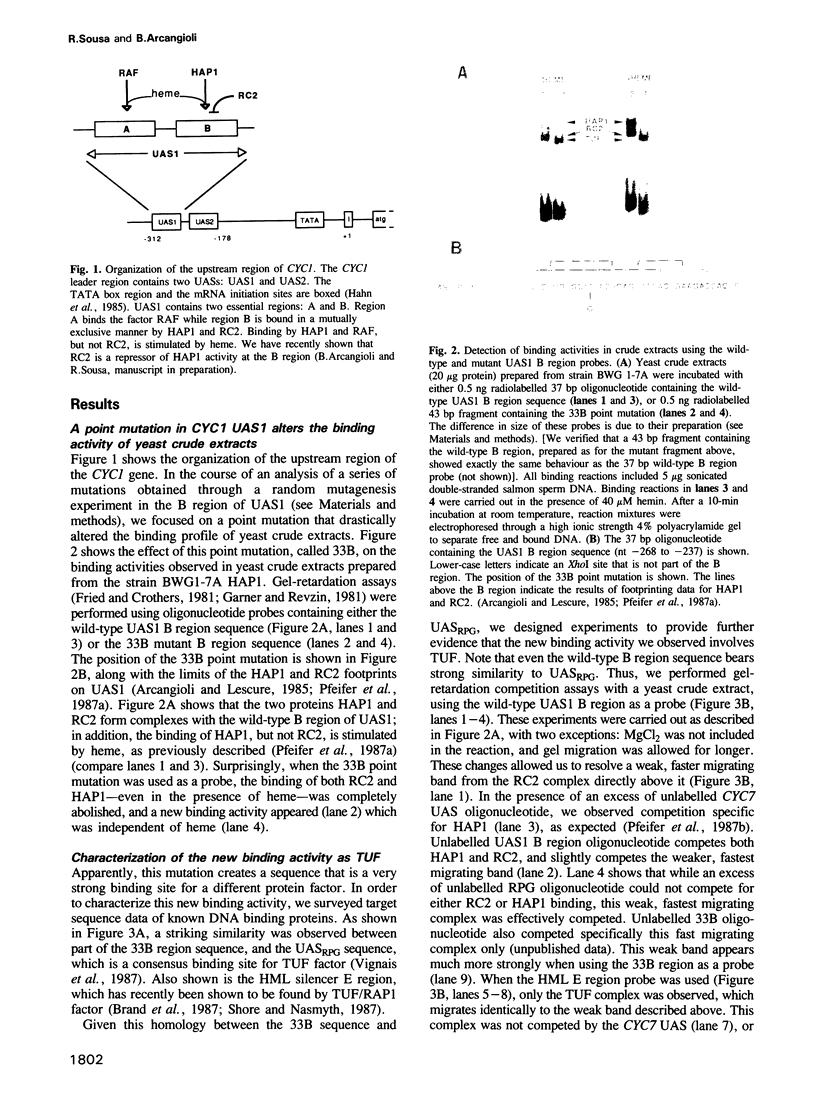
Dissection of the upstream activation site 1 (UAS1) of the yeast CYC1 gene showed that the A and B regions respond individually to regulation by the HAP1 protein, and that a point mutation in the B region converts this region to a translation upstream factor (TUF)-regulated element. Combinatorial analyses revealed that the transacting factors involved with these wild-type and mutant UAS1 target sites combine to activate transcription in a synergistic manner. Furthermore, combinations of heterologous factors, made possible by the point mutation, create a new specificity of regulation that differs from regulation by any one factor individually.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcangioli B., Lescure B. Identification of proteins involved in the regulation of yeast iso- 1-cytochrome C expression by oxygen. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2627–2633. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arcangioli B., Pochet S., Sousa R., Huynh-Dinh T. Preparation and use of a universal primed Sepharose for the purification of DNA-binding proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Feb 1;179(2):359–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt K. T., Styles C., Fink G. R. Multiple global regulators control HIS4 transcription in yeast. Science. 1987 Aug 21;237(4817):874–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3303332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Micklem G., Nasmyth K. A yeast silencer contains sequences that can promote autonomous plasmid replication and transcriptional activation. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kimmerly W. J., Rine J., Kornberg R. D. Two DNA-binding factors recognize specific sequences at silencers, upstream activating sequences, autonomously replicating sequences, and telomeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):210–225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavilier L., Péré-Aubert G., Somlo M., Slonimski P. P. Réseau d'interactions entre des génes non liés : régulation synergique ou antagoniste de la synthèse de l'iso-1-cytochrome c, de l'iso-2-cytochrome c et du cytochrome b2. Biochimie. 1976;58(1-2):155–172. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(76)80366-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Ptashne M. Cooperative DNA binding of the yeast transcriptional activator GAL4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):382–386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Lalonde B., Gifford P., Alani E. Distinctly regulated tandem upstream activation sites mediate catabolite repression of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Mason T. Heme regulates transcription of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae via an upstream activation site. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Regulatory proteins in yeast. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:425–452. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters and lacZ fusions designed to study expression of cloned genes in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:181–191. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters: positive and negative elements. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):799–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Hoar E. T., Guarente L. Each of three "TATA elements" specifies a subset of the transcription initiation sites at the CYC-1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Cottrelle P., Cool M., Vignais M. L., Thiele D., Marck C., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. A general upstream binding factor for genes of the yeast translational apparatus. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3539–3547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakidani H., Ptashne M. GAL4 activates gene expression in mammalian cells. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90504-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Satake M., Furukawa K., Reichel R., Ito Y., Nevins J. R. A factor discriminating between the wild-type and a mutant polyomavirus enhancer. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):87–89. doi: 10.1038/328087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalonde B., Arcangioli B., Guarente L. A single Saccharomyces cerevisiae upstream activation site (UAS1) has two distinct regions essential for its activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4690–4696. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Carey M. F., Ptashne M., Green M. R. GAL4 derivatives function alone and synergistically with mammalian activators in vitro. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):659–664. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliphant A. R., Nussbaum A. L., Struhl K. Cloning of random-sequence oligodeoxynucleotides. Gene. 1986;44(2-3):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Gloss L., Herr W. The SV40 enhancer contains two distinct levels of organization. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):40–45. doi: 10.1038/333040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
