Abstract
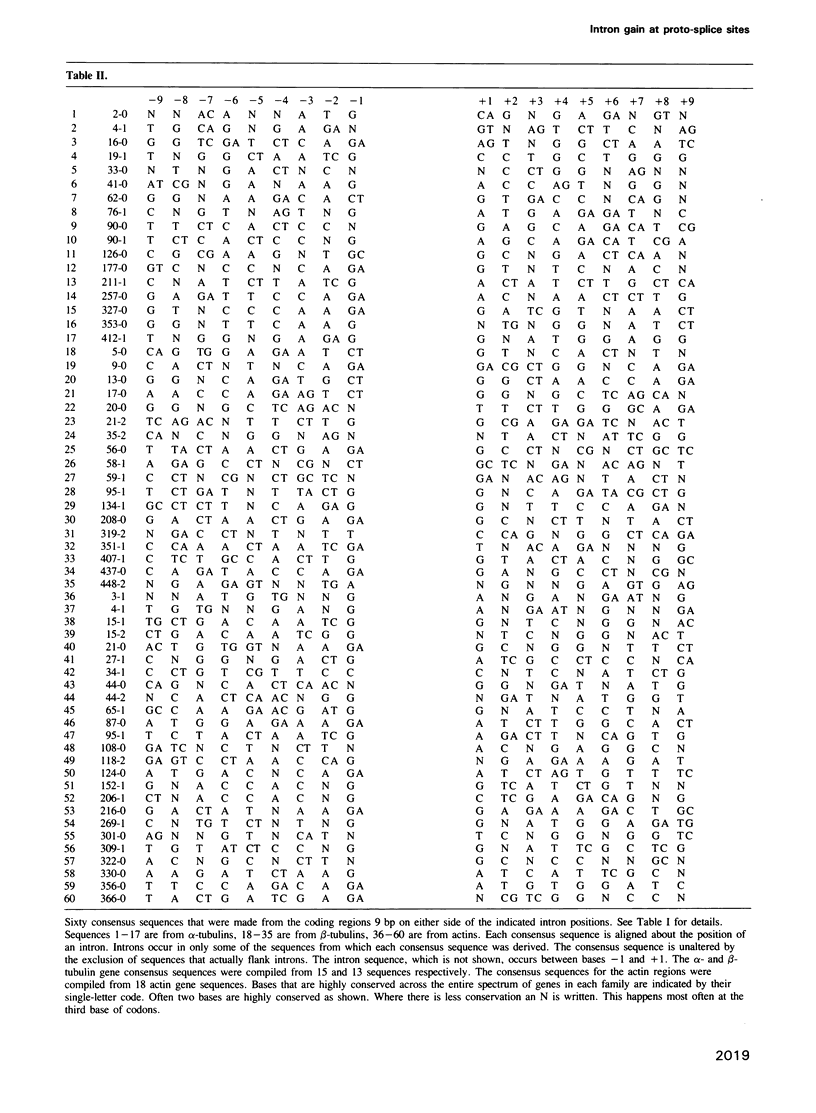
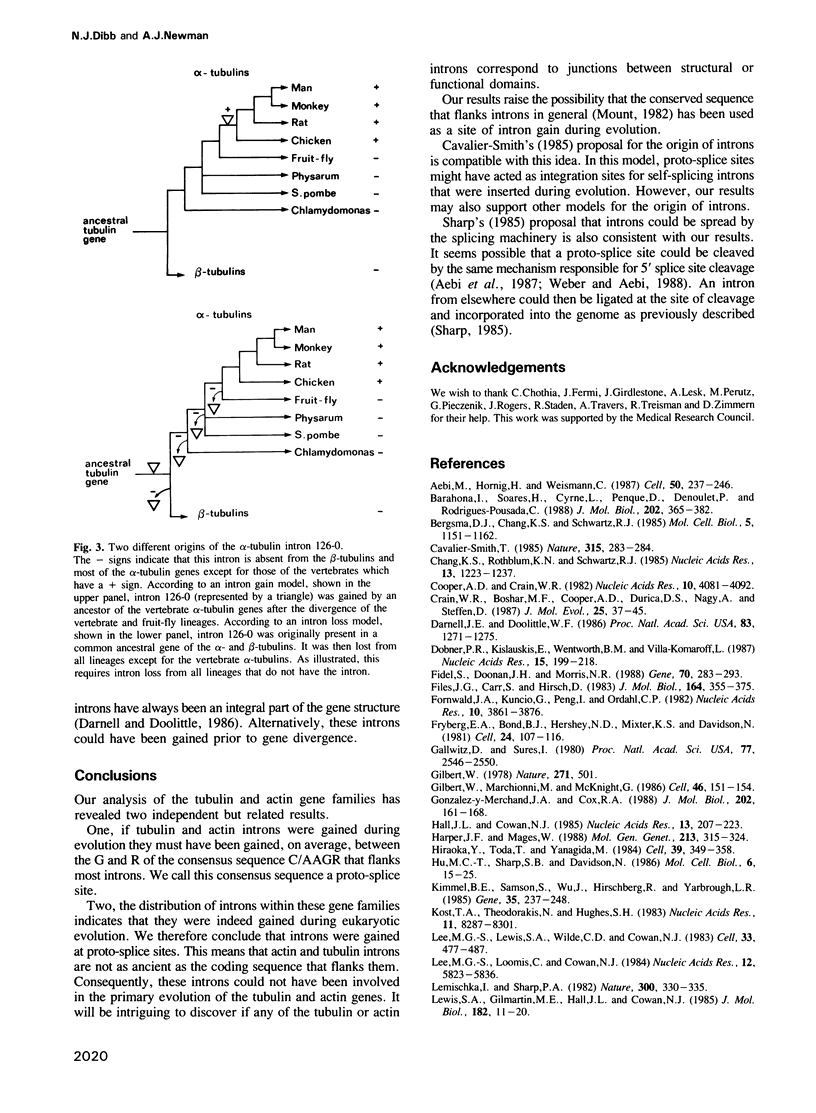
The unexpected discovery of introns raised many questions about gene evolution. We provide evidence that actin and tubulin introns were gained between the G and R of the conserved coding sequence C/AAGR that is known to flank introns in general and which we call a proto-splice site. We conclude that the tubulin and actin introns are less ancient than the coding sequence and so could not have been involved in the primary evolution of the tubulin and actin genes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Hornig H., Weissmann C. 5' cleavage site in eukaryotic pre-mRNA splicing is determined by the overall 5' splice region, not by the conserved 5' GU. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barahona I., Soares H., Cyrne L., Penque D., Denoulet P., Rodrigues-Pousada C. Sequence of one alpha- and two beta-tubulin genes of Tetrahymena pyriformis. Structural and functional relationships with other eukaryotic tubulin genes. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):365–382. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90271-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Chang K. S., Schwartz R. J. Novel chicken actin gene: third cytoplasmic isoform. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1151–1162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalier-Smith T. Selfish DNA and the origin of introns. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):283–284. doi: 10.1038/315283b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. S., Rothblum K. N., Schwartz R. J. The complete sequence of the chicken alpha-cardiac actin gene: a highly conserved vertebrate gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1223–1237. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. D., Crain W. R., Jr Complete nucleotide sequence of a sea urchin actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):4081–4092. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.4081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crain W. R., Jr, Boshar M. F., Cooper A. D., Durica D. S., Nagy A., Steffen D. The sequence of a sea urchin muscle actin gene suggests a gene conversion with a cytoskeletal actin gene. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(1):37–45. doi: 10.1007/BF02100039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Doolittle W. F. Speculations on the early course of evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1271–1275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobner P. R., Kislauskis E., Wentworth B. M., Villa-Komaroff L. Alternative 5' exons either provide or deny an initiator methionine codon to the same alpha-tubulin coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):199–218. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidel S., Doonan J. H., Morris N. R. Aspergillus nidulans contains a single actin gene which has unique intron locations and encodes a gamma-actin. Gene. 1988 Oct 30;70(2):283–293. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Files J. G., Carr S., Hirsh D. Actin gene family of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 5;164(3):355–375. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornwald J. A., Kuncio G., Peng I., Ordahl C. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of the chick a-actin gene and its evolutionary relationship to the actin gene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):3861–3876. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.3861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Bond B. J., Hershey N. D., Mixter K. S., Davidson N. The actin genes of Drosophila: protein coding regions are highly conserved but intron positions are not. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90506-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Sures I. Structure of a split yeast gene: complete nucleotide sequence of the actin gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2546–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W., Marchionni M., McKnight G. On the antiquity of introns. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):151–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90730-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-y-Merchand J. A., Cox R. A. Structure and expression of an actin gene of Physarum polycephalum. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 5;202(1):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90528-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. L., Cowan N. J. Structural features and restricted expression of a human alpha-tubulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 11;13(1):207–223. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Mages W. Organization and structure of Volvox beta-tubulin genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Aug;213(2-3):315–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00339597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka Y., Toda T., Yanagida M. The NDA3 gene of fission yeast encodes beta-tubulin: a cold-sensitive nda3 mutation reversibly blocks spindle formation and chromosome movement in mitosis. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Sharp S. B., Davidson N. The complete sequence of the mouse skeletal alpha-actin gene reveals several conserved and inverted repeat sequences outside of the protein-coding region. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):15–25. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel B. E., Samson S., Wu J., Hirschberg R., Yarbrough L. R. Tubulin genes of the African trypanosome Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense:nucleotide sequence of a 3.7-kb fragment containing genes for alpha and beta tubulins. Gene. 1985;35(3):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kost T. A., Theodorakis N., Hughes S. H. The nucleotide sequence of the chick cytoplasmic beta-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 10;11(23):8287–8301. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.23.8287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Lewis S. A., Wilde C. D., Cowan N. J. Evolutionary history of a multigene family: an expressed human beta-tubulin gene and three processed pseudogenes. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90429-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Loomis C., Cowan N. J. Sequence of an expressed human beta-tubulin gene containing ten Alu family members. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5823–5836. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemischka I., Sharp P. A. The sequences of an expressed rat alpha-tubulin gene and a pseudogene with an inserted repetitive element. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):330–335. doi: 10.1038/300330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Gilmartin M. E., Hall J. L., Cowan N. J. Three expressed sequences within the human beta-tubulin multigene family each define a distinct isotype. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 5;182(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mages W., Salbaum J. M., Harper J. F., Schmitt R. Organization and structure of Volvox alpha-tubulin genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Aug;213(2-3):449–458. doi: 10.1007/BF00339615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G. S., Tsang M. L., Smith H., Fidel S., Morris N. R. Aspergillus nidulans beta-tubulin genes are unusually divergent. Gene. 1987;55(2-3):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Garrett N., Gurdon J. B. Upstream sequences required for tissue-specific activation of the cardiac actin gene in Xenopus laevis embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3185–3193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04628.