Abstract
The title compound, C20H15N3OS, is V-shaped. In the 4-phenoxyphenyl group, the two rings are inclined to one another by 74.52 (13)°. These rings are inclined to the triazole ring by 72.20 (15) and 72.30 (15)°, respectively. The phenyl ring is inclined to the triazole ring by 10.85 (12)°. In the crystal, molecules are linked via N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming chains propagating along [010]. These chains are linked via pairs of C—H⋯S hydrogen bonds, forming sheets lying parallel to the ac plane.
Related literature
For the synthesis, properties and various biological activities of functionalizated 1,2,4-triazole derivatives, see: Holla et al. (2002 ▶, 2003 ▶); Walczak et al. (2004 ▶); Zitouni et al. (2005 ▶); Prasad et al. (2009 ▶); Wael et al. (2012 ▶); Almasirad et al. (2004 ▶); Amir & Shikha (2004 ▶); Kane et al. (1988 ▶); Akhtar et al. (2010 ▶). For the crystal structures of related N-free triazole derivatives, see for example: Qadeer et al. (2007 ▶); and for N-subsituted derivatives, see for example: Zhao et al. (2010 ▶); Wu et al. (2009 ▶). Working with sulfur-containing heterocycles may provide unexpected results and the title compound was obtained within an unprecedented series of results, see: Ben Othman et al. (2014 ▶).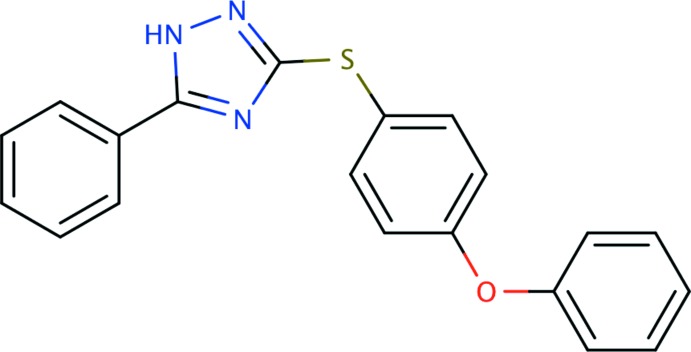
Experimental
Crystal data
C20H15N3OS
M r = 345.41
Monoclinic,

a = 16.6112 (12) Å
b = 5.8445 (5) Å
c = 17.5415 (10) Å
β = 93.131 (5)°
V = 1700.5 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.20 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.35 × 0.25 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Bruker–Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.932, T max = 0.976
44120 measured reflections
3099 independent reflections
2333 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.034
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.052
wR(F 2) = 0.152
S = 1.02
3099 reflections
207 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.28 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3
Data collection: COLLECT (Bruker–Nonius, 1998) ▶; cell refinement: DIRAX/LSQ (Duisenberg, 1992 ▶); data reduction: EVALCCD (Duisenberg et al., 2003 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: OLEX2.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814008204/su2718sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814008204/su2718Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814008204/su2718Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 991904
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3—H3⋯N2i | 0.91 (3) | 2.05 (3) | 2.944 (3) | 170 (2) |
| C16—H16⋯S1ii | 0.93 | 2.77 | 3.694 (2) | 170 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This result is part of a larger research program that was supported by grants from the Région Centre and the Labex IRON (ANR-11-LABX-0018–01).
supplementary crystallographic information
1. Comment
From a medicinal chemistry point of view, it is of great interest to develop efficient methods for the synthesis and the functionalization of 1,2,4-triazoles, as they are known to possess a wide range of biological activities, such as, as anticancer (Holla et al., 2002, 2003) antitubercular (Walczak et al., 2004), antimicrobial (Zitouni et al., 2005; Prasad et al., 2009; Wael et al., 2012), anticonvulsant (Almasirad et al., 2004), anti-inflammatory, analgesic (Amir & Shikha, 2004), antidepressant (Kane et al., 1988), and urease inhibitors (Akhtar et al., 2010). Thus, the synthesis of 1,2,4-triazoles and the investigation of their chemical and biological behaviour have acquired more importance in recent decades for these reasons.