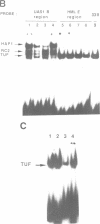
- Pfeifer K., Arcangioli B., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator competes with the factor RC2 for binding to the upstream activation site UAS1 of the CYC1 gene. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90750-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Prezant T., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator binds to two upstream activation sites of different sequence. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90751-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pochet S., Arcangioli B., Huynh-Dinh T. Solid-supported ligation primer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1619–1619. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prezant T., Pfeifer K., Guarente L. Organization of the regulatory region of the yeast CYC7 gene: multiple factors are involved in regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3252–3259. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Nasmyth K. Purification and cloning of a DNA binding protein from yeast that binds to both silencer and activator elements. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano P. G., Tatchell K. Transcription and regulatory signals at the mating type locus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):969–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90431-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdière J., Creusot F., Guarente L., Slonimski P. P. The overproducing CYP1 and the underproducing hap1 mutations are alleles of the same gene which regulates in trans the expression of the structural genes encoding iso-cytochromes c. Curr Genet. 1986;10(5):339–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00418404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignais M. L., Woudt L. P., Wassenaar G. M., Mager W. H., Sentenac A., Planta R. J. Specific binding of TUF factor to upstream activation sites of yeast ribosomal protein genes. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1451–1457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B. Transcription elements and factors of RNA polymerase B promoters of higher eukaryotes. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1988;23(2):77–120. doi: 10.3109/10409238809088317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster N., Jin J. R., Green S., Hollis M., Chambon P. The yeast UASG is a transcriptional enhancer in human HeLa cells in the presence of the GAL4 trans-activator. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90505-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Adam G., Mattes E., Schanz M., Hartig A., Ruis H. Co-ordinate control of synthesis of mitochondrial and non-mitochondrial hemoproteins: a binding site for the HAP1 (CYP1) protein in the UAS region of the yeast catalase T gene (CTT1). EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1799–1804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woudt L. P., Mager W. H., Nieuwint R. T., Wassenaar G. M., van der Kuyl A. C., Murre J. J., Hoekman M. F., Brockhoff P. G., Planta R. J. Analysis of upstream activation sites of yeast ribosomal protein genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):6037–6048. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.6037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Ferrandon D., Rosales R., Vigneron M., Macchi M., Ruffenach F., Chambon P. One cell-specific and three ubiquitous nuclear proteins bind in vitro to overlapping motifs in the domain B1 of the SV40 enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3005–3013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zon G., Gallo K. A., Samson C. J., Shao K. L., Summers M. F., Byrd R. A. Analytical studies of 'mixed sequence' oligodeoxyribonucleotides synthesized by competitive coupling of either methyl- or beta-cyanoethyl-N,N-diisopropylamino phosphoramidite reagents, including 2'-deoxyinosine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8181–8196. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]