Abstract
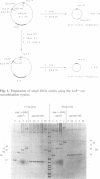
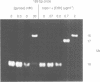
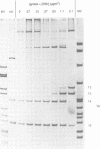
DNA gyrase introduces negative supercoils into closed-circular DNA using the free energy of ATP hydrolysis. Consideration of steric and thermodynamic aspects of the supercoiling reaction indicates that there should be a lower limit to the size of DNA circle which can be supercoiled by gyrase. We have investigated the supercoiling reaction of circles from 116-427 base pairs (bp) in size and have determined that gyrase can supercoil certain relaxed isomers of circles as small as 174 bp, dependent on the final superhelix density of the supercoiled product. Furthermore, this limiting superhelical density (-0.11) is the same as that determined for the supercoiling of plasmid pBR322. We also find that although circles in the range 116-152 bp cannot be supercoiled, they can nevertheless be relaxed by gyrase when positively supercoiled. These data suggest that the conformational changes associated with the supercoiling reaction can be carried out by gyrase in a circle as small as 116 bp. We discuss these results with respect to the thermodynamics of DNA supercoiling and steric aspects of the gyrase mechanism.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abremski K., Hoess R. Bacteriophage P1 site-specific recombination. Purification and properties of the Cre recombinase protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1509–1514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abremski K., Hoess R., Sternberg N. Studies on the properties of P1 site-specific recombination: evidence for topologically unlinked products following recombination. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1301–1311. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90311-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. Supercoiling energy and nucleosome formation: the role of the arginine-rich histone kernel. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1159–1181. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1159-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Nash H. A. DNA gyrase: an enzyme that introduces superhelical turns into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3872–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoess R. H., Fan D. P. Further characterization of a non-essential mutator gene in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):650–660. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.650-660.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoess R., Wierzbicki A., Abremski K. Formation of small circular DNA molecules via an in vitro site-specific recombination system. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz D. S., Wang J. C. Mapping the active site tyrosine of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5339–5344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz D. S., Wang J. C. Torsional rigidity of DNA and length dependence of the free energy of DNA supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 15;173(1):75–91. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Determination of the number of superhelical turns in simian virus 40 DNA by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell A., Gellert M. The DNA dependence of the ATPase activity of DNA gyrase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14472–14480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Mizuuchi M., O'Dea M. H., Gellert M. Cloning and simplified purification of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase A and B proteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9199–9201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Meese K. Topoisomer gel retardation: detection of anti-Z-DNA antibodies bound to Z-DNA within supercoiled DNA minicircles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):21–37. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Sequence dependence of the helical repeat of DNA in solution. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):375–378. doi: 10.1038/292375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rau D. C., Gellert M., Thoma F., Maxwell A. Structure of the DNA gyrase-DNA complex as revealed by transient electric dichroism. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 5;193(3):555–569. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90266-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. Helical periodicity of DNA determined by enzyme digestion. Nature. 1980 Aug 7;286(5773):573–578. doi: 10.1038/286573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Baldwin R. L. Energetics of DNA twisting. II. Topoisomer analysis. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):983–1007. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons R. M., Hill T. L. Definitions of free energy levels in biochemical reactions. Nature. 1976 Oct 14;263(5578):615–618. doi: 10.1038/263615b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanberg S. L., Wang J. C. Cloning and sequencing of the Escherichia coli gyrA gene coding for the A subunit of DNA gyrase. J Mol Biol. 1987 Oct 20;197(4):729–736. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90479-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask D. K., Muller M. T. Biochemical characterization of topoisomerase I purified from avian erythrocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2779–2800. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulanovsky L., Bodner M., Trifonov E. N., Choder M. Curved DNA: design, synthesis, and circularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):862–866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerhoff H. V., O'Dea M. H., Maxwell A., Gellert M. DNA supercoiling by DNA gyrase. A static head analysis. Cell Biophys. 1988 Jan-Jun;12:157–181. doi: 10.1007/BF02918357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi J., Yoshida H., Yamayoshi M., Nakamura S. Nalidixic acid-resistant mutations of the gyrB gene of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Sep;204(3):367–373. doi: 10.1007/BF00331012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]