An efficient and convenient method was developed for the formation of substituted thiotriazoles via an organometallic addition and subsequent ring opening sequence of 3-substituted-[1,2,4]triazolo[3,4-][1,3,4]thiadiazole. This method is applicable to a wide range of substrates containing different functional groups and furnishes excellent yields of the corresponding unsubstituted 3 or 5-alkyl, aryl, alkynyl and alkenyl sulfanyl-1,2,4-triazole products.
Interestingly, working with sulfur-containing heterocycles may provide unexpected results and we report herein on the crystal structure of one derivative obtained within an unprecedented series of results (Ben Othman et al., 2014).
The molecular structure of the title molecule is illustrated in Fig. 1. The molecule is V-shaped about atom S1. In the 4-phenoxyphenyl group the two rings (C9-C14 and C15-C20) are inclined to one another by 74.52 (13) °. These rings are inclined to the triazole ring (N1-N3/C7/C8) by 72.20 (15) and 72.30 (15) °, respectively. The phenyl ring (C1-C6) is inclined to the triazole ring by 10.85 (12) °.
In the crystal, molecules are linked via N-H···N hydrogen bonds forming chains propagating along [010]; see Table 1 and Fig. 2. These chains are linked via pairs of C-H···S hydrogen bonds forming sheets lying parallel to the ac plane (Table 1 and Fig. 2).
2. Experimental
For the synthesis of the title compound, see Fig. 3. In a 25 ml flask, phenyl ZnBr solution in THF (1.5 mmol, 0.5M) was added drop wise under argon at room temperature to a solution of 3-Phenyl-[1,2,4]triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazole (0.5 mmol) in THF (5 ml), and the mixture was stirred for 25 min (see Fig 3). At the end of the reaction, the mixture was quenched with 15 mL of an aqueous solution of saturated NH4Cl, and extracted with CH2Cl2 (2 × 20 ml). The extract was dried over magnesium sulfate, filtered and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was purified by flash column chromatography on silica gel (eluent 6:4 petroleum ether/AcOEt). The title compound was obtained as a white solid in 80% yield. Rf = 0.60 (petroleum ether/EtOAc, 6:4); M.p. 318-320 K. HRMS (EI—MS): m/z calcd for C20H15N3OS: 346.10086 [M + H]+, found: 346.10112. Crystals of the title compound were obtained by vapor diffusion of petroleum ether into a solution of the title compound in a CH2Cl2/Et2O/pentane mixture. Spectroscopic data for the title compound is available in the archived CIF.
3. Refinement
The NH H atom was located in a difference Fourier map and freely refined. The C-bound H atoms were included in calculated positions and treated as riding atoms: C-H = 0.93 Å with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title molecule, with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.

A perspective view along the b axis of the crystal pack of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 for details; H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for calrity).
Fig. 3.

The synthetic route of the title compound.
