Abstract
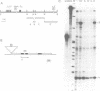
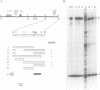
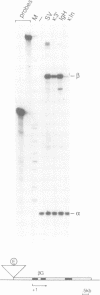
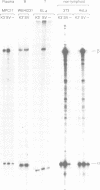
The description of cell lines capable of transcribing immunoglobulin heavy or light chain genes in the apparent absence of an active enhancer has led us to look for novel enhancers in the immunoglobulin gene loci. Here we show that there is a second B-cell-specific enhancer in the mouse kappa locus and that this is located 9 kb downstream of C kappa. This enhancer is some 7-fold stronger than the kappa-intron enhancer and shows striking sequence homologies to the lymphotropic papovavirus, IgH and kappa-intron enhancers. The location of the kappa 3' enhancer between C kappa and the RS element means that it is deleted in some B cells that express lambda light chains.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguilera R. J., Hope T. J., Sakano H. Characterization of immunoglobulin enhancer deletions in murine plasmacytomas. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3689–3693. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04136.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L., Perry R. P. Complementation between two cell lines lacking kappa enhancer activity: implications for the developmental control of immunoglobulin transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4213–4220. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03318.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L., Perry R. P. The role of the kappa enhancer and its binding factor NF-kappa B in the developmental regulation of kappa gene transcription. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90362-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss J. M., Strominger J. L. Regulation of a transfected human class II major histocompatibility complex gene in human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9139–9143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin M., Kuwabara M. D., Sigman D. S., Wall R. Induction of kappa transcription by interferon-gamma without activation of NF-kappa B. Science. 1988 Nov 18;242(4881):1036–1037. doi: 10.1126/science.3143155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Graham M., Webb E., Corcoran L., Adams J. M. Variant (6;15) translocations in murine plasmacytomas involve a chromosome 15 locus at least 72 kb from the c-myc oncogene. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):675–681. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03682.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnick W., Shell B. E., Dery C. DNA sequences near the site of reciprocal recombination between a c-myc oncogene and an immunoglobulin switch region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7269–7273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durdik J., Moore M. W., Selsing E. Novel kappa light-chain gene rearrangements in mouse lambda light chain-producing B lymphocytes. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):749–752. doi: 10.1038/307749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt L. A., Birshtein B. K. Independent immunoglobulin class-switch events occurring in a single myeloma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):856–868. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen H. N., Simms E. S., Potter M. Mouse myeloma proteins with antihapten antibody acitivity. The protein produced by plasma cell tumor MOPC-315. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):4126–4134. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Zachau H. G. Correct transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa gene requires an upstream fragment containing conserved sequence elements. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):71–74. doi: 10.1038/310071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerondakis S., Cory S., Adams J. M. Translocation of the myc cellular oncogene to the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in murine plasmacytomas is an imprecise reciprocal exchange. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Cell-type specificity of immunoglobulin gene expression is regulated by at least three DNA sequence elements. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):885–897. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Marx M. Stable propagation of the active transcriptional state of an immunoglobulin mu gene requires continuous enhancer function. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):645–654. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90223-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein S., Gerster T., Picard D., Radbruch A., Schaffner W. Evidence for transient requirement of the IgH enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8901–8912. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein S., Sablitzky F., Radbruch A. Deletion of the IgH enhancer does not reduce immunoglobulin heavy chain production of a hybridoma IgD class switch variant. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2473–2476. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobeck H. G., Zimmer F. J., Combriato G., Zachau H. G. Linking of the human immunoglobulin VK and JKCK regions by chromosomal walking. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9655–9665. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krimpenfort P., de Jong R., Uematsu Y., Dembic Z., Ryser S., von Boehmer H., Steinmetz M., Berns A. Transcription of T cell receptor beta-chain genes is controlled by a downstream regulatory element. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):745–750. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Lynes M., Haughton G., Wettstein P. J. Novel type of murine B-cell lymphoma. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):554–555. doi: 10.1038/271554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Ellingsworth L. R., Gillis S., Wall R., Kincade P. W. Beta transforming growth factors are potential regulators of B lymphopoiesis. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1290–1299. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S., Gross G., Horowitz M., Givol D. Promoter and enhancer elements in the rearranged alpha chain gene of the human T cell receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3307–3312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02650.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. O., Williams G. T., Neuberger M. S. Transcription cell type specificity is conferred by an immunoglobulin VH gene promoter that includes a functional consensus sequence. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):479–487. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall S., Peterson C. L., Calame K. A transcriptional enhancer 3' of C beta 2 in the T cell receptor beta locus. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):205–208. doi: 10.1126/science.2968651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. W., Durdik J., Persiani D. M., Selsing E. Deletions of kappa chain constant region genes in mouse lambda chain-producing B cells involve intrachromosomal DNA recombinations similar to V-J joining. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6211–6215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosthaf L., Pawlita M., Gruss P. A viral enhancer element specifically active in human haematopoietic cells. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):597–600. doi: 10.1038/315597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S., Calabi F. Reciprocal chromosome translocation between c-myc and immunoglobulin gamma 2b genes. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):240–243. doi: 10.1038/305240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S. Expression and regulation of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene transfected into lymphoid cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1373–1378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Blair D. L., Murphy W. J., Granner D. K. Structure of the 5' ends of immunoglobulin genes: a novel conserved sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2650–2654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlita M., Clad A., zur Hausen H. Complete DNA sequence of lymphotropic papovavirus: prototype of a new species of the polyomavirus genus. Virology. 1985 May;143(1):196–211. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Calame K. L. Complex protein binding within the mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4194–4203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific enhancer in the mouse immunoglobulin kappa gene. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):80–82. doi: 10.1038/307080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. Cell-type preference of immunoglobulin kappa and lambda gene promoters. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2831–2838. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Dale T. C., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon response element of the human gene 6-16. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):85–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Stafford J. Fine mapping of an immunoglobulin gene activator. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1042–1049. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid L. E., Brasnett A. H., Gilbert C. S., Porter A. C., Gewert D. R., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. A single DNA response element can confer inducibility by both alpha- and gamma-interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):840–844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samanta H., Engel D. A., Chao H. M., Thakur A., García-Blanco M. A., Lengyel P. Interferons as gene activators. Cloning of the 5' terminus and the control segment of an interferon activated gene. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11849–11858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavnezer J., Sirlin S., Abbott J. Induction of immunoglobulin isotype switching in cultured I.29 B lymphoma cells. Characterization of the accompanying rearrangements of heavy chain genes. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):577–601. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Zachau H. G., Mach B. Cloning of immunoglobulin kappa light chain genes from mouse liver and myeloma MOPC 173. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3213–3229. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wabl M. R., Burrows P. D. Expression of immunoglobulin heavy chain at a high level in the absence of a proposed immunoglobulin enhancer element in cis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2452–2455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigert M. G., Cesari I. M., Yonkovich S. J., Cohn M. Variability in the lambda light chain sequences of mouse antibody. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1045–1047. doi: 10.1038/2281045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winoto A., Baltimore D. A novel, inducible and T cell-specific enhancer located at the 3' end of the T cell receptor alpha locus. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):729–733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03432.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaller D. M., Eckhardt L. A. Deletion of a B-cell-specific enhancer affects transfected, but not endogenous, immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5088–5092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]