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro M. J., Cox R. A. Primary structure of an alpha-tubulin gene of Physarum polycephalum. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 5;193(3):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90257-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier N., Prudhomme J. C. Isolation of actin genes in Bombyx mori: the coding sequence of a cytoplasmic actin gene expressed in the silk gland is interrupted by a single intron in an unusual position. Biochimie. 1986 Sep;68(9):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)80179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nader W. F., Isenberg G., Sauer H. W. Structure of Physarum actin gene locus ardA: a nonpalindromic sequence causes inviability of phage lambda and recA-independent deletions. Gene. 1986;48(1):133–144. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90359-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel S. D., Boothroyd J. C. The alpha- and beta-tubulins of Toxoplasma gondii are encoded by single copy genes containing multiple introns. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jun;29(2-3):261–273. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn C. J., Winesett L., Ferl R. J. Nucleotide sequence of an actin gene from Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene. 1988 May 30;65(2):247–257. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90461-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima-Iijima S., Hamada H., Reddy P., Kakunaga T. Molecular structure of the human cytoplasmic beta-actin gene: interspecies homology of sequences in the introns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6133–6137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellen W., Gallwitz D. Actin genes and actin messenger RNA in Acanthamoeba castellanii. Nucleotide sequence of the split actin gene I. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 25;159(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Zakut R., Shani M., Neuman S., Levy Z., Yaffe D. The nucleotide sequence of the rat cytoplasmic beta-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1759–1771. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima Y., Gotoh Y. Signals for the selection of a splice site in pre-mRNA. Computer analysis of splice junction sequences and like sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90647-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orbach M. J., Porro E. B., Yanofsky C. Cloning and characterization of the gene for beta-tubulin from a benomyl-resistant mutant of Neurospora crassa and its use as a dominant selectable marker. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2452–2461. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patthy L. Evolution of the proteases of blood coagulation and fibrinolysis by assembly from modules. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):657–663. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patthy L. Intron-dependent evolution: preferred types of exons and introns. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 6;214(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt L. F., Cleveland D. W. A survey of the alpha-tubulin gene family in chicken: unexpected sequence heterogeneity in the polypeptides encoded by five expressed genes. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):931–940. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. Exon shuffling and intron insertion in serine protease genes. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):458–459. doi: 10.1038/315458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. M., Hightower R. C., Meagher R. B. Complete nucleotide sequence of a soybean actin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1022–1026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. On the origin of RNA splicing and introns. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):397–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silflow C. D., Chisholm R. L., Conner T. W., Ranum L. P. The two alpha-tubulin genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardi code for slightly different proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2389–2398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. A., Allaudeen H. S., Whitman M. H., Koltin Y., Gorman J. A. Isolation and characterization of a beta-tubulin gene from Candida albicans. Gene. 1988;63(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90545-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. F., Cleveland D. W. Sequence of a highly divergent beta tubulin gene reveals regional heterogeneity in the beta tubulin polypeptide. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1754–1760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. F., Havercroft J. C., Machlin P. S., Cleveland D. W. Sequence and expression of the chicken beta 5- and beta 4-tubulin genes define a pair of divergent beta-tubulins with complementary patterns of expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4409–4418. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theurkauf W. E., Baum H., Bo J., Wensink P. C. Tissue-specific and constitutive alpha-tubulin genes of Drosophila melanogaster code for structurally distinct proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8477–8481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Adachi Y., Hiraoka Y., Yanagida M. Identification of the pleiotropic cell division cycle gene NDA2 as one of two different alpha-tubulin genes in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90319-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueyama H., Hamada H., Battula N., Kakunaga T. Structure of a human smooth muscle actin gene (aortic type) with a unique intron site. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1073–1078. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber S., Aebi M. In vitro splicing of mRNA precursors: 5' cleavage site can be predicted from the interaction between the 5' splice region and the 5' terminus of U1 snRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):471–486. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G. A putative ancestral actin gene present in a thermophilic eukaryote: novel combination of intron positions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2553–2564. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. W., Rogers J., Harding M., Pohl V., Pattyn G., Lawson D. E. Structure of chick chromosomal genes for calbindin and calretinin. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 20;200(4):615–625. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90475-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngblom J., Schloss J. A., Silflow C. D. The two beta-tubulin genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii code for identical proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2686–2696. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakut R., Shani M., Givol D., Neuman S., Yaffe D., Nudel U. Nucleotide sequence of the rat skeletal muscle actin gene. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):857–859. doi: 10.1038/298857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