Crystal data
| C20H15N3OS | Z = 4 |
| Mr = 345.41 | F(000) = 720 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Dx = 1.349 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 16.6112 (12) Å | µ = 0.20 mm−1 |
| b = 5.8445 (5) Å | T = 293 K |
| c = 17.5415 (10) Å | Block, colourless |
| β = 93.131 (5)° | 0.35 × 0.25 × 0.12 mm |
| V = 1700.5 (2) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker–Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer | 3099 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: sealed X-ray tube | 2333 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.034 |
| profile data from φ scans and ω scans | θmax = 25.4°, θmin = 3.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −20→20 |
| Tmin = 0.932, Tmax = 0.976 | k = −7→6 |
| 44120 measured reflections | l = −21→21 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.052 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.152 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0707P)2 + 1.0533P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3099 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 207 parameters | Δρmax = 0.28 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. Spectroscopic data for the title compound: IR (ATR diamond): ν (cm-1) = 3082, 2927, 2864, 1581, 1482, 1324, 1242, 1006, 869, 786, 601, 725, 688; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ (p.p.m.) = 12.92 (br. s, 1H), 7.90 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 2H), 7.47 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.43–7.28 (m, 5H), 7.15 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 6.96 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 6.84 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR DEPT (101 MHz, CDCl3): δ (p.p.m.) = 134.9 (2CHAr), 130.2 (CHAr), 129.9 (2CHAr), 128.8 (2CHAr), 126.5 (2CHAr), 124.1 (CHAr), 119.7 (2CHAr), 119 (2CHAr). |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| S1 | 0.74490 (4) | 0.10572 (13) | 0.07643 (5) | 0.0708 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.69265 (12) | 0.6140 (4) | 0.19811 (11) | 0.0507 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.74402 (12) | 0.4385 (4) | 0.18506 (11) | 0.0540 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.64442 (12) | 0.4567 (4) | 0.09308 (11) | 0.0539 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.63379 (13) | 0.6216 (4) | 0.14328 (13) | 0.0474 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.56826 (8) | 0.7865 (3) | 0.13936 (9) | 0.0518 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.56878 (10) | 0.9796 (3) | 0.18563 (10) | 0.0661 (7) | |
| H1 | 0.6109 | 1.0031 | 0.2219 | 0.079* | |
| C2 | 0.50635 (12) | 1.1377 (3) | 0.17765 (12) | 0.0811 (9) | |
| H2 | 0.5067 | 1.2669 | 0.2086 | 0.097* | |
| C3 | 0.44340 (10) | 1.1026 (4) | 0.12341 (13) | 0.0885 (11) | |
| H3A | 0.4016 | 1.2083 | 0.1181 | 0.106* | |
| C4 | 0.44288 (9) | 0.9094 (4) | 0.07715 (11) | 0.0903 (11) | |
| H4 | 0.4008 | 0.8859 | 0.0409 | 0.108* | |
| C5 | 0.50531 (11) | 0.7514 (3) | 0.08512 (10) | 0.0746 (8) | |
| H5 | 0.5050 | 0.6222 | 0.0542 | 0.090* | |
| C9 | 0.85042 (16) | 0.1109 (4) | 0.09473 (14) | 0.0575 (6) | |
| C12 | 1.01532 (19) | 0.0906 (5) | 0.1147 (2) | 0.0795 (9) | |
| C8 | 0.71159 (14) | 0.3513 (4) | 0.12111 (13) | 0.0508 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.89725 (16) | 0.2919 (5) | 0.07283 (17) | 0.0676 (7) | |
| H14 | 0.8728 | 0.4205 | 0.0506 | 0.081* | |
| C13 | 0.97963 (17) | 0.2836 (5) | 0.08361 (19) | 0.0751 (8) | |
| H13 | 1.0110 | 0.4074 | 0.0700 | 0.090* | |
| C10 | 0.8872 (2) | −0.0810 (5) | 0.12533 (18) | 0.0750 (8) | |
| H10 | 0.8562 | −0.2039 | 0.1403 | 0.090* | |
| C15 | 1.14533 (12) | 0.2518 (3) | 0.13117 (13) | 0.0779 (9) | |
| C16 | 1.20579 (14) | 0.2829 (4) | 0.08041 (11) | 0.0981 (13) | |
| H16 | 1.2114 | 0.1797 | 0.0407 | 0.118* | |
| C17 | 1.25792 (12) | 0.4683 (5) | 0.08903 (12) | 0.0986 (12) | |
| H17 | 1.2984 | 0.4891 | 0.0551 | 0.118* | |
| C18 | 1.24959 (12) | 0.6225 (4) | 0.14841 (16) | 0.0937 (11) | |
| H18 | 1.2845 | 0.7465 | 0.1542 | 0.112* | |
| C19 | 1.18913 (14) | 0.5914 (3) | 0.19916 (12) | 0.0873 (10) | |
| H19 | 1.1836 | 0.6945 | 0.2389 | 0.105* | |
| C20 | 1.13700 (11) | 0.4060 (4) | 0.19055 (12) | 0.0786 (9) | |
| H20 | 1.0966 | 0.3852 | 0.2245 | 0.094* | |
| C11 | 0.9694 (2) | −0.0913 (5) | 0.1338 (2) | 0.0885 (10) | |
| H11 | 0.9941 | −0.2238 | 0.1527 | 0.106* | |
| H3 | 0.7060 (16) | 0.717 (5) | 0.2355 (16) | 0.070 (8)* | |
| O1 | 1.09730 (15) | 0.0639 (4) | 0.1246 (2) | 0.1279 (16) | 0.997 (9) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0633 (5) | 0.0627 (5) | 0.0859 (5) | −0.0058 (3) | −0.0005 (4) | −0.0210 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0525 (11) | 0.0532 (12) | 0.0451 (11) | 0.0006 (9) | −0.0107 (9) | −0.0013 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0555 (12) | 0.0555 (12) | 0.0496 (11) | 0.0026 (10) | −0.0097 (9) | 0.0026 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0519 (12) | 0.0602 (12) | 0.0485 (11) | −0.0047 (10) | −0.0077 (9) | −0.0014 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0451 (12) | 0.0534 (14) | 0.0431 (12) | −0.0078 (10) | −0.0040 (10) | 0.0065 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0446 (12) | 0.0599 (15) | 0.0501 (13) | −0.0055 (11) | −0.0035 (10) | 0.0106 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0546 (15) | 0.0708 (18) | 0.0727 (17) | 0.0024 (14) | 0.0016 (13) | 0.0024 (15) |
| C2 | 0.0718 (19) | 0.076 (2) | 0.098 (2) | 0.0122 (16) | 0.0194 (17) | 0.0087 (17) |
| C3 | 0.0581 (18) | 0.104 (3) | 0.104 (2) | 0.0201 (18) | 0.0124 (17) | 0.043 (2) |
| C4 | 0.0576 (17) | 0.124 (3) | 0.087 (2) | 0.0107 (19) | −0.0181 (16) | 0.026 (2) |
| C5 | 0.0611 (17) | 0.094 (2) | 0.0662 (17) | −0.0001 (16) | −0.0168 (13) | 0.0056 (16) |
| C9 | 0.0646 (16) | 0.0480 (14) | 0.0596 (15) | 0.0014 (12) | −0.0005 (12) | −0.0038 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0659 (18) | 0.0560 (18) | 0.114 (3) | 0.0176 (14) | −0.0201 (17) | −0.0137 (16) |
| C8 | 0.0505 (13) | 0.0522 (14) | 0.0492 (13) | −0.0070 (11) | −0.0020 (10) | 0.0019 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0598 (16) | 0.0539 (16) | 0.088 (2) | 0.0077 (13) | −0.0042 (14) | 0.0132 (14) |
| C13 | 0.0616 (17) | 0.0563 (17) | 0.107 (2) | 0.0024 (14) | −0.0034 (16) | 0.0073 (16) |
| C10 | 0.087 (2) | 0.0506 (16) | 0.086 (2) | 0.0012 (14) | −0.0052 (16) | 0.0067 (14) |
| C15 | 0.0549 (16) | 0.070 (2) | 0.106 (2) | 0.0231 (15) | −0.0157 (16) | −0.0158 (17) |
| C16 | 0.082 (2) | 0.137 (4) | 0.074 (2) | 0.050 (2) | −0.0119 (18) | −0.029 (2) |
| C17 | 0.069 (2) | 0.148 (4) | 0.079 (2) | 0.026 (2) | 0.0060 (17) | 0.027 (2) |
| C18 | 0.076 (2) | 0.094 (3) | 0.110 (3) | 0.0044 (19) | −0.005 (2) | 0.017 (2) |
| C19 | 0.081 (2) | 0.085 (2) | 0.096 (2) | 0.0046 (18) | 0.0003 (18) | −0.0168 (19) |
| C20 | 0.0653 (18) | 0.083 (2) | 0.088 (2) | 0.0146 (16) | 0.0087 (16) | −0.0074 (17) |
| C11 | 0.098 (2) | 0.0485 (17) | 0.116 (3) | 0.0183 (17) | −0.028 (2) | 0.0039 (16) |
| O1 | 0.0700 (17) | 0.0667 (17) | 0.242 (4) | 0.0247 (12) | −0.0404 (18) | −0.0344 (18) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C9 | 1.765 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.374 (4) |
| S1—C8 | 1.740 (3) | C12—C11 | 1.361 (5) |
| N3—N2 | 1.362 (3) | C12—O1 | 1.372 (4) |
| N3—C7 | 1.334 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| N3—H3 | 0.91 (3) | C14—C13 | 1.372 (4) |
| N2—C8 | 1.320 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C7 | 1.324 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C8 | 1.344 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.366 (5) |
| C7—C6 | 1.453 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.3900 |
| C6—C1 | 1.3900 | C15—C20 | 1.3900 |
| C6—C5 | 1.3900 | C15—O1 | 1.359 (3) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.3900 | C16—C17 | 1.3900 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.3900 | C17—C18 | 1.3900 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9300 | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.3900 | C18—C19 | 1.3900 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3900 | C19—C20 | 1.3900 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C9—C14 | 1.380 (4) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C9—C10 | 1.372 (4) | ||
| C8—S1—C9 | 103.95 (12) | N2—C8—N1 | 115.2 (2) |
| N2—N3—H3 | 119.3 (18) | N1—C8—S1 | 119.43 (18) |
| C7—N3—N2 | 110.2 (2) | C9—C14—H14 | 119.7 |
| C7—N3—H3 | 129.7 (18) | C13—C14—C9 | 120.5 (3) |
| C8—N2—N3 | 101.72 (19) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.7 |
| C7—N1—C8 | 103.21 (19) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.4 |
| N3—C7—C6 | 125.0 (2) | C14—C13—C12 | 119.3 (3) |
| N1—C7—N3 | 109.6 (2) | C14—C13—H13 | 120.4 |
| N1—C7—C6 | 125.33 (19) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.0 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 122.03 (14) | C11—C10—C9 | 120.0 (3) |
| C1—C6—C5 | 120.0 | C11—C10—H10 | 120.0 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 117.92 (14) | C16—C15—C20 | 120.0 |
| C6—C1—H1 | 120.0 | O1—C15—C16 | 119.5 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.0 | O1—C15—C20 | 120.4 (2) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 120.0 | C15—C16—H16 | 120.0 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.0 | C15—C16—C17 | 120.0 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.0 | C17—C16—H16 | 120.0 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.0 | C16—C17—H17 | 120.0 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 120.0 | C18—C17—C16 | 120.0 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.0 | C18—C17—H17 | 120.0 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 120.0 | C17—C18—H18 | 120.0 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C19—C18—C17 | 120.0 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.0 | C19—C18—H18 | 120.0 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C18—C19—H19 | 120.0 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.0 | C18—C19—C20 | 120.0 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.0 | C20—C19—H19 | 120.0 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.0 | C15—C20—H20 | 120.0 |
| C14—C9—S1 | 122.1 (2) | C19—C20—C15 | 120.0 |
| C10—C9—S1 | 118.3 (2) | C19—C20—H20 | 120.0 |
| C10—C9—C14 | 119.3 (3) | C12—C11—C10 | 120.6 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 120.2 (3) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.7 |
| C11—C12—O1 | 116.5 (3) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.7 |
| O1—C12—C13 | 123.2 (3) | C15—O1—C12 | 119.5 (2) |
| N2—C8—S1 | 125.17 (19) | ||
| S1—C9—C14—C13 | −175.8 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 2.4 (5) |
| S1—C9—C10—C11 | 174.0 (3) | C8—S1—C9—C14 | −57.9 (3) |
| N3—N2—C8—S1 | −175.31 (18) | C8—S1—C9—C10 | 128.3 (2) |
| N3—N2—C8—N1 | −0.1 (3) | C8—N1—C7—N3 | 0.4 (3) |
| N3—C7—C6—C1 | 12.0 (3) | C8—N1—C7—C6 | −179.7 (2) |
| N3—C7—C6—C5 | −170.67 (19) | C14—C9—C10—C11 | 0.0 (5) |
| N2—N3—C7—N1 | −0.5 (3) | C13—C12—C11—C10 | −2.8 (6) |
| N2—N3—C7—C6 | 179.66 (19) | C13—C12—O1—C15 | 24.8 (5) |
| N1—C7—C6—C1 | −167.84 (18) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | −2.0 (4) |
| N1—C7—C6—C5 | 9.5 (3) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 0.0 |
| C7—N3—N2—C8 | 0.4 (2) | C16—C15—C20—C19 | 0.0 |
| C7—N1—C8—S1 | 175.31 (17) | C16—C15—O1—C12 | −122.6 (3) |
| C7—N1—C8—N2 | −0.2 (3) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 0.0 |
| C7—C6—C1—C2 | 177.32 (18) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | 0.0 |
| C7—C6—C5—C4 | −177.43 (17) | C18—C19—C20—C15 | 0.0 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.0 | C20—C15—C16—C17 | 0.0 |
| C1—C6—C5—C4 | 0.0 | C20—C15—O1—C12 | 60.7 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.0 | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.8 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.0 | C11—C12—O1—C15 | −158.7 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.0 | O1—C12—C13—C14 | 177.2 (3) |
| C5—C6—C1—C2 | 0.0 | O1—C12—C11—C10 | −179.5 (3) |
| C9—S1—C8—N2 | −34.3 (2) | O1—C15—C16—C17 | −176.7 (2) |
| C9—S1—C8—N1 | 150.7 (2) | O1—C15—C20—C19 | 176.7 (2) |
| C9—C14—C13—C12 | 1.6 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H3···N2i | 0.91 (3) | 2.05 (3) | 2.944 (3) | 170 (2) |
| C16—H16···S1ii | 0.93 | 2.77 | 3.694 (2) | 170 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+3/2, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) −x+2, −y, −z.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SU2718).
References
- Akhtar, T., Hameed, K., Khan, K. M., Khan, A. & Choudhary, M. I. (2010). J. Enz. Inhib. Med Chem 25, 572–576. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Almasirad, A., Tabatabai, S. A., Faizi, M., Kebriaeezadeh, A., Mehrabi, N., Dalvandi, A. & Shafiee, A. (2004). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14, 6057–60059. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Amir, M. & Shikha, K. (2004). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 39, 535–545. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ben Othman, R., Massip, S., Marchivie, M., Jarry, C., Vercouillie, J., Chalon, S., Guillaumet, G., Suzenet, F. & Routier, S. (2014). Eur. J. Org. Chem. In the press. 10.1002/ejoc.201402193.
- Bruker–Nonius (1998). COLLECT Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Duisenberg, A. J. M. (1992). J. Appl. Cryst. 25, 92–96.
- Duisenberg, A. J. M., Kroon-Batenburg, L. M. J. & Schreurs, A. M. M. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst. 36, 220–229.
- Holla, B. S., Poojary, K. N., Rao, B. S. & Shivananda, M. K. (2002). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 37, 511–517. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Holla, B. S., Veerendra, B., Shivananda, M. K. & Poojary, B. (2003). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 38, 759–767. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kane, J. M., Dudley, M. W., Sorensen, S. M. & Miller, F. P. (1988). J. Med. Chem. 31, 1253–1258. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Prasad, D. J., Ashok, M., Karegoudar, P., Boja, P., Holla, B. S. & SuchetaKumari, N. (2009). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44, 551–557. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Qadeer, G., Rama, N. H., Zareef, M. & Li, X.-H. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o88–o89.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wael, A. El.-S., Omar, M. A., Hend, A. H. & Adel, A. H. A. (2012). Chin. J. Chem. 30, 77–83.
- Walczak, K., Gondela, A. & Suwinski, J. (2004). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 39, 849–853. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.-Z., Liu, M.-C., Wu, H.-Y., Huang, X.-B. & Li, J.-J. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B., Liu, Z., Gao, Y., Song, B. & Deng, Q. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o2814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zitouni, G. T., Kaplancikli, Z. A., Yildiz, M. T., Chevallet, P. & Kaya, D. (2005). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 40, 607-613. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814008204/su2718sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814008204/su2718Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536814008204/su2718Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 991904
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



